Are There Supplements That Are Good For My Liver
If a person eats a balanced diet, they will normally get enough vitamins and minerals. People with liver disease should avoid taking large amounts of supplements or mega-vitamins. This is because the liver has to do extra work to process them. Your provider may put you on a general multivitamin without iron.
Educating Clients About Viral Hepatitis
Clients may believe they know about viral , but their understanding of the disease may not be accurate. It is easy to confuse the three main types of viral , B, and C. Clients may have formed impressions based on limited or incorrect information. Counselors should briefly describe hepatitis A, B, and C, including their prevalence, , and relationship to drug use, as well as to other infections, such as HIV and sexually transmitted diseases. Specific strategies for speaking with clients include:
- Speak clearly and keep the message simple, focused, and brief.
- Use language, examples, and concepts that the client understands.
- Use appropriate visual aids.
- Frame numerical statements in terms that are easy to visualize. Say 5 out of 100 people rather than 5 percent of the population say more than half instead of the majority.
- Repeat the information at different times in different ways. The average client retains only approximately one-third of what he or she is told. Summarize essential points.
- Pay attention to a clients response to the information. For example, if a client stiffens his or her posture, consider saying, I notice that this topic seems to make you uncomfortable. It does for a lot of people. Please tell me what youre feeling right now. Id really like to help you with this.
- Use the opportunity to describe the potential detrimental effects of alcohol and other substance use on the liver of a person who is infected with HCV.
The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Go Away On Its Own
Also Check: Royal Canin Hepatic Dog Food
Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
A positive result indicates recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection or acquired immunity from HBV vaccination. This assay does not differentiate between a vaccine-induced immune response and an immune response induced by infection with HBV. A positive total antihepatitis B core result would indicate that the hepatitis B surface antibody response is due to past HBV infection.
Per assay manufacturers instructions for use, positive results, defined as anti-HBs levels of 12.0 mIU/mL or greater, indicate adequate immunity to hepatitis B from past hepatitis B or HBV vaccination. However, per current CDC guidance, individuals with anti-HBs levels greater than 10 mIU/mL after completing an HBV vaccination series are considered protected from hepatitis B.
Negative results, defined as anti-HBs levels of less than 5.0 mIU/mL, indicate a lack of recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B or inadequate immune response to HBV vaccination. The US Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices does not recommend more than 2 HBV vaccine series in nonresponders.
Indeterminate results, defined as anti-HBs levels in the range from 5 to 11.9 mIU/mL, indicate inability to determine if anti-HBs is present at levels consistent with recovery or immunity. Repeat testing is recommended in 1 to 3 months.
Dont Miss: Hepatitis B And Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Question 5 How Do You Interpret Hcv Antibody Reactive And Hcv Rna Not
A reactive HCV antibody test result combined with a not-detected HCV RNA result indicates no laboratory evidence of a current active HCV infection no further action is required in most cases.
If distinction between a true positive and a biologic false-positive result for HCV antibody is desired, the CDC suggests that one can consider testing with another HCV antibody assay. If there is concern regarding the handling or storage of the test specimen, obtain a new sample for repeat testing.6
Don’t Miss: How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than 7 days post collection will not be tested.
What Does A Reactive Hcv Antibody Test Result Mean
A reactive or positive antibody test means you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time.
Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true if they have cleared the virus, have been cured, or still have the virus in their blood.
A reactive antibody test does not necessarily mean that you currently have hepatitis C and a follow-up test is needed.
Don’t Miss: Do I Have Hepatitis C
Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
Dont Miss: Where Can I Get Tested For Hepatitis B
False Reactive Test Results
What if I have a false reactive test result?
Every donation given to Canadian Blood Services is tested for infectious diseases caused by the hepatitis viruses B and C, HIV, syphilis and another uncommon virus called HTLV .
A false reactive test result means your initial screening test was reactivein other words, suggested the presence of something that would prevent you from donating bloodand a more precise follow-up test was negative. Almost all false reactive results occur because of interference with a test and are not necessarily due to testing positive for an infection.
FAQS
How does Canadian Blood Services test blood?
We follow a two-stage testing method that is used in laboratories worldwide. In the first stage, a sensitive screening test looks for the possible presence of infection. If the screening test shows no reaction, the blood is considered free of infection and no further testing is done. However, if the screening test is reactive, further testing is done to sort out whether the reactive result was due to an infection in the blood or interference with the test. The second test identifies markers in the blood that are found only when infection is present.
Do I need to go to my doctor for repeat testing?
Yes. Repeat testing should be discussed with your doctor because he/she is in the best position to offer you personal medical advice.
Do my partner, children, or friends need to worry if I’ve had a false reactive result?
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Clinical Information Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B e antigen is a small polypeptide that exists in a free form in the serum of individuals during the early phase of hepatitis B infection, soon after hepatitis B surface antigen becomes detectable. Serum levels of both HBeAg and HBsAg rise rapidly during the period of viral replication. The presence of HBeAg in serum correlates with hepatitis B virus infectivity, the number of infectious virions, and the presence of HBV core antigen in the infected hepatocytes.
During recovery from acute hepatitis B, HBeAg level declines and becomes undetectable in the serum, while hepatitis B e antibody appears and becomes detectable in the serum. Anti-HBe usually remains detectable for many years after recovery from acute HBV infection.
In HBV carriers and patients with chronic hepatitis B, positive HBeAg results usually indicate presence of active HBV replication and high infectivity. A negative HBeAg result indicates very minimal or no HBV replication. Positive anti-HBe results usually indicate inactivity of the virus and low infectivity. Positive anti-HBe results in the presence of detectable HBV DNA in serum also indicate active viral replication in these patients.
Dont Miss: What Is A Hepatitis Panel
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Don’t Miss: How To Test For Hepatitis
What Do The Results Mean
There are two results from a hepatitis C antibody test.
- A non-reactive or negative test result means that the person does not have the virus. The exception is if someone has come into contact with the virus recently, such as through contaminated blood. If this is the case, they will need to have another test.
- A reactive or positive test result means that the person has had the virus at some point but does not mean that they still have it. Further tests will be needed to check whether the virus is still active in the body and if treatment will be required.
Once diagnosed with hepatitis C, a person will need to undergo a series of different tests to see how the virus has affected their body.
These tests will check for any liver damage, identify how well the liver is working, and help a healthcare professional to decide on treatment.
Hepatitis C is treated with medication known as an antiviral. It gets this name because it aims to clear the virus out of the body.
Another aim of the medication is to slow down damage to the liver. It may also reduce the chance of a person getting liver cancer or developing serious liver scarring, known as cirrhosis.
A person with hepatitis C will require regular testing during treatment to see how well the medication is working. Keeping healthy, getting enough sleep, and avoiding drugs and alcohol can help treatment to work.
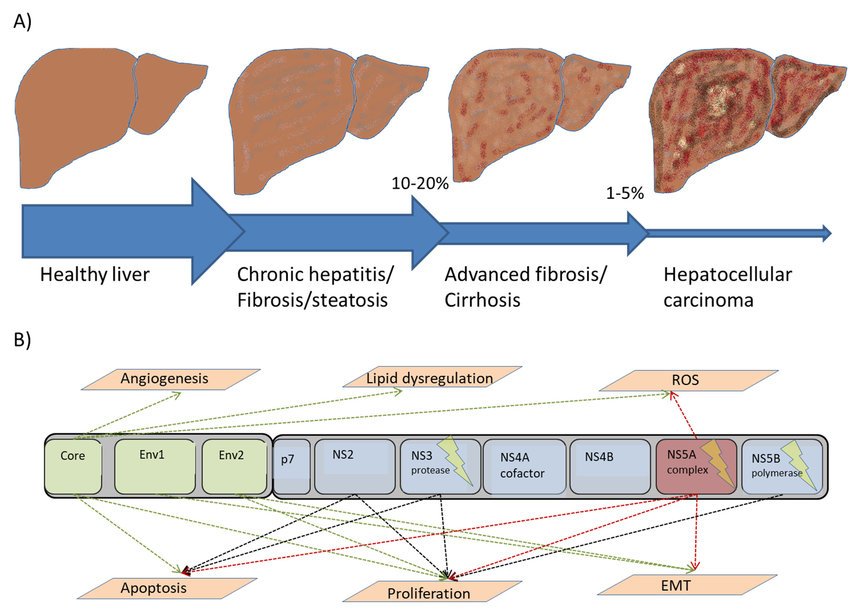
Clinical Features And Natural History
Persons with acute HCV infection are typically either asymptomatic or have a mild clinical illness like that of other types of viral hepatitis . Jaundice might occur in 20%30% of persons, and nonspecific symptoms might be present in 10%20% of persons. Fulminant hepatic failure following acute hepatitis C is rare. The average time from exposure to symptom onset is 212 weeks . HCV antibodies can be detected 410 weeks after infection and are present in approximately 97% of persons by 6 months after exposure. HCV RNA can be detected as early as 12 weeks after exposure. The presence of HCV RNA indicates current infection .
Also Check: Hepatitis C How Is It Transmitted
Virus Description And Transmission
HCV is a small, single-stranded, enveloped RNA virus in the flavivirus family with a high degree of genetic heterogeneity. Seven distinct HCV genotypes have been identified. Genotype 1 is the most prevalent genotype in the United States and worldwide, accounting for approximately 75% and 46% of cases, respectively . Geographic differences in global genotype distribution are important because some treatment options are genotype specific . High rates of mutation in the HCV RNA genome are believed to play a role in the pathogens ability to evade the immune system . Prior infection with HCV does not protect against subsequent infection with the same or different genotypes.
HCV is primarily transmitted through direct percutaneous exposure to blood. Mucous membrane exposures to blood also can result in transmission, although this route is less efficient. HCV can be detected in saliva, semen, breast milk, and other body fluids, although these body fluids are not believed to be efficient vehicles of transmission .
Question 6 Is It Possible To Have Hcv Infection And Have A Non
Yes. Among persons with a non-reactive HCV antibody test, who are suspected of having liver disease or are at high risk of acute infection, testing for HCV RNA or follow-up testing for HCV antibody is recommended if high-risk exposure to HCV occurred within the past 6 months. Additionally, testing for HCV RNA can also be considered in persons who are immunocompromised .
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatic Artery Infusion
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnt receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Dont Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis C Twice
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis B Virus Transmitted
Can A Sample Be Reported As Nonreactive For Hcv
Sample can be reported as nonreactive for HCV antibody. No further action required. If recent exposure in person tested is suspected, test for HCV RNA.* A repeatedly reactive result is consistent with current HCV infection, or past HCV infection that has resolved, or biologic false positivity for HCV antibody.
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Yes, since 2010 enormous progress has been made in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are pills that act on the virus itself to eradicate it from the body, unlike older medicines like interferon injections which work by stimulating an immune response. These new treatments are very effective and can achieve cure rates of over 90%. In most situations now, there is no need for interferon, which was responsible for many of the side effects previously associated with HCV treatment. The new treatment combinations require shorter treatment durations , have reduced side effects and appear to be effective at all stages of the disease.
Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Your primary care physician may refer you to a specialist to determine whether you are eligible for treatment. A specialist will help you decide which drug therapy is best for you based on the severity of your liver disease, your virus genotype and whether or not you have been treated in the past.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Ab W Refl To Hcv Rna Qn Pcr
Why Do I Need This Test
You may need this test if your healthcare provider suspects you have a liver infection caused by HBV. You may also need this test if you have symptoms of hepatitis B. Symptoms usually start slowly. Many people have no symptoms or only feel like they have a mild case of the flu. You may not have symptoms until the infection is chronic or severe.
The most common symptom is extreme tiredness. Other symptoms may include:
-
Nausea
-
Belly pain
-
Swelling and confusion. This is in extreme cases.
You may also have this test if you have a history that puts you at risk for being in contact with the virus. Risk factors for hepatitis B infection include:
-
Having sex with someone infected with the virus
-
Living in close contact with someone who has the virus
-
Being a man who has sex with men
-
Being a child born to a mother who has the virus
-
Sharing needles for intravenous, or IV, drug use
-
Working in a healthcare center where you are exposed to blood
-
Getting a blood transfusion or organ transplant. This is less common with active screening.
You May Like: Hepatitis B How Do You Catch It
How Is Liver Damage Assessed

If you have hepatitis C, doctors can gauge the level of liver damage you’ve experienced. One useful diagnostic tool is called a hepatic function panel, a group of blood tests performed together that examine the levels of certain liver enzymes, bilirubin , and proteins circulating in the blood.
Higher-than-normal levels of the liver enzymes, indicate that your liver is damaged, possibly from cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Albumin may be low, and your total bilirubin levels may also be elevated.
Along with the hepatic function panel, your doctor may also order two other tests: one test to determine the levels of the liver enzyme gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in your blood, and a prothrombin time test that measures how well your blood clots.
A liver biopsy, in which a liver tissue sample is removed with a thin needle inserted through your skin and into your liver, can provide more details about the amount of scarring and damage HCV has caused.
Your doctor may also order an imaging test, such as a computerized tomography scan, magnetic resonance imaging , or ultrasound, to see if your hepatitis C has caused liver cancer, a possible complication of hepatitis C.
Additional reporting by Deborah Shapiro.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B How Do You Get It