How Is A Person Tested For Hepatitis C
A viral-load test is used to check for hepatitis C in the bloodstream. Usually, hepatitis C virus can be found in a persons bloodstream two weeks after he or she becomes infected.
*Except in case of recent risk or in people with a weakened immune system**During the first six months after HCV infection, a person may spontaneously clear the virus if there was a recent risk, repeat viral-load testing to confirm chronic hepatitis C infection
What To Do If The Hcv Antibody Test Is Reactive
If the antibody test is reactive or positive, you need an additional test to see if you currently have hepatitis C. This test is called a nucleic acid test for HCV RNA. Another name used for this test is a PCR test.
If the NAT for HCV RNA is:
- Negative you were infected with hepatitis C virus, but the virus is no longer in your body because you were cured or cleared the virus naturally.
- Positive you now have the virus in your blood.
If you have a reactive antibody test and a positive NAT for HCV RNA, you will need to talk to a doctor about treatment. Treatments are available that can cure most people with hepatitis C in 8 to 12 weeks.
Test Frequency And Turnaround Time
Hepatitis C Serology testing is performed daily Monday to Friday.
Turnaround time is up to 3 days from receipt by PHO laboratory for Non-reactive antibody results. Reactive and Indeterminate HCV antibody results are available and reported within 6 days.
Repeat testing may be indicated in those with ongoing risk factors for the acquisition of HCV.
Once a patient tests positive for HCV antibodies, other than in cases of maternal antibody transfer, there is no value in repeating the test as they will remain antibody positive for life regardless of whether they have cleared the virus or are chronic carriers.
Don’t Miss: Screening For Hepatitis C Icd 10
What Do The Results Mean
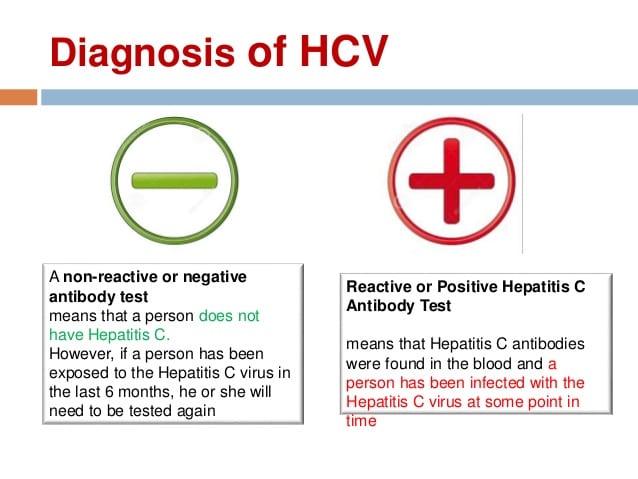
There are two results from a hepatitis C antibody test.
- A non-reactive or negative test result means that the person does not have the virus. The exception is if someone has come into contact with the virus recently, such as through contaminated blood. If this is the case, they will need to have another test.
- A reactive or positive test result means that the person has had the virus at some point but does not mean that they still have it. Further tests will be needed to check whether the virus is still active in the body and if treatment will be required.
Once diagnosed with hepatitis C, a person will need to undergo a series of different tests to see how the virus has affected their body.
These tests will check for any liver damage, identify how well the liver is working, and help a healthcare professional to decide on treatment.
Hepatitis C is treated with medication known as an antiviral. It gets this name because it aims to clear the virus out of the body.
Another aim of the medication is to slow down damage to the liver. It may also reduce the chance of a person getting liver cancer or developing serious liver scarring, known as cirrhosis.
A person with hepatitis C will require regular testing during treatment to see how well the medication is working. Keeping healthy, getting enough sleep, and avoiding drugs and alcohol can help treatment to work.
Hepatitis B Blood Tests

The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
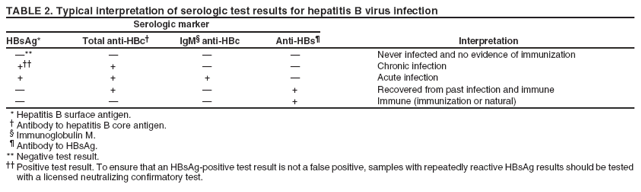
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Don’t Miss: How Would I Know If I Have Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a virus that causes inflammation of the liver. It is a member of the family of viruses that includes hepatitis A and hepatitis B. These viruses behave differently and have different modes of transmission. Hepatitis C can cause serious liver damage, liver failure, liver cancer, and even death.
Hepatitis A : Symptoms Causes Diagnosis And
Hepatitis A is a highly contagious liver infection caused by a virus. Learn more about the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and vaccine for hepatitis A.
Used Resourses:
About Author
Stuart Morrison
Hi everyone, my name is Stuart Morrison and I am the editor-in-chief and author of the Answeregy website. I am 35 years old and live in Miami, Florida. From an early age I loved to learn new things, constantly reading various encyclopedias and magazines. In 1998 I created my first Web site, where I posted interesting facts which you could rarely learn elsewhere. Then, it led me to work as a content manager for a large online publication. I always wanted to help people while doing something I really enjoyed. That’s how I ended up on the Answeregy.com team, where I… Read more
Read Also: Can You Cure Hepatitis C
Taking A Hepatitis C Test
Hepatitis C testing is conducted on a sample of blood. Blood samples can be collected by a doctor, nurse, technician, or other health care provider from an adult patients vein using a small needle or a skin prick on a childs heel.
For an at-home hepatitis C test, patients collect a blood sample according to the manufacturers directions. Instructions provided in the test kit detail the steps to obtain a small sample of blood and mail it for testing.
False Positive Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Due To Recent
Hepatitis B is the most common viral hepatitis, potentially life threatening, with long term complications. Currently, vaccine is the most effective tool against hepatitis B infection. It is worthwhile mentioning that due to rampant use of hepatitis B vaccine , there have been concerns about hepatitis B surface antigen reactivity.
Also Check: Oral Medication For Hepatitis C
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than 7 days post collection will not be tested.
How Does Hepatitis C Progress
When someone is first infected with hepatitis C, most likely they have no symptoms and are unaware. Occasionally people experience fatigue, loss of appetite, weakness or sometimes having a yellow color in their skin or eyes. Although having any symptoms at all is rare, if they do occur, they usually go away within a few weeks.
Around 15-25% of people who are infected will spontaneously fight off the virus on their own and they will not have a chronic hepatitis C infection and no long term damage occurs.
But around 75-85% of people will develop chronic infection. Most of the time, people with chronic hepatitis C have no symptoms at the time of infection and no symptoms for years or even decades of chronic infection. The virus will be with them until they are successfully treated with hepatitis C medications.
Around 10-20% of people with chronic infection will slowly have gradual damage in the liver over years and will eventually develop cirrhosis . This can take 20 years or more from the time of the initial infection.
Cirrhosis is the replacement of liver cells with permanent scar tissue. Cirrhosis can lead to problems such as bleeding from veins in the esophagus, fluid buildup in the belly, and damaged brain function.Approximately 15% of people with cirrhosis will develop liver cancer during their lifetime. Drinking excessively can double the chance of liver cancer in people infected with HCV.
Also Check: How Long Hepatitis C Virus Survive Outside Body
Recommended Reading: The Effects Of Hepatitis C
What Does A Reactive Result To A Hepatitis B Test Mean
In the hepatitis B surface antigen test, a reactive or positive result means that a person is currently infected with the hepatitis B virus, explains the Hepatitis B Foundation. Reactive results from the hepatitis B surface antibody test means that people are now immune to the virus because they have been infected in the past and their immune systems produced
Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
You May Like: Where Can I Get My Hepatitis B Vaccine
Results Of The Hbcab Test
There are two variations of antibodies. The IgM antibody is the largest antibody and the first produced in an infection. It shows that you may have a current, active infection. Sometimes it persists for years, but it usually drops to undetectable levels.
The HBcAb IgG variant is produced later in the course of the infection, and its likely that you will have a positive HBcAb IgG test the rest of your life.
The screening panel usually has a test that is for total HBcAb, which includes both IgM and IgG. The IgM test may be ordered to help determine if you have an acute infection.
A positive HBcAb test must be interpreted along with the results of the other tests. You may have an active or chronic infection, or you may be immune to hepatitis B due to past infection. Discuss the results with your healthcare provider. In any case, a positive HBcAb test means your blood or organs cannot be donated to a recipient.
The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.
You May Like: Royal Canin Hepatic Cat Food
Hepatitis B Virus Dna Testing And Interpretation
Hepatitis B Virus DNA Testing and Interpretation Update Page 2 of 3 LAB-SD-031-003 Content Results Interpretation Table 1: The following table is a guide for the interpretation of HBV DNA results: Hepatitis B DNA Viral Load Reported Result Interpretation Target Not Detected HBV DNA Not Detected < 1.00E+1 IU/mL
What The Qualitative Results Mean
The qualitative results indicate that HCV is present in your blood. The test result will be either detected or undetected.
Detected means that you do have the virus in your blood. Undetected means that you dont have the virus in your blood, or you have a tiny amount that cant be detected by this test.
The qualitative test results may still be positive even if your viral load has decreased drastically due to treatment.
Don’t Miss: How Is Hepatitis C Contracted
How Is Hepatitis Spread
The hepatitis C virus is usually spread when someone comes into contact with blood from an infected person. This can happen through:
Sharing drug-injection equipment Today, most people become infected with hepatitis C by sharing needles, syringes, or any equipment used to prepare and inject drugs.
Birth Approximately 6% of infants born to infected mothers will get hepatitis C.
Healthcare exposures Although uncommon, people can become infected when healthcare professionals do not follow the proper steps needed to prevent the spread of bloodborne infections.
Sex with an infected person While uncommon, hepatitis C can spread during sex, though it has been reported more often among men who have sex with men.
Unregulated tattoos or body piercings Hepatitis C can spread when getting tattoos or body piercings in unlicensed facilities, informal settings, or with non-sterile instruments.
Sharing personal items People can get infected from sharing glucose monitors, razors, nail clippers, toothbrushes, and other items that may have come into contact with infected blood, even in amounts too small to see.
Blood transfusions and organ transplants Before widespread screening of the blood supply in 1992, hepatitis C was also spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants.
All Adults Pregnant Women And People With Risk Factors Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Most people who get infected with hepatitis C virus develop a chronic, or lifelong, infection. Left untreated, chronic hepatitis C can cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even death. People can live without symptoms or feeling sick, so testing is the only way to know if you have hepatitis C. Getting tested is important to find out if you are infected so you can get lifesaving treatment that can cure hepatitis C.
Recommended Reading: Difference Between Hepatitis B And C
Question 5 How Do You Interpret Hcv Antibody Reactive And Hcv Rna Not
A reactive HCV antibody test result combined with a not-detected HCV RNA result indicates no laboratory evidence of a current active HCV infection no further action is required in most cases.
If distinction between a true positive and a biologic false-positive result for HCV antibody is desired, the CDC suggests that one can consider testing with another HCV antibody assay. If there is concern regarding the handling or storage of the test specimen, obtain a new sample for repeat testing.6
Hepatitis C Can Be Prevented
Although there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C, there are ways to reduce the risk of becoming infected.
- Avoid sharing or reusing needles, syringes, or any other equipment used to prepare and inject drugs, steroids, hormones, or other substances.
- Do not use personal items that may have come into contact with an infected persons blood, even in amounts too small to see, such as glucose monitors, razors, nail clippers, or toothbrushes.
- Do not get tattoos or body piercings from an unlicensed facility or in an informal setting.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Tell If You Have Hepatitis C
Discussing Screening Results With Clients
The medical personnel who ordered or arranged the screening test, not counselors, usually explain the results. Hepatitis screening should be part of the intake physical examination in an opioid treatment program, and medical personnel may report the results. However, the client may want to discuss the results with the counselor or ask the counselor questions.
Anxiety might interfere with some clients ability to comprehend or retain information, which might need to be repeated.
Suggestions for conversations with clients when the test results are negative include the following:
- Explain results clearly and simply: So the HCV screening result was negative? This means that, as of 6 months ago, you did not have .
- Emphasize that a negative result to an HCV test does not indicate to and that the client should take precautions to avoid . If a relapse to drug use occurs, advise clients to avoid sharing any drug paraphernalia or equipment. Specify that this includes cookers, cotton, water, needles, syringes, pipes, and straws.
- Emphasize the importance of getting HAV and HBV vaccinations. Provide information about the availability of low- or no-cost vaccinations.
Clients whose screening test results are positive for will need additional tests and examinationsusually with doctors who specialize in diseases of the liver to get accurate diagnoses and to determine their health status and the extent of liver damage. These tests are described in .
Hepatitis A Antibody Igm
Order Name:HEP A M AB Test Number: 3603500 Recent onset of hepatitis A infection. No evidence of recent hepatitis A infection. Indicates that test should be repeated in 1-2 weeks. Test Notes It should be noted that the assay performance characteristics of the IgM anti-HAV assay have not been established for immunocompromised or immunosuppressed patients or on cord blood, neonatal specimens, infants or children less than 12 years age.
Recommended Reading: How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted