The Silent Epidemic Killing More People Than Hiv Malaria Or Tb
Nuru was prepared for the worst when she went to get screened for HIV eight years ago. After caring for her mother in Uganda, who died as a result of the virus, Nuru moved to the United Kingdom to study, and decided to take her health into her own hands. I was ready to be told I had HIV, she says. I felt, Thats okay. Ive looked up to my mother.
What she didnt expect was to be diagnosed with a different viral infection altogether: hepatitis B. The way the health worker delivered it to me, it was like, Its worse than HIV. I was confused, I was suicidal, says Nuru . I just didnt understand what it was because no one ever talks about hep B they talk about HIV. Thats well researched, its well talked about, well documented. Its all over the television. But hep B is not.
The hepatitis B virus , which spreads through blood and bodily fluids and invades liver cells, is thought to kill just under 1 million people every year around the world, mostly from cancer or scarring of the liver. HBV is less likely to be fatal than HIV, and many people who carry the virus dont have symptoms. But because more than 250 million people live with chronic HBV infections, more than 7 times the number with HIV, its global death toll now rivals that of the more-feared virus.
Source: Global Health Estimates 2016
Source: WHO Hepatitis B dashboard
Hepatitis: How Can I Protect Myself From Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis B virus . The virus interferes with the functions of the liver and causes pathological damage. A small percentage of infected people cannot get rid of the virus and become chronically infected these people are at higher risk of death from cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer.
HBV is spread by contact with blood or body fluids of an infected person the same way as the human immunodeficiency virus . However, HBV is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV.
The main ways of getting infected with HBV are:
- from mother to baby at the birth
- from child-to-child
- unsafe injections and transfusions
- unprotected sexual contact.
Worldwide, most infections occur from mother-to-child, from child-to-child , and from reuse of unsterilized needles and syringes. Before the widespread use of the hepatitis B vaccine, almost all children in developing countries used to become infected with the virus.
Structure Of The Hbv Polymerase
Currently, an accurate spatial structure of the HBV DNA polymerase, which also harbors RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity and ribonuclease H activity, is not available. Due to the functional similarity, the structure of the HIV RT is used for modelling the spatial structure of the HBV polymerase . Comparison of HBV polymerase and HIV-1 RT on an amino acid sequence basis revealed only around 14% homologous sites , but the YMDD motif is conserved . The enzymatic pocket is formed by certain structurally exposed amino acids , which enable a possible identical conformation of the pockets of HIV-1 and HBV polymerases . The commonly used drugs effective for HBV and HIV treatment are the nucleoside RT inhibitors , which act by chain termination. Specific substances suitable for HBV and HIV treatment are lamivudine and tenofovir. Telbivudine, adefovir, and entecavir are licensed only for HBV .
As described for the HIV-1 RT, the M204V or I mutation in the YMDD motif of HBV results in complete resistance against lamivudine and emtricitabine . The prominent amino acids that build the enzymatic pocket of the HBV RT are in relation to HIV-1 as shown in figure 1: D19 in the upper left part, M160 in the motif PMG in HBV and PQG in HIV in the lower left part, M204 in yellow the lower right part, and finally L229 in the upper right part. HBV L180, which is selected as a compensatory mutation to M204V or I, does not have a corresponding amino acid in the HIV-1 sequence.
Recommended Reading: Is Viral Hepatitis C Contagious
What Is Chronic Infection With Hepatitis B
Early in the infection, most people will clear the virus without treatment and develop protective immunity. However, in 5-10% of adults hepatitis B continues to reproduce in the body long after infection. These people become chronically infected with hepatitis B, meaning that they continue to be infectious although they may not experience any symptoms at all, or not for many years.
People living with HIV, especially if they have a low CD4 cell count, are less likely to clear the virus naturally than people without HIV.
Without treatment, some people with chronic hepatitis B eventually develop cirrhosis of the liver. About one in 20 people with cirrhosis will go on to develop cancer of the liver.
The Link Between Hepatitis C And Hiv
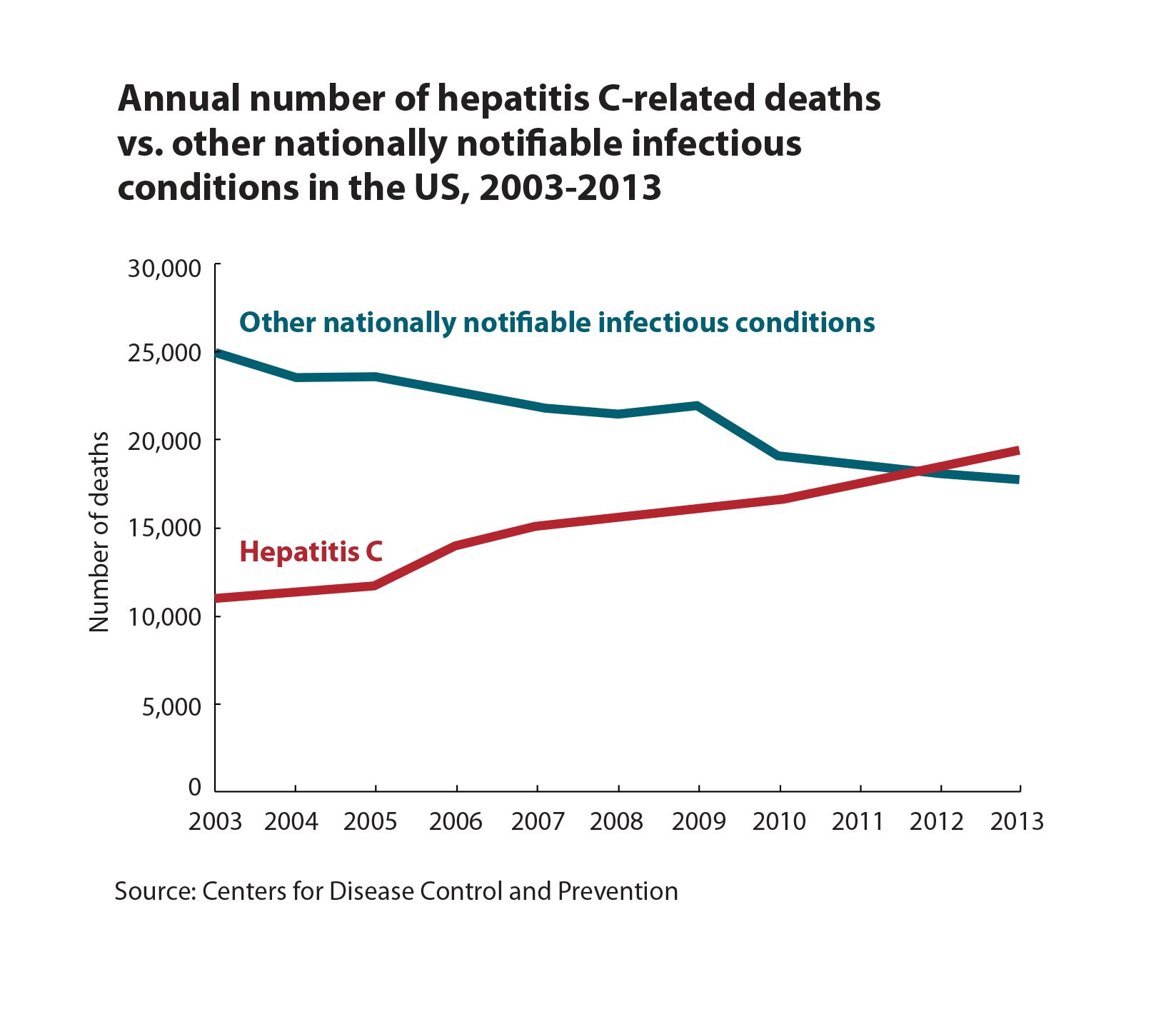
Both hepatitis C and HIV are transmitted the same way, says Dr. Sherman: through unprotected sexual contact with an infected person or by sharing injection drug needles with someone who is infected.
Engaging in high-risk behaviors , such as using injection drugs or not using a condom during sex, can increase your risk of contracting one or both viruses. Infection can happen either from the same person or different people, at the same time or different times.
Both hepatitis C and HIV are transmitted by blood exposure through needle sharing, says Sherman. However, hepatitis C is more transmissible, so many patients get that first, followed later by HIV. Occasionally, both viruses are transmitted at the same time.
The risk of being infected with HIV and hepatitis Cis higher among Black Americans. According to the CDC and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Black Americans account for about 13 percent of the population but 42 percent of new HIV diagnoses and 25 percent of chronic hepatitis C diagnoses. Black Americans have also historically been almost twice as likely to die of hepatitis C compared with white Americans.
Socioeconomic factors due to poverty limited access to healthcare, housing, and education increase the risk for infection, according to the CDC. Stigma, fear, and discrimination may also prevent Black Americans from seeking or having access to prevention and care services, the CDC adds.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Checked For Hepatitis
People Coinfected With Hiv And Viral Hepatitis
People with HIV/AIDS should be vaccinated against hepatitis A and B and tested for hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
Beginning in 2020, CDC and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices began recommending that all people with HIV who are 1 year of age be vaccinated against hepatitis A and receive postvaccination serologic testing 1 month after completing the hepatitis A vaccine series.
Further, CDC and ACIP recommend that unvaccinated people with HIV receive hepatitis B vaccination. Vaccination should be followed by serologic testing to confirm adequate immune response. CDC recommends that people with HIV be tested for hepatitis B.
CDC now also recommends one-time hepatitis C testing of all adults , including those with HIV. CDC continues to recommend people with risk factors, like people who inject drugs, be tested regularly.
People with HIV and Hepatitis A
People with HIV and Hepatitis B
People with HIV and Hepatitis C
What To Start Therapy With When Haart Is Initiated
As described above, if HIV therapy is initiated with tenofovir and emtricitabine as part of an anti-HIV regimen, then additional anti-HBV drugs are not needed because this combination is potent . This is also the best option in patients who may have or are known to have lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B. In a randomized controlled trial from Thailand, 36 HIV-HBV coinfected subjects were randomized to receive either lamivudine, tenofovir, or the combination of tenofovir and lamivudine. At the end of 48 weeks, the average decline in HBV DNA was similar in all three arms, ranging from 4.07-4.73 log10 copies/mL. However, suppression of HBV DNA levels to < 1000 copies/mL was more frequent in the two tenofovir-containing arms compared to the lamivudine arm . Drug resistance developed in only two patients, both of whom were in the lamivudine-only arm. In a cross-sectional study from a lamivudine-experienced HIV-HBV coinfected cohort from Australia and the United States, subjects who received a combination of tenofovir with emtricitabine or lamivudine were more likely to have HBV DNA < 100 IU/mL than those receiving either tenofovir or lamivudine monotherapy. The combination group was also significantly less likely to have HBV DNA > 200,000 IU/mL. The limitation of this study is that it was cross-sectional rather than prospective, but it provided some evidence that combination therapy was superior to monotherapy in HIV-HBV coinfected subjects with lamivudine-resistant HBV.
Also Check: Do I Have Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
Everyone should be tested for hepatitis B soon after their HIV diagnosis to see if they have been infected with the hepatitis B virus as well. This is done through a blood test.
In the UK, pregnant women are screened for hepatitis B. Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B can also be vaccinated soon after birth to prevent the infection being passed on to them.
Treatment For People With Hiv And Hepatitis B Co
In the UK, standards for HIV treatment and care are set and monitored by the British HIV Association , the professional association for HIV doctors and other healthcare professionals. The most recent guidelines on HIV and hepatitis co-infection were produced in 2017 .
“The health of your liver should be regularly monitored during HIV and hepatitis B treatment.”
Like everyone else living with HIV, people with HIV and hepatitis B co-infection are advised to start antiretroviral treatment soon after they are diagnosed with HIV. People with co-infection may particularly benefit from early antiretroviral treatment because undetectable HIV viral load and restored immune function are linked to slower liver disease progression.
Guidelines recommend that all people with HIV and hepatitis B co-infection should use combination antiretroviral therapy containing tenofovir plus either lamivudine or emtricitabine. These drugs are active against both HIV and hepatitis B.
The most widely used option is the Truvada pill combining tenofovir and emtricitabine, along with an additional anti-HIV drug from another class. Fixed-dose combination pills for HIV treatment that contain tenofovir and emtricitabine are also active against hepatitis B. Tenofovir alafenamide is easier on the kidneys and bones than tenofovir disoproxil . People who cannot take tenofovir can use entecavir instead, in addition to combination therapy to treat HIV.
Recommended Reading: Antiviral Drugs For Hepatitis A
Influence Of Host Factors
Finally, there are several host genetic factors that influence the course of the disease, such as CCR532, a mutation in the CCR5 , the coreceptor for HIV entry, and SNPs in the HBV receptor sodium-dependent taurocholic cotransporting polypeptide, which is a G7 protein spanning the cell membrane as CCR5. Additionally, both HIV and HBV RNA stability are partially controlled by the APOBEC3 system.
How Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Spread From Person To Person
Like HIV, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses spread:
- From mother to child: Pregnant women can pass these infections to their infants. HIV-HCV coinfection increases the risk of passing on hepatitis C to the baby.
- Sexually: Both viruses can also be transmitted sexually, but HBV is much more likely than HCV to be transmitted sexually. Sexual transmission of HCV is most likely to happen among gay and bisexual men who are living with HIV.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surf Ab Quant
Is There A Hepatitis C Vaccine
No vaccine exists for hepatitis C right now. While efforts to develop a vaccine for this specific strain are ongoing, it’s proven challenging. That’s because hepatitis C tends to avoid immune responses. In other words, a person can catch hepatitis C repeatedly despite past infection, which is what makes it hard to create a vaccine that works for this virus.
There is an effective treatment for hepatitis C, though, and it involves direct-acting antivirals . Thanks to this treatment, WHO aims to cut 80% of hepatitis C cases worldwide by 2030. Researchers across the globe think that a vaccine is needed to accomplish this goal, so creating one is a high priority.
Treating Hcv And Hiv Coinfection
If you have hepatitis C, be sure to get tested for HIV. The CDC also recommends that all people over 18, including those with HIV, get screened for hepatitis C. You should continue to get tested regularly if you have risk factors for HCV, including injection drug use.
If you test positive for either hepatitis C or HIV, both are treatable. In fact, people who are coinfected and receive treatment for both infections can achieve viral suppression meaning both viruses are undetectable in the blood according to the CDC.
The key is getting diagnosed and starting treatment as soon as possible to prevent serious liver complications.
In general, treatment of hepatitis C in HIV-positive people is similar to the treatments for HCV alone. Direct-acting antivirals , the treatment of choice for hepatitis C, can still be used with HIV antiretroviral drugs.
If youre diagnosed with hepatitis C while on treatment for HIV, do not interrupt or discontinue your HIV care to manage your HCV. While there are possibly harmful interactions between the drugs used to treat the two infections, your healthcare team should work together to prescribe the safest regimen that works best for your coinfection. Be sure to work with healthcare providers who have experience treating both conditions.
Also Check: How Do People Catch Hepatitis B
How Should The Liver Be Monitored
Everyone with HIV should have regular tests to monitor the health of their liver. These tests are especially important in cases of coinfection with hepatitis B. In those cases, doctors should closely monitor liver function using blood tests.
Ultrasound examinations may also be performed, particularly if the liver shows signs of damage. Another test, called a FibroScan, can also test the liver for cirrhosis or fibrosis.
Sometimes, people also need a liver biopsy, where a tiny piece of tissue from the liver is removed for investigation.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis A
Many people with hepatitis A dont have any symptoms. If symptoms do develop, youll usually notice them around two to four weeks after infection. These symptoms will usually pass within two months.
Symptoms include:
- flu-like symptoms, including tiredness, a fever and aches and pains
- loss of appetite
- pain in the upper right part of your tummy
- dark urine and pale faeces
- yellowing of the skin and eyes
- itchy skin.
You May Like: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
When To Initiate Therapy
Decisions regarding when to initiate anti-HBV therapy require consideration of the HIV treatment status because several of the nucleoside analogs are active against both HIV and HBV. If HIV infection needs to be treated, then the first-line therapy for HIV includes tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine as the nucleoside backbone. Because both of these agents are active against HBV, HBV is treated simultaneously by default.
If HIV is not treated, a decision regarding whether to initiate anti-HBV therapy is required. The current recommendations are to weigh both the replication status of HBV as well as the stage of liver disease to guide treatment decisions. There are inadequate data in HIV-HBV coinfection to determine the appropriate cutoff value for HBV DNA levels for treatment initiation, but many experts recommend a level of 2000 IU/mL . The liver disease stage is best obtained by a liver biopsy because serum aminotransferase levels tend to be low in patients with HIV infection, even in the presence of cirrhosis. The presence of more than mild liver disease is an indication for treatment. As described above, noninvasive markers of liver disease have not been well studied in HIV infection thus, they cannot be reliably used to determine liver disease stage. In patients with cirrhosis, treatment is recommended in the presence of any detectable HBV DNA.
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication for people with chronic hepatitis B, which occurs when the virus stays in your body for more than six months.
Antiviral medication prevents the virus from replicating, or creating copies of itself, and may prevent progressive liver damage. Currently available medications can treat hepatitis B with a low risk of serious side effects.
NYU Langone hepatologists and infectious disease specialists prescribe medication when they have determined that without treatment, the hepatitis B virus is very likely to damage the liver over time. People with chronic hepatitis B may need to take antiviral medication for the rest of their lives to prevent liver damage.
There are many different types of antiviral medications available, and your doctor recommends the right type for you based on your symptoms, your overall health, and the results of diagnostic tests. A doctor may take a wait-and-see approach with a person who has a healthy liver and whose blood tests indicate a low viral load, the number of copies of the hepatitis B virus in your bloodstream.
Someone with HIV infection or AIDS may have a weakened immune system and is therefore more likely to develop liver damage. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommends that people with HIV infection who are diagnosed with hepatitis B immediately begin treatment with antiviral medication.
Recommended Reading: Natural Remedies For Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
Hepatitis B is passed on by contact with:
- blood
- vaginal fluids of a person with hepatitis B.
It’s easily passed on:
- during unprotected sex
- from mother to baby during delivery.
It can also be passed on through:
- infected blood getting into an open wound
- tattooing or body piercing done with contaminated equipment
- using items such as toothbrushes or razors contaminated with infected blood.
Hepatitis B is many times more infectious than HIV and it can survive outside the body in dried blood for at least a week.
What Therapy To Start When Haart Does Not Need To Be Started
If HIV treatment is not initiated, anti-HBV treatment options are more limited due to the dual activity of many nucleoside analogs and the risk of developing drug-resistant HIV. The only current options are adefovir, peginterferon-alfa, and telbivudine. Of the three agents, telbivudine is the most potent, but it is limited by development of drug-resistant HBV in the monoinfected patient. Although telbivudine has not been studied in vivo in the setting of high levels of HIV RNA, in vitro evidence suggests that it is not active against HIV. In a single-round replication assay, telbivudine did not affect HIV replication . Peginterferon-alfa has the advantage that drug-resistant HBV will not emerge, so it is a reasonable option if the patient can tolerate the injections and the side effects. It is possible that a combination of one or more of these three agents may be effective in this situation, but it has not been studied. Thus, each of these approaches to anti-HBV therapy in HIV-infected individuals who do not receive concurrent HAART therapy is suboptimal. For these reasons, an additional option is to initiate HAART earlier than is required by HIV guidelines. Early initiation of HAART may be an increasingly attractive option, especially because HIV increases the rate of liver disease progression and earlier HIV treatment is now being advocated even in HIV monoinfection.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis B Do