Hepatitis C A Growing Threat To Moms Babies But Screening Is Inadequate
During her third pregnancy, Jamie Smith was itchy. Crazy itchy. Her obstetrician diagnosed her with cholestasis of pregnancy, a serious complication associated with liver disease. Her baby was at risk for being premature or even stillborn, so she was induced at 38 weeks.
Smith’s baby was healthy, but her own problems continued. She had muscle pain, brain fog and icy white hands and feet. Maybe at age 39, she figured, she was just getting older. Her new primary care doctor suggested some tests, including for hepatitis C. It was just a precaution. Her obstetrician had said her liver enzymes were normal and the regular screening tests were negative. While walking her dog near her home in Ohio, Smith casually scanned the electronic results on her phone.
“It said, ‘positive,'” she recalled, “And I’m like, ‘I don’t even know what hep C means.’ Wait, positive is a bad thing, right?”
At home, she searched “What is hep C?” online, which sent her down an Internet rabbit hole of common risk factors, including IV drug use, tattoos or piercings, having HIV or spending time in prison. She cried.
“I have lived the most boring life,” Smith said. “So it was a shock that I had this virus that comes with this stigma.”
Video: What to know about getting vaccinated if youre pregnant
“We know that risk factor screening doesn’t work,” says Denise Jamieson at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, who reviews clinical practice guidelines for ACOG.
– – –
Related Content
Treating Hepatitis C Can Help Alleviate Skin Conditions
The good news is that there have been great advancements in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C using direct-acting antiviral medications, which reduce the viral load significantly enough to cure the infection.
They involve taking pills once a day for eight to 12 weeks, with cure rates above 95 percent, says Kuo. Unlike past treatments for hepatitis C, direct-acting antivirals are also safe and have minimal side effects. Once the hepatitis C is treated, all related skin issues should clear as well.
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis B is hepatitis caused by the hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B virus spreads through contact with infected blood. Specifically, hepatitis B may be spread through:
- Direct contact with the blood of an infected person
- Unprotected sexual activity with an infected person
- Needle sharing among intravenous drug users
- Sharing razors or other personal items with an infected person
- Being pierced or tattooed with contaminated instruments
- Blood transfusions
- Childbirth, when the virus is passed from mother to child
The hepatitis B virus can cause temporary or long-term hepatitis. The initial infection with the virus may not even cause symptoms.Immunization with the hepatitis B vaccine can greatly reduce the risk of hepatitis B.
People that do develop symptoms following initial infection with the virus have acute hepatitis. Most of them will clear the virus from their liver and blood.
But a minority of people will develop a long-term infection. This is called chronic hepatitis. In chronic hepatitis, the symptoms of hepatitis often disappear then come back later. People with chronic hepatitis remain infectious. They can pass on the virus to others.
Some people are not able to rid their body of the infection. But they do not have any symptoms of disease. These people are called carriers. They also can pass the infection to others.
You May Like: How Does Hepatitis C Transmitted
What Causes Autoimmune Hepatitis
Experts arent sure what causes autoimmune hepatitis. Studies suggest that certain genes make some people more likely to develop autoimmune diseases. In people with these genes, factors in the environment may trigger an autoimmune reaction that causes their immune system to attack the liver.
Researchers are still studying the environmental triggers that play a role in autoimmune hepatitis. These triggers may include certain viruses and medicines.
Some medicines can cause liver injury that resembles autoimmune hepatitis. In most cases, the liver injury goes away when the medicine is stopped. The most common medicines that cause liver injury that resembles autoimmune hepatitis are minocyclinean antibiotic used to treat acneand nitrofurantoinan antibiotic used to treat urinary tract infections. Telling your doctor the names of all the medicines you take, even over-the-counter medicines or herbal or botanical products, is important.
Tips For Stopping The Itch
Below are some tips that may help control the incessant itching:
Read Also: How Soon Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Appear
Got Hbv What Is Your Skin Trying To Tell You
The liver is the largest solid organ in the body, and your skin is the largest organ. It only makes sense that the skin may be a window into what is going on inside your body and your liver. The problem is trying to figure out what your skin is trying to tell you!
The most common skin manifestation associated with hepatitis is the yellowing of the skin and the sclera, or white part of the eye. Jaundice may be associated with a newly acquired or acute hepatitis B infection. It certainly gets your attention and gets you to the door of your doctor, which is a good thing. However, keep in mind that HBV is often asymptomatic, with few or no obvious symptoms, and jaundice is a more severe symptom of an acute HBV infection. Jaundice may also occur in those with advanced liver disease, and a decompensated liver. Jaundice is due to an accumulation of bilirubin, a yellow pigment, in the blood and tissues. Your liver is responsible for controlling the levels of bilirubin. If your liver is having problems performing basic, yet essential functions, yellow skin, eyes, dark urine, and itching may all be due to an inability to filter excess bilirubin. Please see your doctor immediately if you experience jaundice of the skin or eyes.
Alcohol Use With Mavyret
There arent any known interactions between alcohol and Mavyret. But, you shouldnt drink alcohol if you have hepatitis C virus , which Mavyret is used to treat. Alcohol worsens HCV and can potentially lead to cirrhosis in your liver.
Talk with your doctor if you have questions about alcohol use while taking Mavyret.
Read Also: What Are The Effects Of Hepatitis A
Acute Hepatitis C: What Are The Signs And Symptoms
For acute hepatitis C, the incubation period is two weeks to three months after exposure, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
Most people who contract acute hepatitis C do not show any symptoms, the CDC notes. And because there are no symptoms, they never receive a diagnosis. But others with acute hepatitis C have the following symptoms:
- Gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or clay-colored feces
- Joint pain
- Jaundice
For reasons that arent well understood, a small percentage of individuals exposed to HCV about 15 to 25 percent only develop an acute infection that clears out of the body spontaneously, says Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious disease physician and senior scholar at Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security in Pittsburgh. The infection usually clears from the body within six months. The remaining 75 to 85 percent of those exposed to HCV develop chronic hepatitis C.
Among those who develop an acute infection with symptoms, symptoms typically last only 2 to 12 weeks.
Contaminated Needles And Infected Blood
You can get hepatitis C from sharing contaminated needles, syringes and other injecting equipment during recreational drug use. Banknotes and straws used for snorting may also pass the virus on.
Being exposed to unsterilised tattoo and body piercing equipment can also pass hepatitis C on. Occasionally, you can get it from sharing a towel, razor blades or a toothbrush if there is infected blood on them.
Hepatitis C infection is also passed on in healthcare settings, from needle stick injuries or from medical and dental equipment that has not been properly sterilised. In countries where blood products are not routinely screened, you can also get hepatitis C by receiving a transfusion of unscreened blood and blood products.
You can prevent hepatitis C by:
- never sharing needles and syringes or other items that may be contaminated with infected blood
- only having tattoos, body piercings or acupuncture in a professional setting, where new, sterile needles are used
- following the standard infection control precautions, if youre working in a healthcare setting.
You May Like: How Do You Get Hepatitis A B C
Functions Of The Liver
The liver serves several functions: it filters blood, removing toxic substances from drugs, food and body waste it makes bile, which is released into the gut to help digest fat and it breaks down food, releasing energy and storing vitamins and minerals. So the liver is important in getting rid of waste and in giving you energy. The liver also has a role in fighting infections, particularly in the bowel.
Living With Hbv And Dealing With Itchy Skin
The previous Hepbtalk blog discussed skin manifestations associated with hepatitis B and liver disease. This is a follow-up with some suggestions on dealing with rashes and pruritus skin. Unfortunately, I have experience with this.
Most people living with HBV have episodes with rashes that itch, or with an itch without the rash. Rashes can be caused by all kinds of things, but the skin truly does let us know when there is something going on with our body. We may not be able to eliminate the itch, but we can work on providing the body with a little relief, and to be sure we do not do anything to make the persistent itching worse.
First, consider the root of the problem. It is possible that your rash and itching are unrelated to the current status of your HBV infection. Unless you have serious liver disease, this might be difficult to pin down since many living with chronic HBV have compensated livers that perform all of the necessary liver functions required for life. That does not mean you arent going crazy with itchy skin, but it is important to look at other factors that may be contributing to your pruritus.
Here are some simple things you can do to help reduce the degree of pruritus:
Got any tips for reducing the itch? Feel free to comment and share your ideas with others living with HBV.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Is Caused By
How One Black Man Was Cured Of Hep C Despite Racial Bias
According to the CDC, approximately 10 to 20 percent of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over a period of two to three decades.
People with cirrhosis have a 1 to 5 percent annual risk of developing liver cancer and a 3 to 6 percent risk of hepatic decompensation . Theres a 15 to 20 percent risk of death in the year following the development of decompensation.
Age and gender have been shown to affect how chronic hepatitis C progresses, warns Adalja. It doesnt advance to cirrhosis and liver cancer as quickly in premenopausal women as it does in men, according to a report published in July 2013 in Southern Medical Journal.
Adalja notes that other factors that may accelerate chronic hepatitis C progression, increasing the risk of liver damage. These include HIV or hepatitis B coinfection, alcohol overuse, and cigarette smoking. The symptoms of chronic hepatitis C vary depending on the type of liver damage.
Cirrhosis can produce a variety of symptoms:
- Itchiness
- Abdominal bloating from a buildup of fluids
- Swelling in the feet, ankles, or legs
- Spider angiomas
How Long Does Hepatitis A Last
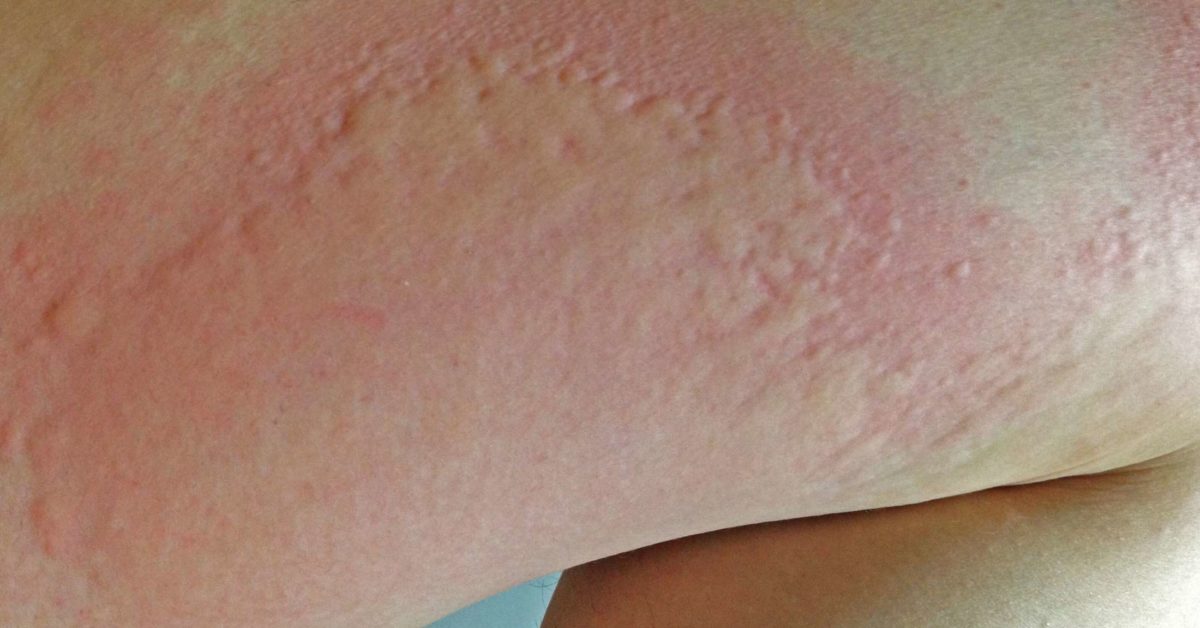
How long it lasts can vary from person to person. Symptoms can range from mild to severe. Some things to keep in mind:
- Mild hepatitis A may last 1 to 2 weeks.
- Most people are much better within 3 weeks.
- Young children who get symptoms usually get better within 2 months.
If you have a severe infection, it can cause problems for several months. You may need to stay in the hospital.
Some people have symptoms that can last more than 3 months or have problems that come and go for 3 to 9 months.
Show Sources
CDC: “Traveler’s Health: Hepatitis A,” “Viral Hepatitis,” Hepatitis A Questions and Answers for the Public,” “Hepatitis A Vaccine.”
National Health Service: “Hepatitis A — Complications.”
Mandell, G.L., Bennett, J.E., Dolin, R., editors, Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 7th edition, Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, 2009.
Long, S.S., editor, Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, 3rd edition, Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, 2008.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Infectious Diseases: “Hepatitis A Vaccine Recommendations.”
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis A.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis A virus infection in adults: Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis.â
Don’t Miss: How Is Hepatitis C And B Transmitted
What To Know About Liver Disease And Covid
Coronavirus disease 2019 is the illness caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Older adults and people of any age who have serious underlying medical conditions, including people with liver disease, might be at higher risk for severe illness from COVID-19. People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C, may have concerns and questions related to their risk.
Some patients hospitalized for COVID-19 have had increased levels of liver enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase . Increased levels of liver enzymes can mean that a persons liver is at least temporarily damaged. People with cirrhosis may be at increased risk of COVID-19. Some studies have shown that people with pre-existing liver disease who were diagnosed with COVID-19 are at higher risk of death than people without pre-existing liver disease.
Adults of any age with certain underlying medical conditions, including people with liver disease , might be at increased risk for severe illness from the virus that causes COVID-19. People might be more likely to have severe disease if their medical conditions are not well controlled. People who are on treatment for hepatitis B or C should continue their treatment unless otherwise directed by their healthcare provider.
If you are a member of any of these groups, contact your healthcare provider to request the hepatitis A vaccine:
What Is Hepatitis A
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. There are a number of things that can cause hepatitis – for example, drinking too much alcohol, various drugs and chemicals and also several different viruses. One virus that causes hepatitis is called the hepatitis A virus. After first contact with the virus, hepatitis A virus is carried in the bloodstream to your liver. It can then affect your liver to cause hepatitis.
Note: hepatitis A should not be confused with hepatitis B or C. Hepatitis B and C are caused by different viruses and are more serious diseases. See the separate leaflets called Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C for more details.
Also Check: Where To Get Hepatitis Vaccine
How Does Hepatitis C Affect Your Body
Hepatitis C is an inflammation of the liver. The hepatitis C virus is most often transmitted through infected blood, such as by sharing needles, says Alexander Kuo, MD, medical director of liver transplantation at Cedars-Sinai in Los Angeles.
Sexual transmission is very uncommon, he says. In healthy adults, youre more likely to catch HCV by sharing a toothbrush or razor than through sexual contact. Using barrier methods during sex decreases the risk further.
People who contract HCV often dont realize they have it. During the early stages of infection, the vast majority of people are symptom free, Dr. Kuo says, so it can be difficult to diagnose before it has already done lasting damage to your liver.
People who may have been exposed children of women who have hepatitis C people who have gotten at-home tattoos and those whove used intravenous drugs should get a onetime blood test to screen for HCV even before they experience symptoms, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . People who actively inject drugs should have routine screenings.
Over time, the chronic inflammation from untreated hepatitis C can lead to fibrosis, or scarring, in the liver. Kuo cautions that if this continues for 20 or more years, there is a risk that the liver can become hard from severe fibrosis, resulting in a condition called cirrhosis.
Serious Side Effects Of Mavyret
Mavyret may cause serious side effects. But its not known to cause side effects that last a long time. The list below may not include all possible serious side effects of the drug. For more information, you can refer to Mavyrets medication guide.
If you develop serious side effects while taking Mavyret, call your doctor right away. If the side effects seem life threatening or you think youre having a medical emergency, immediately call 911 or your local emergency number.
Serious side effects* that have been reported include:
Mavyret may cause several side effects. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about the drugs side effects.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Airborne
What Are The Symptoms Of The Hepatitis A Virus
Low energy is the most common symptom of HAV. Other symptoms include fever, tiredness, loss of appetite, nausea, headache, itchy skin, muscle soreness, pain near the liver, and jaundice .
Symptoms of HAV can occur two to seven weeks after infection and are often mild. Children may not have any symptoms. Symptoms usually go away within two months. If you think you have HAV, it is important to see a doctor symptoms of HAV are similar to other more serious liver diseases.