About Primary Biliary Cholangitis
The principal roles of the liver include removal of toxins from the blood and processing food nutrients into proteins, fats and carbohydrates. The liver produces bile, which is stored in the gall bladder and added to the digestive tract via bile ducts to help break down dietary fats.
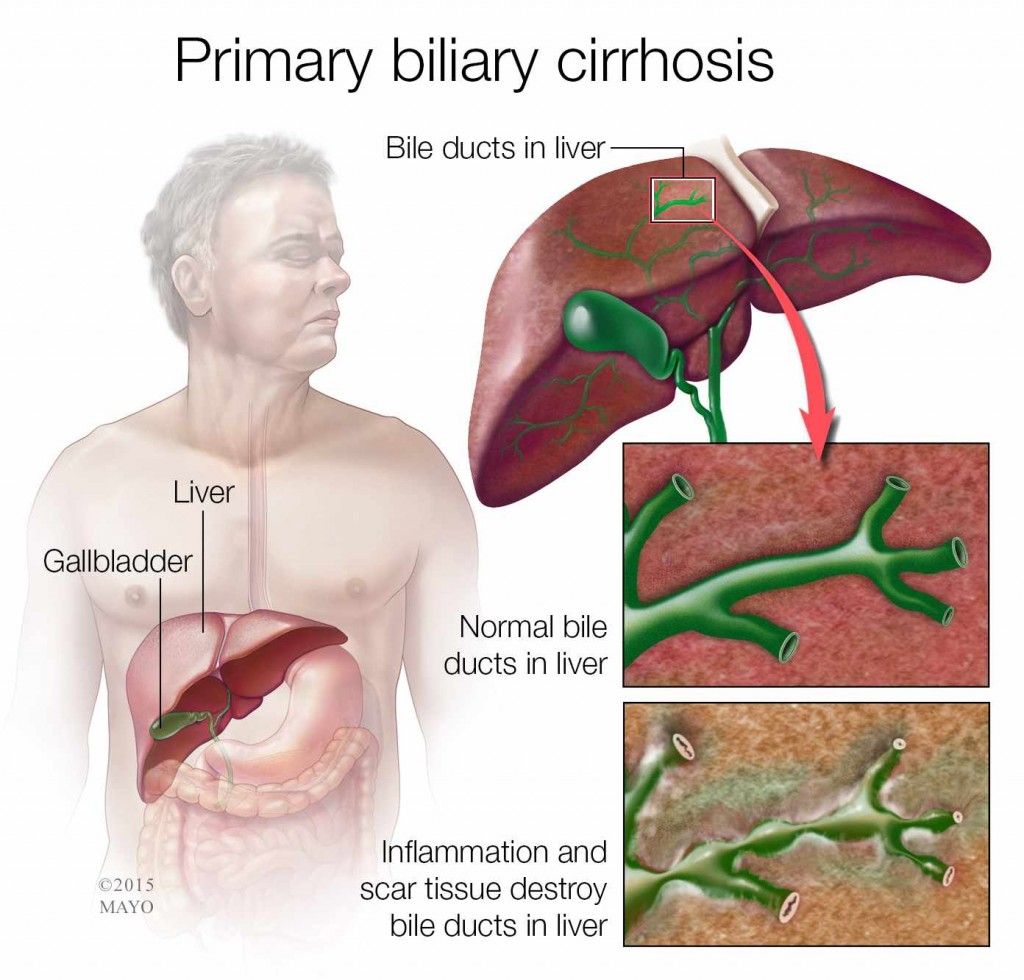
Primary biliary cholangitis is an autoimmune condition characterised by chronic inflammation and subsequent scarring of the bile ducts within the liver. The cause is unknown, although researchers have ruled out alcohol and diet as possible triggers. Women are 10 times more likely to develop PBC than men, for reasons unknown.
The disease is usually diagnosed later in life, between the ages of 35 and 60 years. There is no cure, but treatment can slow the progression of the disease and alleviate symptoms. PBC is associated with other autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma and Sjogrens syndrome.
Paediatric And Young Adults
From early reports of children with PSC it was clear that there were many clinical similarities between PSC and AIH, and in fact these patients had often initially been managed as having AIH.40,41 In approximately a third of these PSC cases, the diagnosis was only made after subsequent investigations, including cholangiography, which revealed features of PSC.
A study that systematically evaluated consecutive children with liver disease and positive antibodies consistent with AIH, with screening cholangiogram and liver biopsy, found ~50% had abnormal cholangiograms.42 The term ASC was used for those with abnormal cholangiograms and positive autoantibodies, who had different characteristics to those with normal cholangiograms. The condition has only been described in paediatric populations.
Donât Miss: What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis
Early Involvement Of The Common Bile Duct : A Specific Predictor Of Disease
We obtained an additional clue to the pathogenesis of ABD by the surprising discovery in young NOD.c3c4 mice of involvement of the CBD illustrated by comparison of the caliber of the CBD and portal vein. The ratio is â¼1:1 in normal mice but considerably greater in NOD.c3c4 mice . This unique dilation of the CBD was found in very young mice. 70% of NOD.c3c4 had CBD dilation at 3 wk of age, a pathology never seen in NOD, B6.G7, 1803, or any other mouse that did not develop ABD. We examined 40 NOD.c3c4 mice aged 24 wk and less. 18 out of 24 female and 11 out of 16 male mice in this age range demonstrated CBDD. To determine whether this finding had predictive power for disease, we examined 20 NOD.c3c4 mice aged > 30 wk and 16 had CBDD. Histologically, there was a 100% correlation for all 16 mice between CBDD and histological evidence of ABD, suggesting that the extrahepatic bile duct lesion is an essential component in the autoimmune process. Histological examination of the CBD confirmed pathological involvement, and, exclusively, NOD.c3c4 mice demonstrated thickening of the wall of the CBD, tortuous dilation, and a substantial subepithelial lymphocytic infiltrate . Notably, anti-CD3 treatment prevented these changes .
Read Also: What Is Mild Hepatic Steatosis
B Cells And Plasma Cells
Plasma cells that originate from B cells are sources of antibodies. As antigen presentation cells, B cells can secrete many kinds of cytokines and present costimulatory signals to active antigen-specific T lymphocytes. Migita et al found that serum B-cell-activating factor levels were significantly higher in PBC patients than in healthy controls and HCV-infected patients, and were positively correlated with aspartate amino-transferase and total bilirubin levels. In liver, CD5+ and CD20+ cells were associated with BEC damage, suggesting that B cells have a role in regulating the portal destruction in PBC. Therefore, B cell depletion therapy might be an alternative to UDCA. In murine experiments, IgNOD.c3c4 mice demonstrated a decreased number of activated NK cells in the liver. The degree of granuloma formation, bile duct destruction, and salivary gland histology were also shown to be significantly attenuated. Moreover, anti-CD20 therapy every 2 wk in transforming growth factor-beta receptor II dominant negative mice at age of 4-6 wk could reduce the number of B cells and CD8+ T cells in liver. In clinical therapy, two doses of 1000 mg rituximab separated by 2 wk were safe and effective in patients with an incomplete UDCA response. After treatment, not only did serum levels of total IgG, IgM, and IgA decrease significantly, but T regulatory cells also increased, which was associated with increased mRNA levels of forkhead box 3 and TGF- in CD4+ T cells.
How Pbc Is Treated
PBC is a progressive condition, which means the damage to the liver can steadily get worse over time.
The rate at which PBC progresses varies between individuals. Sometimes, it can take decades.
Without treatment, the liver can become so badly damaged that it no longer works properly. This is known as liver failure and can be fatal.
Liver failure can be prevented in the majority of people being treated for PBC with current treatments such as ursodeoxycholic acid and obeticholic acid.
Other medicines can help relieve the itchiness associated with PBC. Occasionally, if the liver is severely damaged, a liver transplant may be needed.
Also Check: All Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
What Is Primary Biliary Cholangitis
Primary biliary cholangitis is a chronic autoimmune disease of the liver that slowly destroys its small to medium-sized bile ducts. This causes bile to remain in the liver, which can damage cells and cause scarring that can lead to cirrhosis if unrecognized and untreated.
Bile is a liquid that is made in the liver and travels down the bile ducts to enter the duodenum, the portion of the small bowel next to the stomach. Bile contains acids, which are needed to digest fats and absorb fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K. These acids also act as hormones with important effects in maintaining health.
PBC advances slowly, providing doctors an opportunity for early treatment. Many patients lead active and productive lives for more than 10 to 15 years after diagnosis. In fact, patients who show no symptoms at the time of diagnosis often remain symptom-free for years. And the good news is that patients whose liver tests return to normal on treatment can expect a normal life expectancy.
If cirrhosis develops, PBC may lead to life-threatening complications. Cirrhosis occurs when scar tissue blocks the flow of blood through the liver and impairs its ability to function normally.
If the liver cannot filter waste from the intestine, confusion and altered levels of consciousness can result.
The goals of therapy are to prevent development of cirrhosis in patients with earlier stages of disease and slow progression and prevent deterioration in patients who already have cirrhosis.
What Are The Treatments For Primary Biliary Cholangitis
There is no known cure for PBC. Doctors use medication to manage symptoms and slow the progression of PBC. Ursodiol helps remove bile from the liver. This treatment improves liver function and prevents progression of the liver disease in many cases. Another drug, obeticholic acid is used in combination with ursodeoxycholic acid or alone if UDCA is not effective or cannot be tolerated. This therapy reduces the amount of bile produced and increases the flow of bile out of the liver.
Other drug options are available depending on each patients unique situation and presence of other medical conditions. A liver transplant may be needed if liver function continues to worsen despite medical treatment.
To treat the common problem of intense itching, diphenhydramine or the prescription drugs hydroxyzine or cholestyramine may be prescribed.
Also Check: Antibody Titer Test For Hepatitis B
How Is Pbc Treated
Patients most often respond to bile acid therapy taken by mouth daily for life. The medication has minimal side effects, improves the livers ability to function and retards progression of cirrhosis. Treatment has been shown to extend life expectancy in patients with or without cirrhosis, delaying or preventing the need for a liver transplant.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Primary Biliary Cholangitis
PBC may progress slowly and many people do not have symptoms, particularly in the early stages of the disease. The most common initial symptoms are fatigue and itching of the skin . Other symptoms may include:
- Swelling of the legs and feet
- Enlarged abdomen from fluid accumulation
- Internal bleeding in the upper stomach and esophagus from enlarged veins
Thinning of the bones leading to fractures is another complication of PBC. While this is more common in late stages of the disease, it can occur earlier as well. In addition, people with cirrhosis are at increased risk for liver cancer .
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis C Antibodies
Search For A Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are research studies that test how well new medical approaches work in people. Before an experimental treatment can be tested on human subjects in a clinical trial, it must have shown benefit in laboratory testing or animal research studies. The most promising treatments are then moved into clinical trials, with the goal of identifying new ways to safely and effectively prevent, screen for, diagnose, or treat a disease.
Speak with your doctor about the ongoing progress and results of these trials to get the most up-to-date information on new treatments. Participating in a clinical trial is a great way to contribute to curing, preventing and treating liver disease and its complications.
Start your search here to find clinical trials that need people like you.
How Is Primary Biliary Cholangitis Diagnosed
Because PBC causes no symptoms in its early stages, it may be diagnosed during a routine blood test that your doctor orders for another reason.
Your primary care doctor or a liver specialist called a hepatologist can diagnose PBC. The doctor will first ask about your symptoms, health history, and family medical history. Youll also have a physical exam.
Tests used to diagnose this condition include:
- blood tests: Your doctor may order blood tests to check liver enzymes and other measures of liver function.
- antimitochondrial antibody test : Your doctor may order an antimitochondrial antibody test to check for autoimmune disease.
- liver biopsy: Your doctor may order or perform a liver biopsy, which removes a small piece of the liver for examination.
Your doctor may also order imaging tests to make a diagnosis. These include:
Also Check: Royal Canin Hepatic Dry Dog Food
Antibodies Found In Patients With Psc And Additional Aih
Additional features of AIH are found in approximately 5% of adult patients with PSC but are prevalent in 3565% of children with PSC . In children and adolescents, the primary manifestation of disease may be that of typical AIH, together with cholangiographic and histological changes of sclerosing cholangitis . Testing patients with PSC for ANA, anti-SMA using IFT and for anti-SLA/LP using ELISA should be performed when additional AIH is suspected. Liver histology is mandatory to establish suspected AIH in patients with PSC, which will affect treatment decisions since AIH should be treated with immunosuppression .
Antibodies Against Glycoprotein 2
Recently, IgA-class antibodies against glycoprotein 2 , which were formerly linked to severe types of Crohns disease , were detected in sera of patients with PSC at a prevalence of 46.771.5%. The presence of anti-GP2 IgA was strongly associated with large bile-duct involvement, development of cholangiocarcinoma, and increased mortality . Therefore, anti-GP2 might serve as a novel biomarker of risk stratification in patients with PSC. Moreover, evidence for the involvement of GP2 in immune responses of the intestinal mucosa to gut bacteria provides a further pathophysiological link to the recently discovered aberrant community structure of the gut microbiota in patients with PSC .
Your Digestive System & How It Works
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health. The NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by the NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
The NIDDK would like to thank:John Moore Vierling, M.D., Baylor College of Medicine
Read Also: Hepatitis B And Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Recommended Reading: How Many Times Can You Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Antibodies Found In Patients With Pbc And Additional Signs Of Aih
Features of AIH may be present in 1020% of patients who present with PBC. There are no generally accepted criteria to define these variant syndromes. In most patients, both diseases manifest simultaneously and in these patients, the Paris criteria have been established and endorsed by EASL to indicate additional AIH in a PBC patient . AIH can be diagnosed if two of three criteria are present: elevation of ALT levels > 5 times upper limit the normal , elevation of serum IgG levels > 2 times ULN or positive anti-SMA, and moderate to severe interface hepatitis on histology. In addition, the presence of anti-SLA/LP and anti-dsDNA may raise the suspicion of AIH in patients with PBC .
Antibodies To Biliary Epithelial Cells
Few studies found antibodies of different subtypes in sera of patients with PSC directed against BEC . Levels of IgA antibodies directed against BEC were correlated with adverse patient outcomes . Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that antibodies against BEC and bacterial lipopolysaccharides co-activate cytokine release by BEC and therefore induce biliary immune responses . This provides further evidence for the involvement of microbiota in the pathogenesis of PSC. Testing for anti-BEC antibodies has not been introduced into clinical practice.
Read Also: Hepatitis B And C Test
The Spinal Itch Pathway
After the pruriceptive primary afferent has been activated, the signal is transmitted from the skin into the spinal dorsal horn. In this area, a number of interneurons will either be inhibited or activated to promote activation of projection neurons, mediating the puriceptive signal to the brain. The GRP-GRPR interneuron system has been found to be important for mediating both histaminergic and non-histaminergic itch, where the GRP neurons activate GRPR neurons to promote itch
You May Like: How Do People Catch Hepatitis B
Quick Answers For Clinicians
Antimitochondrial M2 antibodies are present in the serum of > 90% of patients with primary biliary cholangitis , and antinuclear antibodies are often present. Serum antibodies are detected via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays or other immunoassays. The diagnostic performance characteristics of these assays and results may not be commutable. Positive results for ANAs using solid-phase immunoassays are generally meaningless, as PBC-relevant ANA patterns can only be observed via immunofluorescence antibody assays. Immunoassays for detecting specific ANAs are important for confirmation.
Although liver biopsy is no longer recommended for the majority of patients with primary biliary cholangitis , specificity issues may arise with antimitochondrial M2 antibodies and antinuclear antibodies . Thus, histology may be needed if liver biochemistry tests, autoantibody tests, and imaging fail to establish a diagnosis of PBC or are equivocal. Histology is also useful to establish diagnosis in overlap syndromes, such as PBC/autoimmune hepatitis .
Although earlier detection and intervention have reduced the need for liver transplantation in patients with primary biliary cholangitis , the British Society of Gastroenterology recommends consideration of liver transplantation in all patients with bilirubin > 50 µmol/L or with pruritus that is refractory to all medical therapy.
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis Cause Stomach Pain
Autoantibodies In Autoimmune Liver Diseaseclinical And Diagnostic Relevance
- 11st Department of Medicine, University Medical Centre Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany
- 2Martin Zeitz Centre for Rare Diseases, University Medical Centre Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany
Testing for liver-related autoantibodies should be included in the workup of patients with hepatitis or cholestasis of unknown origin. Although most of these autoantibodies are not disease specific, their determination is a prerequisite to diagnose autoimmune hepatitis and primary biliary cholangitis , and they are components of the diagnostic scoring system in these diseases. In primary sclerosing cholangitis , on the other hand, autoantibodies are frequently present but play a minor role in establishing the diagnosis. In PSC, however, data on antibodies suggest a link between disease pathogenesis and the intestinal microbiota. This review will focus on practical aspects of antibody testing in the three major autoimmune liver diseases AIH, PBC, and PSC.
What Are Common Complications Or Side Effects Of Primary Biliary Cholangitis
Some people with PBC develop osteoporosis , which can lead to bone breaks . This complication typically occurs when a person is in the later stages of the disease. Doctors often treat osteoporosis by recommending regular exercise and prescribing medicines such as alendronate or risedronic acid . Both of these treatments help strengthen bones.
Other complications include high cholesterol levels, fat soluble vitamin deficiency, and an increased risk of liver cancer.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Antibody 0.1 Meaning
Cell Purification And Stimulation
CD4+ or CD8+ cells were prepared by magnetic separation using a MiniMACS system . In brief, splenocytes were incubated with anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 magnetic microbeads for 15 min, washed, and collected on a magnetic flow-through column. Purified cells were stimulated as described previously . In brief, cells were suspended in complete medium consisting of RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FCS, 1 mM l-alanyl-glutamine , 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin , 1 mM sodium pyruvate , and 50 μM 2-ME. Cells were then transferred to 24-well plates precoated with anti-CD3 antibody, and 1 μg/ml anti-CD28 antibody was added to each well. The cells were cultured for 72 h at 37°C in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere. The supernatants were collected at the end of culture and stored at â80°C.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Antibody Test Positive
Complementary And Alternative Medicines
Many complementary and alternative medicines are available that may ease the symptoms of liver disease. But certain medications used in non-liver related disease can damage the liver. At present, healthcare professionals are not clear on the role and place of some therapies in managing liver disease. More research needs to be done on the use of these therapies. You may wish to discuss the use of these therapies with your doctor.
Read Also: New Medicine For Hepatitis B
Treatments Aimed At Slowing Disease Progression
Many drugs have used in an attempt to improve prognosis in PBC. These can be broadly divided into two groups of agent, namely exogenous hydrophilic bile acids and immunosupressants. The best studied and most successful of these has been UDCA.
UDCA is a strongly hydrophilic bile acid which is absorbed in the terminal ileum as part of the physiological enterohepatic recirculation. Prolonged treatment results in UDCA replacing a significant proportion of biliary bile acids. The exact mechanism for the action of UDCA is unknown but it is thought to act both by replacing more hepatotoxic hydrophobic bile acids in the bile acid pool and as a choloretic agent stimulating increased biliary flow and reducing stagnation. In addition, UDCA has been reported to modify biliary epithelial HLA expression and may therefore have a local immunosuppressant action.
There has been debate as to whether the biochemical improvement predicts a true improvement in survival . This controversy has recently been highlighted by the publication of the preliminary results of a thorough meta-analysis which failed to find any survival benefit for UDCA.
UDCA has a small beneficial effect on pruritus , but little effect on fatigue.A small number of patients suffer a paradoxical increase in pruritus with UDCA which may necessitate stopping treatment. UDCA does not modify the course of associated autoimmune diseases.
Recommended Reading: How Would You Know If You Had Hepatitis