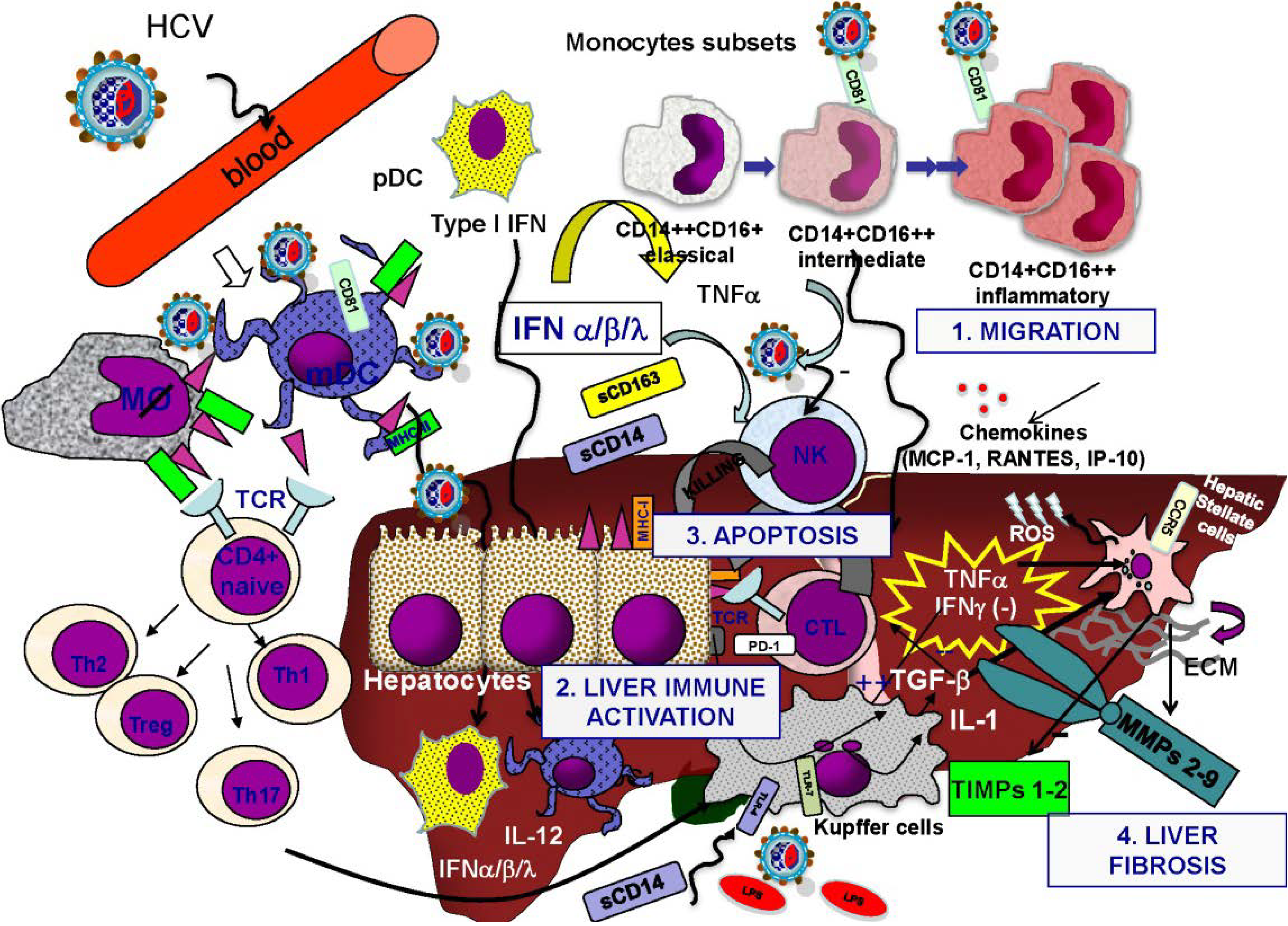
How Does Hcv Cause Fibrosis And Cirrhosis
Generally, when a virus enters the body, it needs to find a place where it can reproduce or replicate in order to survive. HCV prefers liver cells in order to replicate. When HCV enters a liver cell, it uses genetic material in that cell to help it reproduce and generate copies of itself. It releases these new copies into the bloodstream, and they travel to other liver cells to begin the cycle of replication again. The process of reproduction inside a liver cell can result in cell damage or destruction. Additionally, the immune response that the body launches against the virus can also result in cell damage or destruction. Either way, this damage or destruction of cells eventually results in formation of scar tissue or fibrosis. As fibrosis progresses, areas of scarring become interconnected, and the texture of the liver changes. With extensive fibrosis , blood is no longer able to flow through the liver and liver function becomes significantly impaired. 1
When Should You Start Treatment For Hepatitis C
With the new antiviral drugs for hepatitis C, it’s now recommended that everyone with hepatitis C shouldn’t wait to be treated, regardless of liver disease severity.
The aim of this treatment is a cure sometimes described as a sustained virologic response. This means that no hepatitis C virus is detectable in your blood six months after youve finished treatment.
What Is The Risk Of Coinfection
A coinfection is when someone has two or more infections at the same time. People living with HIV are at risk of developing coinfections such as hepatitis C because HIV weakens the immune system, which leaves the body more vulnerable to other infections and illnesses.
HIV and HCV are also transmitted in similar ways, which means that people who have HIV may be at higher risk of exposure to HCV. In the United States, over a third of people living with HIV also have hepatitis C.
Coinfection of HCV and HIV is higher among those who use injected drugs. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , HCV coinfection occurs in between 62 and 80 percent of people with HIV who use injected drugs.
A systematic review of 783 studies concluded that people living with HIV were six times more likely to have hepatitis C than people without HIV.
Hepatitis C infections are more serious in people with HIV and can lead to more severe damage of the liver. HIV and HCV coinfections can increase the risk of:
- liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, which is a buildup of scar tissue in the liver
- end-stage liver disease
A person can contract HCV through direct contact with blood or other body fluids that contain the virus. Possible modes of transmission include:
Ways to prevent hepatitis C include:
- not sharing needles
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Is Liver Transplantation An Option For A Person With Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is the leading reason for 40% to 45% of liver transplants in the U.S. Hepatitis C usually recurs after transplantation and infects the new liver. Approximately 25% of these patients with recurrent hepatitis will develop cirrhosis within five years of transplantation. Despite this, the five-year survival rate for patients with hepatitis C is similar to that of patients who are transplanted for other types of liver disease.
Most transplant centers delay therapy until recurrent hepatitis C in the transplanted liver is confirmed. Oral, highly effective, direct-acting antivirals have shown encouraging results in patients who have undergone liver transplantation for hepatitis C infection and have recurrent hepatitis C. The choice of therapy needs to be individualized and is rapidly evolving.
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B Virus
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus . The abbreviation HBV can stand for either the virus or the infection it causes.
HBV can be a short-term or a long-term illness:
- Acute HBV occurs within 6 months after a person is exposed to HBV. In some people, acute HBV can lead to chronic HBV.
- Chronic HBV is a lifelong disease. Without treatment, chronic HBV can cause liver cancer or liver damage that leads to liver failure.
HBV is a contagious infection that can spread from person to person.
Is Hepatitis Testing Recommended For People With Hiv
Yes. Everyone living with HIV should be tested for HBV and HCV when they are first diagnosed with HIV and begin treatment. People living with HIV who have ongoing risk factors for getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C should be tested annually.
In addition, new HCV screening recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention call for:
- One-time screening for all adults 18 years and older
- Screening of all pregnant women during every pregnancy
- Testing for all persons with risk factors, with testing continued periodic testing those with ongoing risk.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis B The Same As Hiv
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: Vaccination is the best way to prevent all of the ways that hepatitis B is transmitted. People with HIV who do not have active HBV infection should be vaccinated against it. In addition to the 3-dose series of hepatitis B vaccine given over 6 months, as of 2017, there is a 2-dose series given over 1 month.
Hepatitis C: No vaccine exists for HCV and no effective pre- or postexposure prophylaxis is available. The best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to never inject drugs or to stop injecting drugs by getting into and staying in drug treatment. If you continue injecting drugs, always use new, sterile needles or syringes, and never reuse or share needles or syringes, water, or other drug preparation equipment.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C spreads when blood or body fluids contaminated with the hepatitis C virus get into your bloodstream through contact with an infected person.
You can be exposed to the virus from:
- Sharing injection drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV, another STD, several partners, or have rough sex
- Being stuck by infected needles
- Birth — a mother can pass it to a child
- Sharing personal care items like toothbrushes, razor blades, and nail clippers
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unclean equipment
You canât catch hepatitis C through:
- Breastfeeding
- Casual contact
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Have HIV
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Since July 1992, all blood and organ donations in the U.S. are tested for the hepatitis C virus. The CDC says it is now rare that someone getting blood products or an organ would get hepatitis C. That said, The CDC recommends that anyone over the age of 18 get tested for Hepatitis C. If you haven’t been screened, you should consider having it done.
Learn more about the risk factors for hepatitis C.
Also Check: Hepatitis C And Liver Disease
Who Can Get The Hepatitis Vaccine
A vaccine that protects against HBV is freely available on the NHS for newborn babies and people at higher risk of HBV. Visit your GP or a sexual health clinic to ask if you could get the vaccine.
HBV vaccination is also recommended for people travelling to countries where HBV is common. Ask your GP or a travel clinic you will probably need to pay to get the HBV vaccine for travel.
There is no vaccine available to protect from HCV at the moment.
Can Parasites Cause Cancer
Parasites are a type of infection that need to live on, or in another animal to survive. Some parasites can cause liver and bladder cancer. In the UK, cancers caused by parasites are very rare.
Three types of parasite can cause cancer in humans. They are:
- Two small liver worms , which can cause bile duct cancer. They spread through contaminated food, particularly through undercooked fish.
- A blood worm , which can cause bladder cancer. This parasite lives in fresh water in subtropical and tropical regions and is spread through contaminated water. You can read more about this blood worm on the NHS website.
All three of these parasites are very rare in the UK, and cause very few UK cancer cases. But if you have been infected, they can be easily treated with a short course of medicine.
If you have travelled or lived somewhere where these parasites are more common and youre concerned you may have been exposed, talk to your GP.
Don’t Miss: How Did I Get Hepatitis C
Cases Of Hepatitis C In The United States
The CDC reports that in 2018, a total of 15,713 U.S. death certificates had hepatitis C as an underlying or contributing cause of death. This is likely lower than the actual numbers since so many infections go undocumented.
Studies show that baby boomers are more likely than other groups to have been exposed to HCV. Most of them contracted infections between 1970 and 1990 during a peak of new infections.
And since people with an HCV infection might not show symptoms, they may unknowingly transmit the virus to others.
Today, the most common risk factor for hepatitis C in the United States is injection drug use.
Since an HCV infection can show no symptoms, the number of new cases is likely higher than reported, according to the CDC.
Improving Access For Key Populations
For people from key populations, stigma and structural barriers continue to hinder access to diagnosis, treatment and care for hepatitis C.44 .
To ensure equitable access and engage key populations, clinical services for hepatitis C will need to better adapt their models of care. They may need to provide outreach services, be flexible around appointment requirements, train staff, and consult civil society- and community-led organisations .45
Buyers clubs
Buyers clubs pool resources to buy DAA medicines via the internet. There are many buyers clubs around the world enabling people to access treatment who would otherwise be unable to receive it. They exist as a stopgap response to the failure of public health systems to ensure equitable access to hepatitis C treatment.
However, there are concerns that compromise other important aspects of treatment, including treatment monitoring and management of co-infection.46
Recommended Reading: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Treatment Guidelines
Guidelines issued by WHO in April 2016 recommend four preferred regimens, each including the drug sofosbuvir, in order to simplify treatment decisions for hepatitis C.36 Depending on the regimen, treatment may last 12 or 24 weeks.
When these guidelines were issued, the choice of drug regimen was dependent on which of the six genotypes the patient had. Different genotypes, each with its own genetic composition of the virus, are more common in different parts of the world. Each patient therefore required genotype testing before treatment could be provided.
In July 2018, WHO updated these treatment guidelines to reflect certain key developments. It recommended that the use of DAA regimens for all people with chronic hepatitis C infection, rather than reserving DAA treatment for people with more advanced disease as had previously been done. In part, this is linked to the continued substantial reduction in , which has enabled treatment to be rolled out rapidly in a number of low- and middle-income countries. In addition, as several new pangenotypic DAA medicines have now been approved, the need for genotyping to guide treatment decisions has been reduced.37
What’s The Relationship Between Drug Use And Viral Infections
People who engage in drug use or high-risk behaviors associated with drug use put themselves at risk for contracting or transmitting viral infections such as human immunodeficiency virus , acquired immune deficiency syndrome , or hepatitis. This is because viruses spread through blood or other body fluids. It happens primarily in two ways: when people inject drugs and share needles or other drug equipment and when drugs impair judgment and people have unprotected sex with an infected partner. This can happen with both men and women.
Drug use and addiction have been inseparably linked with HIV/AIDS since AIDS was first identified as a disease. According to the CDC, one in 10 HIV diagnoses occur among people who inject drugs.1 In 2016, injection drug use contributed to nearly 20 percent of recorded HIV cases among menmore than 150,000 patients. Among females, 21 percent of HIV cases were attributed to IDU.2 Additionally, women who become infected with a virus can pass it to their baby during pregnancy, regardless of their drug use. They can also pass HIV to the baby through breastmilk.
Read Also: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis C
Should People With Hiv Get Tested For Hbv
CDC recommends that all people with HIV get tested for HBV. Testing can detect HBV even when a person has no symptoms of the infection.
There are several HBV blood tests. Results of different tests show different things. For example, a positive hepatitis B surface antigen test result shows that a person has acute or chronic HBV and can spread the virus to others.
Treating Hepatitis C Together With Hiv
If youre HIV positive and have hepatitis C infection, then you must receive care from a doctor skilled in the treatment of both HIV and hepatitis.
Due to the new direct-acting antiviral drugs, people living with HIV and hepatitis C co-infection can be treated with most of the same hepatitis C drug regimens as HIV-negative people. Research has shown that cure rates are the same.
Unlike treatment for HIV, hepatitis C treatment is not for life. New drugs to treat hepatitis C only need to be taken for up to 3 months.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
Setting Up A National
Activists in Thailand knew from their HIV/AIDS treatment advocacy campaign, which led to antiretroviral therapy being covered under universal health care, that information and education were not enough. First, a critical mass of informed people must get educated then, an action plan must be developed to push urgent priorities onto local and national policy agendas. TTAG mobilized financial support from key donors who were interested in contributing to a stronger response to the problem of viral hepatitis coinfection among Thailands drug users and people living with HIV/AIDS.
Over the next few years, TTAG cultivated additional funding to educate hundreds of people who use drugs and people living with HIV/AIDS across Thailand about viral hepatitis and HIV. By the end of 2011, TTAGs Coinfection Project had trained six teams of four HIV/HCV peer educators in three regions of Thailand , more than 200 people living with HIV/AIDS, and 60 IDUs. In 2012, the Coinfection Project expanded to include the South. In each region, TTAG nurtured more trainers and funding was channeled to local groups of HIV-positive people to continue the movement at the local and provincial level.
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B
How Common Is It
There were an estimated thirty thousand five hundred cases of acute hepatitis C viral infections reported in the United States in 2014. Chronic hepatitis C affects an estimated 2.7 to 3.9 million people in the United States alone. Of all acute hepatitis C cases, up to as many as eighty-five percent will develop a chronic infection that increases the risk of frequent infections, liver damage, cirrhosis of the liver and even liver cancer.
Direct Exposure To Blood
Exposure to large amounts of contaminated blood increases the risk for hepatitis C transmission. If you get a cut and need help tending it, whoever helps you should first put on disposable gloves to prevent exposure in case he or she has a cut. You can also help prevent hepatitis C transmission by covering any cuts or sores with bandages until theyre healed and disposing of used bandages properly.
Uninfected people should take steps to avoid getting someone elses blood in their eyes, nose, and mouth. If an uninfected persons skin is exposed to contaminated blood, wash the area with soap and water immediately. If blood gets in the eyes, rinse them with running water right away and call a doctor to find out about further steps that should be taken.
When cleaning blood from surfaces, Dr. Lee recommends using a solution of one part bleach to 10 parts water. Dried blood should also be handled with care because the virus can live for several days outside the body.
The CDC recommends that if youve ever tested positive for hepatitis C, you should abstain from donating blood, organs, or semen.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Go Away On Its Own