What Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis
Patients infected with HBV and HCV can develop chronic hepatitis. Doctors define chronic hepatitis as hepatitis that lasts longer than 6 months. In chronic hepatitis, the viruses live and multiply in the liver for years or decades. For unknown reasons, these patients’ immune systems are unable to eradicate the viruses, and the viruses cause chronic inflammation of the liver. Chronic hepatitis can lead to the development over time of extensive liver scarring , liver failure, and liver cancer. Liver failure from chronic hepatitis C infection is the most common reason for liver transplantation in the U.S. Patients with chronic viral hepatitis can transmit the infection to others with blood or body fluids as well as infrequently by transmission from mother to newborn.
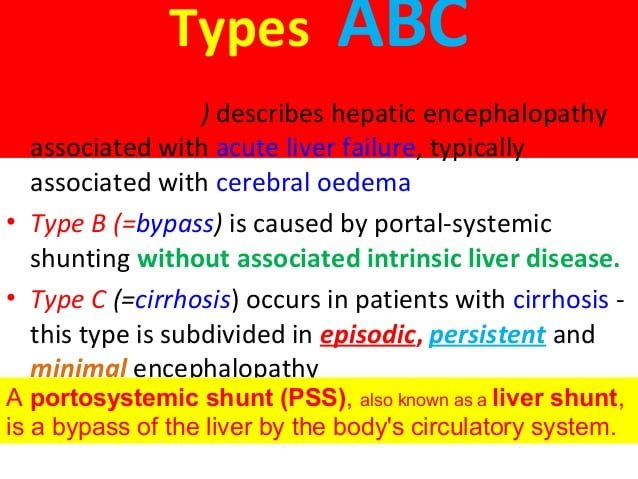
What Is Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is an often-temporary neurological disorder due to chronic, severe liver disease. A diseased liver struggles to filter toxins from the bloodstream. These toxins build up in the body and travel to the brain. Toxicity affects brain function and causes cognitive impairment.
People with hepatic encephalopathy may seem confused or have difficulty processing their thoughts. Treatments can remove the toxins and reverse the problem. As liver disease progresses, the condition may worsen and become less treatable. Hepatic encephalopathy is also known as portosystemic encephalopathy .
What Is The Treatment For Viral Hepatitis
Treatment of acute viral hepatitis and chronic viral hepatitis are different. Treatment of acute viral hepatitis involves resting, relieving symptoms, and maintaining an adequate intake of fluids. Treatment of chronic viral hepatitis involves medications to eradicate the virus and taking measures to prevent further liver damage.
Acute hepatitis
In patients with acute viral hepatitis, the initial treatment consists of relieving the symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain . Careful attention should be given to medications or compounds, which can have adverse effects in patients with abnormal liver function . Only those medications that are considered necessary should be administered since the impaired liver is not able to eliminate drugs normally, and drugs may accumulate in the blood and reach toxic levels. Moreover, sedatives and “tranquilizers” are avoided because they may accentuate the effects of liver failure on the brain and cause lethargy and coma. The patient must abstain from drinking alcohol since alcohol is toxic to the liver. It occasionally is necessary to provide intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration caused by vomiting. Patients with severe nausea and/or vomiting may need to be hospitalized for treatment and intravenous fluids.
Chronic hepatitis
Medications for chronic hepatitis C infection include:
- oral daclatasvir
Medications for chronic hepatitis B infection include:
- oral entecavir
- oral tenofovir
Fulminant hepatitis
You May Like: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
When Should I Call The Doctor
You should call your doctor if you have liver disease and you notice signs of hepatic encephalopathy. Symptoms include impaired thinking, mood changes, sleep problems and hand flapping.
You should also notify your doctor if you have liver disease and become constipated. Bowel movements help rid the body of toxins. Having fewer bowel movements can cause toxins to build up in your body.
What Are The Complications Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Liver disease needs treatment, such as medications and lifestyle changes, including not drinking alcohol. If the underlying cause of liver disease isnt treated, liver function deteriorates, and toxins continue to build. Some people with advanced hepatic encephalopathy lose consciousness and go into a hepatic coma.
But Even If You’ve Been Cured It Can Have Lifelong Health Implications
“Hepatitis C is a lot more than just a liver disease,” Reau says. “It has been associated with many medical conditions, such as an increased risk of developing diabetes, kidney disease and cancer.”
While curing hepatitis C significantly reduces the risk of serious complications, like liver failure, liver cancer and the need for transplantation, it doesn’t completely eliminate the health risks associated with the disease.
“Hep C is linked to scarring of the liver or cirrhosis and the more scar tissue that develops, the greater the likelihood of complications,” Reau says. “If there is a lot of scarring, you will need lifelong monitoring.”
Reau also recommends leading a healthy lifestyle to help prevent re-infection and further liver damage: Limit alcohol consumption, control your weight, avoid high-risk activities and manage diabetes if you have it.
Viral Hepatitis Definition And Overview
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Many illnesses and conditions can cause inflammation of the liver, for example, drugs, alcohol, chemicals, and autoimmune diseases. Many viruses, for example, the virus causing mononucleosis and the cytomegalovirus, can inflame the liver. Most viruses, however, do not attack primarily the liver the liver is just one of several organs that the viruses affect. When most doctors speak of viral hepatitis, they are using the definition that means hepatitis caused by a few specific viruses that primarily attack the liver and are responsible for about half of all human hepatitis. There are several hepatitis viruses they have been named types A, B, C, D, E, F , and G. As our knowledge of hepatitis viruses grows, it is likely that this alphabetical list will become longer. The most common hepatitis viruses are types A, B, and C. Reference to the hepatitis viruses often occurs in an abbreviated form The focus of this article is on these viruses that cause the majority of human viral hepatitis.
Hepatitis viruses replicate primarily in the liver cells. This can cause the liver to be unable to perform its functions. The following is a list of major functions of the liver:
Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis C Infection
For clinicians treating chronic hepatitis C infection. Material covered includes recommendations for treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced persons with chronic HCV infection genotypes 1-6, based on the Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and Infectious Diseases Society of America HCV Guidance.
Track your progress and receive CE credit
Joint And Muscle Pain
A condition called arthralgia causes joint pain and is common in people with hepatitis C. Itâs different from arthritis, which causes pain and swelling in joints. But infected people can also get hepatitis C-related arthritis.
Fibromyalgia, which causes body aches and muscle pain, is also common in people with hepatitis C.
Causes Associated With Chronic Liver Failure
Chronic liver failure is usually a result of cirrhosis or alcohol-related liver disease . The American Liver Foundation states that alcoholism is the most common cause of cirrhosis in the United States.
Usually, your liver breaks down any alcohol that you consume. But if you drink too much, your liver cant break down the alcohol fast enough. Also, toxic chemicals in alcohol can trigger inflammation in your liver and cause your liver to swell. Over time, this damage can lead to cirrhosis.
If you have hepatitis C, youre at greater risk of developing chronic liver failure or cirrhosis. The hepatitis C virus is spread through the blood. If the blood from a person with the infection enters your body, you can catch it. Needle sharing and using dirty needles for tattoos or piercings can spread hepatitis C.
According to the American Liver Foundation, around 25 percent of people in the United States with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis. Its the second leading cause of cirrhosis in the country.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
If you or someone you love has hepatic encephalopathy, you may want to ask your doctor:
- How is liver disease affecting my body?
- What can I do to improve liver function or slow liver disease?
- What liver disease treatment will work best for me now?
- What is the best treatment for hepatic encephalopathy?
- How long do I need to take medication for hepatic encephalopathy?
- Are there any medications I should avoid?
- Should I make any dietary changes to support liver function?
- Could I benefit from a liver transplant?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
Remember, hepatic encephalopathy is a serious but treatable condition. Symptoms often resolve with early detection and proper treatment. If you have liver disease, ask your doctor about warning signs of hepatic encephalopathy so you can start treatment promptly. You should also discuss how to best manage liver disease to keep hepatic encephalopathy from occurring or worsening.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 04/16/2020.
References
It’s Different Than Hepatitis A And B
Each form of hepatitis has its own specific virus that spreads and is treated differently. “Hepatitis simply means inflammation of the liver, or that the virus has an affinity for hurting the liver,” Reau says.
- Hepatitis A is an acute, short-term infection that often does not require treatment.
- Hepatitis B hides deep in the body and, like hepatitis C, is treated in a variety of ways, from antiviral medications to liver transplants.
“The viruses are different, but all of them should be taken very seriously since they can lead to significant liver disease and even death,” she adds.
How Is Acute Hepatitis C Treated
Acute hepatitis C is typically monitored and not treated. Treatment during the acute stage doesnt change the risk that the disease will progress to the chronic form. An acute infection may resolve on its own without treatment. The following treatment may be all thats necessary:
- proper rest
- adequate fluids
- a healthy diet
Some people may need treatment with prescription medication. Your doctor will be able to work with you about what treatment options may be best for you.
Those most at risk for acute and chronic hepatitis C are people who use or share contaminated needles. Mothers can transmit HCV to their babies during childbirth, but not through breastfeeding. Other risk factors for transmission of HCV include:
- healthcare work, especially work around needles
- getting a tattoo or body piercing with unsterile equipment
- undergoing hemodialysis
- living in a household with someone with HCV
- sharing personal hygiene products, such as razors or toothbrushes
- engaging in sexual activity with multiple partners without condoms or dental dams
- having a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992 or receiving clotting factors before 1987
The most serious long-term risk of acute hepatitis C is developing chronic hepatitis C, which can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. In 75 to 85 percent of those with acute hepatitis C, the disease will progress to the more serious chronic hepatitis C.
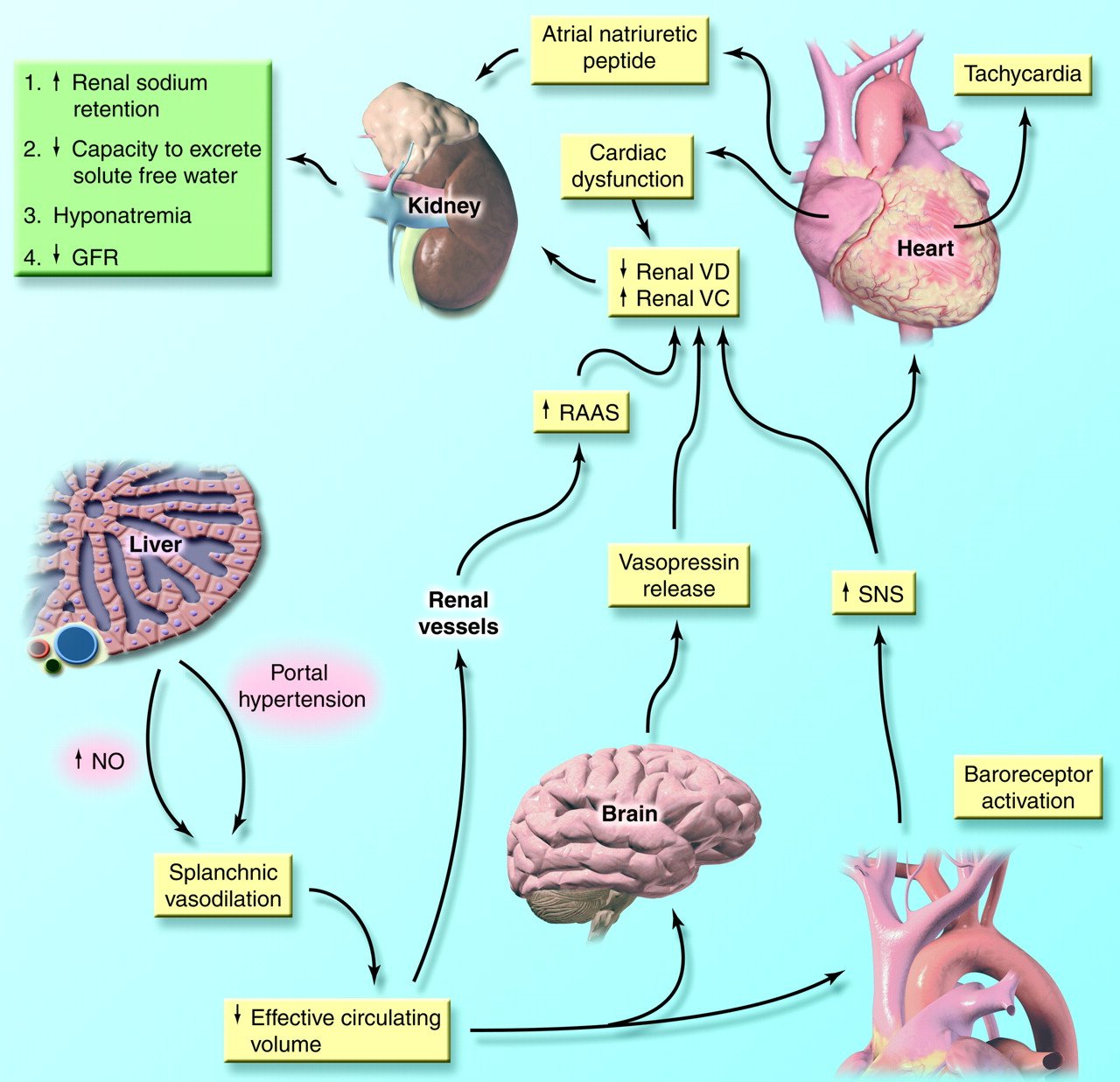
What Causes Hepatic Encephalopathy
When you have liver disease, the liver struggles to filter natural toxins out of the body. Toxins, such as ammonia, accumulate in the blood. Toxins in the bloodstream can travel to the brain and temporarily affect brain function.
People with chronic liver disease are at risk for hepatic encephalopathy. Something usually triggers the condition, such as:
How Is Viral Hepatitis Diagnosed
Diagnosis of viral hepatitis is based on symptoms and physical findings as well as blood tests for liver enzymes, viral antibodies, and viral genetic materials.
Symptoms and physical findings
Diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis often is easy, but the diagnosis of chronic hepatitis can be difficult. When a patient reports symptoms of fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, darkening of urine, and then develops jaundice, the diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis is likely and can be confirmed by blood tests. On the other hand, patients with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HCV often have no symptoms or only mild nonspecific symptoms such as chronic fatigue. Typically, these patients do not have jaundice until the liver damage is far advanced. Therefore, these patients can remain undiagnosed for years to decades.
Blood tests
There are three types of blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis: liver enzymes, antibodies to the hepatitis viruses, and viral proteins or genetic material .
Liver enzymes: Among the most sensitive and widely used blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis are liver enzymes, called aminotransferases. They include aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase . These enzymes normally are contained within liver cells. If the liver is injured , the liver cells spill the enzymes into the blood, raising the enzyme levels in the blood and signaling that the liver is damaged.
Examples of tests for viral antibodies are:
How Serious Is It
- People can be sick for a few weeks to a few months
- Most recover with no lasting liver damage
- Although very rare, death can occur
- 15%25% of chronically infected people develop chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer
- More than 50% of people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop a chronic infection
- 5%-25% of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over 1020 years
If You Notice Symptoms See A Doctor Right Away
Symptoms of hepatitis C include the following:
- Jaundice a yellowish tone to the eyes and skin
- Mild, chronic right belly pain
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
If you believe you have been exposed to hepatitis C or notice any symptoms, visit your primary care doctor as soon as possible. If you test positive for the virus, your doctor can refer you to a hepatologist to discuss your options.
“I strongly encourage all baby boomers and others who are at high risk to get tested, even if you don’t look or feel sick,” Reau says. “If you do have hepatitis C, the earlier we discover it, the more likely we can prevent it from progressing and causing more serious damage.”
Unspecified Viral Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- B19.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B19.20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B19.20 – other international versions of ICD-10 B19.20 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Baby Boomers Are Especially Vulnerable
“The hepatitis C virus didn’t have a name or a screening test until in 1989,” Reau says. “That means people born between 1945 and 1965, the group referred to as ‘baby boomers,’ are at highest risk of infection. They grew up before health care facilities started taking standard precautions, like not sharing vials of medicine among patients and requiring staff to wear gloves.”
The CDC reports that baby boomers are five times more likely to have Hepatitis C than other adults, accounting for 75% of those living with the disease.
These are some other reasons you may be at risk:
- You have engaged in high-risk behaviors like IV drug use or unprotected sex
- Your biological mother has/had hepatitis C
- You received blood transfusions, an organ transplant or dialysis before 1989
- You were or are currently incarcerated
Treatment Of Hepatic Failure
Treatment depends on the stage of the disease.
Your doctor may prescribe medications. If only part of your liver is damaged, surgery may be recommended to remove the damaged part. A doctor can also take imagingtests of your liver to look for damage.
If a healthy liver is damaged, it can grow back.
If the damage is too severe, which can sometimes be the case with fast-acting acute liver failure, a liver transplant may be necessary.
Treating Hepatitis C Matters
When you see your doctor and start treatment for a chronic hep C infection, you can prevent these problems, improve them, or keep them from getting worse. New drugs can clear the virus from your body in a few months with fewer side effects than older medicines. If thereâs no virus in your blood 3 months after treatment, youâre considered cured.
Getting rid of the infection protects others, too. Hepatitis C spreads through blood-to-blood contact. You could infect a loved one if you accidentally use their toothbrush or cut yourself and donât clean up the blood properly. People who get hep C treatment greatly lower the odds that they will pass the virus to someone else.
If you arenât sure if you have hepatitis C, talk to your doctor to see if you should get tested. Learn why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
What Are The Common Types Of Viral Hepatitis
Although the most common types of viral hepatitis are HAV, HBV, and HCV, some clinicians had previously considered the acute and chronic phases of hepatic infections as “types” of viral hepatitis. HAV was considered to be acute viral hepatitis because the HAV infections seldom caused permanent liver damage that led to hepatic failure. HBV and HCV produced chronic viral hepatitis. However, these terms are outdated and not currently used as frequently because all of the viruses that cause hepatitis may have acute phase symptoms . Prevention techniques and vaccinations have markedly reduced the current incidence of common viral hepatitis infections however, there remains a population of about 1 to 2 million people in the U.S. with chronic HBV, and about 3.5 million with chronic HCV according to the CDC. Statistics are incomplete for determining how many new infections occur each year the CDC documented infections but then goes on to estimate the actual numbers by further estimating the number of unreported infections .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
Types D, E, and G Hepatitis
Individuals who already have chronic HBV infection can acquire HDV infection at the same time as they acquire the HBV infection, or at a later time. Those with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HDV develop cirrhosis rapidly. Moreover, the combination of HDV and HBV virus infection is very difficult to treat.
- HIV patients
- People with hemophilia who receive blood clotting factors
Prevention Is The Best Medicine
Even though hepatitis C rarely spreads within a household, if you or a family member have the disease, it’s wise to take precautions to prevent its spread especially if anyone in your home is immune compromised, or has cuts or open sores that increase the risk of infection.
In general, use these common sense preventive tips:
- Unless you are in a long-term, monogamous relationship, practice safe sex.
- Clean up spilled or dried blood with a bleach-based cleaning solution and wear rubber gloves.
- Do not share razors.
- Do not share toothbrushes. “Though hepatitis C is not transmitted through saliva, there might be blood on the toothbrush,” Reau says.
Note that hepatitis C is not transmitted by sharing eating utensils, hugging, kissing, coughing or sneezing.