How Common Is Hepatitis C In The United States
In the United States, hepatitis C is the most common chronic viral infection found in blood and spread through contact with blood.14
Researchers estimate that about 2.7 million to 3.9 million people in the United States have chronic hepatitis C.13 Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have this infection.
Since 2006, the number of new hepatitis C infections has been rising, especially among people younger than age 30 who inject heroin or misuse prescription opioids and inject them.15,16
New screening efforts and more effective hepatitis C treatments are helping doctors identify and cure more people with the disease. With more screening and treatment, hepatitis C may become less common in the future. Researchers estimate that hepatitis C could be a rare disease in the United States by 2036.17
Hepatitis C And Blood Spills
When cleaning and removing blood spills, use standard infection control precautions at all times:
- Cover any cuts or wounds with a waterproof dressing.
- Wear single-use gloves and use paper towel to mop up blood spills.
- Clean the area with warm water and detergent, then rinse and dry.
- Place used gloves and paper towels into a plastic bag, then seal and dispose of them in a rubbish bin.
- Wash your hands in warm, soapy water then dry them thoroughly.
- Put bloodstained tissues, sanitary towels or dressings in a plastic bag before throwing them away.
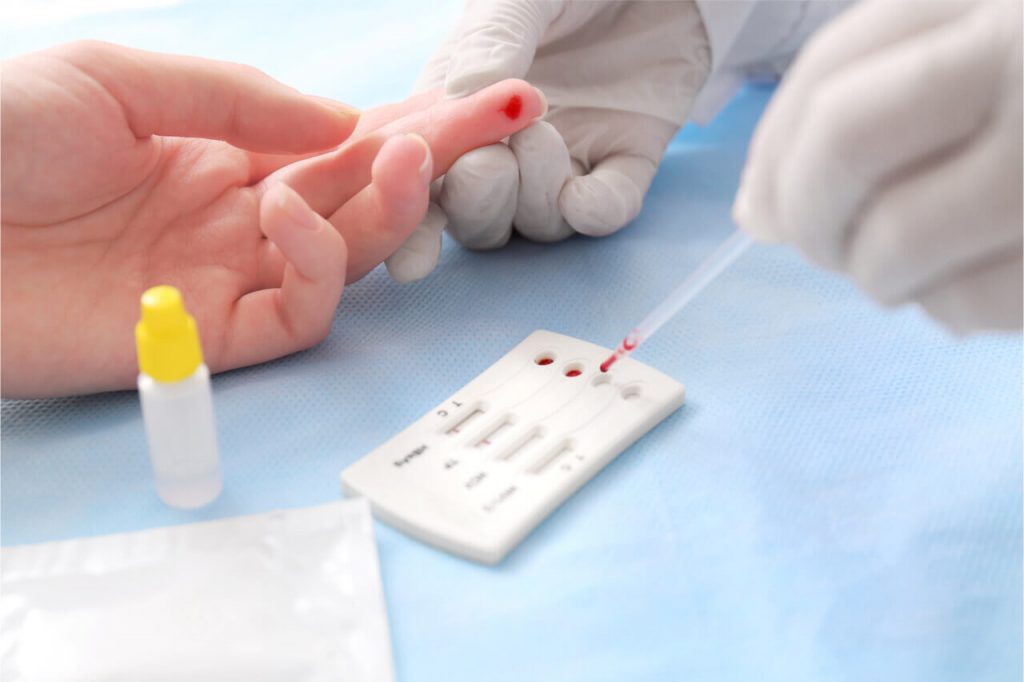
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
Seek medical advice if you have persistent symptoms of hepatitis C or there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you do not have any symptoms.
A blood test can be carried out to see if you have the infection.
GPs, sexual health clinics, genitourinary medicine clinics or drug treatment services all offer testing for hepatitis C.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent or limit any damage to your liver, as well as help ensure the infection is not passed on to other people.
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis C Cause Liver Cancer
Hepatitis C Antibody Test
Certain foreign substances that enter your body trigger your immune system to make antibodies. Antibodies are specifically programmed to only target the foreign substance they were made to fight.
If youve ever had a hepatitis C infection, your body will make hepatitis C antibodies as part of its immune response.
Your body only makes these antibodies if you have hepatitis C or had it in the past. So the hepatitis C antibody test can confirm whether you have the virus by testing for these specific antibodies.
It may take 2 to 3 months after exposure for the test to detect antibodies. If needed, your healthcare professional may order an HCV RNA test, which can detect the virus after just 1 or 2 weeks.
If the antibody test is positive, an HCV RNA test can show whether the infection is current.
While people of any gender experience the same hepatitis C symptoms, 2014 research suggested some effects of the virus may differ, depending on the sex you were assigned at birth.
Researchers noted that:
- women have a higher chance of clearing the virus without treatment
- liver disease may progress more rapidly in men
- men have a higher chance of developing cirrhosis
How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C spreads through contact with the blood of someone who has HCV. This contact may be through:
- Sharing drug needles or other drug materials with someone who has HCV. In the United States, this is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.
- Getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on someone who has HCV. This can happen in health care settings.
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not sterilized after being used on someone who has HCV
- Having contact with the blood or open sores of someone who has HCV
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another person’s blood, such as razors or toothbrushes
- Being born to a mother with HCV
- Having unprotected sex with someone who has HCV
Before 1992, hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Since then, there has been routine testing of the U.S. blood supply for HCV. It is now very rare for someone to get HCV this way.
Read Also: Does Hepatitis B Have A Cure
Additional Tests You Might Need
Once youve been diagnosed with Hepatitis C, your doctor will likely order a number of tests to find out about the health of your liver and decide on a treatment plan thats most appropriate for you.
Hepatitis C genotype
The Hepatitis C genotype refers to a specific strain or type of the Hepatitis C virus. There are six major types of Hepatitis C around the world: genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. In the United States, genotypes 1, 2, and 3 are common:
- Genotype 1: Most Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
- Genotype 2: About 10% of Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
- Genotype 3: About 6% of Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
The genotype of Hepatitis C does not change over time, so you only need to get tested once.
Genotype tests are done before a person starts treatment. Hepatitis C treatment works differently for different genotypes, so knowing your genotype helps your doctor choose the best treatment for you.
Testing for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B
Your doctor may test to see if your body is immune to Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B. If these tests show no prior exposure or protection, he or she will recommend that you be vaccinated against these two viruses to eliminate the chance of becoming infected.
Liver function tests or liver enzymes
- ALT
- AST
Liver function tests also include ALP and total bilirubin, among other things.
Tests to measure liver scarring or fibrosis
- Liver Biopsy
- Elastography
- Serum markers
Imaging tests
What To Do If You Have Hepatitis A Symptoms
If you have been exposed to hepatitis A and show the symptoms above, you need to contact your doctor and/or your local health department as soon as you can, according to the CDC. Once you get to see your doctor, they will run a blood test to confirm the infection diagnosis. Typically, health professionals want to see a patient within two weeks of viral exposure.
The two-week window is important because doctors can help treat hepatitis A with a single dose of the viral vaccine. But treatment only works within the first two weeks of exposure/infection.
Also Check: What Organ Does Hepatitis Affect
Recommended Reading: Why Does Hepatitis Cause Joint Pain
How Can I Prevent Getting Hepatitis C
There are no vaccines available for hepatitis C. However, to reduce the risk of contracting hepatitis C, its a good idea to:
- Always use condoms, gloves and water-based or silicone-based lube if youre fucking, getting fucked or fisting
- Always change condoms between different partners
- Avoid sharing sex toys and use condoms over toys
- Sterilise sex toys completely with disinfectant and rinse in boiling water between sessions
- Wash your hands and sex toys during sex and between partners
- Always use new injecting equipment and avoid sharing injecting equipment
- Always wash your hands before and after injecting
- Avoid sharing personal items such as toothbrushes, razors and nail scissors & clippers
- Make sure body artists use new and sterile equipment for tattooing, body piercing and other body art, and ensure they work at premises registered by the local council
For more information contact NSW Sexual Health Infolink on 1800 451 624 www.shil.nsw.gov.au or visit your local sexual health clinic or doctor.
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost Walgreens
How One Black Man Was Cured Of Hep C Despite Racial Bias
According to the CDC, approximately 10 to 20 percent of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over a period of two to three decades.
People with cirrhosis have a 1 to 5 percent annual risk of developing liver cancer and a 3 to 6 percent risk of hepatic decompensation . Theres a 15 to 20 percent risk of death in the year following the development of decompensation.
Age and gender have been shown to affect how chronic hepatitis C progresses, warns Adalja. It doesnt advance to cirrhosis and liver cancer as quickly in premenopausal women as it does in men, according to a report published in July 2013 in Southern Medical Journal.
Adalja notes that other factors that may accelerate chronic hepatitis C progression, increasing the risk of liver damage. These include HIV or hepatitis B coinfection, alcohol overuse, and cigarette smoking. The symptoms of chronic hepatitis C vary depending on the type of liver damage.
Cirrhosis can produce a variety of symptoms:
- Itchiness
- Abdominal bloating from a buildup of fluids
- Swelling in the feet, ankles, or legs
- Spider angiomas
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
Each type of hepatitis is treated differently.
Hepatitis A often goes away on its own and home treatment is all that is needed to help the liver recover, such as:
- Rest
- Avoiding alcohol
- Avoiding certain medicines that can be harmful to the liver
Hepatitis B often goes away on its own in about 6 months, and can also be treated at home with the above remedies. Other treatments for hepatitis B include:
- Antiviral medications
- Liver transplant in severe cases
Treatment for hepatitis C is effective on certain forms of the hepatitis C virus. The choice of medications depends on the type of hepatitis C you have, whether you have been treated for the illness before, how much liver damage has occurred, any other underlying medical issues, and other medicines you take. Treatment for hepatitis C usually involves 8 to 12 weeks of oral antiviral medications, such as:
- Elbasvir-grazoprevir
- Sofosbuvir-velpatasvir-voxilaprevir
You May Like: How To Diagnose Hepatitis C
What Do You Do If You Become Ill
Talk to your health care provider about getting tested if you think you:
- are at risk
- may have hepatitis C
If you have hepatitis C, tell those who may have been exposed to your blood or bodily fluids. They should get tested and be treated if necessary. Bodily fluids, like semen and vaginal fluid, are a concern because they could be carrying small amounts of infected blood.
Some adults with hepatitis C will recover from the disease on their own within 6 months. Until your health care provider confirms your recovery status, you are still contagious and can spread the disease.
After recovery, you are no longer contagious because you will not have the disease anymore. But you can get hepatitis C again.
Unfortunately, most adults with hepatitis C:
- cannot recover on their own
- develop a more serious form of the disease if they are sick for longer than 6 months
Assessing The Severity Of The Infection
If you are found to have virus present then other tests may be advised to check on the extent of inflammation or damage to the liver. For example:
- Blood tests called liver function tests. These measure the activity of chemicals and other substances made in the liver. This gives a general guide as to whether the liver is inflamed and how well it is working. See the separate leaflet called Liver Function Tests. Other blood tests will also be done for various reasons. For example, tests to check for other illnesses which can be passed on in the same way, such as HIV or hepatitis B. Also tests of other functions of the liver, such as the ability of blood to clot properly, and levels of iron stores.
- An ultrasound scan of the liver.
- Other tests may be done if cirrhosis or other complications develop.
- There are other specialised blood tests being developed which assess the development and severity of cirrhosis.
- A small sample of the liver taken to look at under the microscope used to be recommended before considering treatment. However, this is no longer routine prior to treatment. See the separate leaflet called Liver Biopsy.
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Alcohol Use
Treatment Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is treated with antiviral medications that aim to clear the virus from your body.
New all-tablet treatments have greatly improved the outcomes for people with hepatitis C. These treatments can cure more than 95% of individuals with chronic hepatitis C. There are several new tablets that are used in combination to treat all hepatitis C strains . They are effective for people with no liver damage and those who have more advanced liver damage or cirrhosis.
These new tablet medications are available and subsidised on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, and can be prescribed by specialists, general practitioners and specialised nurse practitioners.
There are no restrictions on accessing treatment it is available for all adults with a Medicare card. People under 18 are able to access treatment and it is recommended they are referred to a pediatrician experienced in the treatment of hepatitis C.
For more information on the new medications for the treatment of hepatitis C, see our video: Hepatitis C Cure what it means for Victorians.
If your doctor does not know about the new treatments, you can call the LiverLine on for information, and to find a GP who can help you.
Talk with your doctor about treatment options and the potential for interactions with other medications, herbal preparations and other drugs. If you take prescribed medication this will be managed so you can access treatment.
In general, if you have hepatitis C you will feel better if you:
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
Don’t Miss: How Do You Transmit Hepatitis C
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
It is very important to know that not everyone with hepatitis C has symptoms. The only way to know if you have hepatitis is by talking to your doctor and getting a blood test.
Many people living with hepatitis C feel well and only have symptoms once the disease has progressed and there is serious liver damage.
If you do not have symptoms this does not mean that the virus isnt causing damage.
When first infected, some people may find:
- their urine becomes dark
- their eyes and skin turn yellow
- they experience a minor flu-like illness.
These symptoms may disappear within a few weeks, but this does not necessarily mean that the infection has been cleared.
Over time, symptoms that may develop include:
- tiredness and fatigue
- flu-like symptoms
- pain in the abdomen where the liver is located
- not feeling hungry and indigestion.
Around 30% of people who have been infected may clear the virus from their blood naturally, with no treatment, within 6 months. These people no longer have the hepatitis C virus and are not infectious, but will always have hepatitis C antibodies in their blood. The presence of hepatitis C antibodies shows that someone has been exposed to the virus, but does not offer any immunity against hepatitis C. People can become reinfected after clearing the virus naturally, or after treatment.
What If Im Hiv Positive
Theres a higher number of cases of hepatitis C amongst poz guys, so its a good idea to get a hepatitis C test at least once a year, and every six months if youve had more than 10 partners in the last six months, use recreational drugs or have had unprotected or group sex.
While guys with both HIV and hepatitis C can be treated for both infections, HIV is usually the priority. Some people, however, need to be treated for both infections, especially in cases where there are hepatitis C-related liver problems.
As you may already know, some HIV treatments can carry a risk of liver inflammation or damage. This is why its important to develop a good relationship with your doctor, especially if you also have hepatitis C, so you can have your liver enzyme levels carefully monitored.
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis Cause Stomach Pain
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
There are some very effective options for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. They are listed on the Medicare PBS , which makes them available at a much lower cost.
Newer treatments differ from those available previously:
- they cure more than 95% of people
- their side effects are minimal
- treatments last just 8 to 12 weeks
- they involve just a few pills each day, with no injections required
Curing hepatitis C means clearing the virus from the body. It helps reduce liver inflammation and can also help reverse scarring and cirrhosis. You can be re-treated if your treatment doesnt work the first time.
You should check with your doctor before taking any other medication or supplements, and whether you need vaccinations against hepatitis A and hepatitis B. You should also avoid alcohol if you have hepatitis. If you have liver damage, you may also need to see a liver specialist
For more information on how to get treatment, contact the National Hepatitis Info Line on 1800 437 222.