How Effective Is Prehevbrio At Preventing Hepatitis B
Most of what we know about PreHevbrios effectiveness comes from two clinical trials. These trials were called PROTECT and CONSTANT. Both studies looked to see how safe and effective PreHevbrio is. The CONSTANT study also studied manufacturing quality.
In clinical trials, a larger percentage of people who received PreHevbrio made enough antibodies to be considered protected against hepatitis B compared to those who received Engerix-B. This difference was most notable in adults 45 years and older.
Additionally, everyone who received PreHevbrio developed more antibodies against hepatitis B compared to those who received Engerix-B. And the percentage of people with protective antibody levels went down less in the PreHevbrio group after about 12 months.
No safety or manufacturing concerns were found in either study. But, like with all vaccines, many people had a few side effects.
What Are Nonviral Causes Of Hepatitis
Other things can cause hepatitis besides viruses. The most common nonviral cause of hepatitis is heavy alcohol use. Certain medications, chemicals, or supplements can also cause hepatitis. The least common type of nonviral hepatitis is autoimmune hepatitis, which results when the bodys immune system attacks the liver.
Who Should And Shouldnt Receive Prehevbrio
As mentioned, the CDC hasnt officially included PreHevbrio into its list of recommended vaccines.
But PreHevbrios labeling helps offer some preliminary insight into who should and shouldnt receive the vaccine. If youre 18 years or older, you may be eligible to get this vaccine.
But if any of the following items apply to you, PreHevbrio may not be the best choice for you:
-
Age 17 or younger
-
Have an active hepatitis B infection
-
Have an allergy to any ingredient in PreHevbrio
-
Have experienced a severe allergic reaction to another hepatitis B vaccine
Its not known how this vaccine affects women who are pregnant or nursing. This is also true for people who are receiving dialysis. For more information, talk to your healthcare provider.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer Test
Prevention Of Hepatitis A Virus Infection
Prevention of HAV infection in adults, adolescents, and children 1 year of age.
Although HAV infection may be asymptomatic or relatively mild in many patients, it can result in substantial morbidity and associated health-care costs and work loss and may be associated with fulminant hepatitis and hepatic failure. Overall HAV case-fatality rate in the US is 0.30.6%, but increases to about 2% in those 40 years of age. HAV is highly contagious . The virus is transmitted person-to-person, principally through the fecal-oral route. HAV infection remains one of the most commonly reported vaccine-preventable diseases in travelers.
USPHS Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices , AAP, and American Academy of Family Physicians recommend that all children be vaccinated against HAV infection at 1 year of age , unless contraindicated.
ACIP, AAP, AAFP, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists , and American College of Physicians also recommend vaccination against HAV for all previously unvaccinated children, adolescents, and adults at high risk of exposure to HAV and for any other unvaccinated individual desiring protection from HAV infection.
HepA vaccine will not prevent hepatitis caused by other infectious agents .
Interchangeability With Other Hepatitis B Vaccines
A controlled study demonstrated that completion of a course of immunization with 1 dose of ENGERIX-B at Month 6 following 2 doses of RECOMBIVAX HB at Months 0 and 1 produced a similar GMT to immunization with 3 doses of RECOMBIVAX HB at Months 0, 1, and 6 . Thus, ENGERIX-B can be used to complete a vaccination course initiated with RECOMBIVAX HB.8
Also Check: How Does One Catch Hepatitis C
How Does Prehevbrio Prevent Hepatitis B
PreHevbrio works by showing your body how to make antibodies against HBV. It helps protect you against hepatitis B infection if youre exposed to HBV.
Specifically, PreHevbrio teaches your body to make antibodies that can recognize three antigens found on the outside of HBV cells. These antibodies help your immune system target and kill HBV cells that have any of the antigens from PreHevbrio.
Of note, PreHevbrio should only be used to help prevent hepatitis B. Its not meant to treat hepatitis B if you already have it.
Adults Recommended To Receive Hepb Vaccine:
- Persons at risk for infection by sexual exposure
- Sex partners of hepatitis B surface antigen positive persons
- Sexually active persons who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship
- Persons seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted infection
- Men who have sex with men
Read Also: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
What If There Is A Serious Problem
An allergic reaction could occur after the vaccinated person leaves the clinic. If you see signs of a severe allergic reaction , call 9-1-1 and get the person to the nearest hospital.
For other signs that concern you, call your health care provider.
Adverse reactions should be reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System . Your health care provider will usually file this report, or you can do it yourself. Visit the VAERS website at or call . VAERS is only for reporting reactions, and VAERS staff members do not give medical advice.
Hepatitis A Vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide
For health professionals
Last partial chapter update
: The immunoglobulin dosage for Hepatitis A pre-exposure and post-exposure prophylaxis was increased based on the Product Monograph update for GamaSTAN®, which is available on Health Canada’s Drug Product Database.
Last complete chapter revision: March 2018
Don’t Miss: Tenofovir Hepatitis B Side Effects
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a viral infection of the liver due to the hepatitis B virus. It causes the liver to swell and can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. There may be no symptoms with hepatitis B.
Treatment may not be needed for hepatitis B besides liver monitoring. A liver transplant may be needed if there is liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may require use of antiviral medications. Common drug classes used to treat hepatitis B are hepatitis B NRTIs and interferon alphas. Vaccinations can also be given.
What Are Warnings And Precautions For Hepatitis B Vaccine
Warnings
This medication contains the hepatitis b vaccine. Do not take Engerix B or Recombivax HB if you are allergic to the hepatitis b vaccine or any ingredients contained in this drug.
Keep out of reach of children. In case of overdose, get medical help or contact a Poison Control Center immediately.
Contraindications
Also Check: Food To Cure Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Vaccine Is Also Recommended For The Following People:
- People whose sex partners have hepatitis B
- Sexually active persons who are not in a long-term monogamous relationship
- People seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease
- Victims of sexual assault or abuse
- Men who have sexual contact with other men
- People who share needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment
- People who have household contact with someone infected with the hepatitis B virus
- Healthcare and public safety workers at risk for exposure to blood or body fluids
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally disabled persons
- People living in jail or prison
- Travelers to regions with increased rates of hepatitis B
- People with chronic liver disease, kidney disease on dialysis, HIV infection, infection with hepatitis C, or diabetes
Hepatitis B vaccine may be given as a stand-alone vaccine, or as part of a combination vaccine .
Hepatitis B vaccine may be given at the same time as other vaccines.
Who Should Receive Hepatitis B Vaccination
- All newborns before hospital discharge. Infants born to hepatitis B-positive women need hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG within 12 hours of birth.
- All children and adolescents not previously vaccinated.
- Children born in the U.S. to individuals born in a country with high hepatitis B endemicity.
- All individuals at risk of hepatitis B infection:
- Sex partners of hepatitis B-positive persons
- Sexually active persons who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship
- Persons seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually-transmitted disease
- Men who have sex with men
- Persons who inject drugs
- Household contacts of hepatitis B-positive persons
- Persons born in countries where hepatitis B infection is endemic should be tested and vaccinated if susceptible
- International travelers to regions with high or intermediate rates of endemic hepatitis B infection
- Health care and public safety workers that may be exposed to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally disabled persons, corrections facilities, and other facilities that serve adults at risk for hepatitis B infection
- Persons with end-stage renal disease, including pre-dialysis, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and home dialysis patients
- Persons with chronic liver disease
- Persons to age 60 years with diabetes
- Persons with HIV infection
- All other persons seeking protection from hepatitis B infection.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C Related To Aids
How Is Hepatitis B Immune Globulin Given
Hepatitis B immune globulin is injected into a muscle or into a vein through an infusion pump. A healthcare professional will give you this injection.
For prevention after exposure to contaminated blood: Hepatitis B immune globulin is usually given as soon as possible after exposure to an infected person, preferably within 7 days. A booster medication is then given 24 hours later. Your doctor may also recommend that you receive a hepatitis B vaccine when you start treatment with hepatitis B immune globulin.
For liver transplant: Hepatitis B immune globulin is given as part of the transplant procedure, and then for several weeks or months afterward. The medication is usually given to transplant patients every day for 7 days, then every 2 weeks for the next 11 weeks, followed by monthly injections from then on.
For prevention after sexual contact with an infected person: Hepatitis B immune globulin is given as a single dose within 14 days after the last contact. You should also receive a hepatitis B vaccine if you will continue to have contact with the infected person.
For prevention in people sharing the home of an infected person: hepatitis B immune globulin should be given to infants younger than 12 months old, caregivers who may come into contact with the infected person’s blood, and people who share razors, toothbrushes, or other personal items with the infected person. Household members may also need to receive hepatitis B vaccine.
Hepatitis A And B Vaccine
These services are offered by the pharmacist owners affiliated with Jean Coutu.
- 1
- 2
- 3
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that can have different causes and can lead to significant health complications.
The best way to protect yourself against hepatitis A and B is through vaccination.
Fortunately, it is possible to receive the preventive vaccine directly at the pharmacy.
Sorry, no matches for your search on
Here are a few tips to help you find what you are looking for:
- Check the spelling
- Search only for one or two terms
- Try with different words or broader terms
Please feel free to use the main search bar located at the top right of the page for more in depth search results.
Book an appointment
Find a pharmacy offering this service
Our offers
Also Check: What Can Cause Hepatitis C
Is Hepatitis B Vaccine
- There are no adequate or well-controlled trials of hepatitis B vaccine use in pregnant women. Therefore, hepatitis B vaccine should be used during pregnancyonly if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
- It is not known if the hepatitis B vaccine is excreted into human milk after administration to the mother. The manufacturer recommends caution when given to nursing mothers.
What Are The Uses For Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B vaccine is used to prevent hepatitis B, a serious infection that affects the liver.
Most children are given their first shot at birth, followed by a 2nd shot at 1-2 months of age, and a 3rd shot at 6-18 months of age. Also, anyone who is 18 years of age or younger and hasn’t received the vaccine should be vaccinated.
Additionally, all unvaccinated adults at risk for hepatitis B infection should be vaccinated. This includes:
- Partners or people infected with hepatitis B
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject street drugs
- People with more than one sex partner
- People with chronic liver or kidney disease
- People under the age of 60 who have type 1 or 2 diabetes
- People with jobs that expose them to human blood or other body fluids
- People who live with a family member infected with hepatitis B
Don’t Miss: Is There A Shot For Hepatitis C
More Information On Side Effects
Reactions listed under âpossible side effectsâ or âadverse eventsâ on vaccine product information sheets may not all be directly linked to the vaccine. See Vaccine side effects and adverse reactions for more information on why this is the case.
If you are concerned about any reactions that occur after vaccination, consult your doctor. In the UK you can report suspected vaccine side effects to the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency through the Yellow Card Scheme
Efficacy And Immunogenicity In Specific Populations
Homosexual Men
ENGERIX-B given at 0, 1, and 6 months was evaluated in homosexual men aged 16 to 59 years. Four of 244 subjects became infected with hepatitis B during the period prior to completion of the 3-dose immunization schedule. No additional subjects became infected during the 18-month follow-up period after completion of the immunization course.
Adults with Chronic Hepatitis C
In a clinical trial of 67 adults aged 25 to 67 years with chronic hepatitis C, ENGERIX-B was given at 0, 1, and 6 months. Of the subjects assessed at Month 7 , 100% responded with seroprotective titers. The geometric mean antibody titer was 1,260 mIU/mL .
Adults on Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis patients given hepatitis B vaccines respond with lower titers, which remain at protective levels for shorter durations than in normal subjects. In a clinical trial of 56 adults who had been on hemodialysis for a mean period of 56 months, ENGERIX-B was given at 0, 1, 2, and 6 months. Two months after the fourth dose, 67% of patients had seroprotective antibody levels and the GMT among seroconverters was 93 mIU/mL.
Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Mayo Clinic
What Populations Are Most At Risk For Hepatitis B Infection
Some people are more at risk of being exposed to the hepatitis B virus than others. These groups include:
-
Healthcare workers
-
Feeling tired or being fatigued
-
Yellowing of the eyes or skin
-
Dark urine
These symptoms can appear as early as 2 weeks or as late as 4 months after you are exposed to the virus. Because so many people do not have symptoms or develop symptoms months later, they may not realize they have the hepatitis B virus and that they can spread the infection to others.
Recommended Dose And Schedule

Persons from Birth through 19 Years
Primary immunization for infants , children , and adolescents consists of a series of 3 doses given on a 0-, 1-, and 6-month schedule.
Persons Aged 20 Years and Older
Primary immunization for persons aged 20 years and older consists of a series of 3 doses given on a 0-, 1-, and 6-month schedule.
Adults on Hemodialysis
Primary immunization consists of a series of 4 doses given as a single 2-mL dose or two 1-mL doses on a 0-, 1-, 2-, and 6-month schedule. In hemodialysis patients, antibody response is lower than in healthy persons and protection may persist only as long as antibody levels remain above 10 mIU/mL. Therefore, the need for booster doses should be assessed by annual antibody testing. A 2-mL booster dose should be given when antibody levels decline below 10 mIU/mL.1
|
Group |
|
0, 1, 2, 12 months |
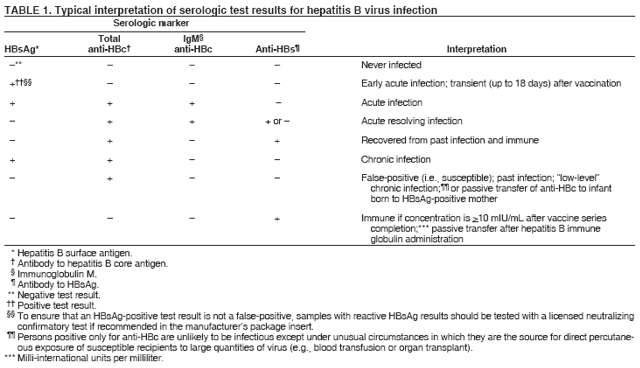
HBsAg = Hepatitis B surface antigen.
a 0.5 mL 1 mL .
b Infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers should receive vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours after birth .
c For children and adolescents for whom an extended administration schedule is acceptable based on risk of exposure.
Also Check: What To Do If You Have Hepatitis B
What Other Drugs Interact With Hepatitis B Vaccine
If your doctor has directed you to use this medication, your doctor or pharmacist may already be aware of any possible drug interactions and may be monitoring you for them. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicine before checking with your doctor, health care provider, or pharmacist first.
- Severe Interactions of Hepatitis B Vaccine include:
- belimumab
This information does not contain all possible interactions or adverse effects. Therefore, before using this product, tell your doctor or pharmacist of all the products you use. Keep a list of all your medications with you, and share this information with your doctor and pharmacist. Check with your health care professional or doctor for additional medical advice, or if you have health questions, concerns, or for more information about this medicine.