Molecular Pathology Of Hepatic Fibrosis And Cirrhosis
The scar tissue in cirrhosis is composed of a complex assembly of different extracellular matrix molecules, comprising the fibril forming interstitial collagens type I and III, basement membrane collagen type IV, noncollagenous glycoproteins like fibronectin and laminin, elastic fibers and glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans among others . Toxins, viruses, cholestasis, or hypoxia can trigger a wound healing reaction termed fibrogenesis, i.e., the excess synthesis and deposition of ECM. Initially, fibrogenesis is counterbalanced by removal of excess ECM by proteolytic enzymes, such as certain matrix metalloproteinases . Chronic damage usually favours fibrogenesis over fibrolysis, with an upregulation of tissue inhibitors of MMPs . The major hepatic ECM producing cells are myofibroblasts that either derive from activated hepatic stellate cells or perivascular fibroblasts . Myofibroblast activation is mainly driven via fibrogenic cytokines and growth factors that are released by activated macrophages , other inflammatory cells and bile duct epithelia . The most prominent profibrogenic cytokine is transforming growth factor β which suppresses inflammation, but drives fibrogenic gene expression in these Myofibroblasts .
Initiation and maintenance of fibrogenesis
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcoholic beverages and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annuallythough twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
Nsbbs In Patients With Ascites Or Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
- In retrospective cohort studies, NSBBs and carvedilol have shown worsening of renal function or higher mortality in patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites or spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
- These adverse outcomes seem to be associated with an NSBB-induced decrease in arterial pressure and with the dosage of NSBB
- This has led to the recommendation of using lower doses of NSBBs in patients who have cirrhosis and ascites and are trying to avoid carvedilol
*Nodolol is not offered on the VA formulary
Also Check: Hepatitis B How Do You Catch It
If I Have No Symptoms How Would I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
To confirm whether or not you have hepatitis B, you will need blood tests.
If you have at least one risk factor , you should ask your health care provider to be tested for hepatitis B. Also, you should be tested for hepatitis B if:
- you were born in a region where hepatitis B is more common, including Asia, Africa, southern and eastern Europe, the Pacific Islands, the Middle East, and the Arctic
- one or both of your parents immigrated from a region where hepatitis B is more common
- you live or travel to regions where hepatitis B is more common
- you have a family history of liver disease or liver cancer
- you have been in prison
- you are pregnant
- you have ever used injection drugs, even just once
- you have unexplained abnormal liver enzymes or if
- you receive medicines that suppress the immune system.
Making The Diagnosis Of Compensated Vs Decompensated Cirrhosis
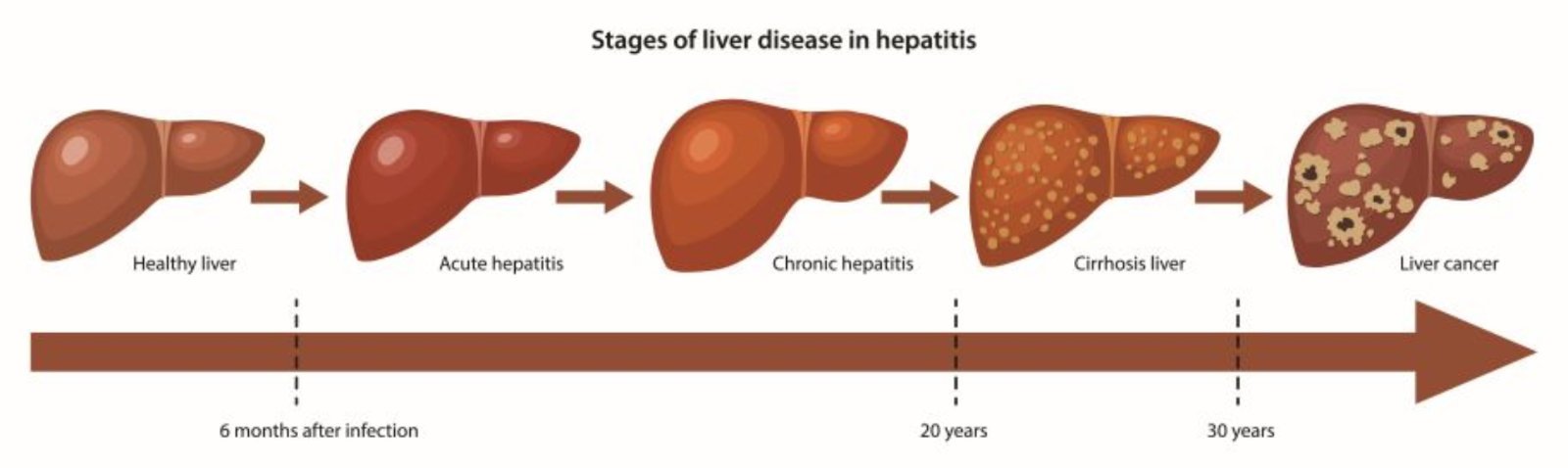
- Cirrhosis can be diagnosed with clinical, laboratory, radiologic, elastographic, or biopsy findings
- The diagnosis of compensated cirrhosis is more challenging since patients may lack clinical, laboratory, and radiologic findings and may require biopsy for diagnosis
- The diagnosis of decompensated cirrhosis is easier as the patient history, physical exam, and laboratory findings are usually more evident
Child-Turcotte-Pugh score
- TheChild-Turcotte-Pugh score is used as a prognostic scoring system in cirrhosis based on 2 clinical and 3 laboratory parameters:
- Ascites: none diuretic-sensitive or mild/moderate diuretic-refractory or tense
- Encephalopathy: none episodic or overt grade 2 recurrent/chronic or grade 3-4
- Albumin in g/dL:> 3.5 3.4-2.8 < 2.8
- Bilirubin in mg/dL:< 2 2-3 > 3
- INR:< 1.7 1.7-2.3 > 2.3
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
If I Have Hepatitis B And Feel Healthy Do I Need To Keep Going To My Doctor
Chronic hepatitis B is a silent disease because often no symptoms appear until your liver is severely damaged. Although many people with chronic hepatitis B have an inactive disease and will remain healthy, about one in four will have an active disease that may lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer.
Because hepatitis B has no symptoms until your liver is badly damaged, a blood test is the only way for your doctor to find out if your hepatitis B is active or inactive, and to offer treatment, if needed. To help your doctor monitor how your disease behaves over time, you will need lifelong repeat blood tests every six to 12 months. Some tests, such as HBV DNA may need to be done more frequently . No treatment is required while the virus is inactive, but you should continue to get regular blood tests from your doctor to monitor your liver disease.
Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis C Go Away On Its Own
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
You can become infected with hepatitis B through exposure to blood, semen and other bodily fluids of an infected person. You can get the infection by:
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
- Breastfeeding.
Diseases That Damage Destroy Or Block Bile Ducts
Doctors usually treat diseases that damage, destroy, or block bile ducts with medicines such as ursodiol . Doctors may use surgical procedures to open bile ducts that are narrowed or blocked. Diseases that damage, destroy, or block bile ducts include primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis.
Read Also: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Treatment For Suspected Exposure
Anyone who has had potential exposure to HBV can undergo a postexposure prophylaxis protocol.
This consists of HBV vaccination and hepatitis B immunoglobin . Healthcare workers give the prophylaxis after the exposure and before an acute infection develops.
This protocol will not cure an infection that has already developed. However, it decreases the rate of acute infection.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B And C
In most patients, hepatitis B develops slowly over the course of several decades, and thus most patients have no symptoms. People who have advanced liver disease such as cirrhosis of the liver may experience complications and symptoms that reflect liver failure. Other symptoms include:
- A buildup of fluid within the abdominal cavity
- Confusion and tremors , which are complications due to the inability of the liver to filter out toxins that are normally cleaned out by a healthy liver
- Vomiting of blood, or blood within the stool . This is a complication in which enlarged veins within the esophagus or stomach bleed as a consequence of increased pressure around the diseased liver.
Most patients with chronic hepatitis C infection report no symptoms. But some patients may have very nonspecific symptoms related to fatigue and discomfort on the right side of the abdomen. Often, symptoms that lead to a diagnosis of hepatitis C are noticeable only at the end stage of liver disease, when the patient has developed liver cirrhosis and liver failure.
Because hepatitis B and C typically have no specific symptoms, many people who have the viruses dont even know it.
Also Check: Hep C Without Hepatic Coma
Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis B And Cirrhosis With Peg
Several studies have demonstrated the efficacy of PEG-IFN in the treatment of HBV infection in HBeAg-positive and HBeAg-negative patients . The recommended treatment duration is 48 weeks at a dosage of 180 g once weekly for PEG-IFN alfa-2a. In HBeAg-positive patients, the main goal is to achieve anti-HBe seroconversion and/or anti-HBe seroconversion with normalized ALT. The main reasoning is the finding that anti-HBe seroconversion after IFN treatment is associated with a significantly increased likelihood of survival . About one third of the patients achieve a sustained anti-HBe seroconversion 6 months after end of treatment . In HBeAg-negative patients, success of therapy is defined by HBV DNA < 2,000 IU/ml and/or normalized ALT. Normalization of ALT was achieved in 59% of patients, and a reduction of HBV DNA < 2,000 IU/ml was seen in 19% of patients . Importantly, subanalysis of the phase III studies of PEG-IFN showed a similar or even better efficacy in patients with compensated cirrhosis .
Fig. 1
Response rates of patients with advanced fibrosis and liver cirrhosis 24 weeks after the end of PEG-IFN therapy . ISHAK score was used to quantify the degree of liver fibrosis.
Fig. 2
Management of hepatitis B infection and liver cirrhosis.
For patients with cirrhosis, HBsAg loss should be the main goal if PEG-IFN is considered. If HBV DNA remains positive after the end of therapy or during follow-up, treatment with NUC should be initiated.
C Counseling Of Hbsag
All pregnant women should be screened for HBsAg. Pregnant women with CHB should be encouraged to discuss with their obstetrician and/or pediatrician the prevention of mother-to-child transmission. Hepatitis B immune globulin and HBV vaccine should be administered to their newborn < 12 hours after delivery., Antiviral therapy in the third trimester is recommended for pregnant women with serum HBV DNA > 200,000 IU/mL.,
A proportion of women have hepatitis flares with or without HBeAg seroconversion within the first months after delivery. Seroconversion rates of up to 17% have been described. It has been postulated that the rapid decrease in cortisol levels characteristic of the postpartum state is analogous to the steroid withdrawal therapy that has been used to elicit seroconversion. Although the flares are often mild and resolve spontaneously, cases of acute liver failure have been described in the peripartum period.- Extending third trimester antiviral therapy from 2 to 12 weeks postpartum did not protect against postpartum flares in one study, supporting the AASLD guideline recommendation that antiviral therapy given for prevention of mother-to-child transmission be discontinued at the time of delivery or up to 4 weeks postpartum.
Although antiviral drug labels do not recommend breastfeeding when taking these drugs, clinical studies support the safety of these drugs during breastfeeding.,
Guidance Statements on Counseling of Women in Pregnancy
Don’t Miss: Fast Track Hepatitis B Vaccine In Houston Tx
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
Treatment Of Hepatitis Delta
Superinfection with HDV has detrimental effects on the course of the liver disease. When compared to HDV-negative patients, HDV-positive patients with compensated cirrhosis have their risk for HCC, decompensation, and mortality increased by the factor of 3.2, 2.2, and 2.0, respectively . However, it is unclear whether HDV induces HCCs directly or indirectly. HDV is able to modify DNA methylation which could be directly carcinogenic . In contrast, the increased development of cirrhosis in hepatitis D may already explain the higher frequency of HCC in individuals co-infected with HDV irrespective of direct oncogenic effects . Thus, patients with hepatitis D have an urgent treatment indication . Obviously, the main goals are prevention of disease progression and prevention of HCC. However, no definite clinical end point has been defined.
Healthy Tips & Diet For Liver Cirrhosis Patients:
- Include in your diet green vegetables such as bottle gourd, ridge gourd, bitter gourd, cauliflower, cabbage, kale, fenugreek, coriander, pumpkin, etc.
- Drink limited amount of water & can drink one green coconut water.
- Also include vegetables like carrot, turnip, beetroot, radish, etc.
- Eat fresh fruits like berries, apple, pear, peach, orange, papaya, guava, etc.
- Daily walk for 30 minutes to keep you fit.
- Avoid milk & dairy products.
- Totally avoid fried, fast, & processed food items.
- Do perform yoga poses & pranayam such as kapalbhati pranayam, dhanurasana, ardh mastsyendrasana, naukasana, Gomukhasana, etc.
Genetic Predisposition For Cirrhosis
The variable rates of development of cirrhosis amongst individuals with similar risk factors such as HCV or alcohol abuse had long been unexplained. Recently, a growing number of functional genetic polymorphisms that likely increase the risk of fibrosis progression has been described. Implicated genes encode cytokines/chemokines and their receptors , molecules involved in fibrogenesis or fibrolysis , blood coagulation , antigen presentation , iron uptake , oxidative and antioxidative metabolism , detoxification and polygenetic traits linked to the metabolic syndrome and NASH. In a recent gene association study 1,609 out of 24,882 single nucleotide polymorphisms were found to be associated with fibrosis progression in chronic hepatitis C, with the DDX5 gene having a high positive predictive value . Together with established extrinsic risk factors like excess alcohol consumption, obesity or advanced age these SNPs will allow the establishment of risk profiles for the individual patient .
Causes Of Chronic Hepatitis
The most common causes of chronic hepatitis are
-
Alcohol-related liver disease Alcohol-Related Liver Disease Alcohol-related liver disease is liver damage caused by drinking too much alcohol for a long time. In general, the amount of alcohol consumed determines… read more
Hepatitis C virus causes about 60 to 70% of cases of chronic hepatitis, and at least 75% of acute hepatitis C cases become chronic.
About 5 to 10% of hepatitis B cases in adults, sometimes with hepatitis D Hepatitis D Hepatitis D virus is infection of the liver that occurs only in people who have hepatitis B. Hepatitis D can be spread by contact with blood and other body fluids. Coinfection with hepatitis… read more coinfection, become chronic. Acute hepatitis B becomes chronic in up to 90% of infected newborns and in 25 to 50% of young children.
Rarely, hepatitis E virus causes chronic hepatitis in people with a weakened immune system, such as those who are taking drugs to suppress the immune system after an organ transplant, who are taking drugs to treat cancer, or who have HIV infection.
Hepatitis A virus does not cause chronic hepatitis.
Less often, chronic hepatitis results from
-
Autoimmune hepatitis
-
Drugs
In autoimmune hepatitis, the chronic inflammation resembles inflammation caused by the body attacking its own tissues . Autoimmune hepatitis is more common among women than men.
Distinguishing Compensated And Decompensated Cirrhosis
One important step in treating HCV in persons with cirrhosis is to determine whether the cirrhosis is compensated or decompensated. The Child-Turcotte-Pugh score is an important component of determining the status of the cirrhosis and predicts morbidity and mortality. The treatment approach and goals are divergent based on the classification of compensated versus decompensated cirrhosis. In particular, HCV protease inhibitor-based regimens are not recommended for use in persons with decompensated cirrhosis due to the risk of hepatotoxicity with some medications and lack of data with the others.
Effect Of Antiviral Therapy On Fibrosis And Cirrhosis Regression
Treatment of HBV infection in patients with fibrosis and compensated cirrhosis can lead to histological regression. Chang et al. studied the effect of entecavir in 57 patients with a median follow-up of 6 years. 88% of all patients had regression of fibrosis and all patients with cirrhosis at the time of inclusion showed histological improvement. Marcellin et al. showed similar data for tenofovir in a larger cohort of 348 patients in which 97 patients had cirrhosis at baseline. After 5 years histological regression was found in 74% of all cirrhotic patients. Interestingly, the main factor that reversion of cirrhosis did not occur was obesity. Regression of fibrosis was also shown in other studies. One study showed improvement of liver fibrosis/cirrhosis in 43-59% of patients treated with entecavir and in 33-53% of patients treated with lamivudine after 48 weeks. No major difference was found between HBeAg-positive and HBeAg-negative patients . Another study demonstrated that long-term telbivudine treatment with profound and durable viral suppression significantly improved liver histology . This study also confirmed that non-invasive analysis of liver stiffness by elastography could be used to track improvement of fibrosis.
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.