What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a liver infection that can lead to serious liver damage. Itâs caused by the hepatitis C virus. About 2.4 million people in the U.S. have the disease. But it causes few symptoms, so most of them don’t know. The virus spreads through an infected personâs blood or body fluids.
There are many forms of the hepatitis C virus, or HCV. The most common in the U.S. is type 1. None is more serious than any other, but they respond differently to treatment.
Which Drugs Can Cure Hepatitis C Virus
Several agents are available by prescription in the U.S. that can lead to a sustained virologic response , considered a cure for HCV.
Drug combination antivirals for HCV treatment, often taken as one daily dose, are now approved to ease treatment regimens and tend to be more tolerable.
The newer direct-acting antiviral agents medications to treat HCV include:
Learn more: Oral Hepatitis C Treatments: The Evolving Landscape
Hepatitis C virus is transmitted through contact with infected blood. It can lead to chronic liver disease like cirrhosis, liver cancer, and death. Symptoms of chronic HCV may not appear for 20 to 30 years after infection.
It is important to seek medical testing and treatment for hepatitis C so you can help prevent its spread and have adequate medical care, if needed. Fifteen to twenty percent of people may eliminate the HCV virus completely from their body within 6 months, but most people remain infected and develop chronic hepatitis C.
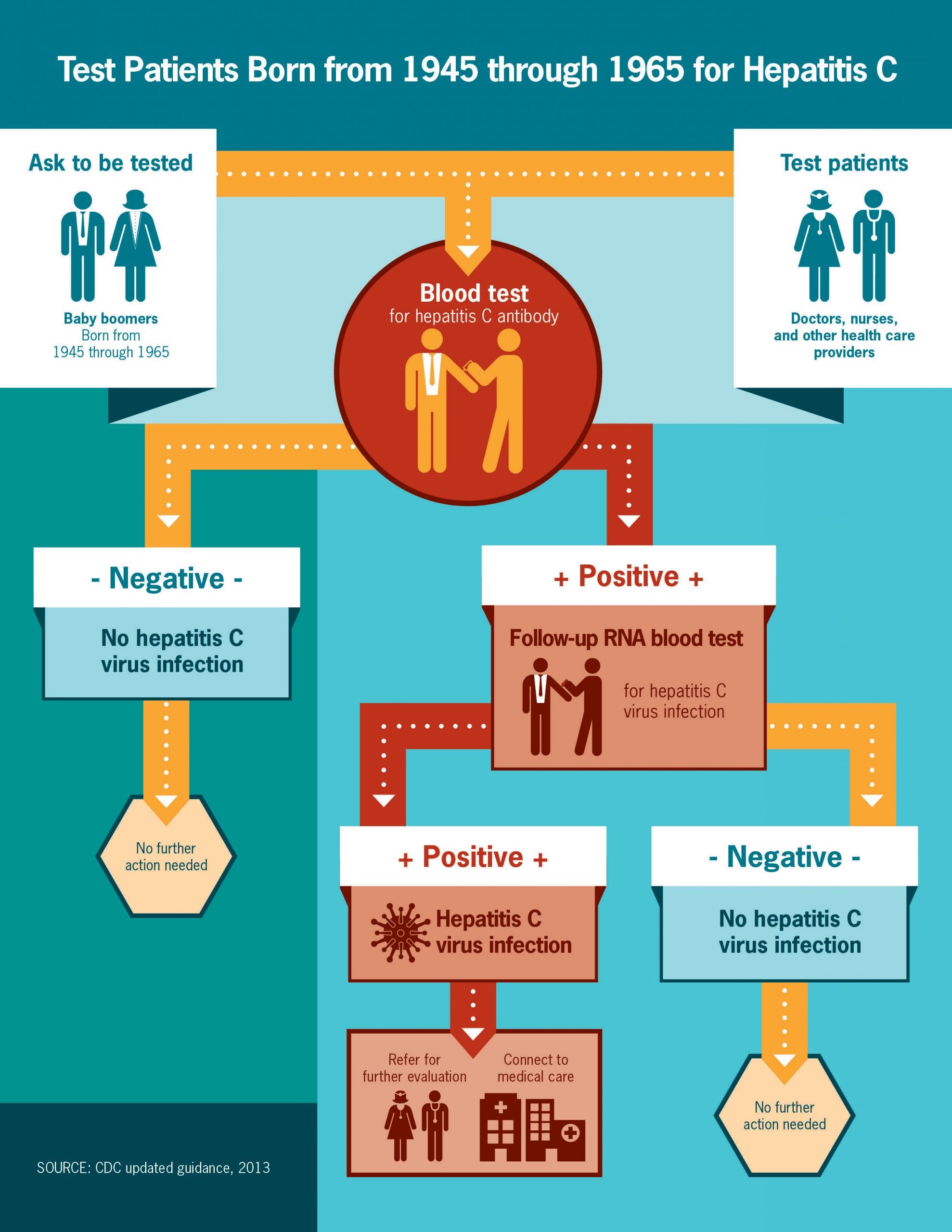
If you were born from 1945 through 1965, or are at increased risk for HCV infection for other reasons like sharing drug injection equipment, speak to your doctor about being tested for HCV.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention now recommends a one-time hepatitis C test for all adults 18 years of age and older and all pregnant women for each pregnancy. CDC continues to recommend people with risk factors, including people who inject drugs, be tested regularly.
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
You May Like: Cure For Hepatitis A And B
Analysis Of The Inflammatory Infiltrate
Immunolabeling of B lymphocytes , CTL , NK cells , Th lymphocytes , and Th1 , Treg and Th17 at PP areas was observed with scattered lymphocytes in the lobular region . Concerning PP cell frequency, Th lymphocytes were predominant followed by CTL, B lymphocytes, and NK cells. When analyzing Th subset frequency, Th17 showed the lowest counts . On the other hand, there was predominance of CTL and Th1 at the lobular area, together with absence of B lymphocytes and NK cells .
Table 2 Quantification of liver cell populations.
CTL and Th1 cells are well known components of the antiviral immune response. In this cohort despite their lobular predominance, they did not correlate with the number of infected hepatocytes, but they disclosed a negative correlation with viral load . Since viral load mirrored HCV liver replication, this could indirectly suggest CTL and Th1 immune control of the liver process.
Figure 2 Relationship between viral load and frequency of both lobular CTL and Th1. Correlation between viral load and the frequency of lobular CTL and Th1 . Relationship between Treg lymphocytes with both CTL and Th1. Correlation between the frequency of Treg with CTL and Th1 at portal-periportal area. Correlation between the frequency of Treg with CTL and Th1 at lobular area. Spearmans nonparametric correlation was used to compare these data sets.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Don’t Miss: How Common Is Hepatitis C
Treatment Objectives And Outcomes
The goal of therapy is to prevent complications and death from HCV infection. Because of the slow evolution of chronic HCV infection over several decades, it has been difficult to demonstrate that therapy prevents complications of liver disease. Accordingly, treatment responses are defined by a surrogate virological parameter rather than a clinical endpoint. Short-term outcomes can be measured biochemically , virologically , and histologically ., Several types of virological responses may occur, labeled according to their timing relative to treatment. The most important is the sustained virological response , defined as the absence of HCV RNA from serum by a sensitive PCR assay 24 weeks following discontinuation of therapy . This is generally regarded as a âvirological cure,â although liver cancer has been identified years later, especially if cirrhosis existed at the time of achieving an SVR.
| Virological Response |
|---|
Graphic display of virological responses. RVR, rapid virological response EVR, early virological response SVR, sustained virological response relapse, reappearance of HCV RNA in serum after therapy is discontinued nonresponder, failure to clear HCV RNA from serum after 24 weeks of therapy partial nonresponder, 2 log decrease in HCV RNA but still HCV RNA positive at week 24 null nonresponder, failure to decrease HCV RNA by < 2 logs after 24 week of therapy.
Prevalence And Transmission Of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Hepatitis C virus is transmitted by parenteral or permuscosal exposure to infected blood or body fluids. Many patients will give a history of injecting drug use or transfusion of blood products before the implementation of antihepatitis C virus screening of blood donors in 1992. Seroprevalence among injecting drug users is more than 80%, and this remains a major risk factor for newly acquired hepatitis C virus infection in the developed world. Community based strategies for prevention of infection in these high risk groups are needed urgently but depend on resources . Screening of volunteer blood donations in developed nations has significantly reduced transfusion related hepatitis. Most countries in the developing world do not, however, have adequate screening procedures, and only about 40% of donated blood is tested for the virus. Occupational, vertical, and sexual transmission account for only a minority of new cases of hepatitis C virus infection. Sexual transmission of hepatitis C virus among monogamous partners is rare, but testing is often carried out for reassurance . See bmj.com for contact details for information on screening recommendations.
Box 1 Prevention strategies to reduce transmission of hepatitis C virus through injecting drug use
Summary points
Complications of liver disease related to hepatitis C virus infection are expected to increase over the next 10 to 20 years
You May Like: Signs Of Hepatitis C In Adults
Assessment Prior To Treatment And Monitoring During And After Therapy
It is advisable to assess the risk of underlying coronary heart disease, to control preexisting medical problems, such as uncontrolled diabetes and hypertension, and to pre-screen all candidates for symptoms of depression prior to iniating therapy. A number of validated self-rated or clinician-rated scales to assess depression are available.-
Patients should be monitored during therapy to assess the response to treatment and for the occurrence of side effects. A reasonable schedule would be monthly visits during the first 12 weeks of treatment followed by visits at 8 to 12 week intervals thereafter until the end of therapy. At each visit the patient should be questioned regarding the presence of side effects and depression. They should also be queried about adherence to treatment. Laboratory monitoring should include measurement of the complete blood count, serum creatinine and ALT levels, and HCV RNA by a sensitive assay at weeks 4, 12, 24, 4 to 12 week intervals thereafter, the end of treatment, and 24 weeks after stopping treatment. Thyroid function should be monitored every 12 weeks while on treatment.
Recommendations
9. Treatment decisions should be individualized based on the severity of liver disease, the potential for serious side effects, the likelihood of treatment response, the presence of comorbid conditions, and the patient’s readiness for treatment .
11. The optimal therapy for chronic HCV infection is the combination of peginterferon alfa and ribavirin .
This Is Your Liver On Hep C
by Health Writer
The liver, by all accounts, is one of the most important organs in the human body. It literally cleans the blood by keeping the good things in and getting rid of toxins and helps your body maintain healthy glucose levels. So when the liver is damaged due to hepatitis C , its many functions are thrown out of whack. Often described as acute or chronic, hepatitis C can range from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, long-term condition. What makes hepatitis C challenging is that there is no vaccine for it, says Ava Williams, M.D. a primary care doctor at Doctor Spring, an online physician consultation platform, with expertise in chronic care.
Recommended Reading: How Does A Person Catch Hepatitis C
Evaluation Of The Peripheral Immune Response
Quantification of Peripheral Lymphocytes Frequency
The comparative analysis of T and B lymphocyte populations did not reveal significant differences between donors and patients and depicted the same frequency proportion as described for portal hepatic infiltrate . In contrast, NK cells showed a significant decrease in absolute values in patients accompanied by a decreased in NK dim along with an increase in NK bright .
Table 3 Quantification of peripheral cell populations.
As to liver damage, none of the peripheral lymphocyte population percentages disclosed differences with respect to hepatitis or fibrosis severity . The same was observed in the analysis of absolute and nMFI values.
Peripheral T Lymphocyte Differentiation and Functional Characterization of NK Cells and CTLs
The distribution of naïve, central memory, effector memory, effectors and activated CTL and Th lymphocytes was determined. As shown in Figure 5A, a decrease in the frequency of both naïve Th and CTL and an increase of activated lymphocytes were observed in CHC patients. In turn, a trend to higher frequency of effector memory CTL and Th was demonstrated .
Appropriate Uses Of The Hcv Rna Test
There are 4 major reasons that HCV RNA tests are used:
More rarely, HCV RNA is used when either very acute HCV infection is suspected or a false HCV Ab is suspected.
It would not be appropriate to repeatedly order HCV RNA viral load screening for a patient who is not on or was recently on HCV treatment, or to use the HCV viral load to determine the severity of the patient’s infection or the patient’s risk of developing significant liver disease.
Read Also: Different Types Of Hepatitis C
Chronic Hepatitis C Pathogenesis: Immune Response In The Liver Microenvironment And Peripheral Compartment
- 1Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Multidisciplinary Institute for Investigation in Pediatric Pathologies , CONICET-GCBA, Pathology Division, Ricardo Gutiérrez Childrens Hospital, Buenos Aires, Argentina
- 2Liver Unit, Italians Hospital of Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina
- 3Immunology Unit, Multidisciplinary Institute for Investigation in Pediatric Pathologies , CONICET-GCBA, Ricardo Gutiérrez Childrens Hospital, Buenos Aires, Argentina
- 4Liver Unit, Ramos Mejía Hospital, Buenos Aires, Argentina
Diagnosis Natural History And Treatment Of Persons With Hiv Coinfection
Approximately 25% of HIV-infected persons in the Western world have chronic HCV infection. In the United States, up to 8% of those with chronic HCV infection may be HIV coinfected., , Since the advent of highly active antiretroviral therapy in 1996, HCV-related liver disease has become an increasingly important cause of morbidity and mortality in HIV-infected persons.-
Because of the high prevalence of HIV/HCV coinfection, and because the management of each infection can differ in dually-infected persons, all HIV-infected persons should be tested for HCV and all HCV-infected persons with HIV risk factors should be tested for HIV. As in HIV-uninfected persons, the usual approach is to first test for anti-HCV and to confirm the positive results with a highly sensitive assay. However, approximately 6% of HIV-positive persons fail to develop HCV antibodies therefore, HCV RNA should be assessed in HIV-positive persons with unexplained liver disease who are anti-HCV negative.,
The urgency for treatment of persons who are co-infected is greater than it is in those with HCV infection alone. Progression of liver disease is more rapid in HIV/ HCV-co-infected persons, in whom there is an approximately twofold increased risk of cirrhosis., Successful treatment of HCV also might improve the tolerability of HAART by reducing the risk of hepatotoxicity.,
| Characteristic |
|---|
| 11 |
- * Total for both groups
Recommendations
You May Like: First Signs Of Hepatitis C
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C spreads when blood or body fluids contaminated with the hepatitis C virus get into your bloodstream through contact with an infected person.
You can be exposed to the virus from:
- Sharing injection drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV, another STD, several partners, or have rough sex
- Being stuck by infected needles
- Birth — a mother can pass it to a child
- Sharing personal care items like toothbrushes, razor blades, and nail clippers
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unclean equipment
You canât catch hepatitis C through:
- Breastfeeding
- Casual contact
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Have HIV
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Since July 1992, all blood and organ donations in the U.S. are tested for the hepatitis C virus. The CDC says it is now rare that someone getting blood products or an organ would get hepatitis C. That said, The CDC recommends that anyone over the age of 18 get tested for Hepatitis C. If you haven’t been screened, you should consider having it done.
Learn more about the risk factors for hepatitis C.
How Many People Have Hep C
According to the CDC, an estimated 2.4 million people are living with hep C in the United States. However, the number may be higher since many people do not have symptoms, and therefore dont seek care from a health provider. Often called the silent infection, people with hep C can go symptom-less for years until the virus damages the liver enough to cause fatigue, nausea, weight loss, and pain in the abdomen. For this reason, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all adults ages 18 to 79 years be screened for hepatitis C at least once in their lifetime, even those without symptoms or known liver disease.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis C Considered A Liver Disease
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
How Does Hep C Progress
Once its confirmed that a person has hep c, the next step is determining the extent of damage. Tests such as a CT scan, MRI or ultrasound can provide detailed images of the liver and a liver biopsy may be necessary to determine the degree of damage inside. The presence of hepatitis C is known to increase the development of liver cancer, especially when hepatitis C causes more scar formation, such as cirrhosis, says Hwan Y. Yoo, M.D. from the Institute for Digestive Health and Liver Diseases at Mercy Medical Center in Baltimore, MD. Heres what happens when your liver is infected with hep C .
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis B Mean
How Effective Is Treatment
Direct-acting antivirals cure 9 out of 10 patients with hepatitis C.
Successful treatment does not give you any protection against another hepatitis C infection. You can still catch it again.
There’s no vaccine for hepatitis C.
If treatment does not work, it may be repeated, extended, or a different combination of medicines may be tried.
Your doctor or nurse will be able to advise you.
Side Effects Of Treatment
Treatments with direct-acting antivirals have very few side effects. Most people find DAA tablets very easy to take.
You may feel a little sick and have trouble sleeping to begin with, but this should soon settle down.
Your nurse or doctor should be able to suggest things to help ease any discomfort.
You need to complete the full course of treatment to ensure you clear the hepatitis C virus from your body.
If you have any problems with your medicines, speak to your doctor or nurse straight away.
Side effects for each type of treatment can vary from person to person.
For a very small number of people, more severe side effects from hepatitis C treatments may include:
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis Be Transmitted Sexually
How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis C To Others
If you have hepatitis C, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Tell your sex partner you have hepatitis C, and talk with your doctor about safe sex practices. In addition, you can protect others from infection by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care providers that you have hepatitis C. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.