Hepatitis C Virus Infection In Adolescents And Adults: Screening
Recommendations made by the USPSTF are independent of the U.S. government. They should not be construed as an official position of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality or the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
| Adults aged 18 to 79 years | The USPSTF recommends screening for hepatitis C virus infection in adults aged 18 to 79 years. | B |
- View the Clinician Summary in PDF
Limitations Of Screening For Hepatitis C
Barriers to screening for hepatitis C include limited access to healthcare, inadequate health insurance coverage, individuals’ decreasing recall of past risky behaviors, lack of knowledge of hepatitis C prevalence, natural history, and available tests and treatments for hepatitis C at the provider level.- Moreover, nearly 42% of primary care physicians reported being unfamiliar with the CDC guidelines in a survey of community-based physicians.
Cdc Recommendations For Hcv Screening
On April 10, 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued new recommendations for hepatitis C screening among adults in the United States . This new guidance augments prior CDC guidance on HCV screening with two new major recommendations: all adults aged 18 years and older should have HCV screening at least once in their lifetime, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%, and HCV screening should be performed for all pregnant persons during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%. The CDC continues to recommend screening persons for HCV regardless of age if risk factors for acquiring HCV are present, with repeat periodic screening in persons who have ongoing risk for acquiring HCV. These new CDC HCV screening recommendations expand prior guidance that recommended routine HCV screening for all persons born between 1945-1965.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis C And What Are The Symptoms
Other Risks Can Include:
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another persons blood, such as razors, toothbrushes or nail clippers
- Inoculation practices involving multiple use needles or immunization air guns
- Exposure of broken skin to HCV infected blood
- HIV infected persons
People with current or past risk behaviors should consider HCV testing and consult with a physician. HCV testing is currently not available at most public health clinics in Missouri. For information about HCV testing that is available, call the HCV Program Coordinator at 573-751-6439.
Potential Sites For Screening For Hepatitis C
Screening for hepatitis C can be offered in several venues the most likely are primary care offices, emergency rooms, urgent care clinics, and public health fairs.
Following the CDC recommendation, 3 studies were presented at the 2013 meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases in Washington, DC. One study was conducted in an emergency department, the second in the outpatient clinics of the US Department of Veterans Affairs, and the third involved individuals undergoing screening colonoscopies for colorectal cancer at a community hospital.- All 3 studies confirmed the higher prevalence of positive serum anti-HCV in individuals born in the years 1945-1965.
Don’t Miss: What Happens When You Get Hepatitis C
Cdc Updates Hepatitis C Screening Recommendations
Editors note: The following article was submitted by Patricia A. Tichnell, a registered nurse and manager of the Telemedicine/County Program, Division of Infectious Diseases, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
The month of May is designated as Hepatitis Awareness Month in the United States, and May 19 is Hepatitis Testing Day. These observances are an opportunity for us to raise awareness of hepatitis C and encourages people to be tested.
Unfortunately, due to COVID-19, we were unable to have a testing event this year.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates 2.7 million people in the United States have chronic hepatitis C and almost half are unaware they have it. People can live with chronic hepatitis C for years or even decades without symptoms, while the virus slowly damages their liver. By the time symptoms do appear, liver damage is often advanced.
Left untreated, chronic hepatitis C can cause liver damage, cirrhosis and even liver cancer. Its one of the leading causes for liver transplants today.
Injection drug use or intranasal illicit drug use, current or ever.
Tattoos or body piercings in an unclean environment using unsterile equipment.
Worked in a place where you came in contact with infected blood or needles, for example, health care workers.
Received clotting factor concentrates produced before 1987 or a blood transfusion before 1992.
Hemodialysis.
Summary Of The Literature
For the all-adult review, the initial literature search yielded 4,867 studies. Twenty-nine duplicates were identified. Of 4,838 unique studies, 4,170 were deemed irrelevant by title/abstract screening, resulting in 668 full texts for review. Among these, 368 studies had data available to extract.
For the pregnancy review, the initial literature search yielded 1,500 studies. Two duplicates were identified. Of 1,498 unique studies, 1,412 were deemed irrelevant by title/abstract screening, resulting in 86 full texts for review.
The supplementary review yielded an additional 1,038 and 195 studies among all adults and pregnant women, respectively. Of these, 912 and 168 , respectively, were deemed irrelevant by title/abstract screening, resulting in 126 and 27 , respectively, full texts for review. One study was added to the pregnant women review outside of the formal literature search .
Considering all 104 applicable studies, the median anti-HCV positivity prevalence among all adults was 6.6% . Median anti-HCV positivity prevalence was 1.7% for the general population , 7.5% for ED patients , 3.3% for birth cohort members , 9.3% for others/multiple risk factors , 54.2% for persons who use drugs , 5.2% for persons with HIV or sexual risk , and 4.7% for immigrants . Considering 26 applicable studies among pregnant women, median anti-HCV positivity prevalence was 1.2% .
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis A
Feasibility Acceptability Cost And Equity
The majority of individuals identified by screening are anticipated to be asymptomatic and in early stages of HCV . At the time of writing this guideline, certain provinces had negotiated a price reduction with pharmaceutical companies that produce DAA-based treatment regimens. However, more advanced fibrosis and presentation with comorbidities is still needed to qualify for treatment in Canada., As a result, it is likely that most individuals who would be identified by screening would not qualify for drug coverage under their provincial plan. Given the high listed cost of DAA-based regimens , few people with HCV are likely to have the funds to pay out of pocket for a course of treatment. Therefore, a recommendation in favour of screening would increase the number of people with known HCV who could not access treatment, thus deriving no clear benefit despite the potential for harm from a diagnosis combined with treatment ineligibility. To the extent that wealthier individuals with screen-detected HCV could access treatment, a recommendation for screening has potential to increase health inequity.
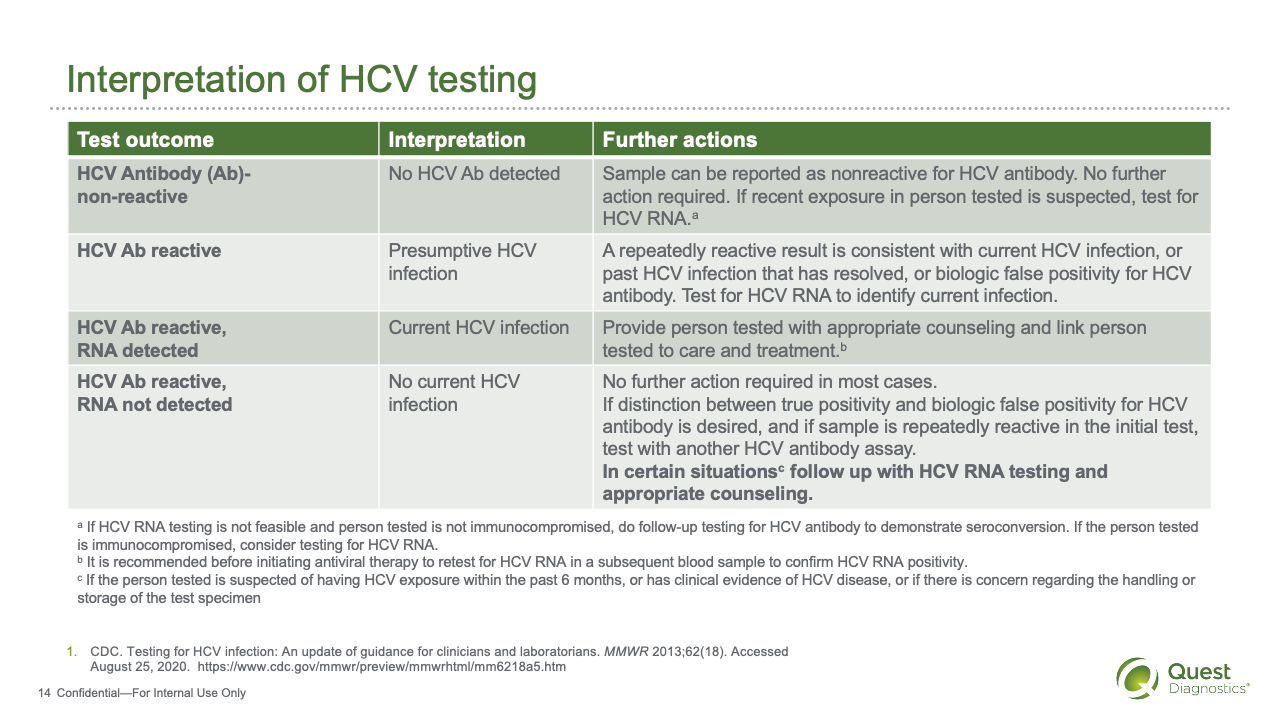
Evaluation Of Individuals With Positive Screening Test
Patients with a positive screening test for anti-HCV antibody should be tested for serum HCV RNA. Serum HCV RNA quantifies the amount of viral RNA in serum and indicates ongoing infection. If HCV RNA is detectable, tests should be performed to determine the extent of hepatic fibrosis. These tests typically include liver biopsy or noninvasive measures, such as biochemical markers of fibrosis or transient elastography., An ultrasound of the abdomen should also be performed to identify the possible presence of cirrhosis and focal lesions in the liver suspicious for hepatic malignancy.
Patients who have a positive anti-HCV on a screening test but have no detectable HCV RNA should have a confirmatory HCV RNA test a few months later. If HCV RNA remains undetectable, these individuals should be reassured that they do not have hepatitis C infection and that the anti-HCV may remain persistently positive. Such individuals have either cleared the virus or the true specificity of the test is lower than the reported 100%, and the test result was a false positive.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surf Ab Quant 3.1 Low
With Spike In Hepatitis C Virus Infections Cdc Recommends Screening For All Adults
This page was fact checked by our expert Medical Review Board for accuracy and objectivity. Read more about our editorial policy and review process.
All adults age 18 and older should be screened for hepatitis C virus infection at least once in their lifetime, while women should be screened during every pregnancy, say new U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendations.
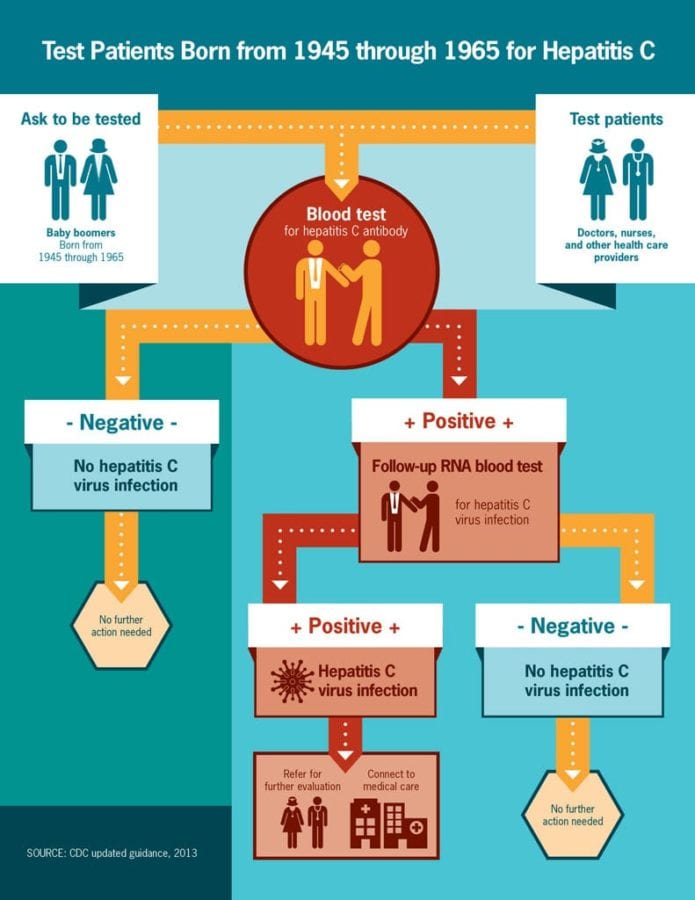
These latest recommendations, published on April 10, 2020, expand CDCs 2012 call for one-time HCV screening of all baby boomers, adults born from 1945 through 1965, along with people of any age with certain risk factors. This group includes injection drug users, dialysis patients, people with HIV, children born to mothers with HCV, and incarcerated people, among others. Individuals with any ongoing risk should be screened for HCV periodically, according to the CDC.
The new recommendations do not apply in areas of the U.S. where less than 0.1% of adults have HCV infections, says the CDC. However, no U.S. state currently meets this criterion.
HCV and screeningMost often transmitted by intravenous drug users sharing needles, HCV causes the liver infection hepatitis C. Less commonly, the virus is spread via sexual contact, unregulated tattooing, needlestick injuries in healthcare workers, and from mothers to babies during pregnancy or childbirth.
Staying Healthy With Hepatitis
Not everyone needs treatment right away, but its important to be monitored regularly by an experienced doctor and discuss treatment options of the best way to keep you healthy.
- Get vaccinated against Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B
- Avoid alcohol and drugs
- Eat a healthy & balanced diet. Include a lot of vegetables and fruits try to stay away from too much salt, sugar and fat.
- Exercise regularly. Walking is one of the best exercises, and it helps to make you feel less tired.
- Check with a health professional before taking any prescription pills, supplements, or over-the-counter medications.
- Do not share razors, nail clippers, needles or other items that come in contact with blood with other people.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Hepatitis A
Determining The Prevalence Threshold For The Recommendations
Although the intent of public health screening is usually to identify undiagnosed disease, many persons previously diagnosed with hepatitis C are not appropriately linked to care and are not cured of their HCV infection, thereby representing an ongoing source of transmission. Therefore, the prevalence threshold of 0.1% should be determined on the basis of estimates of chronic hepatitis C prevalence, regardless of whether hepatitis C has been diagnosed previously.
Benefits Of Early Detection Or Treatment
The USPSTF found no direct evidence on the benefits of HCV screening vs no screening on health outcomes or the effects of prenatal HCV screening on the risk of vertical transmission.1 Treatment studies focused on populations without cirrhosis who are more likely to be asymptomatic and identified by screening. Of the trials of DAA regimens , 14 were multinational 11 were conducted in the US or Canada and the remainder were conducted in New Zealand, Egypt, France, or Asia. In 29 trials, 60% to 100% of patients were white.1 The trials evaluated a variety of DAA regimens recommended in current guidelines. Treatment duration was 12 weeks in all but 2 trials, which allocated patients to either 8 or 12 weeks of treatment. Eleven trials were of good quality and 22 were of fair quality. Forty-nine trials found DAA regimens to be associated with pooled SVR rates ranging from 95.5% to 98.9% across genotypes. Evidence was greatest for genotype 1 infection , the most frequent genotype in the US.1 Sustained virologic response rates were similar in trials that stratified patients according to age, sex, race/ethnicity, or treatment experience with non-DAA regimens.1
Recommended Reading: Natural Treatment For Hepatitis C
Why Cdc Wants More People Screened For Hepatitis C
In addition to those at high risk for the virus, new screening guidelines call for all adults, 18 and older, to have the blood test at least once in their lifetime. Also, pregnant women during each pregnancy.
Hepatitis C is a virus that infects the body and causes liver damage. If left untreated, it can eventually lead to liver failure, liver cancer and death.
Hepatitis C has been the most common liver disease that we have historically seen in our clinic, said Dr. James Trotter, medical director of Transplant Hepatology at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas. It has been until recently the most common cause for liver transplant, meaning that it was the most lethal disorder that we have historically had in our clinic.
Today, hepatitis can be cured. Thats one major reason the CDC wants to expand screening for the virus.
Trotter talked about this with KERAs Sam Baker.
INTERVIEW HIGHLIGHTS:
About Hepatitis C
It’s a blood-borne pathogen. The ways to acquire it historically have been through blood transfusions, IV drug use or similar exposures through transplant, dialysis and through contaminated sources that could infect the blood. With testing that was developed in the late 80s and early 90s, the blood supply has been largely freed from hepatitis C.
It’s Silent
Can Hepatitis C Transmit Between Mother And Unborn Child?
Why The Call Now For Greater Screening?
I think there are several issues in play:
Theres Also A Higher Infection Rate Among Young Adults
RESOURCES:
The Daily Journal Of The United States Government
Legal Status
This site displays a prototype of a Web 2.0 version of the daily Federal Register. It is not an official legal edition of the Federal Register, and does not replace the official print version or the official electronic version on GPOs govinfo.gov.
The documents posted on this site are XML renditions of published Federal Register documents. Each document posted on the site includes a link to the corresponding official PDF file on govinfo.gov. This prototype edition of the daily Federal Register on FederalRegister.gov will remain an unofficial informational resource until the Administrative Committee of the Federal Register issues a regulation granting it official legal status. For complete information about, and access to, our official publications and services, go to About the Federal Register on NARA’s archives.gov.
Legal Status
You May Like: Can Hepatitis B Cause Meningitis
Table 2 Indications For Hav Hbv And Hcv Testing19
Suspect acute hepatitis
- Most chronic viral hepatitis infections are asymptomatic.
- ALT may or may not be elevated. No need to routinely test for AST.
- If HBsAg is positive for > 6 months, this confirms chronic HBV infection.
- The presence of anti-HCV can indicate current or past HCV infection. An HCV RNA is needed to confirm active HCV infection. Around 75% of initial HCV infections progress to chronic infection, usually within 6 months.
- If already diagnosed with viral hepatitis, see Appendix 7 Recommended Test for Individuals Already Diagnosed with Viral Hepatitis. Consult with a specialist as needed for HCV infection. Consultation with, or referral to a specialist is strongly recommended for chronic HBV infection.
Illicit drug use current or ever
Persons who are, or were incarcerated
Gay, bisexual and men who have sex with men
* See Appendix 2 for further information on Hepatitis Laboratory Tests and Appendix 3 for Hepatitis B Serology Results and Interpretation.
Controversies In Care: Birth Cohort Hepatitis C Testing
Based on an increased hepatitis C prevalence in certain birth cohorts, a one-time offer of HCV testing has been recommended for those born between 1945-1965. However, there is a lack of agreement with respect to the age-range cut-offs and value of onetime age cohort testing:
- In 2020, the US Preventive Services Task Force recommended HCV screening for all individuals 18 to 79 years of age, based upon SVR rates of greater than 95% with new all-oral DAA treatments and associated improved clinical outcomes.20
- In 2020, the CDC recommended HCV screening for all adults 18 years of age, except where HCV prevalence < 0.1%. It was expected that there would be very few settings where HCV prevalence would drop this low in the US.
- In 2017, the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care recommended against birth cohort testing.30 However this recommendation was made prior to the wide availability of effective HCV treatments when hepatitis C was not considered routinely curable for everyone, so identification of cases was of limited value. With the dramatic improvements in curability and availability of treatment coverage regardless of fibrosis staging, birth cohort testing is now recommended.
- In 2018, the Canadian Association for the Study of the Liver recommended birth cohort testing for those born between 1945-1975 based on the estimated prevalence of hepatitis C in Canada.2
Don’t Miss: Is Milk Thistle Good For Hepatitis C
Other Indications For Measuring Anti
In addition to screening, measuring anti-HCV can be useful in patients with symptoms of chronic liver disease patients who have other viral infections, including chronic fatigue, hepatitis B, HIV, intermittently abnormal ALT, or cirrhosis found on imaging tests or patients undergoing evaluation for organ transplantation.
Hepatitis C In Canada And The Importance Of Risk
Ha S1*, Totten S1, Pogany L1, Wu J1, Gale-Rowe M1
1 Centre for Communicable Diseases and Infection Control, Public Health Agency of Canada, Ottawa, ON
Ha S, Totten S, Pogany L, Wu J, Gale-Rowe M. Hepatitis C in Canada and the importance of risk-based screening. Can Comm Dis Rep 2016 42:57-62. https://doi.org/10.14745/ccdr.v42i03a02
Read Also: How Many Hepatitis Are There
Benefits Of Screening For Hepatitis C
If individuals with chronic hepatitis C are identified before they develop advanced fibrosis, cirrhosis, or hepatocellular carcinoma, 90%-100% can now be expected to respond to treatment, whereas previously only 66%-75% of individuals responded to treatment.-,- Thus, detecting individuals with hepatitis C before they develop signs or symptoms of the disease can have an important impact on their subsequent clinical course. Sustained virologic clearance for more than 6 months after treatment of hepatitis C is also associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality.
Summary Of Recommendations For Clinicians And Policy

We recommend against screening for HCV in adults who are not at elevated risk .
This recommendation applies only to adults who are not at elevated risk for HCV. It does not apply to pregnant women or adults who are at elevated risk for hepatitis C, such as:
-
Individuals with current or history of injection drug use
-
Individuals who have been incarcerated
-
Individuals who were born, travelled or resided in HCV-endemic countries
-
Individuals who have received health care where there is a lack of universal precautions
-
Recipients of blood transfusions, blood products or organ transplant before 1992 in Canada
-
Patients on hemodialysis
-
Individuals who have had needle-stick injuries
-
Individuals who have engaged in other risks sometimes associated with HCV exposure, such as high-risk sexual behaviours, homelessness, intranasal and inhalation drug use, tattooing, body piercing or sharing sharp instruments or personal hygiene materials with someone who is HCV positive
-
Anyone with clinical clues suspicious for HCV infection
Don’t Miss: Natural Cure For Hepatitis A