Reasons To Delay Treatment
Pregnancy
Hepatitis C treatment is generally not recommended during pregnancy. There is not a lot of information on the effects of DAAs during pregnancy. Research is being done on taking DAAs during pregnancy so this may change in the future.
Treatment that includes ribavirin can cause severe birth defects and must not be taken during pregnancy. When a couple wants to have a baby, both partners should avoid using ribavirin for at least six months before trying to get pregnant.
A healthcare provider can help determine a treatment plan and timeline for a person who has hepatitis C and wants to have a baby.
Children and adolescents
Hepatitis C treatment for children over the age of 12 is available in Canada. It is recommended that children who require treatment for hepatitis C be connected to a specialist with experience treating the pediatric population.
Resources for service providers
Complications Of Hepatitis C
If the infection is left untreated for many years, some people with hepatitis C will develop scarring of the liver .
Over time, this can cause the liver to stop working properly.
In severe cases, life-threatening problems, such as liver failure, where the liver loses most or all of its functions, or liver cancer, can eventually develop.
Treating hepatitis C as early as possible can help reduce the risk of these problems happening.
Hcv Core Antigen Assay
Recently, a new quantitative HCV core antigen assay was approved by the EMA. This assay comprises 5 different antibodies targeted the HCV core. The test is highly specific , equally effective for different HCV genotypes, and shows a relatively high sensitivity for the determination of chronic hepatitis C . However, HCV core antigen correlated well, but not fully linearly, with HCV RNA serum levels, and false-negative results might be obtained in patients with an impaired immunity. Another study has shown that the HCV core antigen quantification could be an alternative to the HCV RNA quantification for on-treatment antiviral response monitoring. Here, a HCV core antigen below the limit of quantification at treatment 1 wk was strongly predictive of RVR, whereas patients with a less than 1 log10 decline in HCV core antigen at treatment 12 wk had a high probability of achieving nonresponse. The new HCV core antigen assay could be a cheaper, though somewhat less sensitive, alternative for nucleic acid testing.
Don’t Miss: What Does Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive Mean
What Do You Do If You Become Ill
Talk to your health care provider about getting tested if you think you:
- are at risk
- may have hepatitis C
If you have hepatitis C, tell those who may have been exposed to your blood or bodily fluids. They should get tested and be treated if necessary. Bodily fluids, like semen and vaginal fluid, are a concern because they could be carrying small amounts of infected blood.
Some adults with hepatitis C will recover from the disease on their own within 6 months. Until your health care provider confirms your recovery status, you are still contagious and can spread the disease.
After recovery, you are no longer contagious because you will not have the disease anymore. But you can get hepatitis C again.
Unfortunately, most adults with hepatitis C:
- cannot recover on their own
- develop a more serious form of the disease if they are sick for longer than 6 months
What The Cdc Recommends
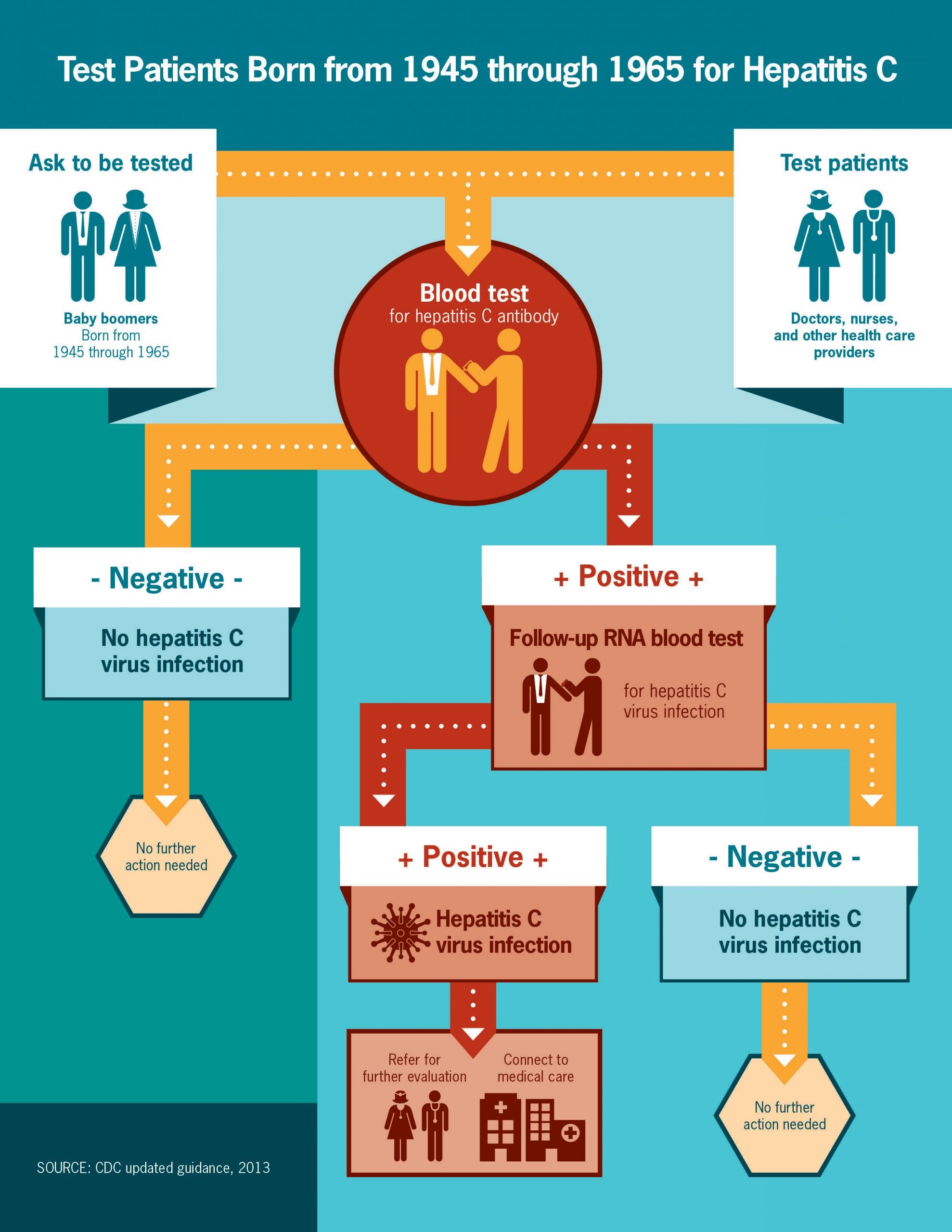
Were you born between 1945 and 1965? If so, then youre a member of the Hepatitis C generation. The CDC recently recommended that all people born between during this time have a 1-time screening test for Hepatitis C. We now have new drugs that can treat and cure Hepatitis C so you should go get tested today.
The life you save may be your own! Please contact your local healthcare provider.
Recommended Reading: After Being Cured Of Hepatitis C
What Drugs Treat And Cure Hepatitis C
The treatment of chronic hepatitis C has gone through several generations of medications. Not long ago, treatment was limited to interferon alpha-2b or pegylated interferon alpha-2b , and ribavirin . Interferon and pegylated interferon need to be injected under the skin , while ribavirin is taken by mouth. This combination therapy is infrequently used today, being recommended for only the least common genotypes of hepatitis C virus .
Since 2010, direct-acting antiviral drugs have been in use. The second generation of antivirals for HCV was the protease inhibitors telaprevir and boceprevir , both taken by mouth. These were used in combination with the earlier drugs to increase effectiveness . These drugs are also no longer in common use, and have been replaced by better options.
As more has been learned about how hepatitis C virus multiplies within the liver cells, new drugs continue to be developed to interfere with this multiplication at different stages. As such, we no longer think in terms of generations of drugs, but rather categories of action. Research and development of these direct-acting antivirals continue, with new agents coming to market every few months. Each category is improved and expanded by the addition of new drugs, which are safer and more effective.
Currently available and commonly used direct-acting antiviral drugs include:
- simeprevir
- Muscle aches
Causes And Risk Factors
THe HCV virus causes hepatitis C.
People contract the virus through blood-to-blood contact with contaminated blood. For transmission to occur, blood containing HCV must enter the body of a person without HCV.
A speck of blood, invisible to the naked eye, can carry hundreds of hepatitis C virus particles. The virus is not easy to kill.
The CDC offers advice on cleaning syringes if it is not possible to use clean and sterile ones. Although bleach might kill the HCV in syringes, it may not have the same effect on other equipment. Boiling, burning, and using alcohol, peroxide, or other common cleaning fluids to wash equipment may reduce the amount of HCV, but it might not stop a person contracting the infection.
It is extremely dangerous to inject bleach, disinfectant, or other cleaning products, so be sure to rinse the syringe thoroughly. Only ever use bleach to clean equipment if new, sterile syringes and equipment are not available.
A person cannot contract the virus from casual contact, breathing, kissing, or sharing food. There is no evidence that mosquito bites can transfer the virus.
The report the following risk factors for developing hepatitis C:
- using or having used injectable drugs, which is currently the most common route in the U.S.
- receiving transfusions or organ transplants before 1992, which is before blood screening became available
- exposure to a needle stick, which is most common in people who work in healthcare
- being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
Read Also: Hepatitis B Shot Side Effects
How Is Monitoring Done After Treatment For Hepatitis C
Once patients successfully complete treatment, the viral load after treatment determines if there is an SVR or cure. If cure is achieved , no further additional testing is recommended unless the patient has cirrhosis. Those who are not cured will need continued monitoring for progression of liver disease and its complications.
While cure eliminates worsening of fibrosis by hepatitis C, complications may still affect those with cirrhosis. These individuals still need regular screening for liver cancer as well as monitoring for esophageal varices that may bleed.
Because hepatitis B co-infection may reactivate or worsen even after treatment for HCV, monitoring for hepatitis symptoms may be needed after the end of therapy.
How Can I Protect Myself From Hepatitis C Infection
If you dont have hepatitis C, you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
Hepatitis C can spread from person to person during sex, but the chances are low. People who have multiple sex partners, have HIV or other sexually transmitted diseases, or who engage in rough or anal sex have a higher chance of getting hepatitis C. Talk with your doctor about your risk of getting hepatitis C through sex and about safe sex practices, such as using a latex or polyurethane condom to help prevent the spread of hepatitis C.
If you had hepatitis C in the past and your body fought off the infection or medicines cured the infection, you can get hepatitis C again. Follow the steps above, and talk with your doctor about how to protect yourself from another hepatitis C infection.
If you think you may have been exposed to the hepatitis C virus, see your doctor as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent liver damage.
Read Also: My Husband Has Hepatitis A Can I Get It
How Is Hepatitis C Infection Prevented
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To reduce your risk of getting hepatitis C:
- Injection drug use is the most common way people get hepatitis C. Avoid injecting drugs to reduce your risk. If you do inject drugs, use sterile injection equipment. Avoid reusing or sharing.
- Avoid sharing personal care items that might have blood on them
- If you are a health care or public safety worker, follow universal blood/body fluid precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps
- Consider the risks if you are thinking about tattooing, body piercing, or acupuncture are the instruments properly sterilized?
- If youre having sex with more than one partner, use latex condoms correctly and every time to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, including hepatitis C.
What Are Cdcs Hepatitis C Screening Recommendations
All patients 18 years and older should be screened for hepatitis C at least once in their lifetime, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is < 0.1%.
Patients with recognized exposures should be tested for hepatitis C regardless of age or setting prevalence, and regular periodic testing should continue as long as risk persists.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis B And Hiv The Same
How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted
The hepatitis C virus is spread primarily by exposure to blood.
People may get hepatitis C from needles, through exposure to blood in the workplace, from unsterile equipment used for body piercing, tattoos or acupuncture, exposure to dental or medical practices with poor infection control practices or by sharing personal care items including toothbrushes, nail clippers, razors, scissors with infected people. Sharing drug paraphernalia such as needles, spoons, pipes, and straws contaminated with blood has also been associated with a risk. The risk of getting this virus from a blood transfusion is minimal but still exists. All donated blood is screened for the hepatitis C virus.
Hepatitis C has been transmitted between sex partners. It has also been transmitted, although rarely, among household members, possibly because of frequent physical contact with small cuts or skin rashes. An infected mother can pass HCV to her child at birth.
There is no evidence that hepatitis C virus is spread by casual contact. Sneezing, coughing, kissing, and hugging do not pose the risk for hepatitis C. In addition, there is no evidence that hepatitis C virus is spread by food or water.
The hepatitis C virus can survive on surfaces outside the body for up to 3 weeks.
Alterations Of Lipid Metabolism
Lipids are required for the HCV replication and particles assembly. As mentioned above, HCV can modify the host serum lipid profile and this modification can provoke the steatosis. The steatosis is more frequent and more severe in patients with HCV gt 3 and it is correlated with a high HCV RNA levels. On one hand, in HCV-infected patients, the steatosis can be considered as a marker of the liver disease progression and, on the other hand, as an indication of the reduced response to therapy. However, if it is not metabolic or alcoholic steatosis, an efficient antiviral therapy is capable to reduce it.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Hepatitis Panel
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
Blood tests for hepatitis C
There are several blood tests for the diagnosis of hepatitis C infection. Blood can be tested for antibody to hepatitis C . It takes about 8-12 weeks on average, and up to 6 months, for antibodies to develop after the initial infection with hepatitis C, so screening for antibodies may miss a few newly infected individuals. Having antibodies is not an absolute indication of active, multiplying hepatitis C virus, but if the antibody test is positive , the statistical probability of active infection is greater than 99%.
Several tests are available to measure the amount of hepatitis C virus in a person’s blood . The hepatitis C virus’s RNA can be identified by a type of test called polymerase chain reaction that detects circulating virus in the blood as early as 2-3 weeks after infection, so it can be used to detect suspected acute infection with hepatitis C early infection. It also is used to determine whether active hepatitis is present in someone who has antibodies to hepatitis C, and to follow the viral load during treatment.
Blood tests are also performed to identify the genotypes of HCV. Genotypes respond differently to different treatment, so this information is important in selection of the most appropriate treatment regimen.
Estimation of liver fibrosis using blood tests also is quite reliable in diagnosing clinically significant scarring these include FIB-4, FibroSure, Fibrotest, and aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index .
Preventive Measures For Hcv Infection
Treatment options for hepatitis C are expensive, noncurative, and out of reach for the majority of people living in less-developed countries. Hence, prevention of infection remains an important public health goal.
HCV has a high mutation rate and multiple genotypes, which have challenged the development of an HCV vaccine. As a result, the primary means of prevention include infection-control practices in health care settings , the screening and testing of blood and organ donors, and viral inactivation in plasma-derived products. The development in the 1990s of highly effective assays to screen for HCV in donor blood greatly reduced the transmission of the virus in health care settings.
Risk-reduction counseling may help prevent the transmission of HCV among individuals who inject drugs.
Recommended Reading: Can You Catch Hepatitis C Through Sex
Treatment And Medication For Hepatitis C
If you have acute hepatitis C, there is no recommended treatment. If your hepatitis C turns into a chronic hepatitis C infection, there are several medications available.
Interferon, peginterferon, and ribavirin used to be the main treatments for hepatitis C. They can have side effects like fatigue, flu-like symptoms, anemia, skin rash, mild anxiety, depression, nausea, and diarrhea.
Now youâre more likely to get one of these medications:
Find out more on treatment options for hepatitis C.
Prevention Of Acute Hepatitis C
Patients should be advised to avoid high-risk behavior .
Blood and other body fluids are considered infectious. Risk of infection after a single needlestick exposure is about 1.8%. Barrier protection is recommended, but isolation of patients is of no value in preventing acute hepatitis C.
Risk of transmission from HCV-infected medical personnel appears to be low, and there are no CDC recommendations to restrict health care workers with hepatitis C infection.
Posttransfusion infection is minimized by avoiding unnecessary transfusions and screening all donors for hepatitis B and C. Screening has decreased the incidence of posttransfusion hepatitis B and hepatitis C, which are now extremely rare in the US.
No product exists for immunoprophylaxis of HCV. The propensity of HCV for changing its genome hampers vaccine development.
Preexposure or postexposure prophylaxis with antiviral therapy is not recommended.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis C Turn Into Hiv
Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
What Causes Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18
You May Like: Vaccine Available For Hepatitis B