Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Can Hepatitis C Infection Be Spread By Sexual Contact
Yes, but the risk of getting HCV from sexual contact is believed to be low. The risk increases for those who have multiple sex partners, have a sexually transmitted infection, engage in “rough sex” or other activities that might cause bleeding, or are infected with HIV. More research is needed to understand how and when HCV can be spread by sexual contact.
Treatment And Medication For Hepatitis C
If you have acute hepatitis C, there is no recommended treatment. If your hepatitis C turns into a chronic hepatitis C infection, there are several medications available.
Interferon, peginterferon, and ribavirin used to be the main treatments for hepatitis C. They can have side effects like fatigue, flu-like symptoms, anemia, skin rash, mild anxiety, depression, nausea, and diarrhea.
Now youâre more likely to get one of these medications:
Find out more on treatment options for hepatitis C.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Hepatitis C Sexually
Alcohol And Other Toxins
Excessive alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and inflammation. This is sometimes referred to as alcoholic hepatitis. The alcohol directly injures the cells of your liver. Over time, it can cause permanent damage and lead to liver failure and cirrhosis, a thickening and scarring of the liver.
Other toxic causes of hepatitis include overuse or overdose of medications and exposure to poisons.
How Are Hepatitis B And C Diagnosed
Hepatitis B is diagnosed by a series of blood tests. The test may show an ongoing infection or antibodies that indicate that the patient is protected against hepatitis B. In patients who have a positive screening test that suggests the possibility of ongoing infection, further testing is done to determine the levels of the virus in the bloodstream.
Hepatitis C is diagnosed via a blood test called a Hepatitis C Antibody Test. A positive result means that hepatitis C antibodies are present in the blood. But a positive antibody test doesnt necessarily mean a person has hepatitis C. A further blood test is needed to confirm the diagnosis. This second blood test quantifies the amount of the virus or the viral load in the liver and the bloodstream.
Recommended Reading: What Do You Get Hepatitis C From
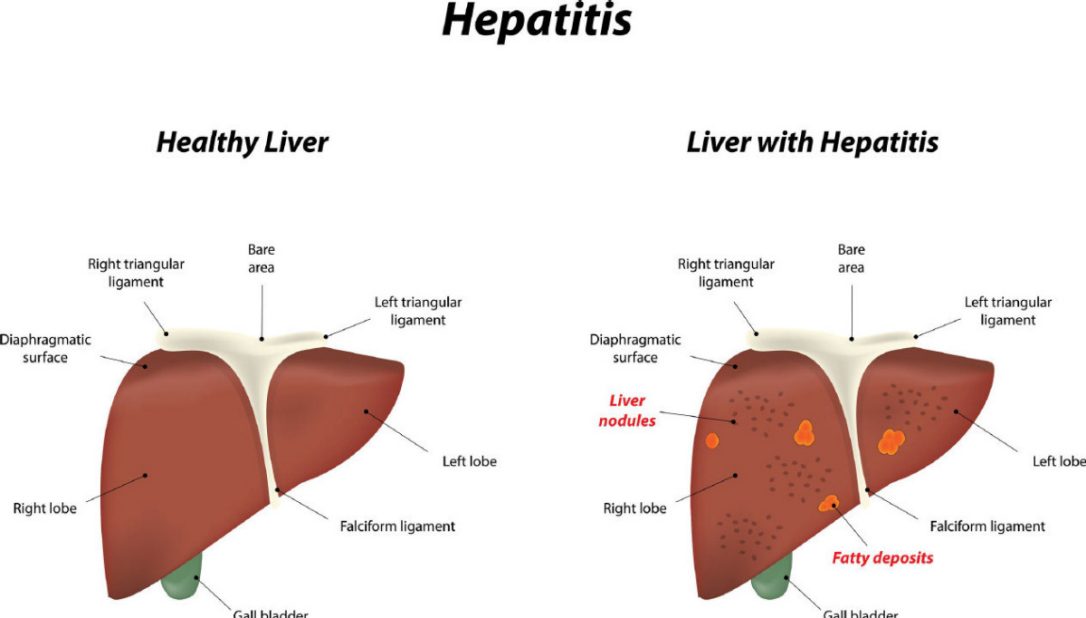
How Hepatitis C Damages The Liver
Hepatitis C causes damage to the liver mainly in the form of inflammation, which then leads to scarring or fibrosis.
Hepatitis C results in the death of liver cells. It is uncertain whether the virus kills the cells or if it is the immune systems response to invasion by the virus. At present it is thought that it is probably a combination of the two, but that the immune systems response is what causes the most damage. The death of liver cells triggers the dispatching of inflammatory cells to the affected area. Inflammation leads to the enlargement of the liver in over 60% of people infected with hepatitis C and can cause the fibroelastic sheath surrounding the liver to stretch, which may be the cause of pain in the liver area.
Inflammation begins the processes that lead to fibrosis. Fibrosis is not a disease but is a condition caused by the bodys response to liver damage. Inflammation triggers a reaction by a group of cells in the liver called stellate or fat cells. When the liver is functioning normally stellate cells store fat and vitamin A in the liver. They also help regulate the flow of blood through the liver. But when the liver is inflamed by the presence of hepatitis C, a reaction occurs amongst different liver cells. This leads stellate cells to dispense with vitamin A, altering their function.
Free Radicals and Fibrosis
Free radicals are of concern for people with hepatitis C for a number of reasons:
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
You May Like: Daa Drugs For Hepatitis C
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Hcv Infection
Most people with HCV have no symptoms. But even without symptoms, they can develop health problems decades later and can still pass the disease to others.
If symptoms do happen, it’s usually when the disease is very advanced. Symptoms can be similar to those of hepatitis A and hepatitis B and include:
- jaundice
- fever
- darker than usual urine or gray-colored stools
What Makes Yale Medicine’s Approach To Treating Hepatitis B And C Unique
The Viral Hepatitis Program at Yale Medicine represents one of the leading viral hepatitis treatment programs in the country and is engaged in innovative research focused on advancing the care of patients with chronic hepatitis B, C and D infections.
A multidisciplinary team of faculty physicians and mid-level providers offer a coordinated approach to preparing patients for success with antiviral therapy, including comprehensive laboratory testing services to characterize your infection, non-invasive liver fibrosis testing with techniques such as FibroScan liver elastography, structured hepatitis patient education classes, mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques , a formal physician-guided weight-loss program and access to clinical trials evaluating current and new therapies that are not available in routine clinical practice. Our program is a core member of several national and international observational cohort studies which contributes to the advancement of science of hepatitis treatment around the world.
Also Check: Difference Between Hepatitis B And C
How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis C To Others
If you have hepatitis C, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Tell your sex partner you have hepatitis C, and talk with your doctor about safe sex practices. In addition, you can protect others from infection by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care providers that you have hepatitis C. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.
Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Cirrhosis is the scarring of the liver. The liver is fairly unique in its ability to regenerate after injury, yet with repeated injury or chronic infections, such as chronic hepatitis, this process is interrupted. Eventually, the liver becomes incapable of working effectively, and scarring begins to develop.
The causes of cirrhosis are essentially the same as those that cause hepatitis, but that overcome the ability of the liver to heal itself, such as when the insult to the liver is repeated or as with chronic infections. The most common causes of cirrhosis in the United States include alcoholic liver disease and hepatitis C.
Cirrhosis may also be caused by conditions other than hepatitis, including hemochromatosis alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, a hereditary absence of an enzyme and bile duct conditions, such as congenital biliary atresia .
As cirrhosis worsens, the function of the liver is lost and, simultaneously, the organ becomes smaller and solidifies. If you have an unhealthy liver, fluid accumulates in the legs and abdomen. Bile salts can easily build up in the skin, which can lead to jaundice and itching. Bleeding from the large veins in your GI tract and esophagus may occur. Toxins can also accumulate in the blood, which can result in confusion and mental slowing. For those individuals with advanced cirrhosis, the only true treatment for this disease is a liver transplant.
Read Also: How Can You Transmit Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
The doctor will take the patients medical history and perform a physical examination. As part of the physical exam, the doctor will look for signs of liver damage, including tenderness in the abdomen, swelling in the legs, feet or ankles, or signs of jaundice, such as yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
Several blood tests may be used to test for hepatitis C. The first blood test is antibody testing for hepatitis C.
If antibodies are found, that means that the person was exposed to hepatitis C at some point. A blood test called a PCR RNA can determine if the blood is still infected with the active virus. If the result is positive, it means that the person is currently infected with hepatitis C. If the PCR RNA is negative but the antibody testing was positive, this means that the patient has been exposed to the virus in the past but currently does not have an active infection.
A person who has hepatitis C may have to have a liver biopsy or a liver fibrosis scan to tell if the liver is damaged, and how much damage has occurred.
You should be referred to a specialist who has experience in treating hepatitis C as soon as you are diagnosed with active hepatitis C infection.
What Happens To Your Health When You Arent Treated For Hepatitis C
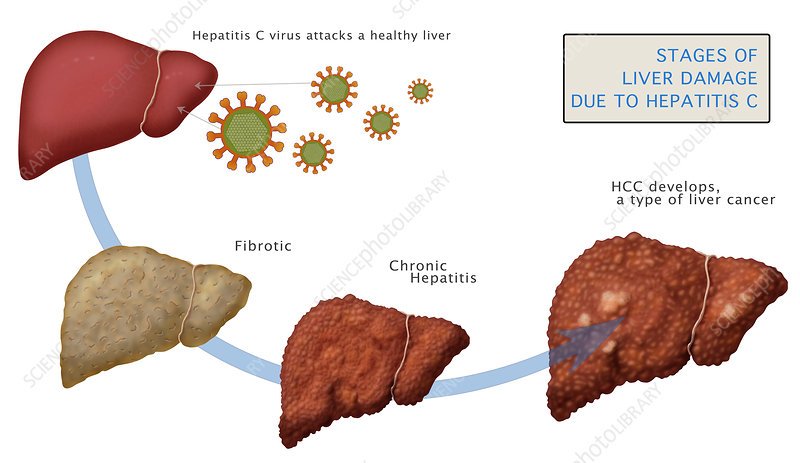
Although medication can cure hepatitis C, millions of people arent taking it. The problem: Left untreated, the virus can lead to serious health complications.
Theres a reason the hepatitis C virus is called the silent killer. All too often, people dont realize theyve been infected. Out of the estimated 2.4 million people in the United States who have hepatitis C, more than half dont know they have it, according to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Usually when someone gets infected with hepatitis C, they initially until the disease gets fairly advanced, says Hardeep Singh, MD, a gastroenterologist and hepatologist at St. Joseph Hospital in Orange, California. The median time it takes for symptoms…to develop is 30 years.”
While some people are able to clear the virus on their own, most arent, and more than 50 percent go on to develop long-term, or chronic, hepatitis C, says the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Over time, untreated hepatitis C can cause hardening and scarring of the liver, which can cause complications that eventually lead to liver failure.
Liver cirrhosis and liver failure usually cannot be reversed sometimes a liver transplant is the only treatment option once advanced liver damage occurs. With hepatitis C, your risk of liver cancer also rises.
Here are a few other conditions that can be caused by untreated hepatitis C.
Read Also: What Is A Hepatitis Panel
Alcohol Hcv And Liver Damage
HCC pathogenesis by ethanol seems to require several factors including the presence of cirrhosis, oxidative stress, altered methyl transfer resulting in DNA hypomethylation, and a decrease in retinoic acid. In addition, co-morbidities such as viral hepatitis, diabetes mellitus and obesity are known to accelerate HCC development in patients with ALD. ROS play an important role in hepatocarcinogenesis. Chronic ethanol consumption results in the generation of ROS via multiple pathways leading to lipid peroxidation and LPO-byproducts such as 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal and malondialdehyde . These DNA-reactive aldehydes in turn form mutagenic exocyclic DNA adducts including 1, N6-ethenodeoxyadenosine and 3, N4-ethenodeoxycytidine.
What Are Liver Enzymes
Enzymes are types of proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the body. Liver enzymes can inform if there is a problem with the liver, but they dont always tell the whole story. A person with chronic active hepatitis C can have liver enzymes that go up and down and even return into normal or near-normal limits, but without treatment, liver damage can still be occurring.1-5
Don’t Miss: Treatment For Liver Cirrhosis Hepatitis B
What Causes Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18
Alcohol Consumption Hcv Replication And Response To Hcv Therapy
A great number of studies emphasize the fact that alcoholics respond poorly to interferon therapy. More than ten years ago, Mochida et al showed that almost 30% of non-alcoholics responded biochemically and virologically to interferon therapy compared to less than 10% of alcoholics. The question remained open whether this is due to a direct inhibitory effect of alcohol on interferon response or due to poor compliance of these patients. Pessione et al studied serum HCV RNA in HCV patients with increasing alcohol intake . In this study a significant dose-dependent increase in serum HCV RNA was noted starting from 70 g alcohol per week. In line with this observation, a decrease of alcohol consumption prior treatment of hepatitis C significantly reduced viral load. In addition, Cromie et al showed that viral load decreased highly significantly within 4 mo when patients cut down on alcohol consumption from 39-100 g/d to 0-50 g/d. More recent data, however, clearly suggest that the poor response of alcoholics towards interferon therapy is more likely due to reduced compliance. In this study, the recorded alcohol consumption during the months before HCV treatment was associated with an increased rate of therapy drop out while the response rate was comparable after correction for this confounding factor. In conclusion, poor compliance of alcoholics is probably the major cause for poor antiviral response to HCV therapy.
Also Check: Ways To Contract Hepatitis C
What To Know About Liver Disease And Covid
Coronavirus disease 2019 is the illness caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Older adults and people of any age who have serious underlying medical conditions, including people with liver disease, might be at higher risk for severe illness from COVID-19. People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C, may have concerns and questions related to their risk.
Some patients hospitalized for COVID-19 have had increased levels of liver enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase . Increased levels of liver enzymes can mean that a persons liver is at least temporarily damaged. People with cirrhosis may be at increased risk of COVID-19. Some studies have shown that people with pre-existing liver disease who were diagnosed with COVID-19 are at higher risk of death than people without pre-existing liver disease.
Adults of any age with certain underlying medical conditions, including people with liver disease , might be at increased risk for severe illness from the virus that causes COVID-19. People might be more likely to have severe disease if their medical conditions are not well controlled. People who are on treatment for hepatitis B or C should continue their treatment unless otherwise directed by their healthcare provider.
If you are a member of any of these groups, contact your healthcare provider to request the hepatitis A vaccine:
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Recommended Reading: Hepatic Steatosis Treatment Step By Step
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Yes, since 2010 enormous progress has been made in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are pills that act on the virus itself to eradicate it from the body, unlike older medicines like interferon injections which work by stimulating an immune response. These new treatments are very effective and can achieve cure rates of over 90%. In most situations now, there is no need for interferon, which was responsible for many of the side effects previously associated with HCV treatment. The new treatment combinations require shorter treatment durations , have reduced side effects and appear to be effective at all stages of the disease.
Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Your primary care physician may refer you to a specialist to determine whether you are eligible for treatment. A specialist will help you decide which drug therapy is best for you based on the severity of your liver disease, your virus genotype and whether or not you have been treated in the past.