Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
What Is Hepatitis A
For kids, hep A is the most common type of hepatitis to get. The virus lives in poop from people who have the infection. That’s why it’s so important to wash your hands before eating and after going to the bathroom. If you don’t, and then go make yourself a sandwich, hep A virus might end up on your food, and then in you!
Vegetables, fruits, and shellfish also can carry hepatitis if they were harvested in contaminated water or in unsanitary conditions. Hepatitis A affects people for a short time, and when they recover, it does not come back.
Recommendations For Frequency Of Repeat Testing In An Asymptomatic Patient
The frequency of testing depends on the history of sexual exposure and number of sexual partners. However, in the case of hepatitis A and B, once the patient has completed a course of vaccination no further repeat testing is required.
For those at continuing risk and who have not received a course of vaccination, the following is recommended.
You May Like: Where To Get Hepatitis B Test
How Do You Get It
HAV can be present in the stool and blood of someone with the virus. Its mainly transmitted through the fecal-oral route, which involves ingesting virus thats present in the stool of someone with hepatitis A.
There are several ways you can get hepatitis A:
- having close person-to-person contact with someone who has hepatitis A, such as:
- taking care of someone whos currently sick
- having sex with someone who has the virus
What Happens With Hepatitis C
Is hepatitis C a virus? Yes. With acute hepatitis C, the virus is eliminated in 25% of people. The rest of the people become chronically infected and later may develop serious complications such as liver failure and liver cancer. There is treatment, however, for hepatitis C that usually can prevent the complications.
Don’t Miss: What Does Hepatitis B Come From
Hepatitis A: Who Is At Risk
A prime risk factor for hepatitis A is traveling to or living in a country with high infection rates. You can check the CDC’s travel advisories to learn about recent outbreaks. Eating raw foods or drinking tap water can raise your risk while traveling. Children who attend daycare centers also have a higher risk of getting hepatitis A.
Can Hepatitis Be Treated
There are no treatments to cure hepatitis A, aside from carefully monitoring liver function. If you know you have hepatitis A early enough, you might be able to stop the infection if you get a dose of the hepatitis A vaccine or something called hepatitis A immune globulin.
Hepatitis B, when chronic, can often be treated successfully. The most commonly used drugs to treat chronic hepatitis B are:
- Entecavir .
For hepatitis C, the following drugs are used:
- Simeprevir .
- Sofosbuvir sofusbuvir/velpatasvir sofusbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir ledipasvir/sofosbuvir .
- Ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir/dasabuvir .
- Elbasivir/grazoprevir .
- Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir .
These new drugs are sometimes given with older drugs like ribavirin and peginterferon alfa-2a and peginterferon-2b. You might have to take these medicines for some time, even as long as six months.
If you have chronic hepatitis D, your doctor may prescribe drugs with interferons and might also add medicines for hepatitis B. Hepatitis E treatments include peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin.
You May Like: Hepatitis C And Liver Disease
How Does Hepatitis B Spread
Persons infected with hepatitis B can pass the virus to others through blood or body fluids. In the U.S., the most common way of becoming infected is through unprotected sex, although sharing an infected person’s needles to inject illicit drugs also is quite common. Less common ways are by contaminated razors or toothbrushes. As previously mentioned, hepatitis B is passed from infected mother to infant in over 90% of cases.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis A And B
Not all infected adults will experience symptoms. That means you could contract hepatitis A or B, and spread the viruses to others, without realizing it.
Symptoms of hepatitis A may include*:
Fever
Jaundice
Loss of appetite
Dark urine
Fatigue
* TWINRIX is not indicated to treat the symptoms of, or reduce serious consequences associated with hepatitis A and B.
Possible consequences of hepatitis A.*Hepatitis A infection can have mild to severe consequences on infected individuals that can last from a few weeks to several months.
Chronic hepatitis and carrier states are not linked with hepatitis A infection.
However, relapsing hepatitis, a condition where a person gets worse again after a period of improvement, can last up to a year in 15% of cases.
While most infected people recover, the older you are, the more severe hepatitis A can be.
Approximately 25% of infected adults are hospitalized.
The overall case fatality rate, which is the proportion of deaths among the number of hepatitis A cases, is approximately 0.5%, but can reach 2.6% in adults over 60 years of age.
* TWINRIX is not indicated to treat the symptoms of, or reduce serious consequences associated with hepatitis A and B.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may include*:
Fatigue
Jaundice
Loss of appetite
Dark urine
Clay-coloured stool
* TWINRIX is not indicated to treat the symptoms of, or reduce serious consequences associated with hepatitis A and B.
Don’t Miss: How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, semen, or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
What If You Test Positive For Hepatitis
If testing discloses that you have viral hepatitis there are steps to prevent your passing the viruses to family and friends. Washing the hands helps prevent transmission of hepatitis A. Not sharing needles, razors, nail clippers, or toothbrushes also will reduce transmission of viral hepatitis. Everyone should be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Go Away On Its Own
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
How Do I Avoid Getting Sick
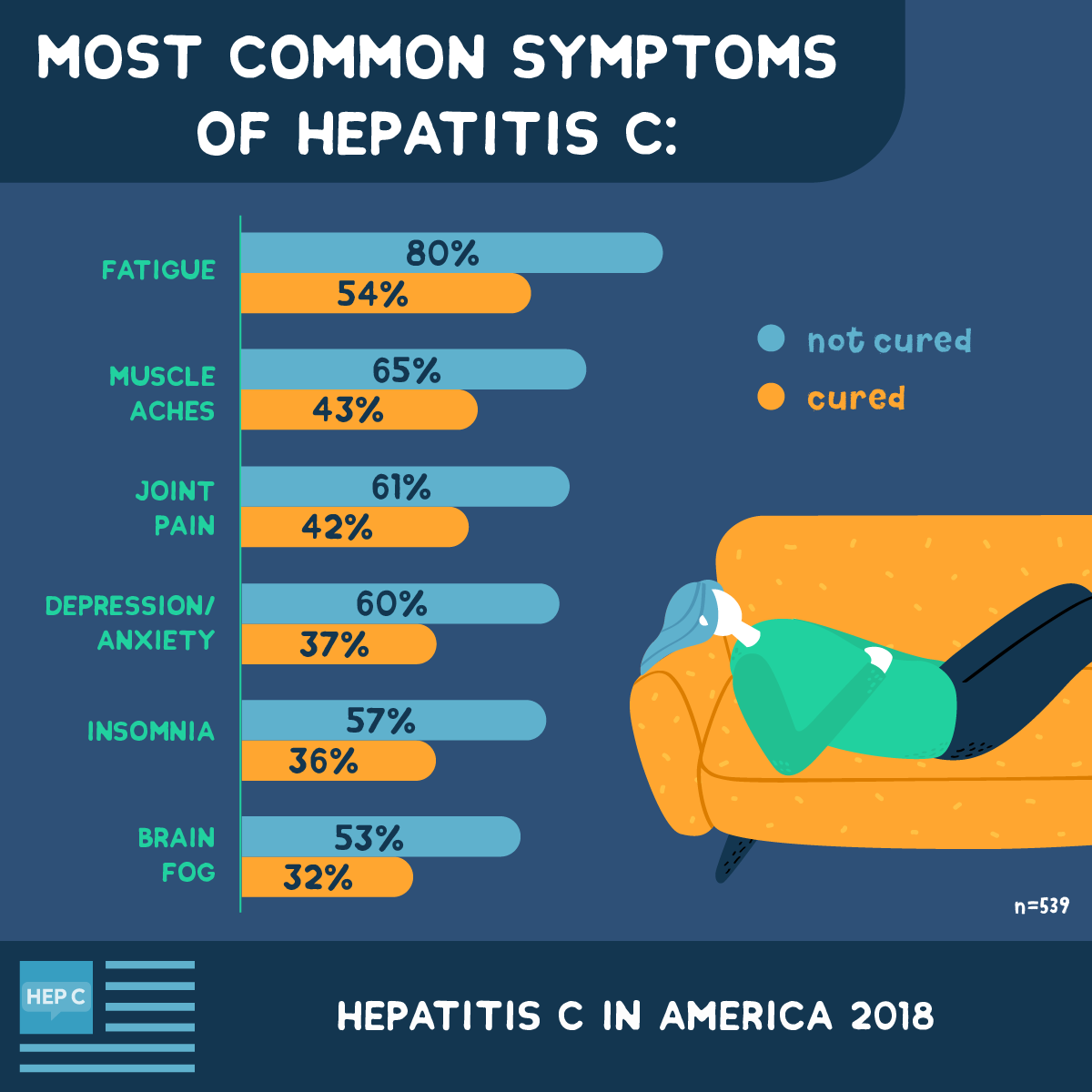
These tips will help protect you and your family from Hepatitis A:
- Wash your hands after using the washroom and changing diapers, and before preparing or eating food.
- When travelling, especially to developing countries:
- drink water from a safe supply
- avoid ice cubes in drinks
- eat only freshly cooked food
- avoid non-peelable raw fruit or vegetables
Also, these safe food practices will reduce your risk of contracting Hepatitis A and other foodborne illnesses.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis B The Same As Hiv
How Is Hepatitis Diagnosed
Chronic hepatitis can quietly attack the liver for years without causing any symptoms. Unless the infection is diagnosed, monitored, and treated, many of these people will eventually have serious liver damage. Fortunately, blood tests can determine whether you have viral hepatitis, and if so, which kind.
Hepatitis C And The Hep C Virus
Hepatitis C is a liver infection that can lead to serious liver damage. Its caused by the hepatitis C virus. About 2.4 million people in the U.S. have the disease. But it causes few symptoms, so most of them don’t know. The virus spreads through an infected persons blood or body fluids.
There are many forms of the hepatitis C virus, or HCV. The most common in the U.S. is type 1. None is more serious than any other, but they respond differently to treatment.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Symptoms In Females
Cross References To Published Guidelines
The following published guidelines were reviewed and cross referenced with the recommendations made in this guideline.
-
Brook MG. European guideline for the management of hepatitis B and C virus infections. Int J STD AIDS 2001 12:4857
-
Brook MG. National guideline for the management of the viral hepatitides A, B and C. www.mssvd.org.uk/CEG/ceguidelines.htm.
-
Cramp M, Rosenberg W. Guidance on the treatment of hepatitis C incorporating the use of pegylated interferons. www.bsg.org.uk/clinical_prac/guidelines/pegylated.htm).
How Do You Treat Hepatitis B
Like hepatitis A, medical treatment for acute hepatitis B is focused on getting plenty of rest and fluids and eating a healthy diet, although sometimes antiviral drugs are recommended for severe cases to help prevent liver failure. Patients with chronic hepatitis B may be given an oral antiviral drug to control the viral infection and minimize liver damage. These drugs are effective, but they rarely cure chronic hepatitis B. Therefore, these medications often have to be taken for life.
Don’t Miss: Fast Track Hepatitis B Vaccine In Houston Tx
Hepatitis C: How Does It Spread
It spreads through infected blood. In the U.S., sharing needles or other items used to inject drugs is the most common cause of infection. Getting a tattoo or body piercing with an infected needle is another means of exposure. A mother may pass the virus to their child at birth. In rare cases, unprotected sex spreads hepatitis C, but the risk appears small. Having multiple sex partners, HIV, or rough sex seems to raise risk for spreading hepatitis C.
Difference Between Hepatitis A And B
Difference between hepatitis A and B
Hepatitis A and B have most likely been mentioned to you before. Its an inevitable topic, whether you heard about it via the news, a headline, or a coworker whos had it in the past. However, you may be completely unaware of the dangers of hepatitis A and B, who is most at risk, or how to protect yourself. Take a closer look at the specifics, so you know what to expect and how to stay healthy all year long.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B: Although most commonly acquired early in life, adults can also contract it. Hepatitis B is largely transmitted through bodily fluids. It can be passed at birth from a hepatitis B-infected mother or through exposure in early childhood to body fluids, blood or contaminated medical instruments. Hepatitis B can also be transmitted through intranasal and injection drug use as well as infected tools used during tattooing and body piercing.
Hepatitis C: The key risk factors are also intranasal and injection drug use, tattoos and body piercings, high-risk sexual contact, blood transfusions before 1992 and organ transplantation.
Another key risk factor for hepatitis C is being born from 1945 to 1965, during the baby-boom years. Eighty percent of all people who currently have hepatitis C in the United States were born in that timeframe.
Although the reasons that baby boomers are more likely to have hepatitis C than others arent entirely understood, its believed that most were infected in the 1970s and 1980s, when rates of hepatitis C were at their peak.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend that all U.S. adults born from 1945 to 1965 undergo a one-time screening test for hepatitis C. Connecticut is one of several states that has written this recommendation into law. In Connecticut ,the law requires that primary care clinicians screen all adults born within those years.
What Causes The Different Types
The type of virus that’s causing your hepatitis affects how severe your disease is and how long it lasts.
Hepatitis A. You usually get it when you eat or drink something that’s got the virus in it. It’s the least risky type because it almost always gets better on its own. It doesn’t lead to long-term inflammation of your liver.
Even so, about 20% of people who get hepatitis A get sick enough that they need to go to the hospital. There’s a vaccine that can prevent it.
Hepatitis B. This type spreads in several ways.You can get it from sex with someone who’s sick or by sharing a needle when using street drugs. The virus also can pass from mothers to their newborn child at birth or soon afterward.
Most adults with hepatitis B get better, but a small percentage can’t shake the disease and become carriers, which means they can spread it to others even when their own symptoms disappear.
Hepatitis C. You get this type if you have contact with contaminated blood or needles used to inject illegal drugs or draw tattoos.
Sometimes you don’t get any symptoms, or just mild ones. But in some cases hepatitis C leads to cirrhosis, a risky scarring of your liver.
Hepatitis D happens only if you’re already infected with hepatitis B. It tends to make that disease more severe.
It can be spread from mother to child and through sex.
Like hepatitis A, you usually get it by eating or drinking something that’s been contaminated with the virus.
Don’t Miss: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
It only takes one exposure to hepatitis C to become chronically infected, so people who have injected illegal drugs even one time or many years previously could have chronic hepatitis C, and not know it since there are often no symptoms. People with blood transfusions prior to 1992 – when they started testing blood for transfusion for hepatitis C – also may have become chronically infected.
Also Check: Hep C Without Hepatic Coma
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis C
The latest drug to be approved by the FDA is glecaprevir and pibrentasvir . This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with all types of HCV who donât have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated. The length of treatment is longer for those who are in a different disease stage. The prescribed dosage for this medicine is 3 tablets daily.
There are several other combination drugs available, as well as some single drugs that may be used in combination. Your doctor will choose the right one for you depending on the type of hepatitis C you have, how well your liver is functioning and any other medical problems you may have. Also be sure to discuss your insurance coverage since these medications are expensive.
Vaccination For Hepatitis A And Hepatitis B
Vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B are the most effective preventive measures against those viruses. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recommended these vaccines for all babies as part of routine healthcare since the 1990s.
The vaccine can be administered to people of any age. If you were not vaccinated as a baby, it is fine to be vaccinated now. Vaccination provides long-term protection from infection.
Even if you have recently been exposed to the virus, the vaccine may prevent infection. Ideally, vaccination takes place within 24 hours of a possible exposure.
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. Our doctors recommend adopting certain behaviorssuch as avoiding shared needles and other risk factorsto prevent infection.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Virus