How To Get Your Anemia Under Control
While you take medicine to treat hepatitis C, your doctor will likely order blood tests every few weeks or months to check your hemoglobin level. If youre at high risk for anemia, you may need blood testing every week.
After a couple of months on treatment, your hemoglobin levels should stabilize. Once you go off the drugs, the anemia will likely go away.
In the meantime, if anemia symptoms bother you, your doctor may lower your dose of ribavirin. Your doctor may stop the drug altogether if your hemoglobin level dips too low.
Your doctor may also prescribe injections of the hormonal medicine epoetin alfa to relieve symptoms of anemia. Epoetin alfa stimulates your bone marrow to produce more red blood cells.
More red blood cells can bring additional oxygen to your body. Possible side effects from these medicines include chills, sweating, and muscle aches.
Although anemia can make you feel tired and cold, it isnt entirely bad. A drop in hemoglobin level has been linked with a sustained virologic response .
A SVR means no trace of the hepatitis C virus is detectable in your blood 6 months after you finish treatment. Essentially, SVR means a cure.
Symptoms And Signs Of Chronic Hepatitis
Clinical features of chronic hepatitis vary widely. About one third of cases develop after acute hepatitis, but most develop insidiously de novo.
Many patients are asymptomatic, regardless of the etiology. However, malaise, anorexia, and fatigue are common, sometimes with low-grade fever and nonspecific upper abdominal discomfort. Jaundice is usually absent.
Often, the first findings are
-
Complications of cirrhosis , schistosomiasis , or hepatic vascular abnormalities… read more , ascites Ascites Ascites is free fluid in the peritoneal cavity. The most common cause is portal hypertension. Symptoms usually result from abdominal distention. Diagnosis is based on physical examination and… read more , encephalopathy Portosystemic Encephalopathy Portosystemic encephalopathy is a neuropsychiatric syndrome that can develop in patients with liver disease. It most often results from high gut protein or acute metabolic stress
A few patients with chronic hepatitis develop manifestations of cholestasis .
In autoimmune hepatitis, especially in young women, manifestations may involve virtually any body system and can include acne, amenorrhea, arthralgia, ulcerative colitis, pulmonary fibrosis, thyroiditis, nephritis, and hemolytic anemia.
. Symptoms of cryoglobulinemia include fatigue, myalgias, arthralgias, neuropathy, glomerulonephritis, and rashes asymptomatic cryoglobulinemia is more common.
Incorporation Of World Health Organization And Macrobiotic Diet Recommendations
Incorporating elements of the macrobiotic diet and nutritional guidelines from the World Health Organization may increase platelet count. The macrobiotic diet and World Health Organization guidelines have been used to prevent and treat disease.
Nutrient recommendations include an adequate intake of calories and fresh whole foods. This includes plant-based proteins, healthy fats, fruits, and vegetables. Fewer animal products are consumed, while sugar, sodium, and saturated and trans fats are avoided.
Chemical pesticides, herbicides, additives, and preservatives may lower platelet counts. These diet recommendations incorporate foods without these compounds.
Read Also: Where To Get A Hepatitis B Shot
What Is The Prognosis For People With Thrombocytopenia
A low platelet count increases your risk of hemorrhage or severe bleeding. Excessive bleeding whether internal or external can be life-threatening. Many people with thrombocytopenia have mild to moderate symptoms. Platelet levels often go up when you treat the underlying cause or change medications.
Connective Tissue And Lymphoproliferative Disorders
-
Rifampin
-
Vancomycin
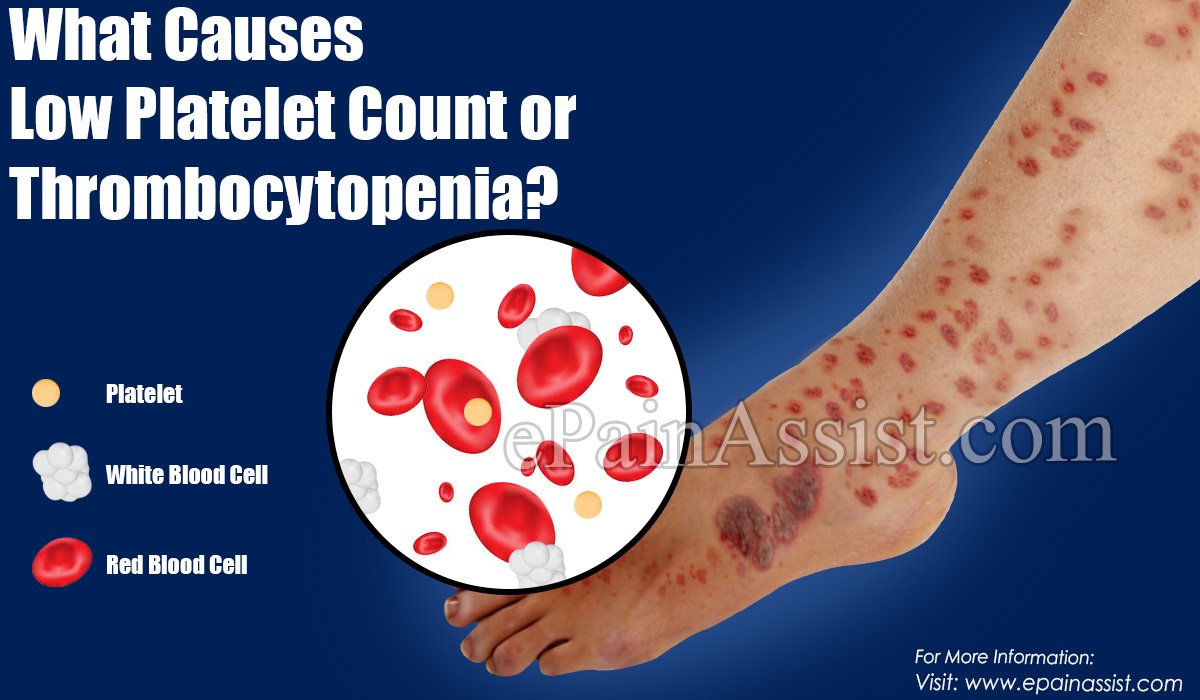
Drug-induced thrombocytopenia occurs typically when a drug bound to the platelet creates a new and foreign antigen, causing an immune reaction. This disorder is indistinguishable from ITP except for the history of drug ingestion. When the drug is stopped, the platelet count typically begins to increase within 1 to 2 days and recovers to normal within 7 days.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Contact Hepatitis A
Splenectomy And Splenic Artery Embolization
Splenectomy and splenic artery embolization have been used to correct thrombocytopenia in patients with hypersplenism, producing significant and persistent increases in platelet count., Akahoshi et al. studied the effect of splenectomy in patients with HCV-associated thrombocytopenia and found above 200% rise in mean platelet count at 1 month after splenectomy. In cases of IFN-based antiviral therapy, the positive effect is known to persist even after the initiation of antiviral therapy, with the mean platelet count nearly 80% above baseline after 12 months of the therapy. Splenectomy, however, is an invasive procedure with high risk of bleeding, sepsis and portal vein thrombosis. Asplenic patients are susceptible to overwhelming post-splenectomy infection. Splenic artery embolization may be an alternative option. In a study by Barcena et al., the mean platelet count increased by 342% from the baseline after 12 weeks of partial splenic artery embolization. Splenic artery embolization, though associated with lower morbidity and mortality than splenectomy, is not free of complications.
Which Types Of Doctors Treat Low Platelet Counts
Thrombocytopenia may be identified during blood work ordered by a primary care provider, including internists, pediatricians, and family medicine specialists. Hematologists are specialists in blood disorders, and they may be called upon to treat patients with thrombocytopenia. Patients with thrombocytopenia due to an underlying disease or condition will also be managed by the specialists that treat these underlying conditions, including infectious disease specialists, rheumatologists, oncologists, and others.
Don’t Miss: Best Treatment For Hepatitis C
Who Should Not Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Generally seen as a safe vaccine, there are some circumstances in which doctors advise against receiving the HBV vaccine. You shouldnt have the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- youve had a serious allergic reaction to a previous dose of the hepatitis B vaccine
- you have a history of hypersensitivity to yeast or to any other vaccine components
- youre experiencing a moderate or severe acute illness
If youre currently experiencing an illness, you should postpone receiving the vaccine until your condition has improved.
What Are Platelets What Are Normal Ranges
Platelets are important elements in the blood that are important for blood coagulation . Thrombocytopenia refers to having a low platelet count in the blood compared to the normal range.
- The normal platelet count ranges between 150,000 and 450,000 per microliter .
- Only about 2/3 of platelets released into the bloodstream circulate in the blood, and the remaining third are typically found in the spleen.
- The life cycle of platelets is usually about 7-10 days therefore, the old ones are continuously being replaced by new ones.
Recommended Reading: How Did I Get Hepatitis B
Thrombocytopenia In The Cardiac Patient
Several mechanisms can induce thrombocytopenia in patients undergoing open heart surgery. Cardiopulmonary bypass may result in mechanical destruction of platelets, hemodilution in the bypass circuit, and drug-induced platelet destruction. More rare causes include sepsis, intra-aortic balloon pumping, and posttransfusion purpura. The nadir platelet count is typically seen on the second or third day after surgery, with a rapid platelet count recovery thereafter.
Severe thrombocytopenia is observed in 0.1%-2% of patients after exposure to GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors during percutaneous coronary intervention. The peculiarity of this DITP is its rapid onset, usually within a few hours after surgery. This phenomenon has been attributed to the presence of naturally occurring Abs against neoepitopes exposed by alteration of the GPIIb/IIIa molecule. In typical cases, thrombocytopenia resolves within 10 days. Delayed development of thrombocytopenia 3-6 days after treatment with abciximab has been described in a few patients. The mechanism of the thrombocytopenia in these cases is the production of Abs against murine peptide sequences of abciximab, which react with other target epitopes on abciximab-coated platelets.
Ask Questions About Your Lab Results
It can be alarming to see a word like “thrombocytopenia” or a low number compared with the baseline on your lab results.
For most patients, having mild-to-moderate low platelets won’t change your pregnancy care or birth plan much, if at all. Moore, despite the changes to her plan, that her healthy baby boy arrived on his due date in late February.
However, it is important to talk with your doctor about your risks for complications related to low platelets. If your lab results indicate low platelets, follow Moore’s lead ask your provider to explain what that means for you. We’re hear to help you make informed decisions and have a healthier, safer pregnancy and delivery.
To visit with an Ob/Gyn about low platelets in pregnancy, call orrequest an appointment online.
You May Like: Purina Pro Plan Hepatic Cat
Causes Behind Low Platelet Count
Low platelet count is also known as thrombocytopenia. An average person has platelets in the range of 150,000 to 400,000 per microlitre of blood. If this falls below 150,000, it is thrombocytopenia. Since, platelets help in clotting, this is a serious condition as it can lead to internal bleeding. This condition may be due to a fall in the production of platelets, destruction of platelets as well as trapping of platelets in the spleen.
A low platelet level is not a serious condition in most cases. But If your platelets fall too low, it can prevent clotting. This can lead to excessive bleeding in certain circumstances and this is when it becomes a serious issue. Let us take a look at a few health conditions that can cause platelet count to fall.
Observation Of The Peripheral Blood Smear
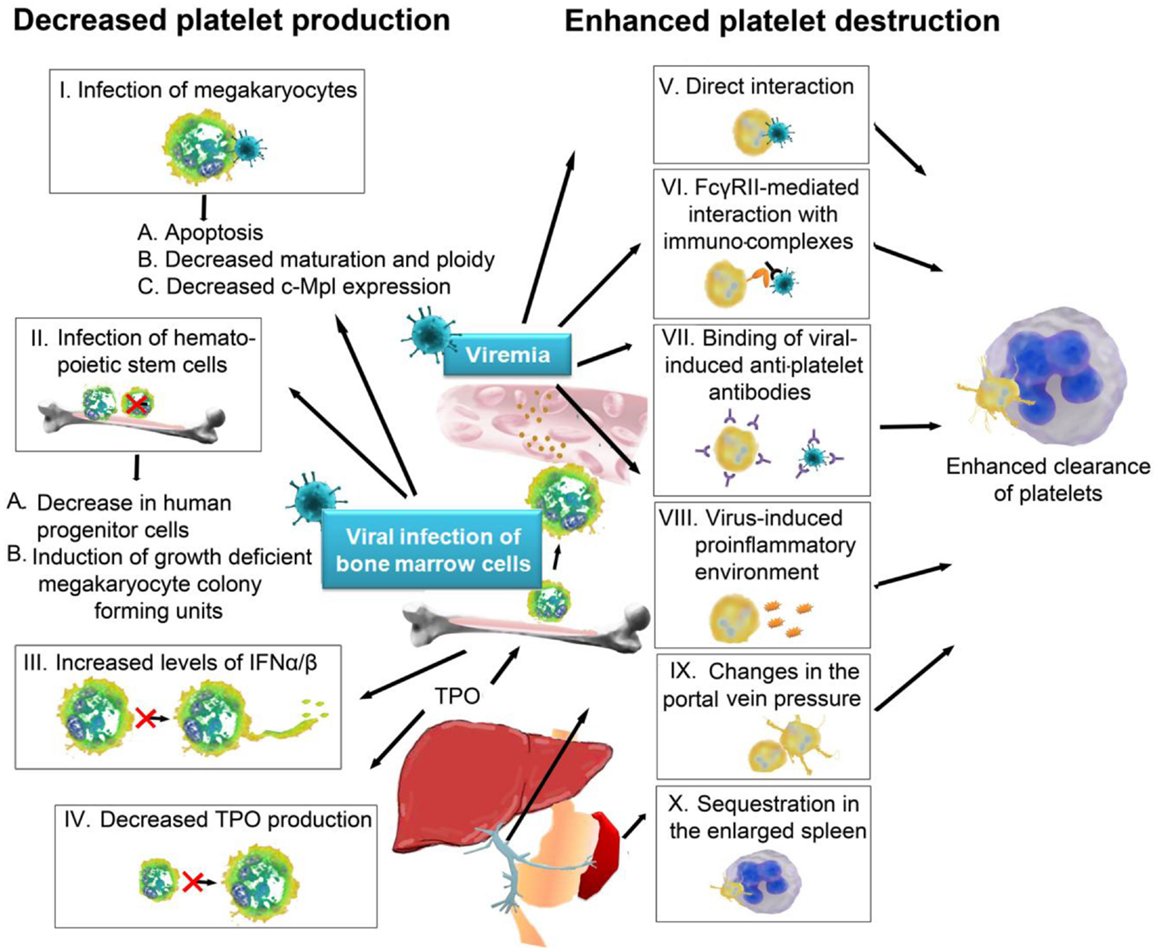
In the era of genomic medicine and widespread molecular testing, examination of the peripheral blood film still remains the most important investigation guiding our diagnostic approach to thrombocytopenia . All 3 blood cell lineages should be assessed carefully . From a practical perspective, when we are investigating thrombocytopenia in a critically ill patient, the immediate information we need to obtain is whether it is thrombotic microangiopathy or acute leukemia . Even a short delay in making these diagnoses may prove fatal for the patient if appropriate treatment is not initiated promptly.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B Shot For
What Are Low Platelet Count Treatments
The treatment for thrombocytopenia depends largely on its severity and the underlying cause.
- For the most part, patients with thrombocytopenia do not require regular platelet transfusion. If any surgery or other invasive procedure is planned in a patient with a platelet count less than 50,000, then transfusion may be necessary to keep the platelet count greater than 50,000.
- Other general recommendations for platelet transfusion are active bleeding in patients with platelet counts less than 20,000 to 50,000 and patients with platelet counts less than 10,000 with or without active bleeding.
Prognosis For Chronic Hepatitis
Prognosis for patients with chronic hepatitis is highly variable and often depends on the cause and availability of treatment.
Chronic hepatitis caused by a drug often regresses completely when the causative drug is withdrawn.
Without treatment, cases caused by HBV can resolve , progress rapidly, or progress slowly to cirrhosis over decades. Resolution often begins with a transient increase in disease severity and results in seroconversion from hepatitis B e antigen to antibody to hepatitis B e antigen . Coinfection with HDV causes the most severe form of chronic HBV infection without treatment, cirrhosis develops in up to 70% of patients with coinfection.
Untreated chronic hepatitis due to HCV causes cirrhosis in 20 to 30% of patients, although development may take decades and varies because it is often related to a patient’s other risk factors for chronic liver disease, including alcohol use and obesity.
Chronic autoimmune hepatitis usually responds to therapy but sometimes causes progressive fibrosis and eventual cirrhosis.
Chronic HBV infection increases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma Hepatocellular Carcinoma Hepatocellular carcinoma usually occurs in patients with cirrhosis and is common in areas where infection with hepatitis B and C viruses is prevalent. Symptoms and signs are usually nonspecific… read more . The risk is also increased in other liver disorders , but usually when cirrhosis or advanced fibrosis has developed.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine For
Possible Side Effects From Vaccines
Any vaccine can cause side effects. For the most part these are minor and go away within a few days. Listed below are vaccines licensed in the United States and side effects that have been associated with each of them. This information is copied directly from CDCs Vaccine Information Statements , which in turn are derived from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommendations for each vaccine.
Remember, vaccines are continually monitored for safety, and like any medication, vaccines can cause side effects. However, a decision not to immunize a child also involves risk and could put the child and others who come into contact with him or her at risk of contracting a potentially deadly disease.
What Is Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia occurs when your blood platelet count is low. Platelets are also called thrombocytes. This type of blood cell clumps together to form blood clots to help stop bleeding at the site of a cut or wound. Another name for a blood clot is thrombus.
Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue inside bones that makes all blood cells including platelets. People who have thrombocytopenia dont have enough platelets to form a blood clot. If you get a cut or other injury, you may bleed too much and the bleeding can be hard to stop.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
What Caregivers Can Do
- Keep the home environment safe to help prevent injury and falls.
- For nosebleeds, have the patient sit up with head tilted forward, to keep blood from dripping down the back of the throat. Put ice on the nose and pinch the nostrils shut for 5 minutes before releasing them. Ice on the back of the neck may also help.
- For bleeding from other areas, press on the bleeding area with a clean, dry washcloth or paper towel until bleeding stops.
What Is Splenic Sequestration
Splenic sequestration occurs when the spleen enlarges and captures, or sequesters, more platelets from the circulation than normal. This could lead to thrombocytopenia.
In infants, many conditions similar to these listed above can lead to neonatal thrombocytopenia. There are also some rare genetic conditions that can also lead to thrombocytopenia in children at birth.
Pseudothrombocytopenia is term given to situations in which there is a falsely low platelet count on the blood smear reviewed by the laboratory. This can happen because of occasional clumping of the platelets together when the blood is drawn. Therefore, small number of individual platelets may be seen under the microscope, and this can be confused with true thrombocytopenia. A repeat blood draw, preferably in a tube which prevents clumping, typically solves this issue.
Dilutional thrombocytopenia is another condition that may be seen when several units of red blood cells have been transfused in a short period time. As the volume of blood expands, platelets may appear more scarce as they are distributed in a larger volume.
Don’t Miss: What Happens When You Get Hepatitis C
Inf Based Antiviral Therapy
Although IFN based antiviral therapy is uncommonly used in developed countries nowadays, the prohibitive cost of DAA may require the use of INF based therapy along with the addition of thrombopoietin mimetics, if required, in economically disadvantaged areas. Additionally, in chronic hepatitis C cases treated with pegylated INF plus ribavirin, single nucleotide polymorphisms at or near the IL-28B gene have been shown to be a predictor of SVR., The American Gastroenterological Association recommends dose reduction of INF with a platelet count between 25,000â50,000 and withdrawal of INF-based treatment with a count below 25,000. This is important because the antiviral therapy itself may cause a further drop in platelet count. Studies have shown IFN-based therapy to cause severe thrombocytopenia in up to 13% of patients, with the incidence higher in patients with lower baseline platelet count., The modifications in IFN-based therapy have potential to lower the chances of attaining SVR. The increased risk of bleeding may also impede the initiation and maintenance of different invasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedures such as liver biopsy, variceal banding, paracentesis and thoracentesis, central line insertion, endoscopy and elective surgery.
Thrombocytopenia In The Hospitalized Patient
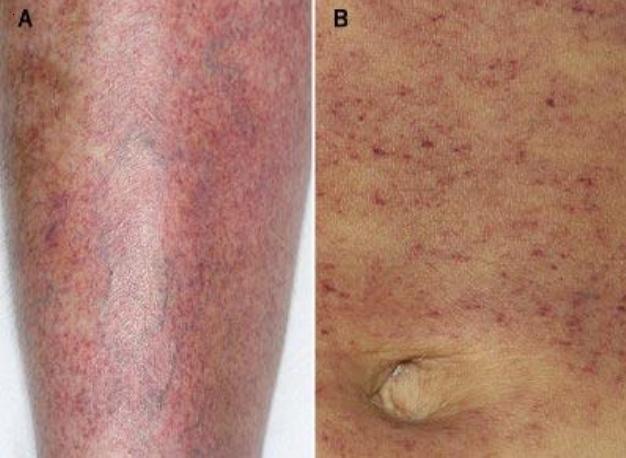
Thrombocytopenia may complicate the course of the hospital stay of patients with a variety of medical and surgical problems. In one study, thrombocytopenia was observed in approximately 1% of adult inpatients in an acute care hospital. However, less than 30% of these patients presented with bleeding manifestations. As expected, thrombocytopenia is much more common in ICUs, where it is found in in 8%-68% of patients on admission, and in 13%-44% of patients during the stay in the unit. Many potential etiologies are often concomitant in the acute care setting , and it is not always possible to elucidate the cause of the thrombocytopenia. However, because of its frequency, consideration should always be given to DITP. The frequency of DITP in critically ill patients is approximately 20%. Antibiotics in this setting are a frequent etiology., Tests for the detection of drug-dependent antiplatelet Abs are not widely available, are time-consuming, and are not sensitive enough to be incorporated in a diagnostic algorithm for the urgent management of patients with severe thrombocytopenia. The decision to discontinue a potential causative drug in such cases should rely solely on clinical criteria.
Read Also: How Often Does Hepatitis B Vaccine Need To Be Given
Diagnosis Of Chronic Hepatitis
-
Liver test results compatible with hepatitis
-
Viral serologic tests
-
Possibly autoantibodies, immunoglobulins, alpha-1 antitrypsin level, and other tests
-
Occasionally biopsy
-
Serum albumin, platelet count, and prothrombin time/international normalized ratio
recommendations for testing, managing, and treating hepatitis C virus infection and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Forces clinical guideline Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Adolescents and Adults: Screening.)
Chronic hepatitis is suspected in patients with any of the following:
-
Suggestive symptoms and signs
-
Incidentally noted elevations in aminotransferase levels
-
Previously diagnosed acute hepatitis
In addition, to identify asymptomatic patients, the CDC recommends testing of all adults 18 years at least once.