Effective Treatments Are Available For Hepatitis C
New medication to treat for HCV have been approved in recent years. These treatments are much better than the previously available treatment because they have few side effects and do not need to be injected. There are several direct-acting antiviral HCV treatments that cure more than 95% of people who take them in 8 to 12 weeks. HCV treatment dramatically reduces deaths among people with HCV infection, and people who are cured of HCV are much less likely to develop cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Take Action! CDCs National Prevention Information Network Service Locator helps consumers locate hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevention, care, and treatment services.
Will The Baby Be Infected If The Mother Or Father Has Hepatitis C
The baby’s risk of becoming infected with hepatitis C in the womb varies, depending on whether the parent with hepatitis C is the father or the mother.
If the mother is infected, whether or not the father is infected, there is a 5% chance that the baby will be born with hepatitis C. The risk is the same regardless of whether the birth occurs by vaginal delivery or by cesarean section. The risk is higher if the mother is also living with HIV.
If the father has hepatitis C but the mother does not, the baby cannot become infected because a father cannot pass the virus directly to a baby. If the father first passes the virus to the mother through sex, then the baby possibly could be infected by the mother. However, the chance of the virus being transmitted both from father to mother and then from mother to baby is almost zero.
All children born to HCV-infected women should be tested for HCV infection. Testing is recommended using an antibody-based test at or after 18 months of age. Approximately 25-50 % infants with hepatitis C will clear the infection without any medical help by age 4. For those who become chronically infected, most have no symptoms .
Risk Factors For Reinfection
Even if youre cured, or have entered SVR from previous hepatitis C treatment, this doesnt mean youre immune to new infections in the future. Antivirals help get rid of existing HCV infections only. Unlike some other types of viruses, having hepatitis C in the past doesnt mean youre then immune to HCV for the rest of your life.
You may be at an increased risk of contracting HCV if you:
- were born between 1945 and 1965
- received a blood transfusion or an organ transplant before 1992
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- work in a healthcare setting where you may be exposed to others blood
- have a history of imprisonment
- have used, or are currently using, illicit drugs
Currently, theres no vaccine available for hepatitis C. The only way you can avoid contracting HCV is through preventive measures.
You can help prevent new hepatitis C infections by avoiding the following:
- having sex without a condom or other barrier method
- sharing needles and syringes
- getting homemade tattoos or piercings
- sharing razors and toothbrushes
- needlestick injuries at doctors offices and hospitals
HCV can cause some symptoms. But most cases of hepatitis C arent detectable until the infection reaches an advanced stage and starts affecting the liver.
It can take 4 to 10 weeks for an HCV antibody test to become positive after your initial exposure. This means you could unknowingly transmit HCV to others before youre aware of your own infection.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know You Have Hepatitis C
Can Hepatitis C Be Spread During Vaginal Sex
Its rare for the hepatitis C virus to be transmitted through vaginal intercourse. Unless the vaginal walls arent lubricated or intercourse is very rough and leads to tears in the vaginal wall, theres no opportunity for blood to be exchanged. The risk for transmission with vaginal intercourse is about 1 in 190,000, according to research published in the March 2013 issue of the journal Hepatology.
Research published in the Journal of Coagulation Disorders in March 2014 reinforces these findings, emphasizing that transmission of the hepatitis C virus by sex in monogamous heterosexual couples is rare. And the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that couples in monogamous heterosexual relationships do not need to use condoms routinely, even if one partner has hepatitis C. Concerned couples, however, can discuss using a condom to lower the already very low risk of spreading the virus, says Talal.
Just how safe sex is when a partner has hepatitis C hinges on some other factors as well. For example, its important to use a new condom with each sexual act that has the potential to expose the uninfected partner to the infected persons blood, even if youre in a committed relationship, says the CDC. Some of these situations include sex when you or your partner:
- Has an open cut or sore
- Has another sexually transmitted infection , especially one that causes sores or lesions
- Is having her menstrual period
You May Like: Is There Now A Cure For Hepatitis C
Is Svr Considered A Cure
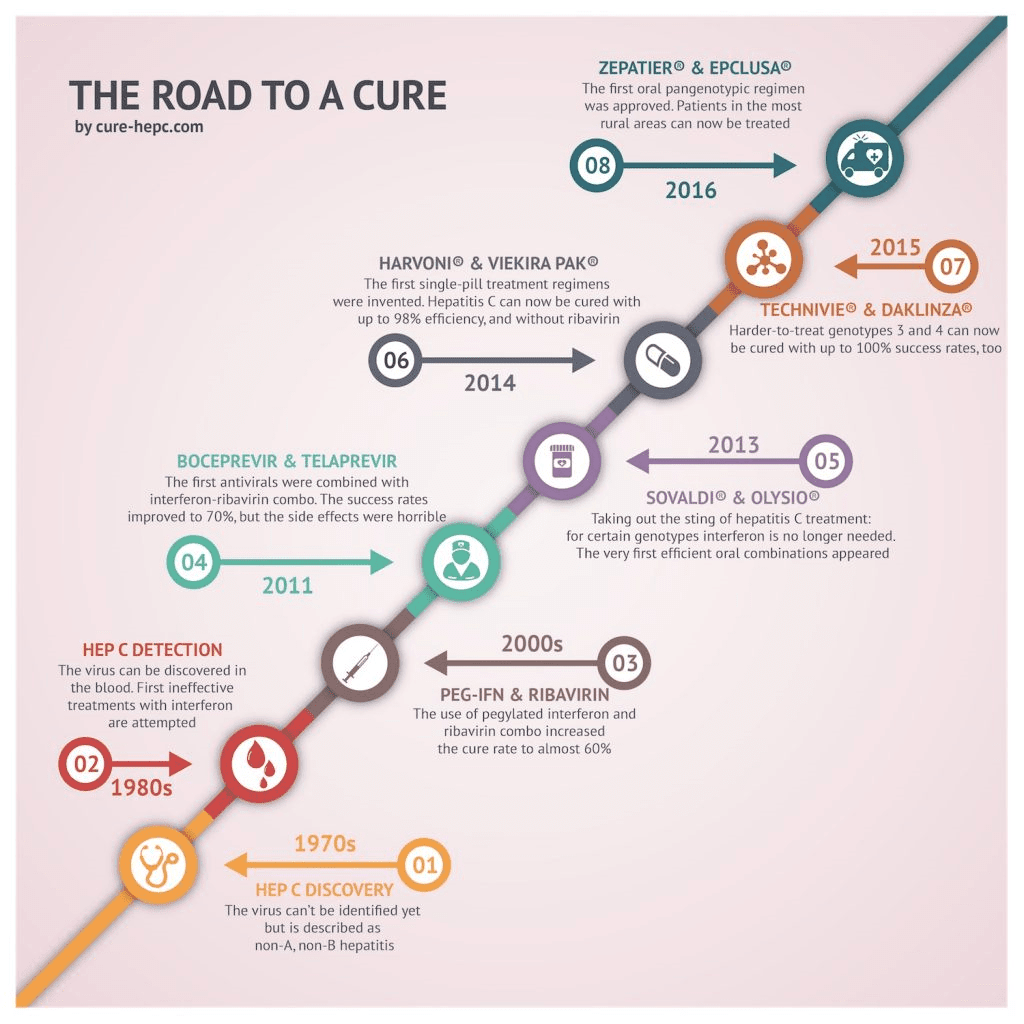
The oral DAA treatments are capable of causing a sustained virologic response , which means that the hepatitis C virus is not detected in the blood 12 weeks or more after completing treatment. Your doctor will monitor your virologic response with blood tests. Most people are considered cured when the virus is no longer present after 12 weeks.
Two or more oral antiviral drugs are typically used together to help prevent resistance in patients treated for HCV. Sometimes these treatments still need to be used with older medications such as ribavirin if you have advanced liver disease. Your chances for a cure may be better if you do not have advanced liver disease and have never received HCV treatment before.
Once you reach an SVR, it is highly unlikely for the hepatitis C virus to be detected again unless you are reinfected. Studies have shown this type of relapse occurs in less than 1% of patients who complete treatment. Also, when the virus is cleared from your blood you can no longer transmit the virus to others. However, you should still take precautions to help prevent catching and spreading HCV.
Any liver damage you have wont be reverse after you reach SVR, but further damage may be minimized with treatment.
Don’t Miss: What To Do When You Have Hepatitis B
Recurrence Of Hepatitis C
Approximately 99 percent of people who achieve SVR are cured of hepatitis C for life. The risk of hepatitis C returning after SVR is extremely rare. Also, once you reach SVR, you arent at risk of passing HCV on to others.
In some cases, your hepatitis C symptoms may flare up again before you reach SVR. But this isnt considered a recurrence because the infection isnt cured to begin with. A more likely explanation for recurrence is a new infection altogether.
What Is The Risk That Hcv Infected Women Will Spread Hcv To Their Newborn Infants
About 5 out of every 100 infants born to HCV infected women become infected. This occurs at the time of birth, and there is no treatment that can prevent this from happening. Most infants infected with HCV at the time of birth have no symptoms and do well during childhood. More studies are needed to find out if these children will have problems from the infection as they grow older. There are no treatments or guidelines for the treatment of infants or children infected with HCV. Children with elevated ALT levels should be referred for evaluation to a specialist familiar with the management of children with HCV-related disease.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Virus Symptoms And Treatment
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is only contracted through contact with another person who is infected with the hepatitis C virus . It is not acquired through contact with animals or insects.
Hepatitis C is present primarily in the blood, and to a lesser degree in specific other body fluids, of an infected person. Today, it is passed most commonly through the sharing of used needles by injection drug users. Prior to 1990, it was commonly passed through blood transfusions. However, since 1990, all donated blood is tested for hepatitis C virus, so it is extremely rare for hepatitis C to be acquired through a blood transfusion.
Transmission of hepatitis C occasionally occurs in healthcare settings, such as hospitals and clinics, when established infection control protocols are not followed. Health care professionals who do not follow these protocols can become infected if they sustain a needle stick from a patient who carries hepatitis C virus.
While uncommon, one mode of transmission is through organ transplantation when the donated organ comes from a person who carries the hepatitis C virus. The use of HCV-positive organs is currently reserved for the most serious cases requiring transplantation.
How Does Hepatitis C Spread?
Tattooing and body piercing have been documented to transmit the hepatitis C virus when recommended sterilization and infection control procedures are not followed.
Do People With Hiv Fare Worse After Being Cured Of Hepatitis C
The risk of liver complications appears similar for HIV-positive and HIV-negative people, but those with HIV had more non-liver problems.
People living with HIV fare no worse than their HIV-negative counterparts when it comes to liver disease complications and liver-related death after being treated for hepatitis C, but they do appear more likely to die of other causes, according to a report last week at the Digital International Liver Congress.
Previous studies have found that people with HIV and hepatitis C virus coinfection tend to have more severe liver disease and respond less well to HCV treatment than those with hep C alone, but much of this research was done years ago, before the advent of effective antiretroviral treatment for HIV and direct-acting antiviral therapy for HCV. Less is know about outcomes among people with HIV and HCV who receive optimal treatment.
Mathieu Chalouni, of the University of Bordeaux in France, presented findings from a study comparing the risk of liver disease complications, liver-related death and non-liver-related mortalitydeaths due to any other causein people with HIV/HCV coinfection versus those with HCV alone after DAA treatment. Liver-related events included liver decompensation , hepatocellular carcinoma and liver transplantation.
Most participants were treated with Harvoni or Sovaldi plus Daklinza . Almost everyone93% in the HIV/HCV coinfection group and 95% in the HCV monoinfection groupwas cured of hep C.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B What Causes It
Treating The Remaining 5%
If a treatment is 95% successful, though, that still means that as many as 5% of people who take it wont be cured. Fortunately, there are other options. If your hepatitis C was not cured by taking a first-line therapy like Epclusa, Dr. Terrault says, you should see a hep C specialist. That doctor will likely recommend a triple therapy called Vosevi . Also taken as a daily pill for 12 weeks, its about 95% effectiveyes, even if previous treatments did not work for you.
Hepatitis C Treatment: Lifestyle Changes And Vaccines
There are also lifestyle changes you should make if you are diagnosed. If you are diagnosed with hepatitis C, you should:
- Discontinue alcohol consumption immediately. The combination of alcohol with hepatitis C is particularly dangerous for many patients.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity can speed the progression of liver scarring.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B if you are not already immune, There are currently no vaccines for hepatitis C.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Symptoms In Women
If You Have Hepatitis C Should You Get A Flu Shot
Yes. Having chronic hepatitis C is actually a good reason to get the flu shot. Chronic hepatitis C is a condition that can increase your risk of complications if you do get influenza. That’s why it is recommended for people with hepatitis C, and most chronic liver diseases, to be vaccinated against the flu.
To stay up to date with your influenza vaccinations, you need to be vaccinated every year–ideally, early in the flu season or as soon as the vaccine becomes available. Typically, flu season is considered to be October to March. It’s best to get vaccinated annually because the vaccine is designed differently each year to target the strains of influenza that are expected to circulate during that particular flu season.
How Do My Healthcare Professional And I Decide On Treatment
Your healthcare professional will look at your health history and decide if treatment is right for you. The treatment you receive and the length of treatment may depend on:
- How much virus is in your body
- Your genotype of hep C
- Whether you have liver damage
- Whether or not youve been treated previously
Next:
Recommended Reading: What Is The Treatment For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Causes And Risk Factors
HCV causes hepatitis C. People contract the virus through blood-to-blood contact with contaminated blood. For transmission to occur, blood containing HCV must enter the body of a person without HCV.
A speck of blood, invisible to the naked eye, can carry hundreds of hepatitis C virus particles, and the virus is not easy to kill.
The report the following risk factors for developing hepatitis C:
- using or having used injectable drugs, which is currently the most common route in the U.S.
- receiving transfusions or organ transplants before 1992, which is before blood screening became available
- having exposure to a needle stick, which is most common in people who work in healthcare
- being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
The CDC offer advice on cleaning syringes if it is not possible to use clean and sterile ones. Although bleach can kill the HCV in syringes, it may not have the same effect on other equipment. Boiling, burning and using alcohol, peroxide, or other common cleaning fluids to wash equipment can reduce the amount of HCV but might not stop a person from contracting the infection.
It is extremely dangerous to inject bleach, disinfectant, or other cleaning products, so people should make sure they rinse the syringe thoroughly. A person should only ever use bleach to clean equipment if new, sterile syringes and equipment are not available.
People who are at risk due to these factors can have screening to rule out HCV.
- peginterferon alfa-2a
Is There A Cure
Though there is no vaccine for Hepatitis C, treatments can reduce the viral load to undetectable levels which is considered cured or in remission.
The virus is considered cured when it is not detected in your blood 12 weeks after treatment is completed. This is otherwise known as a sustained virologic response .
Hepatitis C is one of the most serious hepatitis viruses. However, with newer treatments developed over the past few years, the virus is much more manageable than it was in the past.
Current antiviral drugs that help cure hepatitis C may also help prevent the health complications of chronic liver disease.
The reports less than half of people who contract the hepatitis C virus may clear it from their bodies without treatment. For this group of people, the virus will be a short-term acute condition that goes away without treatment.
But for most people, acute hepatitis C will likely develop into a chronic condition that requires treatment.
Since the virus often doesnt produce symptoms until after more significant liver damage occurs, its important to get tested for hepatitis C if you think you might have been exposed.
approved the antiviral drug Mavyret for an 8-week treatment period for people with all genotypes of hepatitis C.
This treatment is now being used for many people instead of the 12-week treatment that was previously required.
Noninvasive ways to test for liver damage caused by hepatitis C are also now available to aid in diagnosis.
Read Also: Where Can You Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Assessing Fibrosis Regression Vs Progression After Cure Of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Natural history studies have established that regression of fibrosis can occur if the cause of the chronic liver injury is removed.22,23 This is true for patients with chronic HCV infection, and even cirrhosis regression has been documented. In a paired biopsy study of 38 patients with cirrhosis who achieved SVR, regression was observed in 61%, and collagen content, assessed morphometrically, decreased in 89%.24 Currently, liver biopsy is rarely used to stage fibrosis, as noninvasive measures such as hepatic elastography are available. Serial measurements of liver stiffness show that values decrease dramatically during treatment and in the early SVR period, but then plateau or decrease more slowly. For example, in a study of 112 patients with serial measurements of liver stiffness, the mean baseline liver stiffness was 12.3 kPa , with the sharpest decline occurring by the end of treatment and at SVR24 and then slower thereafter .25 This pattern reflects an initial improvement in stiffness related to reduction in necroinflammation and later a slower decline reflective of fibrosis remodeling and regression.
Defining Cure For Hepatitis C Virus Infection
In the registration trials leading to approval of HCV therapies, an HCV RNA level below the limit of quantitation 12 weeks after completing the therapy defined treatment successthat is, sustained virologic response 12. This time point is highly correlated with SVR24. However, because relapses beyond SVR12 have rarely been reported, treatment guidelines recommend confirming cure by testing for HCV RNA at 24 to 48 weeks after the end of treatment ., Late relapse, when it occurs, typically happens between 12 and 24 weeks posttreatment. In a large study evaluating late relapse, 12 of 3004 patients with SVR12 were found to be HCV RNApositive between weeks 12 and 24. Interestingly, using phylogenetic sequencing, it was determined that 7 of 12 relapses were actually new infections and 5 of 12 were true relapses. Thus, the rate of late relapse was 0.2%. Very late relapse, beyond 24 weeks posttreatment, is exceedingly rare. However, the takeaway point is that the determination of cure requires repeat HCV RNA testing beyond 12 weeks posttreatment. I recommend obtaining both SVR12 and SVR48. If HCV RNA is undetectable at the later time point, the patient can be confidently informed that he or she is cured, and no further testing is indicated unless the patient is at risk for reinfection.
You May Like: Pro Plan Hepatic Dog Food
Also Check: What Is The Test For Hepatitis