Hepatitis A And B Vaccines
There are vaccines to protect against hepatitis A and B. The CDC recommends hepatitis A vaccination for all children ages 12 to 23 months and for adults who plan to travel or work in areas with hepatitis A outbreaks or who have other risk factors. People with chronic hepatitis B or C should also get the hepatitis A vaccine if they don’t already have immunity to the disease. The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all infants at birth and for adults who have any of the risk factors we discussed earlier. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
How Do You Get It
HAV can be present in the stool and blood of someone with the virus. Its mainly transmitted through the fecal-oral route, which involves ingesting virus thats present in the stool of someone with hepatitis A.
There are several ways you can get hepatitis A:
- having close person-to-person contact with someone who has hepatitis A, such as:
- taking care of someone whos currently sick
- having sex with someone who has the virus
How Do I Test For Hepatitis B And C
If you are worried about your symptoms or feel you may been exposed to the virus, it is important to get tested immediately. Testing for hepatitis B & C requires a small blood sample. You can get a home-test kit online or at selected pharmacies.
LetsGetChecked offer the Standard 6 test which lets you check for hepatitis B and hepatitis C, chlamydia, gonorrhoea, syphilis and HIV.This is a convenient and confidential alternative to getting tested in a clinic.
Also Check: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
How To Prevent Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by a virus . It can be serious and theres no cure, but the good news is its easy to prevent. You can protect yourself by getting the hepatitis B vaccine and having safer sex. If you have oral, anal, and vaginal sex, use condoms and dental dams to help stop the spread of hepatitis B and other STDs.
How Hepatitis Is Spread

Hepatitis A: About 20,000 people in the U.S. contract hepatitis A each year. The hepatitis A virus is found in the stool of the infected person. It is spread through contaminated food or water or by certain types of sexual contact.
Children who get hepatitis A often don’t have symptoms, so they can have the virus and not know it. However, they can still spread it easily. Fortunately, children are now routinely vaccinated against hepatitis A.
Most people who get hepatitis A recover completely within two weeks to six months and don’t have any liver damage. In rare cases, hepatitis A can cause liver failure and even death in older adults or people with underlying liver disease.
Hepatitis B: Every year, about 40,000 people in the U.S. become infected with hepatitis B. Acute hepatitis lasts from a few weeks to several months. Many infected people are able to clear the virus and remain virus-free after the acute stage. However, for others, the virus remains in the body, and they develop chronic hepatitis B infection, which is a serious, lifelong condition. About 1.2 million people in the U.S. have chronic hepatitis B. Of these, 15% to 25% will develop more serious health problems, such as liver damage, cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer, and some people die as a result of hepatitis B-related disease.
Hepatitis B cannot be spread by contaminated water, food, cooking, or eating utensils, or by breastfeeding, coughing, sneezing, or close contact such as kissing and hugging.
Don’t Miss: Hep C Without Hepatic Coma
What Is The Outlook
Most people with hepatitis A recover without any complications. Once youve had hepatitis A, you cant get it again. Antibodies to the virus will protect you for life.
Some people may be at an increased risk for serious illness from hepatitis A. These include:
- older adults
acute hepatitis B infections in the United States in 2018.
Vaccination Is The Best Way To Prevent Hepatitis A And B Infection
Narrator: ÂYou are a traveller…Â .
Narrator: …and you are already dreaming of your next getaway. .
Disclaimer on-screen reads: TWINRIX is a combined hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine used in adults, adolescents, children, and infants over the age of 1 year to prevent hepatitis A and hepatitis B diseases
Narrator: ÂWhile your travel plans probably donÂt include hepatitis A or hepatitis B…Â .
Disclaimer reads: 100% protection cannot be guaranteed and booster doses may be required.
Narrator: Â…you know that many common travel activities can put you at risk of acquiring these two serious liver diseases…Â .
Disclaimer reads: TWINRIX does not protect against hepatitis C or E, and is not indicated to treat or reduce the severity of hepatitis A or B infections. .
Narrator: Â…which is why you plan on talking to your doctor about TWINRIX, right? … Of course, right…Â Â…because you are a traveller.Â
Video concludes with TWINRIX logo, GSK logo, You are a traveller slogan, and safety information: Very commonly reported adverse events in adults were pain or discomfort, redness at the infection site, headache, and tiredness. Common adverse events were swelling at the injection site, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, and generally feeling unwell. Allergic reactions may also occur. Full product information can be found on Twinrix.ca. If you need to report an adverse event, please call 1-800-387-7374.
Twinrix.ca
Don’t Miss: Fast Track Hepatitis B Vaccine In Houston Tx
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis A And Hepatitis B
You’ve undoubtedly heard hepatitis A and B mentioned many times before. Whether it was by watching the news, reading a headline, or overhearing a coworker say they had it in the past, it’s an unavoidable topic. But you may not really know what hepatitis A and B are, how dangerous they can be, who’s most at risk, or how you can protect yourself. Let’s look at the specifics so you have the facts to help keep yourself healthy year-round.
Safety Of Hepatitis Vaccines
Hepatitis vaccines have been given to millions of people all across the world without any evidence of serious side effects. “They’re very safe, and they’re extremely effective,” says Poland.
If you are not sure whether you should have hepatitis vaccines, talk with your doctor about your specific concerns.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
Treatments For Hepatitis B
Treatment for hepatitis B depends on how long you have been infected for.
If you have been exposed to the virus in the past few days, emergency treatment can help stop you becoming infected.
If you have only had the infection for a few weeks or months , you may only need treatment to relieve your symptoms while your body fights off the infection.
If you have had the infection for more than 6 months , you may be offered treatment with medicines that can keep the virus under control and reduce the risk of liver damage.
Chronic hepatitis B often requires long-term or lifelong treatment and regular monitoring to check for any further liver problems.
What Is The Hepatitis A & B Vaccine
The hepatitis A & B vaccine contains both hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines to prevent these two forms of hepatitis. It is administered either as three doses over a period of six months, or three shots administered over one month with the addition of a booster shot after one year.
View more information on the Hepatitis B vaccine.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
What If You Test Positive
If a test says you have viral hepatitis, you can take steps to protect the ones you love. For hepatitis A, wash hands frequently. For hepatitis B and C, avoid sharing nail clippers, razors, or toothbrushes. Hepatitis B, and sometimes hepatitis C, can be passed through sexual contact. Make sure everyone in your household gets the hepatitis B vaccine. An important step is to see a specialist to discuss treatment options.
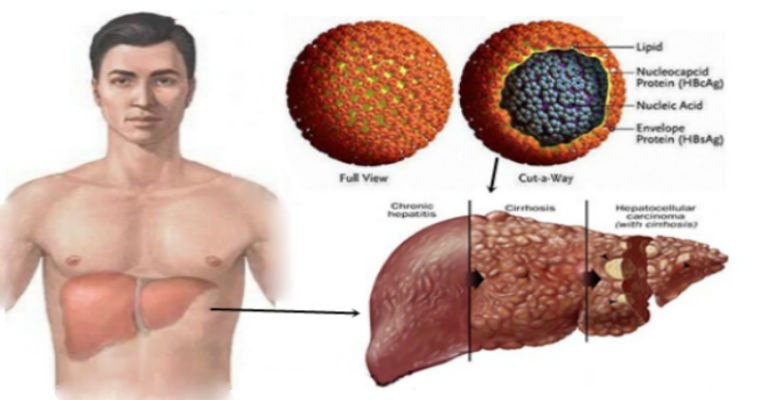
Liver Anatomy And Function

Main Function of the Liver
The liver is an essential organ that has many functions in the body. The liver plays an important role in detoxifying the body by converting ammonia, a byproduct of metabolism in the body, into urea that is excreted in the urine by the kidneys. The liver also breaks down medications and drugs, including alcohol, and is responsible for breaking down insulin and other hormones in the body. The liver also stores vitamins and chemicals that the body requires as building blocks.
Many different disease processes can occur in the liver, including infections such as hepatitis, cirrhosis , cancers, and damage by medications or toxins.
Symptoms of liver disease can include:
- Jaundice
Also Check: Can Hepatitis C Go Away On Its Own
Guidance On Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization
Vaccine providers are asked to report, through local public health officials, any serious or unexpected adverse event temporally related to vaccination. An unexpected AEFI is an event that is not listed in available product information but may be due to the immunization, or a change in the frequency of a known AEFI.
Refer to Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization in Canada and Adverse events following immunization in Part 2 for additional information about AEFI reporting.
Recommendations For Frequency Of Repeat Testing In An Asymptomatic Patient
The frequency of testing depends on the history of sexual exposure and number of sexual partners. However, in the case of hepatitis A and B, once the patient has completed a course of vaccination no further repeat testing is required.
For those at continuing risk and who have not received a course of vaccination, the following is recommended.
Read Also: Hepatitis B How Do You Catch It
Hepatitis A: Who Is At Risk
A prime risk factor for hepatitis A is traveling to or living in a country with high infection rates. You can check the CDC’s travel advisories to learn about recent outbreaks. Eating raw foods or drinking tap water can raise your risk while traveling. Children who attend daycare centers also have a higher risk of getting hepatitis A.
Why Should Baby Boomers Get Tested
While anyone can get Hepatitis C, more than 75% of adults infected are baby boomers . Most people with Hepatitis C dont know they are infected.
- Baby boomers are five times more likely to have Hepatitis C.
- Liver Disease, liver cancer, and deaths from Hepatitis C are on the rise.
- The longer people live with Hepatitis C, the more likely they are to develop serious, life-threatening liver disease.
- Getting tested can help people learn if they are infected and get them into lifesaving care and treatment.
- For many people, treatments are available that can cure Hepatitis C and prevent liver damage, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer.
You May Like: Treatment For Liver Cirrhosis Hepatitis B
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis C
The latest drug to be approved by the FDA is glecaprevir and pibrentasvir . This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with all types of HCV who donât have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated. The length of treatment is longer for those who are in a different disease stage. The prescribed dosage for this medicine is 3 tablets daily.
There are several other combination drugs available, as well as some single drugs that may be used in combination. Your doctor will choose the right one for you depending on the type of hepatitis C you have, how well your liver is functioning and any other medical problems you may have. Also be sure to discuss your insurance coverage since these medications are expensive.
Reducing The Risk Of Hepatitis B
Simple steps that everyone can take to protect themselves against hepatitis B include:
- Making sure you and your children are immunised this is the best protection.
- Using condoms every time you have anal or vaginal sex with new partners until you both get a check-up .
- Avoiding oral sex if you or your partner have herpes, ulcers or bleeding gums it is unlikely that you will contract hepatitis through oral sex unless blood is present.
- Choosing to have any body piercing or tattooing done by an experienced practitioner who follows good sterilisation and hygiene practices, and who works at premises registered by the local council.
- Wearing single-use gloves if you give someone first aid or need to clean up blood or body fluids.
- Never sharing needles and syringes or other equipment , if you inject drugs. Always use sterile needles and syringes. These are available from needle and syringe programs and some pharmacists. Always wash your hands before and after injecting.
If you have hepatitis B:
If you think you have been exposed to hepatitis B, see a doctor immediately. Your doctor can give you treatment in some instances, which greatly reduces the risk of you becoming infected with hepatitis B.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis B The Same As Hiv
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is an inflammation of your liver that’s caused by a virus. There are five types, but the most common ones in the U.S. are hepatitis A, B, and C. All of them affect your liver. Some of the symptoms are similar, but they have different treatments.
Hepatitis A. This type won’t lead to long-term infection and usually doesn’t cause any complications. Your liver heals in about 2 months. You can prevent it with a vaccine.
Hepatitis B. Most people recover from this type in 6 months. Sometimes, though, it causes a long-term infection that could lead to liver damage. Once you’ve got the disease, you can spread the virus even if you don’t feel sick. You won’t catch it if you get a vaccine.
Hepatitis C. Many people with this type don’t have symptoms. About 80% of those with the disease get a long-term infection. It can sometimes lead to cirrhosis, a scarring of the liver. There’s no vaccine to prevent it.
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Cross References To Published Guidelines
The following published guidelines were reviewed and cross referenced with the recommendations made in this guideline.
-
Brook MG. European guideline for the management of hepatitis B and C virus infections. Int J STD AIDS 2001 12:4857
-
Brook MG. National guideline for the management of the viral hepatitides A, B and C. www.mssvd.org.uk/CEG/ceguidelines.htm.
-
Cramp M, Rosenberg W. Guidance on the treatment of hepatitis C incorporating the use of pegylated interferons. www.bsg.org.uk/clinical_prac/guidelines/pegylated.htm).
Take These Precautions To Prevent Hav From Spreading:
- Wash hands often, and always after using the bathroom or changing diapers and before preparing food or eating. Work up a good lather with soap and warm water. Scrub for at least 1015 seconds, then rinse.
- Avoid work and public areas until symptoms are gone.
- Once youve had hepatitis A, you cannot get it again, so you dont need the hepatitis A vaccine. But you should consider vaccination against hepatitis B, a more serious form of hepatitis.
- Members of the household should be vaccinated against hepatitis A and B if they havent been already.
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
Hepatitis C: Who Is At Risk
People who have injected illegal drugs at any time, even one time, many years ago, could be walking around with chronic hepatitis C. Because there are often no symptoms, many former drug users may not realize they have the infection. People who received a blood transfusion before 1992 also have a higher risk. Before that year, donated blood was not screened for the hepatitis C virus.
Who Should Be Tested For Hepatitis
Testing is important for anyone with the risk factors we’ve mentioned, particularly injected drug users and people who have had multiple sex partners. Health advocates are also urging people of Asian heritage to get tested. Stanford University’s Asian Liver Center estimates that 1 in 10 Asians living in the U.S. has chronic hepatitis B. Many of them have probably had the virus since birth.
Also, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that health care providers offer a one-time hepatitis C screening for anyone born between 1945 and 1965.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B & Hepatitis C
Carrying the virus for over six months means Hepatitis B or C become chronic infections. Chronic infections generally remain dormant for many years, until the virus damages the liver enough to cause the signs and symptoms of liver disease. Among these signs and symptoms are:
- Bleeding easily
- Yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes
- Dark-colored urine
- Fluid buildup in your abdomen
- Swelling in your legs
- Confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech
- Spider-like blood vessels on your skin
In the acute stages, symptoms may include jaundice, fatigue, nausea, fever or muscle aches. If acute hepatitis symptoms are to arise, they usually appear one to three months after exposure to the virus lasting two weeks to three months time. Acute hepatitis infection doesnt always become chronic. Some people clear the infection from their bodies after the acute phase, this outcome is known as spontaneous viral clearance.