How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
If autoimmune hepatitis leads to cirrhosis, doctors can treat health problems and complications related to cirrhosis with medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If you have cirrhosis, you have a greater chance of developing liver cancer. Your doctor may order an ultrasound or other types of imaging tests to check for liver cancer.
If autoimmune hepatitis causes acute liver failure or cirrhosis with liver cancer or liver failure, you may need a liver transplant.
What Other Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
In rare cases, acute hepatitis B can cause liver failure.
Chronic hepatitis B can develop into a serious disease that causes long-term health problems such as cirrhosis , liver cancer, and liver failure.
If you have ever had hepatitis B, the virus may become active again, or reactivated, later in life. This could start to damage the liver and cause symptoms.
Immunise Test And Treat
Before chronic hepatitis B can be cured, we need to know who is infected and their stage of disease. Only 10% of the estimated number of individuals living with HBV infection in 2016 knew of their status, and of those diagnosed, only 5% of those who were eligible for treatment actually received treatment. WHO aims to eliminate viral hepatitis as a major public health threat by 2030, and while increasing preventive vaccine coverage is the main cornerstone of this global effort to achieve elimination, WHO also proposes an increase of the proportion of eligible individuals treated for chronic hepatitis B to 80%. This will require a concomitant increase in global HBV testing worldwide. Priority should be given to development of rapid point-of-care tests for use in countries of low and middle income, where HBV is highly endemic. Since there are already effective treatments that have a marked effect on HBV replication and liver disease, increased efforts must be made to improve access globally. Large-scale accessible diagnosis and treatment facilities in countries of low and middle income should be established to reduce mortality and ensure HBV cure preparedness, while also investing in HBV cure strategies, which could allow important cost-savings for health systems in the long run.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Symptoms In Females
Current Immunotherapies For Chronic Hbv Infection
Key points of immune regulation that can be targeted for therapy have been identified in studies done in animal models and HBV-infected patients. Injection of ligands targeting Toll-like receptors or RIG-I leads to suppression of viral replication in HBV mouse models., This observation has led to the development of drugs targeting TLR-7, TLR-8, and RIG-I for use in chronically HBV-infected patients. Numerous experiments have revealed that blocking inhibitory receptors can enhance expansion and function of HBV-specific T cells, both in vitro and in vivo., This has motivated the use of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in phase 1 studies in chronically HBV-infected patients. Furthermore, interleukin-12 appears critical to restoring T-cell expansion and function in chronic infection. This has led to interleukin-12, or adjuvants inducing it, being incorporated into the new generation of therapeutic vaccines for chronic HBV.
Prognosis Improvement After Hbsag Clearance

These related studies provide clear recommendations that patients who achieve HBsAg clearance have favourable clinical outcomes compared to patients who achieve only HBV DNA suppression and HBeAg seroconversion. HBsAg clearance leads to biochemical, virological and liver histological improvements, and it significantly reduces the risk of HCC. However, HCC may occur after HBsAg seroclearance despite it being the ultimate treatment endpoint recommended by current guidelines. The risk factors associated with HCC include the presence of cirrhosis, male sex, and age50 years at the time of HBsAg clearance . Closer attention should be given to patients with one or more of these risk factors.
These high-risk patients should be re-examined in a timely manner even if HBsAg clearance is obtained. These results also suggest that achieving a functional cure early in the absence of cirrhosis results in a better prognosis .
Don’t Miss: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis C Untreated
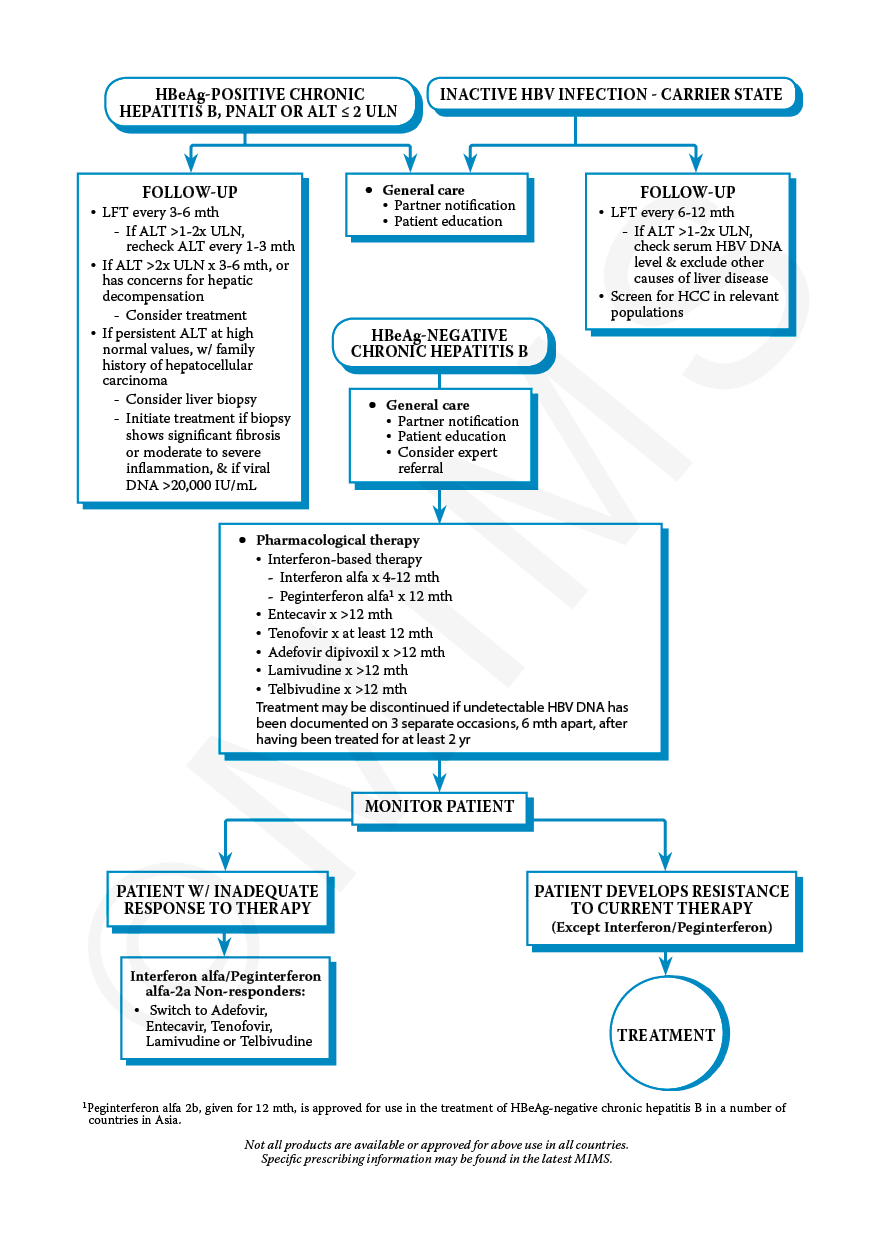
Treatment For Chronic Hepatitis B
If blood tests show that you still have hepatitis B after 6 months, your doctor may recommend medication to reduce the risk of complications of hepatitis B and regular tests to assess the health of your liver.
Treatment is usually offered if:
- your immune system is unable to control the hepatitis B by itself
- there’s evidence of ongoing liver damage
Hepatitis B medications can help keep the virus under control and stop it damaging your liver, although they will not necessarily cure the infection and some people need lifelong treatment.
The main medicines for chronic hepatitis B include peginterferon alfa 2-a and antiviral medicines.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Many people with hepatitis B will not experience any symptoms and may fight off the virus without realising they had it.
If symptoms do develop, they tend to happen 2 or 3 months after exposure to the hepatitis B virus.
Symptoms of hepatitis B include:
- flu-like symptoms, including tiredness, a fever, and general aches and pains
- loss of appetite
- tummy pain
- yellowing of the skin and eyes
These symptoms will usually pass within 1 to 3 months , although occasionally the infection can last for 6 months or more .
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Liver Cancer Symptoms
Medical Treatment For Hepatitis A B & C
Treatment for hepatitis A, B, or C is based on which type of hepatitis is present in the bloodstream and the severity of the resulting liver damage. Depending on the results of diagnostic tests, our specialists at NYU Langone may recommend antiviral medication to stop the virus from replicating and protect your liver from further damage.
How Is Acute Hepatitis B Treated
Acute hepatitis B doesnt always require treatment. In most cases, a doctor will recommend monitoring your symptoms and getting regular blood tests to determine whether the virus is still in your body.
While you recover, allow your body to rest and drink plenty of fluids to help your body fight off the infection. You can also take an over-the-counter pain reliever, such as ibuprofen , to help with any abdominal pain you have.
See a doctor if your symptoms are severe or seem to be getting worse. You may need to take a prescription antiviral medication to avoid potential liver damage.
Like acute hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis B may not require medical treatment to avoid permanent liver damage. In some patients, monitoring symptoms and getting regular liver tests is appropriate.
Treatment generally involves antiviral medications, such as:
- peginterferon alfa-2a injections
- antiviral tablets, such as tenofovir or entecavir
Antiviral medications can help to reduce symptoms and prevent liver damage. But they rarely completely get rid of the hepatitis B virus. Instead, the goal of treatment is to have the lowest viral load possible. Viral load refers to the amount of a virus in a blood sample.
Theres no cure for hepatitis B, but the condition is easily preventable by taking a few precautions. Hepatitis B is often spread through sexual contact, shared needles, and accidental needle sticks.
You can reduce your risk of developing hepatitis B or spreading the virus to others by:
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis B Contracted
How Do Doctors Treat Autoimmune Hepatitis
Doctors treat autoimmune hepatitis with medicines that suppress, or decrease the activity of, your immune system, reducing your immune systems attack on your liver. The medicines doctors most often prescribe are corticosteroidsprednisone or prednisolonewith or without another medicine called azathioprine.
Doctors typically start with a relatively high dose of corticosteroids and then gradually lower the dose. Your doctor will try to find the lowest dose that works for you. Your doctor will use blood tests to find out how you are responding to the treatment. A decrease in levels of the liver enzymes alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase shows a response to treatment. ALT and AST falling to normal levels shows a full response. In some cases, a doctor may repeat a liver biopsy to confirm the response to treatment and find out whether the damage has resolved.
Treatment can relieve symptoms and prevent or reverse liver damage in many people with autoimmune hepatitis. Early treatment of autoimmune hepatitis can lower the chances of developing cirrhosis and other complications. A minority of people who have no symptoms or only a mild form of the disease may or may not need medicines.
How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
Signs and symptoms can vary, in particular by the age of the individual. Many individuals may not show symptoms . When symptoms develop, they include fever, joint pain, abdominal pain, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, clay-coloured bowel movements, or jaundice.
Most infections are asymptomatic or mild. Occasionally, people with serious cases of hepatitis B require hospitalization. A very small proportion of these patients develop a critical form of the disease called fulminant hepatitis B. This condition results from a sudden breakdown of liver function.
Also Check: How Does Hepatitis C Affect The Liver
Also Check: Help With Hepatitis C Treatment
How Do People Get The Hbv Virus
Hepatitis B virus is found in the blood of people with HBV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Reliable blood tests for HBV were developed many years ago. Since blood donors and blood products are tested for HBV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
In many parts of the world, hepatitis B virus infects more than 8% of the population. HBV-infected women pass the infection to their babies during the birth process. People can also get hepatitis B by sharing needles for injection drug use, through sexual contact with an infected person, by an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or from improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
Finding A Cure For Hepatitis B: Are We Close
Causing more than 887 000 deaths each year, HBV is a major threat to global public health. Some 257 million people worldwide are chronically infected with HBV, and the disease causes around 40% of all primary liver cancers the second most deadly cancer.
In 2016, global partners joined forces to create the International Coalition to Eliminate Hepatitis B , with the aim of fast-tracking the discovery of a cure for HBV. The ICE-HBV formed international working groups comprising more than 50 global scientific leaders in HBV virology, immunology, technology and clinical research. The fruits of this partnership are now starting to show.
At the International Liver Congress in Paris in April 2018, ICE-HBV members reported on encouraging developments towards an HBV cure. There are now almost 50 new anti-HBV and hepatitis D virus treatments being openly investigated, and 17 of these are already undergoing phase II clinical trials.
While a vaccine to prevent HBV exists, lifelong treatment is needed for those already chronically infected. Treatment helps keep HBV under control, but it is not a cure because it cannot completely clear HBV from infected cells. In addition, even with ongoing treatment, people are still at a higher risk of developing liver cancer, particularly those with underlying cirrhosis due to chronic HBV.
However, none of the approaches have so far had an effect on reaching the viral reservoir in the liver this remains a major objective for future strategies.
Read Also: Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Who Is At Risk
All people who are sexually active may be at risk for hepatitis B. Specific populations in Canada that are disproportionately affected with hepatitis B include Aboriginal peoples, people who inject drugs, men who have sex with men , people who are street involved or homeless, those who have been incarcerated or institutionalized, and those with close household or sexual contact with any of the people listed above.
Certain factors may put individuals at an increased risk of hepatitis B infection. Sexual factors , a family history of hepatitis B, or being the recipient of a blood transfusion or medical procedure before 1970 are also related to an increased risk of hepatitis B infection.
Regional factors may also be related to an increased risk of hepatitis B infection. For example, birth in a region with a high prevalence rate of hepatitis B , household exposure for more than seven years to family members from a high prevalence region, travel to or residing in a high prevalence region, exposure to blood or blood products in a high prevalence region.4,5
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis C Mean
Panel : Reagent And Specimen Repositories Required To Advance Hbv Cure Research
-
Viral DNA, RNA, and protein standards
-
Monoclonal antibodies against HBV proteins
-
Replication competent HBV clones of various genotypes and subgenotypes
-
Stably transfected cell lines of various genotypes and subgenotypes
-
Cell lines susceptible to HBV replication and cell to cell spread
-
Mouse and primate models susceptible to HBV infection
-
Chemical libraries for studies in experimental models
-
Collection of serum and liver biopsy samples from cohort study for research purposes
-
Peptide libraries for clinical immunology studies
You May Like: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B Virus
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the best ways to control the disease. It is safe, effective and widely available. More than one billion doses of the vaccine have been administered globally since 1982. The World Health Organization says the vaccine is 98-100% effective in guarding against the virus. Newborns should be vaccinated.
The disease has also been more widely prevented thanks to:
- Widespread global adoption of safe blood-handling practices. WHO says 97% of the blood donated around the world is now screened for HBV and other diseases.
- Safer blood injection practices, using clean needles.
- Safe-sex practices.
You can help prevent hepatitis B infections by:
- Practicing safe sex .
- Never sharing personal care items like toothbrushes or razors.
- Getting tattoos or piercings only at shops that employ safe hygiene practices.
- Not sharing needles to use drugs.
- Asking your healthcare provider for blood tests to determine if you have HBV or if you are immune.
Treatment For Suspected Exposure
Anyone who has had potential exposure to HBV can undergo a postexposure prophylaxis protocol.
This consists of HBV vaccination and hepatitis B immunoglobin . Healthcare workers give the prophylaxis after the exposure and before an acute infection develops.
This protocol will not cure an infection that has already developed. However, it decreases the rate of acute infection.
Read Also: Is There A Pill That Cures Hepatitis C
A Global Scientific Strategy To Cure Hepatitis B
What Happens After A Hepatitis B Infection
Some people carry the virus in their bodies and are contagious for the rest of their lives. They should not drink alcohol, and should check with their doctor before taking any medicines to make sure these won’t cause more liver damage.
Anyone who has ever tested positive for hepatitis B cannot be a blood donor.
Also Check: How Does Hepatitis Affect The Body
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication for people with chronic hepatitis B, which occurs when the virus stays in your body for more than six months.
Antiviral medication prevents the virus from replicating, or creating copies of itself, and may prevent progressive liver damage. Currently available medications can treat hepatitis B with a low risk of serious side effects.
NYU Langone hepatologists and infectious disease specialists prescribe medication when they have determined that without treatment, the hepatitis B virus is very likely to damage the liver over time. People with chronic hepatitis B may need to take antiviral medication for the rest of their lives to prevent liver damage.
There are many different types of antiviral medications available, and your doctor recommends the right type for you based on your symptoms, your overall health, and the results of diagnostic tests. A doctor may take a wait-and-see approach with a person who has a healthy liver and whose blood tests indicate a low viral load, the number of copies of the hepatitis B virus in your bloodstream.
Someone with HIV infection or AIDS may have a weakened immune system and is therefore more likely to develop liver damage. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommends that people with HIV infection who are diagnosed with hepatitis B immediately begin treatment with antiviral medication.
If I Have Hepatitis B And Feel Healthy Do I Need To Keep Going To My Doctor
Chronic hepatitis B is a silent disease because often no symptoms appear until your liver is severely damaged. Although many people with chronic hepatitis B have an inactive disease and will remain healthy, about one in four will have an active disease that may lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer.
Because hepatitis B has no symptoms until your liver is badly damaged, a blood test is the only way for your doctor to find out if your hepatitis B is active or inactive, and to offer treatment, if needed. To help your doctor monitor how your disease behaves over time, you will need lifelong repeat blood tests every six to 12 months. Some tests, such as HBV DNA may need to be done more frequently . No treatment is required while the virus is inactive, but you should continue to get regular blood tests from your doctor to monitor your liver disease.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Symptoms In Women
How Hcv Is Spread
The hepatitis C virus is transmitted primarily through blood to blood contact, meaning that a person can become infected with the virus should the blood of a person who carries the virus be introduced into another persons bloodstream.
Therefore, as with hepatitis B, blood transfusions , tattooing and body piercing, occupational exposure, medical procedures, and intravenous drug use can all lead to possible exposure to the virus. Unlike hepatitis B, however, sexual contact and childbirth have both been shown to be an inefficient route of exposure to HCV.
The hepatitis G virus is thought to be transmitted in a similar way to HCV.