Approved Drugs For Adults
There are currently 7 approved drugs in the United States for adults living with chronic hepatitis B infection. These include 5 types of antiviral drugs that are taken as a pill once a day for 1 year or longer. And there are 2 types of immune modulator drugs called interferon that are given as an injection for 6 months to 1 year.
It is important to know that not everyone needs to be treated. A liver specialist should evaluate your health through a physical exam, blood tests, and an imaging study of your liver . Then you can discuss together whether you are a good candidate for treatment since the approved drugs are most effective when there are signs of active liver disease. In addition, talk to your provider about HBV Clinical Trials since there are several new drugs being tested that are available for infected adults.
All adults, however, should be seen regularly by a liver specialist whether they are on treatment or not.
Take Precautions To Avoid Hbv
Other ways to reduce your risk of HBV include:
- Know the HBV status of any sexual partner. Don’t engage in unprotected sex unless you’re absolutely certain your partner isn’t infected with HBV or any other sexually transmitted infection.
- Use a new latex or polyurethane condom every time you have sex if you don’t know the health status of your partner. Remember that although condoms can reduce your risk of contracting HBV, they don’t eliminate the risk.
- Don’t use illegal drugs. If you use illicit drugs, get help to stop. If you can’t stop, use a sterile needle each time you inject illicit drugs. Never share needles.
- Be cautious about body piercing and tattooing. If you get a piercing or tattoo, look for a reputable shop. Ask about how the equipment is cleaned. Make sure the employees use sterile needles. If you can’t get answers, look for another shop.
- Ask about the hepatitis B vaccine before you travel. If you’re traveling to a region where hepatitis B is common, ask your doctor about the hepatitis B vaccine in advance. It’s usually given in a series of three injections over a six-month period.
What Is My Risk
Your risk depends of several factors: destination, length of stay, what you do when you are travelling and whether you have direct contact with blood or other body fluids. In certain destinations, your risk may be higher, as some areas have higher numbers of people with chronic hepatitis B in the general population.
The risk increases with certain activities, such as unprotected sex, sharing needles, tattooing and acupuncture.
Aid and health care workers and anyone who receives medical or dental care with unsterilized or contaminated equipment in a country where hepatitis B occurs are also at greater risk.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cvs Cost
Also Check: How Can You Cure Hepatitis C
Spread Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is spread through blood-to-blood contact when blood from a person with hepatitis C enters another persons bloodstream.
The most common way people become infected with hepatitis C in Australia is by sharing injecting equipment such as needles, syringes, spoons and tourniquets. It is possible to be infected with hepatitis C after only one risk event.
Hepatitis C may also be spread through:
- tattooing and body piercing with equipment that has not been properly cleaned, disinfected or sterilised such as backyard tattoosâ. Registered parlours with appropriate infection control procedures are not a risk
- needlestick injuries in a healthcare setting
- receiving blood transfusions in Australia prior to 1990 before hepatitis C virus testing of blood donations was introduced
- medical procedures, blood transfusions or blood products and mass immunisation programs provided in a country other than Australia
- pregnancy or childbirth there is a 5% chance of a mother with chronic hepatitis C infection passing on the virus to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
Breastfeeding is safe, however if nipples are cracked or bleeding cease breastfeeding until they have healed.
Less likely possible routes of transmission of hepatitis C include:
Hepatitis C cannot be transmitted by:
- sharing food, cups or cutlery
- shaking hands or day-to-day physical contact.
Dont Miss: Is Hepatitis Contagious Through Saliva
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
Read Also: How Much Are Hepatitis B Shots
Screening Healthy People For Hepatitis B
Doctors sometimes test certain healthy people for hepatitis B infection because the virus can damage the liver before causing signs and symptoms. Talk to your doctor about screening for hepatitis B infection if you:
- Live with someone who has hepatitis B
- Have had many sexual partners
- Have had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- Are a man who has sex with men
- Have a history of a sexually transmitted illness
- Have HIV or hepatitis C
- Have a liver enzyme test with unexplained abnormal results
- Receive kidney dialysis
- Take medications that suppress the immune system, such as those used to prevent rejection after an organ transplant
- Use illegal injected drugs
- Were born in a country where hepatitis B is common, including Asia, the Pacific Islands, Africa and Eastern Europe
- Have parents or adopted children from places where hepatitis B is common, including Asia, the Pacific Islands, Africa and Eastern Europe
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis C
For people with hepatitis C, the goal of treatment with antiviral medication is to prevent the virus from replicating, or copying itself, and to eliminate the virus from the bloodstream. If the hepatitis C virus has been in the body for more than six months, the infection is considered chronic. Without treatment, most people with acute hepatitis C develop the chronic form of the disease.
Your doctor decides which antiviral medicationor combination of medicationsto prescribe based on the results of a blood test called a genotype test. There are six genotypes, or strains, of the hepatitis C virus, and people with certain genotypes respond more quickly to medical treatment.
For many years, the standard treatment for chronic hepatitis C consisted of the antiviral medications pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Ribavirin is taken by mouth every day, and interferon is an injection that you or a caregiver can administer once a week at home.
In 2013 and 2014, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a group of new medications for the treatment of hepatitis C. These medications, which include sofosbuvir, are very effective and have fewer side effects than older medications, particularly interferon.
You May Like: What Is The Hepatitis B Shot For
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
Stool Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
**When you think about hepatitis, the first thing that comes to mind is probably your liver.
If you are experiencing serious medical symptoms, seek emergency treatment immediately.
** But infection with the hepatitis C virus can lead to stool symptoms as well. Diarrhea can occur in the early or late stages of hepatitis C infection, or it may be a side effect of medications used to treat the virus. Severe liver disease may also cause pale, oily, bloody or tar-like stools. If you have hepatitis C, it is important to be aware of stool symptoms, as they are often an indicator of disease severity, and some require prompt medical care.
Read Also: Good Food For Hepatitis C
How Long Does It Last
According to the World Health Organization , the complete vaccine series induces protective antibody levels in of the infants, children, and adolescents who receive it.
Immune memory induced by the HBV vaccine can last for in healthy people. That said, studies into the duration of the protection that the vaccine offers are ongoing.
Hepatitis B During Pregnancy
If a woman with HBV becomes pregnant, they may transmit the virus to their baby. Women should inform the doctor who delivers their baby that they have HBV.
The infant should receive an HBV vaccine and HBIG with 1224 hours of birth. This significantly reduces the risk that they will develop HBV.
The HBV vaccine is safe to receive while pregnant.
People with a high risk of HBV include:
- the infants of mothers with HBV
- the sexual partners of people with HBV
- people who engage in sexual intercourse without contraception and those who have multiple sexual partners
- men who have sex with men
- people who inject illicit drugs
- those who share a household with a person who has a chronic HBV infection
- healthcare and public safety workers who are at risk of occupational exposure to blood or contaminated bodily fluids
- people receiving hemodialysis, which is a type of kidney treatment
- people taking medications that suppress the immune system, such as chemotherapy for cancer
People can prevent HBV infection by:
- wearing appropriate protective equipment when working in healthcare settings or dealing with medical emergencies
- not sharing needles
- following safe sexual practices
- cleaning any blood spills or dried blood with gloved hands using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts water
A vaccine against HBV has been available since 1982.
People who should receive this vaccine include:
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Infection
What Is The Medical Treatment For Hepatitis B
Acute hepatitis B infection
Acute hepatitis B infection is not treated with antiviral medications.
- If the infected person is dehydrated from vomiting or diarrhea, a doctor may prescribe IV fluids to help them feel better. Medications may also be used to control these symptoms.
- People with mild symptoms can be cared for at home.
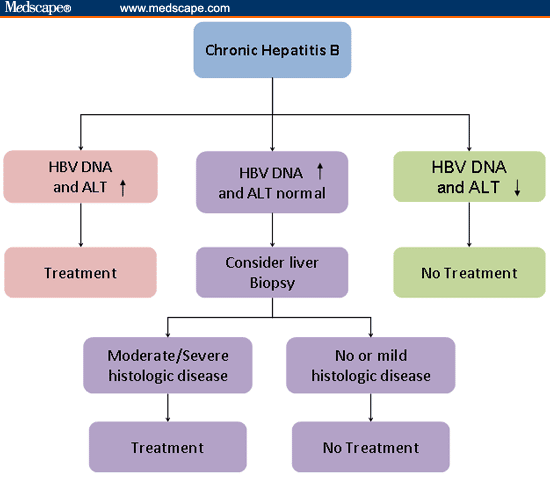
Chronic hepatitis B infection
The degree of liver damage is related to the amount of active, replicating virus in the blood and liver. Regularly measuring the amount of HBV DNA in the blood gives your physician a good idea of how fast the virus is multiplying. The treatments now in use are classified as antiviral drugs because they work by stopping the virus from multiplying.
Treatment is usually started when blood tests indicate that liver functions are deteriorating and the amount of replicating HBV is rising. Many people never reach this point. For those who do, the interval between diagnosis and starting treatment is quite variable.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis C
With The Momentum Growing Around Hepatitis B Drug Discovery Research We Are Closer Than Ever To A Cure
From the Spring 2016 B Informed Newsletter
With the momentum growing around hepatitis B drug discovery research, how far are we from a cure?
Closer than ever, according to Timothy Block, PhD, president and co-founder of the Hepatitis B Foundation and its research arm, the Baruch S. Blumberg Institute. He points out that hepatitis C, initially thought to be incurable, can now be cured with new combination treatments.
Hepatitis B is in a similar position, Block believes. And the need for a cure has never been greater, with over 240 million people living with chronic hepatitis B infection worldwide, resulting in 1 million deaths per year from related liver failure and liver cancer.
Treatments are available, explains Block, but we have become a little too comfortable with the seven medications that are currently approved for use. While these drugs are effective, the interferons have many side effects and the oral antivirals require lifelong use. Moreover, they work in only about half of the infected population, and reduce the rate of death due to liver disease by only about 40 to 70 percent.
For those who benefit from treatment, the antiviral drugs prove that medications can be effective. However, there are millions who do not benefit and are still left vulnerable. We should not accept that a significant number of people will still die from hepatitis B-related complications despite taking the current drugs, Block declares.
What would a cure look like?
cccDNA Inhibitors
You May Like: Hepatitis B Can It Be Cured
Who Is At Risk
All people who are sexually active may be at risk for hepatitis B. Specific populations in Canada that are disproportionately affected with hepatitis B include Aboriginal peoples, people who inject drugs, men who have sex with men , people who are street involved or homeless, those who have been incarcerated or institutionalized, and those with close household or sexual contact with any of the people listed above.
Certain factors may put individuals at an increased risk of hepatitis B infection. Sexual factors , a family history of hepatitis B, or being the recipient of a blood transfusion or medical procedure before 1970 are also related to an increased risk of hepatitis B infection.
Regional factors may also be related to an increased risk of hepatitis B infection. For example, birth in a region with a high prevalence rate of hepatitis B , household exposure for more than seven years to family members from a high prevalence region, travel to or residing in a high prevalence region, exposure to blood or blood products in a high prevalence region.4,5
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis Turn Into Hiv
Low Response Rates And Nonresponders
Low vaccination response rates have been associated with obesity, smoking, immunosuppression, and advanced age. Approximately 25-50% of persons who initially do not have a vaccine response will show a response to 1 additional vaccine dose, and 50-75% of individuals will have a response to a second 3-dose series.
It is recommended that testing for anti-HBs be obtained 4-12 weeks following vaccination. Revaccinate nonresponders, with another series of 3-dose hepatitis B vaccine. Consider delaying revaccination for several months after initiation of antiretroviral therapy in patients with CD4 counts below 200 cells/mm3 or those with symptomatic HIV disease. The delay in these individuals is an attempt to maximize the antibody response to the vaccine.
Do not defer vaccination in pregnant patients or patients who are unlikely to achieve an increased CD4 count. Individuals at increased risk of severe complications due to HBV infection include those unlikely to achieve CD4 counts of 200 cells/mm3 or above after antiretroviral therapy and HIV-infected pregnant women.
A combined hepatitis A virus /HBV vaccine is licensed in many countries and offers the advantage of protection against both of these viruses at the same time. The vaccine seems to be safe, although some questions exist regarding neurologic complications.
Lifestyle And Home Remedies
If you’ve been infected with hepatitis B, take steps to protect others from the virus.
- Make sex safer. If you’re sexually active, tell your partner you have HBV and talk about the risk of transmitting it to him or her. Use a new latex condom every time you have sex, but remember that condoms reduce but don’t eliminate the risk.
- Tell your sexual partner to get tested. Anyone with whom you’ve had sex needs to be tested for the virus. Your partners also need to know their HBV status so that they don’t infect others.
- Don’t share personal care items. If you use IV drugs, never share needles and syringes. And don’t share razor blades or toothbrushes, which may carry traces of infected blood.
Recommended Reading: Can You Catch Hepatitis B