What Is Being Tested
Hepatitis C is a virus that causes an infection of the liver that is marked by liver inflammation and damage. Hepatitis C tests are a group of tests that are performed to diagnose hepatitis C infection and to guide and monitor treatment of the infection.
Hepatitis C tests include:
Hepatitis C is one of five viruses identified so far, including A, B, D, and E, that are known to cause hepatitis.
HCV is spread when contaminated blood enters the body, primarily though sharing needles and syringes during IV drug use. HCV is spread less commonly by sharing personal items contaminated with blood , through sex with an infected person, needlestick injuries to healthcare workers, unregulated tattooing, and from mother to baby during pregnancy and childbirth. Before tests for HCV became available in the 1990s, HCV was often transmitted by blood transfusions. Currently, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C.
Antibody Testing After Treatment
For many years, we have said that people will always have antibodies present when tested, even after being cured. It has mostly been in the context of a person being tested in some future medical investigation unrelated and showing a positive antibody test result. Some who have been cured have shared some confusion when they are informed they have hep C, despite being cured. As this is not always understood well in healthcare, there is no good explanation in that instance from the care provider.
To be fair, I am hearing this less from people, but I suspect it may still occur. I have had a few tests done in recent years as part of my work in testing and linkage to care. The most recent test was with a proven testing mode commonly used, point of care testing . In the process of filming an instructional video to show how these POCTs are done, I was the testing subject. I expected a positive result, as I had lived with hep C and I was cured 10 years ago. My test showed up as negative to my surprise. I retested and got the same result.
Hepatitis A Test Results
A total antibody test detects both IgM and IgG antibodies but does not distinguish between them. If the total antibody test or hepatitis A IgG result is positive and someone has never been vaccinated against HAV, then the person has had past exposure to the virus.
Hepatitis A infection is typically diagnosed through blood tests. Fortunately, blood tests are widely available to accurately diagnose hepatitis A, including tests for antibodies, or the affected persons immune response to hepatitis A proteins. The IgG antibodies are present for life, indicating immunity.
Treatment generally involves supportive care, with specific complications treated as appropriate. Liver transplantation, in selected cases, is an option if the patient has fulminant hepatic failure . Patients at risk of developing acute hepatitis A virus infection should undergo immunization for the virus.
Recommended Reading: New Drug To Cure Hepatitis C
Looking Further: Hcv Vaccines
Vaccine development for HCV is currently one of the most challenging fields in virology today. Various obstacles that hinder the development of an effective preventive or therapeutic vaccine for HCV include:
Considerable genetic heterogeneity of isolates within and between geographic locales .
Evolution and existence of quasispecies in an individual .
Poorly defined immunological correlates of protection.
Lack of efficient in vitro propagation to isolate the virus.
Despite these obstacles, both preventive as well as therapeutic vaccines for HCV are under development and also under various phases of vaccine trials, but a successful vaccine remains to be developed.
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
Patients receiving hepatitis C testing may find it helpful to ask questions about their test results. Questions to consider include:
- What type of hepatitis C test did I receive?
- What was my test result?
- How do you interpret the results of the hepatitis C tests that I had?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my test result?
Read Also: What Is The Definition Of Hepatitis B
When To Get Tested
For screening: at least once when you are age 18 years or older when you are pregnant when you have risk factors for HCV infection, regardless of age
For diagnosis: when you may have been exposed to the hepatitis C virus, such as through injection drug use, or when you have signs and symptoms associated with liver disease
For monitoring: before, during, and after hepatitis C treatment
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
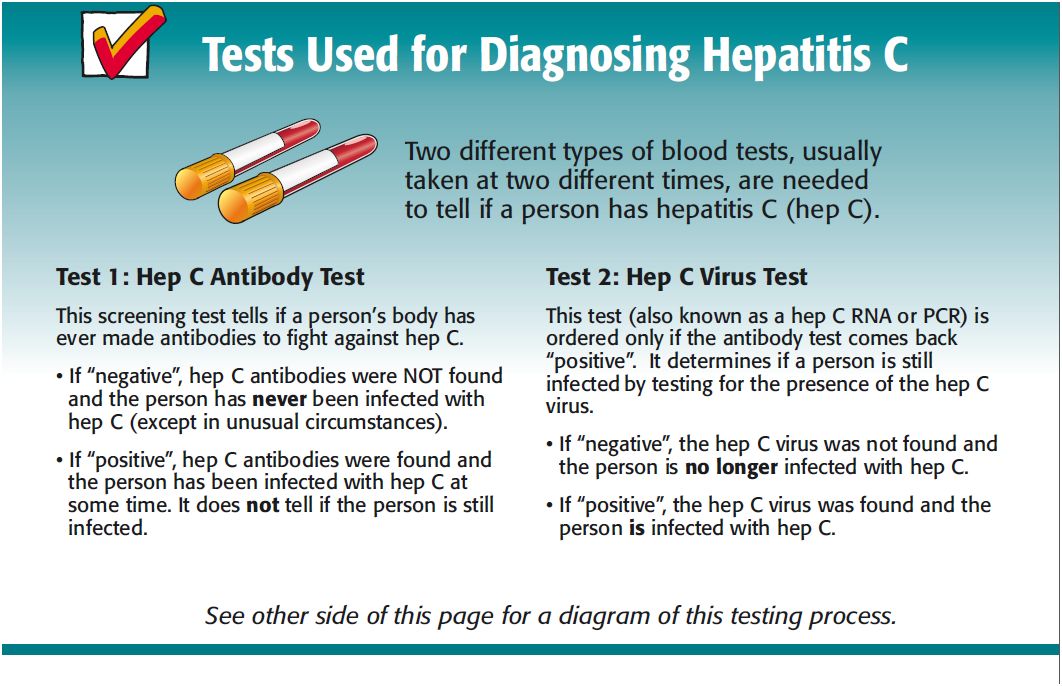
A blood test, called an HCV antibody test, is used to find out if someone has ever been infected with the hepatitis C virus. The HCV antibody test, sometimes called the anti-HCV test, looks for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus in blood. Antibodies are chemicals released into the bloodstream when someone gets infected.
Test results can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks to come back. Rapid anti-HCV tests are available in some health clinics and the results of these tests are available in 20 to 30 minutes.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis C
How Can I Tell If I Am Contagious And Can Spread The Infection To Others
If you have detectable HCV RNA in your blood, you have the potential to spread the disease to other people. Hepatitis C is spread by exposure to contaminated blood. The most common mechanism of exposure is the sharing of needles or other ‘works’ used in consuming drugs such as cocaine or heroin. Other routes of transmission include use of contaminated equipment for body piercing and tattooing, occupational exposure of healthcare workers to used needles or other sharp objects, and, less commonly, through sexual activity that results in tissue tears or from mother to baby during childbirth.
Interpreting Hcv Rna Test Results
It is essential that the provider understands how to interpret HCV RNA test results, especially during the course of HCV treatment.
| Result of HCV RNA Test | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| A quantified viral load — any exact number | Ongoing HCV infection |
| “Detected” | The HCV RNA is detectable but the number of international units is so low that it cannot be quantified accurately. This indicates extremely low level of virus is present. |
| “< 12 IU/mL” or “< 15 IU/mL” or “< 25 IU/mL” All of these are “less than the LLOQ” | HCV RNA is undetectable. No virus is detected at all in the patient’s serum specimen. |
Recommended Reading: How Do You Contract Hepatitis B Virus
Understanding Your Test Results
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
Appropriate Uses Of The Hcv Rna Test
There are 4 major reasons that HCV RNA tests are used:
More rarely, HCV RNA is used when either very acute HCV infection is suspected or a false HCV Ab is suspected.
It would not be appropriate to repeatedly order HCV RNA viral load screening for a patient who is not on or was recently on HCV treatment, or to use the HCV viral load to determine the severity of the patient’s infection or the patient’s risk of developing significant liver disease.
Don’t Miss: What Does Hepatitis B Do
Who Should Get A Hepatitis C Screening
If youre under 18, you may or may not need a parents or guardians consent to get tested. State laws on minor consent for medical care vary. If youve been exposed to hepatitis C or feel that you need a test for any reason, dont let your age stop you from getting the medical help you need.
If left untreated, hepatitis C can have serious consequences for your health. If you test positive, you can also pass the virus onto others.
The recommends universal hepatitis C screening for:
- all adults aged 18 and over
- pregnant people
Iatrogenic Exposure And Postexposure Prophylaxis
The potential of health care delivery to transmit HCV to healthcare worker is increasingly being recognized especially if infection control or disinfection practices are inadequate and contaminated equipment is shared among patients. The mechanisms of transmission in the healthcare setting are related to:
-
Improperly cleaned, disinfected, or sterilized equipment
-
Medication administration
-
Blood sampling
The CDC in collaboration with healthcare infection control practices advisory committee has issued recommendations following occupational exposure to HCV. These recommendations emphasize that each institution should have its own policy regarding follow-up of personnel who sustain percutaneous or permucosal exposure to suspected HCV infected blood. They minimally recommend:
Baseline testing for anti-HCV in source.
Baseline and follow-up testing for anti-HCV and alanine aminotransferase levels in exposed at 6 months and 1 year postexposure.
Confirmation by NAT of all anti-HCV reactive results.
Education of workers about the risk for and prevention of blood-borne infections.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Ab W Reflex Hcv Rna Quant Rt Pcr
Inherited Forms Of Hepatitis
Several inherited diseases affecting the liver can become apparent, primarily by causing symptoms of acute or chronic hepatitis. Some examples include:
- Hemochromatosis is the most common form of inherited hepatitis and is associated with absorption and accumulation of too much iron in the body. The liver is one of the principal organs damaged, and chronic hepatitis may be due to iron overload.
- Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency is the most common genetic cause of liver disease in children. In adults, the disorder is more likely to affect the lungs, but cirrhosis and liver cancer are both more common in those with alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency.
- Wilson disease is a rare inherited disorder that causes a buildup of excess copper in the liver, brain, kidneys, and eyes. This disease may cause both acute and chronic hepatitis. Unless Wilson disease is treated, it becomes progressively worse and is eventually fatal.
Signs and symptoms of inherited forms of hepatitis are varied and specific to the individual diseases. Click on the links above to find out more about them. Signs and symptoms of the liver involvement in these conditions correspond to those of hepatitis in general. See the section on Signs and Symptoms for detailed information on those.
Laboratory TestsInherited hepatitis may be suspected if there is a family history of liver disease. Some common tests to look for the presence of inherited liver diseases include:
Clinical Features And Natural History
Persons with acute HCV infection are typically either asymptomatic or have a mild clinical illness like that of other types of viral hepatitis . Jaundice might occur in 20%30% of persons, and nonspecific symptoms might be present in 10%20% of persons. Fulminant hepatic failure following acute hepatitis C is rare. The average time from exposure to symptom onset is 212 weeks . HCV antibodies can be detected 410 weeks after infection and are present in approximately 97% of persons by 6 months after exposure. HCV RNA can be detected as early as 12 weeks after exposure. The presence of HCV RNA indicates current infection .
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis C Test Done
What Is A False Positive
A false-positive result means that a test indicated that you have a disease or condition when you actually dont.
There are two blood tests used to diagnose hepatitis C. The antibody test, also called the anti-HCV test, tests for HCV antibodies that the body has produced in response to the infection.
One drawback is that the anti-HCV test cant differentiate between an active infection versus a chronic or previously acquired infection.
A positive anti-HCV test doesnt necessarily mean that you have hepatitis C. Antibodies picked up by the test may have been triggered by an infection other than HCV, leading to a positive result.
This phenomenon is known as cross-reactivity, and it often results in a false positive. The results may be verified through a second blood test.
The hepatitis C viral load test, also called an RNA test, will show whether you have chronic hepatitis C or a false positive.
2017 report , 22 percent of 479 subjects received a false-positive anti-HCV test.
According to a 2020 report, the rate of false-positive test results among 1,814 reactive serum samples was 10 percent.
Nat: Detection Of Hcv Rna
Molecular virological techniques play a key role in diagnosis and monitoring of treatment for HCV. Because it is difficult to cultivate the virus in cell culture, molecular techniques were instrumental in first identifying HCV, making it one of the first pathogens to be identified by purely molecular methods. NAT is considered the gold standard for detecting active HCV replication. HCV NAT is extremely useful in establishing the diagnosis of acute HCV infection, since RNA is detectable as early as 1 week after exposure via needle-stick or blood transfusion, and at least 4-6 weeks prior to seroconversion as demonstrated in a number of transmission settings. The diagnosis of HCV infection is established with antibody screening followed by NAT for HCV RNA for confirmation as well as for follow-up of patients on treatment. Viral load assessment at baseline is also critical for determining response kinetics during therapy. enumerates the role of NAT in HCV diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Alcohol
When Should I Get Hepatitis C Testing
When used for early detection in patients without symptoms of hepatitis C, screening is recommended at least once for all adults aged 18 years or older, except in locations with very low prevalence of HCV. Screening is also recommended during pregnancy and for patients of any age with risk factors for HCV infection. In patients with risk factors, periodic screening is recommended for as long as risk factors persist.
Risk factors for HCV include:
- Current or past injectable drug use
- Having a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- Receiving kidney dialysis
- Pain in the abdomen or joints
- Nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite
- Jaundice or yellowish skin and eyes
Hepatitis C testing may also be performed when liver tests are abnormal or when diagnosing the cause of existing liver damage.
Enzyme Immunoassays For Detection Of Hepatitis C Antibody
The HCV Ab test is used for initial screening for hepatitis C. The test is performed by enzyme immunoassays , which detect the presence of hepatitis C antibodies in serum. The result of the test is reported as positive or negative. Third-generation EIAs have a sensitivity/specificity of approximately 99%. However, the presence of HCV Ab does not indicate whether the infection is acute, chronic, or resolved. A positive antibody test result should be followed up with an HCV RNA test to confirm that viremia is present.
Don’t Miss: What Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis C
Treatment For Hcv Infection
Treatment for HCV infection is available. The role of treatment in acute infection is being evaluated and currently the existing data shows that response to 6 months of standard therapy with interferon in terms of absence of HCV RNA from serum is excellent and progression to chronicity is reduced. The recommended treatment for chronic HCV infection is a combination of a pegylated IFN alpha and ribavirin. The treatment duration depends on the genotype of the virus and it has two goals. The first is to achieve sustained eradication of HCV, that is, sustained virologic response , which is defined as the persistent absence of HCV RNA in serum for 6 months or more after completing antiviral treatment. The second goal is to prevent progression to cirrhosis, HCC, and decompensated liver disease requiring liver transplantation.
When Is It Ordered
The CDC, the Infectious Diseases Society of America , the American Association of the Study of Liver Diseases , and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend screening with an HCV antibody test at least once in your lifetime when you are 18 years old or older . The CDC also recommends HCV screening for women with each pregnancy or for anyone who requests it.
One-time screening is recommended regardless of age if you:
- Have ever injected illegal drugs
- Received a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992*
- Have received clotting factor concentrates produced before 1987
- Were ever on long-term dialysis
- Are a child born to HCV-positive women
- Have been exposed to the blood of someone with hepatitis C
- Are a healthcare, emergency medicine, or public safety worker who had needlesticks, sharps, or mucosal exposure to HCV-positive blood
- Have evidence of chronic liver disease
- Have HIVabout 21% of those with HIV are also infected with HCV .
*The blood supply has been monitored in the U.S. since 1992, and any units of blood that test positive for HCV are rejected for use in another person. The current risk of HCV infection from transfused blood is about one case per two million transfused units.
Screening at regular intervals is recommended if you have ongoing risk of HCV infection, such as current injection drug use and sharing needles or syringes.
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting
- Dark urine
- Yellowing of eyes and skin
An HCV RNA test is ordered when:
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis B Come From