Hepatitis B Immunization And Postimmunizationserology
Michael John, MB, Ch.B., FRCP
Before the introduction of avaccine, hepatitis B virus was a major occupational risk to health care workers.Some of the highest infection rates were found in dentists and surgeons.1Infected health care workers have a 5-10% risk of developing chronic hepatitis B. A numberof clusters of dentist-to-patient HBV transmissions have been reported over the years,although these have decreased since the introduction of universal precautions.2Recent guidelines from Health Canada recommend restriction of practice of health careworkers who test positive for hepatitis B e antigen.3
The development of hepatitis vaccines in the 1980s has substantially decreased dentalworkers risk of acquiring HBV. A recent survey4 of dentists in Canadashowed that more than 90% had completed an immunization series and an additional 3% hadnatural immunity. However, rates of immunization among dental assistants and hygienistswas found to be much lower.
Hepatitis B Vaccines
The vaccine is administered intramuscularly into the deltoid muscle, as glutealinjection may result in decreased response rates. Response to vaccine following a 3-doseseries is typically greater than 95% in young, healthy people, although it decreases withage . Other factors such assmoking, obesity and chronic disease decrease vaccine efficacy and may be used to predictrisk of nonresponse.6 Adverse events are minimal, although mild injection-sitereactions may occur in 20% of recipients.
References
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
Hepatitis B disease affects the liver and commonly spreads through body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Blood Test
This test is used to determine the status of a persons immunity to the Hepatitis B virus . Immunity is determined by screening for antibodies which provide protection against infection. The results of this test are quantitative.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection of the liver spread through contact with contaminated bodily fluids including blood. Transmission can occur through various types of exposure including sexual contact. It is possible for a pregnant woman to spread the infection to her infant during childbirth. More than half of Hep B infections display no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, the most common are loss of appetite, fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, jaundice, and dark colored urine. Chronic Hepatitis B infections may lead to the development of Cirrhosis or Liver Cancer.
A person can have immunity to Hepatitis B for several reasons.
1.) They have been vaccinated for Hep B. Vaccinations do not always provide permanent immunity. It is possible for a person to have been vaccinated and lose their immunity over time.
2.) They have been infected with Hep B, recovered, and now have a natural immunity. Because Hepatitis B does not always display symptoms, it is possible for a person to have been exposed and not be aware of it.
A person who wishes to screen for a current Hepatitis B infection may want to order the Hep B Surface Antigen test.
The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody test typically sees results in 1 business day.
Detection Period:
Read Also: How Hepatitis C Is Transmitted Sexually
Primary Responses To Hbv Vaccination
All subjects were confirmed to have tested negative for the HBs antigen. Prior to HBV vaccination, 3 of 693 subjects were positive for anti-HBc antibodies . To evaluate the primary response to HBV vaccination, the anti-HB titers of 690 study subjects were measured. No subjects experienced any side-effects associated with the vaccination. The age distribution of the subjects in the present study is presented in . Based on these measurements, the classifications of the subjects were as follows: non-responders, n=29 low responders, n=159 and sufficient responders, n=502 . The mean ages of the subjects in each of these groups were as follows: non-responders, 23.5 years low responders, 22.7 years and sufficient responders, 21.1 years . The sufficient responders were significantly younger in comparison to both low responders and non-responders.
Age distribution of the subjects in the present study. The vertical axis shows the total number of subjects and the subjects classified by the vaccination response . The horizontal axis shows the age of the subjects. Circles, squares and triangles indicate non-responders, low-responders and responders, respectively.
Is Hep B Titer Positive Or Negative
If this test is positive, then your immune system has successfully developed a protective anti- body against the hepatitis B virus. This will provide long-term protection against future hepatitis B infection. Some- one who is surface antibody positive is not infected, and cannot pass the virus on to others.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A Curable Or Not
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to hepatitis B, your body mounts an immune reaction against it as an invader. This happens whether you are exposed due to blood or sexual contact or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The hepatitis B virus has proteins on its surface that cause your immune system to produce antibodies. With the vaccine, the sample contains the protein only and not the virus itself.
The first response your body will make when exposed to hepatitis B is to manufacture hepatitis B IgM antibodies. These early antibodies are produced to fight against several parts of the virus including its core. These antibodies are seen in the initial response, but they eventually fade away.
Your immune system then begins to produce IgG antibodies. It continues to produce these antibodies for the rest of your life. In this way, your immune system is always ready to attack hepatitis B virus when it is exposed to it.
What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
Recommended Reading: How You Get Hepatitis B And C
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
The Correlation Between The Anti
We evaluated correlations between the anti-HBs titers at 1 and 2 years after vaccination and the anti-HBs titer at the primary response . The anti-HBs titers at 1 and 2 years after vaccination were significantly correlated with the anti-HBs titer at the primary response . Age, sex, and primary response were included in a multivariate linear regression analysis to identify factors associated with anti-HBs titers at 1 and 2 years after vaccination the primary response was the only significant factor .
Don’t Miss: How Do You Spread Hepatitis C
What Are Normal Titer Levels
The normal values of an antibody titer depend on the type of antibody. If the testing is done to detect autoantibodies, the normal value should essentially be zero or negative. In the case of testing the efficacy of a vaccine, the normal test result depends on the definite value that is specific for that immunization.
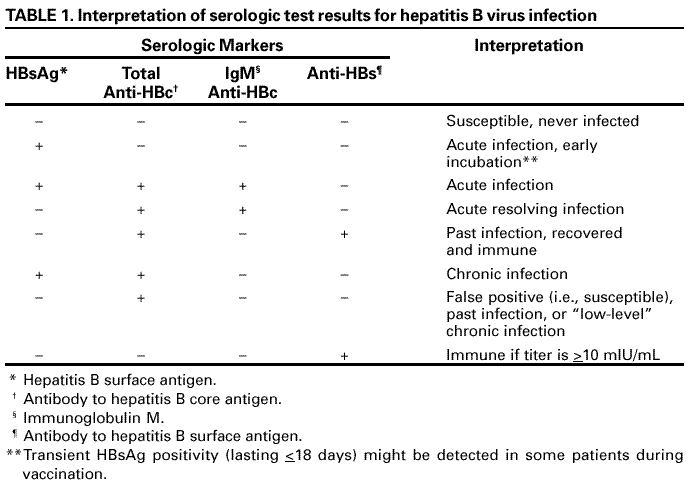
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
Don’t Miss: Can I Donate Blood If I Had Hepatitis A
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with an infected partner
- injection-drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to an infected mother
- contact with blood from or open sores on an infected person
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with an infected person that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts of water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected people
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health-care and public-safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Hemodialysis patients
Who should be screened for HBV?
CDC recommends that the following people be screened for HBV :
- fever,
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
- Description
-
The Quantitative detection Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody in human sera using the FDA approved Abbott ARCHITECT AUSAB-DIL test two-step chemiluminescent immunoassay.
In the first step, sample, assay diluent, and recombinant Hepatitis B surface Antigen coated paramagnetic microparticles are combined. Anti-HBs present in the sample binds to the rHBsAg coated microparticles. In the second step, rHBsAg acridinium-labeled conjugate is added, which binds to IgG anti-HBs. Then pre-trigger and trigger solutions are added to the reaction mixture. The resulting chemiluminescent reaction is measured as relative light units .
A direct relationship exists between the amount of anti-HBs in the sample and the RLUs. The concentration of anti-HBs in the sample is determined using an active ARCHITECT AUSAB calibration curve. Results are reported as mIU/mL.
For Batteries containing HBSAb see:
Hepatitis B Antibodies , Quantitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody and Hepatitis B virus Core IgG and IgM antibodies
Hepatitis B Battery , Quantitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody , Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface Antigen and Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Core IgG and IgM antibodies
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen & Antibody , Quantitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody and Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface Antigen
- Synonyms
Read Also: New Cure For Hepatitis B
Sequence Following An Initial Negative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
As you obtain documentation, please submit documentation of each step to CastleBranch
- Initial Hepatitis B titer negative for immunity
- Receive Hepatitis B challenge dose/booster
- Repeat Hepatitis B titer 4-6 weeks after challenge/booster vaccine
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Blood Test
This test is used to screen for infection with the Hepatitis B virus. The Surface Antigen test looks for a protein which is present on the surface of the virus. This protein will be present in the blood with an acute or chronic Hep B infection. Because it has a fairly early detection window, the Surface Antigen Test is often ordered by people who believe they have had a recent exposure. This test can detect the presence of Hepatitis B in chronic or long-term infections even if the person has no symptoms.
Hepatitis B is a viral liver infection which is spread through exposure to infected blood or bodily fluids. It is the most common cause of acute viral Hepatitis. Hepatitis B infections often show no symptoms but when symptoms do occur they are often described as flu-like. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, fever, loss of appetite, nausea, joint pain, fatigue, jaundice, and dark colored urine. Chronic Hep B infections can cause serious health complications like Cirrhosis and Liver Cancer.
Turnaround time for the Hepatitis B Surface Antigen test is typically 1 business day.
Note: Result turn around times are an estimate and are not guaranteed. Our reference lab may need additional time due to weather, holidays, confirmation/repeat testing, or equipment maintenance.
Detection Period:
For the majority of people, this test will have the highest level of accuracy at 12 weeks from an exposure or any time after. Some people may be detectable as early as 4 weeks from exposure.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis Cause Low Platelets
The Immunological Effect Of Booster Vaccination In Non
To confirm the efficacy of booster HBV vaccination in non-responders and low-responders, we evaluated 33 subjects at 1 year after booster vaccination and 10 subjects at 2 years after booster vaccination. Although the anti-HBs titer increased significantly after booster vaccination, this response was not sustained .
Serial changes in the anti-HB titers of subjects who received a booster vaccination. The vertical axis shows the change in anti-HB titer over time. The horizontal axis shows the indicated time points at which the anti-HB titer was measured at 1 year and 2 years after vaccination. Statistical significance was evaluated using the Friedman test. P values of < 0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance. n.s.: not significant
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Antigens And Antibodies
When And How To Perform Post
Which test to use: If testing is needed following vaccination, use quantitated HBsAb only
- Post-vaccination testing is needed for certain groups who are at especially high risk for HBV infection
- The purpose of post-vaccination testing is to confirm if patients have achieved adequate immune response as measured by hepatitis B surface antibody
- Perform testing 1-2 months after final dose of the HBV vaccine series
- Persons with HBsAb concentrations of > 10 mIU/ml are considered immune
- Post-vaccination testing is recommended for some patients:
- Infants born to HBsAg+ women
- Infants born to women whose HBSAg status remains unknown
- Health care personnel and public safety workers at risk for blood or body fluid exposure
- Hemodialysis patients
- Other immunocompromised persons such as hematopoietic stem-cell transplant patients or persons receiving chemotherapy
- Sex partners of HBSAg+ persons
Occupational Safety And Health Administration
- Standard Number: 1910.1030
OSHA requirements are set by statute, standards and regulations. Our interpretation letters explain these requirements and how they apply to particular circumstances, but they cannot create additional employer obligations. This letter constitutes OSHA’s interpretation of the requirements discussed. Note that our enforcement guidance may be affected by changes to OSHA rules. Also, from time to time we update our guidance in response to new information. To keep apprised of such developments, you can consult OSHA’s website at .
Richard L. Raimondo, Jr., D.D.S.12521 Nacogdoches #103San Antonio, Texas78217
Dear Dr. Raimondo:
Thank you for your February 17, 2015, follow-up letter to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration’s Directorate of Enforcement Programs. After our previous correspondence, you requested additional clarification of OSHA’s Bloodborne Pathogens standard, 29 CFR 1910.1030, concerning its requirements for hepatitis B virus vaccination and antibody testing. This letter constitutes OSHA’s interpretation only of the requirements discussed and may not be applicable to any question not delineated within your original correspondence. For clarification, your specific questions are paraphrased below, followed by OSHA’s responses.
Collection and testing of blood for HBV and HIV serological status
Sincerely,
Also Check: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Hepatic Formula Dry Dog Food
Spontaneous Decrease In Anti
To confirm the spontaneous decreases in anti-HB titers, we re-measured anti-HB titers in 247 and 91 subjects who did not receive a booster HBV vaccination at 1 and 2 years after completing the initial vaccination schedule, respectively . Overall, the mean anti-HB titers at 1 and 2 years after vaccination were lower than the mean primary response titers . During the observation period, 18 of the 247 and 17 of the 91 subjects showed anti-HB titers of < 10 mIU/mL at 1 and 2 years after vaccination, respectively.
Correlation between the primary response and the anti-HB titer at 1 and 2 years after vaccination. The vertical axis shows the anti-HB titers at 1 year and 2 years after vaccination. The horizontal axis shows the primary response to vaccination. Spearmans correlation coefficient was used to assess the correlation between the anti-HB titer and the primary response at both time periods both values were statistically significant: r=0.893, p< 0.0001 r=0.902, p< 0.001.