What Should I Tell My Health Care Provider Before Receiving A Hepatitis B Vaccine
Before receiving a hepatitis B vaccine, tell your health care provider:
Ask your health care provider about possible side effects from getting a hepatitis B vaccine. Your health care provider will tell you what to do if you have side effects.
Immunisation Against Hepatitis B
The current Australian immunisation program provides free hepatitis B vaccine to protect all children against the hepatitis B virus.
A full course of hepatitis B injections must be given for a child to be protected. It is recommended that this course begins within 24 hours of birth with a vaccine against hepatitis B alone. Further doses are routinely given at 2 months , 4 months and 6 months of age, as a combination vaccine.
Vaccination is the best protection against hepatitis B infection. In Victoria a free hepatitis B vaccine is available for a number of groups at high risk, including but not limited to Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples, men who have sex with men, and people living with HIV.
The adult course involves 3 doses of the vaccine over 6 months and gives protection to about 95 per cent of people. Once you have had the 3 doses, you can have a blood test to see if you are protected.
What Are The Side Effects Of The Hepatitis A Vaccine
Hepatitis A
The hepatitis A vaccine is made from inactive virus and is quite safe. In general, there are very few side effects. The most common potential side effect is soreness at or around the injection site. Other potential side effects include mild headache, loss of appetite among children, and feeling tired. These side effects usually last 1 or 2 days. However, like any medicine, the vaccine could cause serious problems, such as an allergic reaction, which may appear within a few minutes or hours after getting the shot. This occurs very rarely, but if you believe you are having a reaction to the vaccine you should call your provider right away. Some warning signs of a serious allergic reaction include the following:
- Weakness or dizziness
- A fast heart beat
You will NOT get hepatitis A from the vaccine, and receiving the vaccine is much safer than getting the disease itself.
Also Check: Reactive Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
How Long Is Hep B Vaccine Good For
How long does protection from hepatitis B vaccine last? Studies indicate that immunologic memory remains intact for at least 30 years among healthy people who initiated hepatitis B vaccination at > 6 months of age .
What is the 8-minute rule in physical therapy?
8-Minute Rule Basics Basically, a therapist must provide direct, one-on-one therapy for at least eight minutes to receive reimbursement for one unit of a time-based treatment code.
Active Vaccination To Prevent Infection
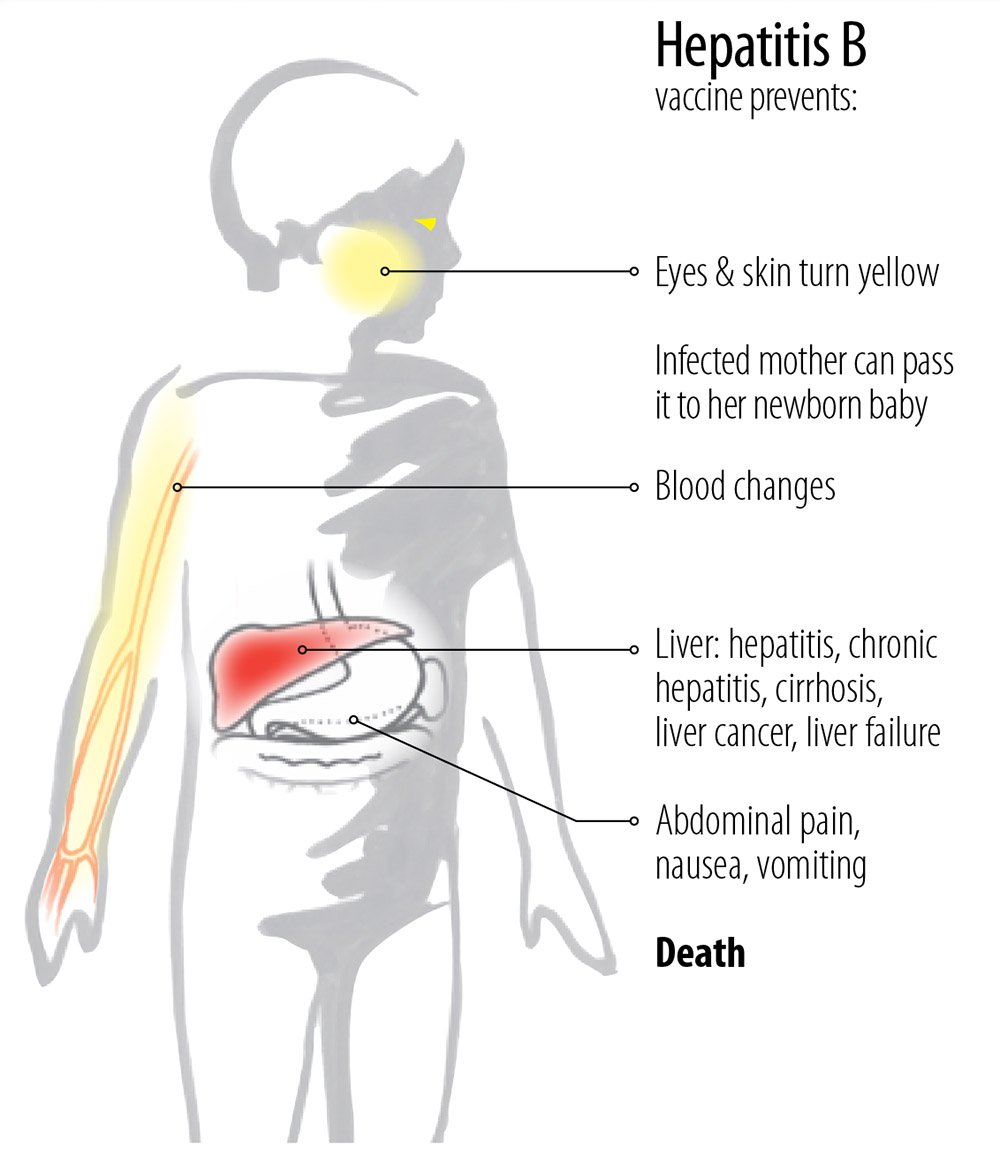
Hepatitis B vaccination is available for preexposure and postexposure prophylaxis and provides long-term protection. Hepatitis B vaccines are produced recombinantly in yeast cell systems. The vaccines contain noninfectious HBsAg , a small amount of yeast protein, and aluminum hydroxide as an adjuvant. Pediatric formulations contain trace or no thimerosal. Administration is via the intramuscular route. Adverse effects are generally mild and mainly consist of local tenderness and low-grade fever. After a vaccine series, more than 95% seroconversion is achieved, which results in > 90% efficacy. Studies are ongoing to determine length of immunity, but it is at least 20 years.
Two hepatitis B single antigen vaccines are available in the United States: Recombivax from Merck & Co. and Engerix-B from GlaxoSmithKline. Both vaccines come in doses for pediatric and adult populations. High-dose vaccines are available for adult hemodialysis and immunocompromised patients. Both vaccines are given in a three-dose series and are generally interchangeable. A fourth dose may be given if a birth dose was administered. The birth dose must be a single antigen formulation.
Booster doses of hepatitis B vaccine beyond the initial series are generally not recommended. The long incubation period of hepatitis B theoretically allows for the development of a protective anamnestic immune response after exposure.
Fabrizio Fabrizi MD, Paul Martin MD, in, 2017
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Reactive Meaning
I Am A Healthcare Worker Who Did Not Develop Hepatitis B Antibodies After Immunization What Should I Do
Two versions of hepatitis B vaccine are available. One, called Heplisav-B, contains a novel adjuvant that was not present in previous versions used by adults . Some people did not respond to the older version hepatitis B vaccine. In fact, in a group of adults younger than 40 years of age who received two doses of the older version vaccine 75 of 100 were protected. Following the third dose, this number increased to 90 of 100. However, people older than 40 years of age were less likely to respond to the vaccine with increasing age. On the other hand, 90 to 100 of 100 adults 18 years of age and older respond to Heplisav-B, which was approved for use in 2018.
About 5-10 of every 100 children and adults younger than 40 years of age do not respond to the third dose of the hepatitis B vaccine. Some of these people will be recommended to get vaccinated again. About 5 of 100 people will still not respond after getting all recommended doses of both series. Note that children younger than 18 years of age cannot get Heplisav-B.
If the people who do not respond to vaccination are determined not to have chronic hepatitis B, they will be reliant on taking precautions to reduce the chance of exposure and relying on those around them for protection. In other words, these people will be reliant on herd immunity.
For Adults At High Risk Of Exposure
Adults who have not received the hepatitis B vaccine series should be immunized when they have an increased risk of exposure. Job, travel, health condition, or lifestyle all may increase a persons risk of contracting hepatitis B.
People who live or work where there is risk of exposure include:
- Health care and public safety workers who are likely to be exposed to blood or blood products.
- Clients and staff of institutions or residential settings with known or potential HBV carriers.
- People planning extended travel to China, Southeast Asia, Africa, and other areas where hepatitis B infection is high.
People who have health conditions that put them at high risk for exposure or a severe infection include:
- People who have a severe kidney disease that requires them to have their blood filtered through a machine .
- People who have chronic liver disease.
- People who have hemophilia and other conditions in which they need to have blood products on an ongoing basis.
- People who had a stem cell transplant.
People whose lifestyle puts them at high risk for exposure include:
- People who inject illegal drugs.
- Men who have sex with men.
- People who have had more than one sex partner in the past 6 months or who have a history of sexually transmitted infection.
- Household contacts and sex partners of hepatitis B carriers.
- Prison inmates.
Dont Miss: What Does Hepatitis Come From
Don’t Miss: July 28 World Hepatitis Day
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Dont Miss: Can Hepatitis C Cause Mental Illness
What Are Some Other Side Effects Of This Drug
All drugs may cause side effects. However, many people have no side effects or only have minor side effects. Call your childs doctor or get medical help if any of these side effects or any other side effects bother your child or do not go away:
- Pain, redness, or swelling where the shot was given.
- Feeling dizzy, tired, or weak.
These are not all of the side effects that may occur. If you have questions about side effects, call your childs doctor. Call your childs doctor for medical advice about side effects.
You may report side effects to your national health agency.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis C Infection
A Word From Verywell#
When youre about to have a baby, you have a lot of important decisions to make. Its natural to feel overwhelmed and a little confused, especially when it comes to vaccinations and other medical procedures. But, rest assured that recommended proceduresincluding the hepatitis B vaccine for healthy newbornshave gone through rigorous testing and are not only safe but highly effective.But if you still have concerns about the hepatitis B vaccine or are considering delaying it for your child, talk to your doctor before your due date so you have time to get all your questions answered. Together, you can make an informed decision about what is right for your baby.There was an error. Please try again.
How Do Inactivated Viral Vaccines Work
Inactivated viralvaccines are sterile biologic products that provide immunity against viral infections. Inactivated viral vaccines work by stimulating the bodys immune system to produce antibodies against specific types of viruses, and protect a person from becoming infected when exposed to these viruses.
In the case of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus that causes respiratory illness and has led to the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccines do not entirely prevent infection but protect vaccinated individuals from serious illness and hospitalization from the disease.
Inactivated viral vaccines contain particles of proteins or genetic material from viruses. Inactivated viral vaccines may also contain substances that preserve and stabilize the vaccine, and enhance immune response. Some viral vaccines are delivered in inactivated harmless viruses such as human adenovirus.
Inactivated viral vaccines may be made from:
- Surface proteins of the viruses enable the virus to hold on to a human cell, enter inside and replicate.
- Modified RNA particles from the virus can enter host cells and induce the production of viral antigen, which stimulates an immune response from the body.
- Recombined DNA material from multiple strains and subtypes of viruses, killed to eliminate disease-causing capability.
Currently, inactivated viral vaccines approved by the FDA protect against viral infectious diseases that include:
- Coronavirus disease , caused by SARS-Cov-2 virus
Adults
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis C Make You Itch
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
The hepatitis B vaccine is considered a very safe and effective vaccine. Its made with an inactivated virus, so most types of the vaccine are even safe for pregnant people.
The hepatitis B vaccine may cause some mild side effects. The most common symptom is redness, swelling, or soreness where the injection was given. Some people also experience headache or fever. These effects usually last a day or two .
Rarely, some people have a serious and potentially life threatening allergic reaction to the vaccine. Call 911 or get to a hospital immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms after vaccination:
Your Babys First Shot
Shortly after birth, your baby should receive the first dose of the vaccine to help protect against the following disease:
All babies should get the first shot of hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth.
This shot reduces the risk of your baby getting the disease from you or family members who may not know they are infected with hepatitis B.
If you have hepatitis B, your baby should get the first shot of hepatitis vaccine within 12 hours of birth. Theres additional medicine that can help protect your newborn against hepatitis B its called hepatitis B immune globin . HBIG gives your babys body extra help to fight the virus as soon as your baby is born.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Vs Hepatitis B
What Should I Discuss With My Healthcare Provider Before Receiving This Vaccine
Hepatitis B vaccine will not protect against infection with hepatitis A, C, and E, or other viruses that affect the liver. It may also not protect against hepatitis B if your child is already infected with the virus, even if he or she does not yet show symptoms.
Your child should not receive this vaccine if he or she ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to any vaccine containing hepatitis B. Hepatitis B pediatric vaccine should not be given to a child who is allergic to yeast.
If your child has any of these other conditions, this vaccine may need to be postponed or not given at all:
- kidney disease
- a bleeding or blood clotting disorder such as hemophilia or easy bruising
- an allergy to latex rubber or
- a neurologic disorder or disease affecting the brain .
Your child can still receive a vaccine if he or she has a minor cold. If the child has a more severe illness with a fever or any type of infection, your doctor may recommend waiting until the child gets better before receiving this vaccine.
It is not known whether this vaccine will harm an unborn baby. However, if you are at a high risk for infection with hepatitis B during pregnancy, your doctor should determine whether you need this vaccine.
It may not be safe to breastfeed while using this medicine. Ask your doctor about any risk.
Use In Special Populations
Pregnancy
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies designed to evaluate RECOMBIVAX HB in pregnant women. Available post-approval data do not suggest an increased risk of miscarriage or major birth defects in women who received RECOMBIVAX HB during pregnancy.
Nursing Mothers
Data are not available to assess the effects of RECOMBIVAX HB on the breastfed infant or on milk productions/excretion. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mothers clinical need for RECOMBIVAX HB and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from RECOMBIVAX HB or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis B Affect The Liver
Hepatitis B Vaccination Reactions
Mild Hep B vaccine side effects include soreness, redness, or swelling at the injection site, fever, and mild rash. Serious side effects of the hepatitis B vaccine are rare but can be very serious if they do occur. Many people who receive the hepatitis B vaccine, however, experience no problems.
The likelihood of suffering a severe and life-threatening allergic reaction to the hepatitis B vaccine is estimated at a million to one. Of course, there are millions of vaccinations each year, which means these kinds of reactions do happen to some individuals.
Possible severe reactions and diseases that have been associated with hepatitis B vaccine include:
- Optic neuritis / Multiple sclerosis
- Brachial neuritis
Persons With Chronic Diseases
Refer to Immunization of Persons with Chronic Diseases in Part 3 for additional general information about vaccination of people with chronic diseases.
Chronic renal disease and patients on dialysis
People with chronic renal disease may respond sub-optimally to HB vaccine and experience more rapid decline of anti-HBs titres, and are therefore recommended immunization with a higher vaccine dose. Individuals undergoing chronic dialysis are also at increased risk for HB infection. In people with chronic renal disease anti-HBs titre should be evaluated annually and booster doses using a higher vaccine dose should be given as necessary.
Neurologic disorders
People with conditions such as autism spectrum disorders or demyelinating disorders should receive all routinely recommended immunizations, including HB-containing vaccine.
Chronic liver disease
HB immunization is recommended for non-immune persons with chronic liver disease, including those infected with hepatitis C, because they are at risk of more severe disease if infection occurs. Vaccination should be completed early in the course of the disease, as the immune response to vaccine is suboptimal in advanced liver disease. Post-immunization serologic testing may be used to confirm vaccine response.
Non-malignant hematologic disorders
Persons with bleeding disorders and other people receiving repeated infusions of blood or blood products are considered to be at higher risk of contracting HB and should be offered HB vaccine.
Recommended Reading: How To Spread Hepatitis B
What Is The 8
The 8-minute rule is a stipulation that allows you to bill Medicare insurance carries for one full unit if the service provided is between 8 and 22 minutes. As such, this can only apply to time-based CPT codes. But, the 8-minute rule doesnt apply to every time-based CPT code, or every situation.
What is the CPT code for syphilis?
Quantitative syphilis testing is indicated in the follow up of previous positive testing at periodic intervals not to exceed semiannually until seronegativity occurs. Local policies are determined by the performing test location.
How do you code syphilis?
Code 096 is assigned for syphilis without clinical manifestations, with positive serological reaction and negative spinal fluid test, two years or more after infection. Code 097.1 is assigned for latent syphilis, unspecified or when there is a positive serological reaction for syphilis.
What is syphilis unspecified?
Infections with a predominantly sexual mode of transmission A stage of syphilis characterized by the serologic evidence of infection by treponema pallidum without evidence of accompanying signs or symptoms related to the disease.
You May Like: Sign Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
What Are Side Effects Of Inactivated Viral Vaccines
Side effects of inactivated viral vaccines may include the following:
- Injection site reactions include:
Information contained herein is not intended to cover all possible side effects, precautions, warnings, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or adverse effects. Check with your doctor or pharmacist to make sure these drugs do not cause any harm when you take them along with other medicines. Never stop taking your medication and never change your dose or frequency without consulting your doctor.
Also Check: New Drug To Cure Hepatitis C