Clinical Utility Of Testing
The clinical utility of testing for hepatitis C in pregnancy is limited by the lack of effective treatment options to avoid mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy or childbirth .
However, new treatment options for people living with hepatitis C have become available and were recently listed on the Australian Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme . While these treatments have not been proven to be safe in pregnancy or during breastfeeding , women who are diagnosed with hepatitis C during pregnancy could commence such curative treatment after completion of breastfeeding , thus reducing their risk of significant liver disease and the risk of perinatal infection for subsequent pregnancies.
In addition, knowledge of a womans hepatitis C status means interventions that may increase the risk of mother-to-baby transmission can be avoided.
Duration Of Hepatitis C
The other 75 to 85 percent of people go on to become hepatitis C carriers and develop a chronic infection, which can last a lifetime if left untreated. Chronic hepatitis C can lead to hepatitis Crelated complications, including chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Hepatitis C
If hepatitis C leads to cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Doctors can treat the health problems related to cirrhosis with medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If you have cirrhosis, you have an increased chance of liver cancer. Your doctor may order an ultrasound test to check for liver cancer.
If hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Symptoms In Females
Can You Be A Blood Or Organ Donor
People with hepatitis C cant currently donate blood. The American Red Cross eligibility guidelines prohibit people who have ever tested positive for hepatitis C from donating blood, even if the infection never caused symptoms.
According to the Department of Health and Human Services , information on organ donation, those with underlying medical conditions shouldnt rule themselves out as organ donors. This reflects new guidelines for organ donation announced by the HHS.
People with HCV are now able to be organ donors. This is because advances in testing and medical technology can help the transplant team determine which organs or tissues can be safely used for transplantation.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
Some people are at increased risk for hepatitis C, including:
- Current injection drug users .
- Past injection drug users, including those who injected only one time or many years ago.
- Recipients of donated blood, blood products, and organs .
- People who received a blood product made before 1987 for clotting problems.
- Hemodialysis patients or persons who spent many years on dialysis for kidney failure.
- People who received body piercing or tattoos done with non-sterile instruments.
- People with known exposures to the hepatitis C virus, such as:
- Health care workers injured by needlesticks.
- Recipients of blood or organs from a donor who tested positive for the hepatitis C virus.
Less common risks include:
- Having sexual contact with a person who is infected with the hepatitis C virus.
- Sharing personal care items, such as razors or toothbrushes, that may have come in contact with the blood of an infected person.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Virus
How To Prevent Hepatitis C
There is currently no vaccine for hepatitis C. Avoiding contact with infected blood is the only way to prevent the condition.
The most common way for people to contract hepatitis C is by injecting street drugs. Because of this, the best way to prevent hepatitis C is to avoid injecting.
Treatments can help many people quit. People in the U.S. can call the National Helpline for help with finding treatments.
If a person finds it difficult to stop, they can reduce the risk of contracting hepatitis C by never sharing drug equipment, ensuring a clean, hygienic environment, and always using new equipment, including syringes, ties, alcohol swabs, cottons, and cookers.
People who may come into contact with infected blood, such as healthcare workers and caretakers, should always wash the hands thoroughly with soap and water after any contact, or suspected contact, with blood. They should also wear gloves when touching another persons blood or open wounds.
People can also reduce their risk by making sure that any tattoo artist or body piercer they visit uses fresh, sterile needles and unopened ink.
The risk of contracting hepatitis C through sexual contact is low. Using barrier protection, such as condoms, reduces the risk of most sexually transmitted infections.
People who have hepatitis C can reduce the risk of transmitting it to others by:
There are many misconceptions about how hepatitis C spreads. People cannot transmit or contract the virus through:
Sexual Transmission And Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B can be transmitted through sexual activity. Unvaccinated adults who have multiple sex partners, along with sex partners of people with chronic hepatitis B infection, are at increased risk for transmission. Injection-drug use and sexual contact are other common modes of hepatitis B transmission in the United States.
Among adults seeking treatment in STD clinics, as many as 10%40% have evidence of past or current hepatitis B virus infection. Many of these infections could have been prevented through universal vaccination during delivery of STD prevention or treatment services. Offering vaccination to all adults as part of routine prevention services in STD treatment facilities has been demonstrated to increase vaccination coverage among adults at risk for hepatitis B infection, as the behavioral risk factors for STDs and hepatitis B are similar.
Also Check: How To Find Out If You Have Hepatitis
Favorite Hep C Financial Resources
This nonprofit devotes its energies to help people afford healthcare and medication. It offers a free drug discount card that extends a discount of up to 80 percent at more than 65,000 pharmacies nationwide. Anyone can use the card regardless of income level or insurance status.
RxAssist guides people to free or low-cost medicine programs. Visitors to the website can type a drug’s name into the search tool to find patient assistance programs that can help with costs. The group also gives a wealth of information on various drug discount cards.
Those who qualify can get awards of up to $15,000 a year to pay for hep C treatment. Eligibility requirements include an income below 400 percent of the federal poverty guidelines. In addition, the foundation presents links to other financial resources and pharmaceutical assistance programs.
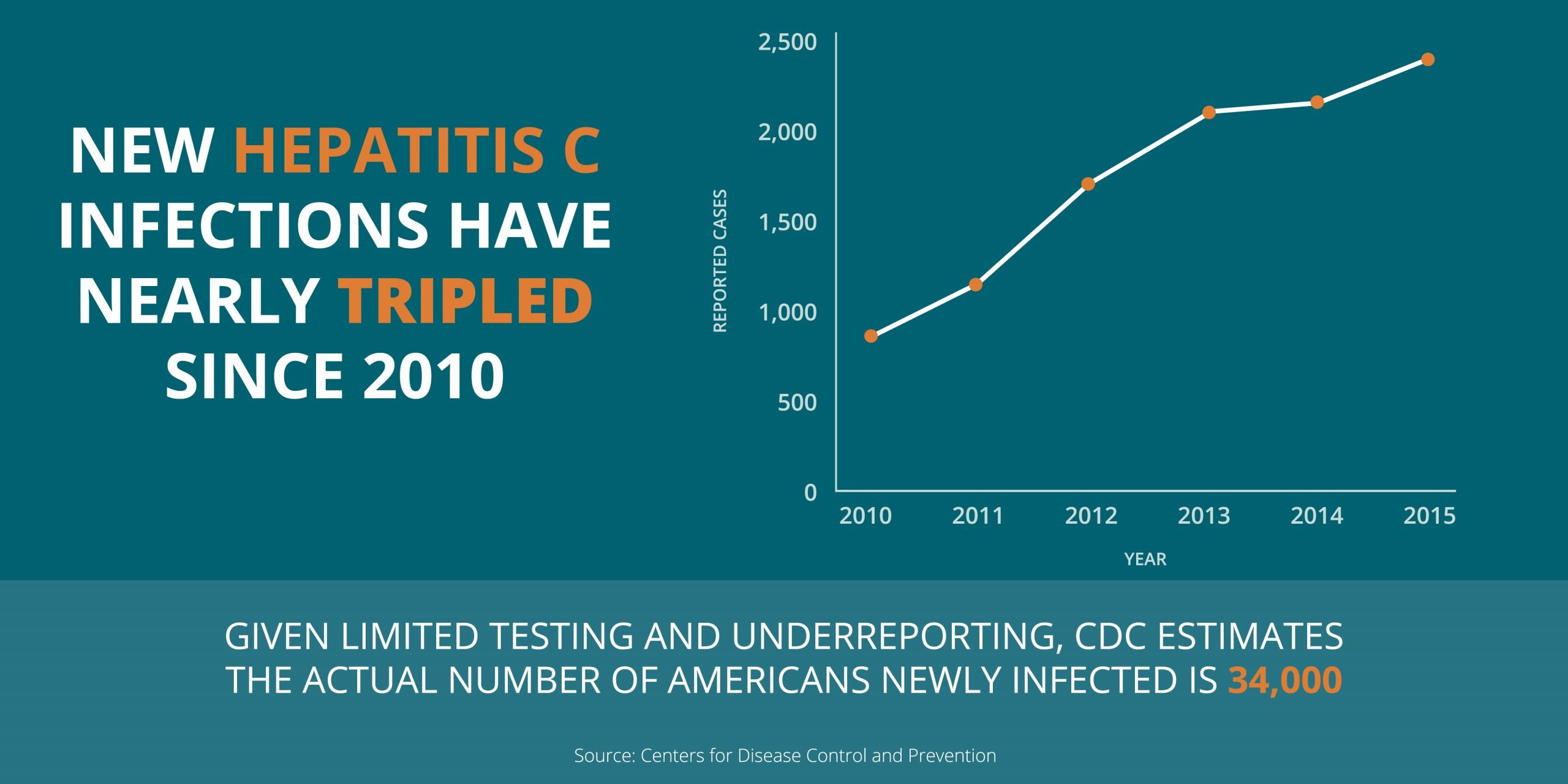
Research And Statistics: Who Has Hepatitis C How Many People Have Hepatitis C
Health officials reported 2,967 cases of acute hepatitis C in 2016, but the CDC estimates that the actual number of acute cases is 13.9 times the number of reported cases in any year. The CDC put the real number of acute hepatitis C cases in 2016 at an estimated 41,200.
Despite these estimates, “we really do not know how many people are infected with HCV,” Dr. Branch says, adding that the U.S. estimates come from specific datasets that “do not include prisoners or the homeless and have too small a sample size to yield precise data.”
The Journal of Infectious Diseases
It’s unclear how many people fail to get treatment in time and die from HCV-related issues. According to the CDC, there were 18,153 reported deaths related to HCV, but this is likely an underestimate.
“HCV may be causing 3 to 5 times more deaths than we know,” Branch says. “Better information about the number of HCV-related deaths would help make HCV testing and treatment more of a priority.”
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis C Do To You
No Identifiable Source Of Infection
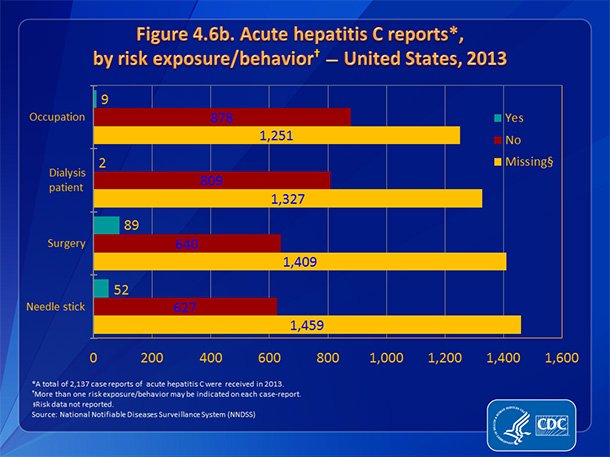
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, injection drug use accounts for approximately 60% of all HCV infections in the United States, while other known exposures account for 20-30%. Approximately 10% of patients in most epidemiological studies, however, have no identifiable source of infection. HCV exposure in these patients may be from a number of uncommon modes of transmission, including vertical transmission, and parenteral transmission from medical or dental procedures prior to the availability of HCV testing. There are no conclusive data to show that persons with a history of exposures such as intranasal cocaine use, tattooing or body piercing are at an increased risk for HCV infection based on these exposures solely. It is believed, however, that these are potential modes of HCV acquisition in the absence of adequate sterilization techniques.
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a contagious liver disease that ranges in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness that attacks the liver. It results from infection with the hepatitis C virus, which is spread primarily through contact with the blood of an infected person. Hepatitis C can be either acute or chronic.
Acute hepatitis C virus infection is a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after someone is exposed to the hepatitis C virus. For most people, acute infection leads to chronic infection.
Chronic hepatitis C virus infection is a long-term illness that occurs when the hepatitis C virus remains in a persons body. Hepatitis C virus infection can last a lifetime and lead to serious liver problems, including cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Recommended Reading: Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
Should pregnant women be tested for HCV antibodies?
Yes. All pregnant women should be screened for anti-HCV during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is < 0.1% . Pregnant women with known risk factors should be tested during each pregnancy, regardless of setting prevalence. Any pregnant women testing positive for anti-HCV should receive a PCR test for HCV RNA to determine current infection status.
Can a mother with hepatitis C infect her infant during birth?
The overall risk of an infected mother transmitting HCV to her infant is approximately 4%8% per pregnancy . Transmission occurs during pregnancy or childbirth, and no prophylaxis is available to protect the newborn from infection. The risk is significantly higher if the mother has a high HCV viral load, or is coinfected with HIV with which the rate of transmission ranges from 8%15% . Most infants infected with HCV at birth have no symptoms.
Should a woman with hepatitis C be advised against breastfeeding?
When should children born to HCV-infected mothers be tested to see if they were infected at birth?
Sharing Personal Care Items
The chances of spreading hepatitis C within your household are low but possible. To be safe, don’t share personal care items that could be contaminated with blood, Lee says. These include razors, toothbrushes, cuticle scissors, and nail clippers.
In addition, be mindful when you go to nail salons or barbershops, where the same tools are used on all customers. A study published in the November-December 2014 issue of the Journal of Public Health Management & Practice found that while regulations to safeguard the public exist in most states, it’s unknown how many businesses comply with them. Ask about tool-sterilization procedures before you frequent these establishments. You can also bring your own nail care supplies.
Also Check: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis C
Ways You Wont Spread Hepatitis C
There are some ways in which you wont spread HCV, though. Go ahead and let your significant other have a bite of your sandwich or dessert. According to the CDC, hepatitis C isnt spread by sharing silverware or drinking glasses, or through water or foods. Showing affection by holding hands, hugging, or kissing is also safe, Lee says. And although germs from sneezing or coughing might cause you to get a cold, they wont give you hepatitis C.
Sexual Transmission And Hepatitis C
Although not common, hepatitis C can be transmitted through sexual activity. Having a sexually transmitted infection, having sex with multiple partners, and engaging in anal sex appear to increase a persons risk for hepatitis C. MSM with multiple sex partners who are coinfected with HCV and HIV have been shown to transmit hepatitis C. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. The best way to prevent hepatitis C is by avoiding behaviors that can spread the disease, especially sharing needles or other equipment to inject drugs. CDC recommends one-time hepatitis C testing of all adults and regular testing for people with risk factors. The American Association for the Study of Liver Disease and the Infectious Diseases Society of America also recommend that people who are infected with HCV be provided with curative, direct-acting antiviral medicationsexternal icon to treat their HCV infection.
You May Like: Fast Track Hepatitis B Vaccine In Houston Tx
How Many People Have Hepatitis C
During 2013-2016 it was estimated that about two and half million people were chronically infected with HCV in the United States. The actual number may be as low as 2.0 million or as high as 2.8 million.Globally, hepatitis C is a common blood-borne infection with an estimated 71 million people chronically infected according to the World Health Organization .
Sexual Transmission And Viral Hepatitis
Certain adults who are sexually active should be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
CDC and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommend hepatitis B vaccination for
- sexually active people with more than one sex partner during the previous 6 months
- people seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease
- sex partners of people with hepatitis B and
- men who have sex with men .
CDC recommends one-time hepatitis C testing of all adults and regular testing for people with risk factors.
You May Like: Can Chronic Hepatitis B Be Cured
Treatment And Medication Options For Hepatitis C
The last few years have seen extraordinary advances in the treatment of hepatitis C.
For decades, the standard treatment was a combination antiviral therapy consisting of a pegylated interferon and ribavirin, sometimes called PEG-riba therapy. This involved weekly injections of the pegylated interferons along with twice-daily oral doses of ribavirin. Sometimes interferon was prescribed without ribavirin.
The treatment by interferon lasted six months to a year, and cured only 40 to 50 percent of hepatitis C patients. The painful injections often made patients feel ill with flu-like symptoms.
But now, hepatitis C can be treated with a number of direct-acting antiviral pills that act faster and much more effectively than the older interferon treatment. These combination oral medicines have 90 to 100 percent cure rates, and they work in weeks instead of months. Some of these drugs may be used in combination with ribavirin.
Favorite Hep C Alternative Medicine Resource
Although hep C can be successfully treated with modern medicine, many people turn to dietary supplements with the goal of curing their illness. The most commonly used is silymarin . Although the NCCIH says that no supplement is effective for hep C, the center provides the latest scientific data on a range of products, including probiotics, zinc, licorice root, and colloidal silver.
Read Also: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
Other Risks Can Include:

- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another persons blood, such as razors, toothbrushes or nail clippers
- Inoculation practices involving multiple use needles or immunization air guns
- Exposure of broken skin to HCV infected blood
- HIV infected persons
People with current or past risk behaviors should consider HCV testing and consult with a physician. HCV testing is currently not available at most public health clinics in Missouri. For information about HCV testing that is available, call the HCV Program Coordinator at 573-751-6439.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
Is Hepatitis Testing Recommended For People With Hiv
Yes. Everyone living with HIV should be tested for HBV and HCV when they are first diagnosed with HIV and begin treatment. People living with HIV who have ongoing risk factors for getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C should be tested annually.
In addition, new HCV screening recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention call for:
- One-time screening for all adults 18 years and older
- Screening of all pregnant women during every pregnancy
- Testing for all persons with risk factors, with testing continued periodic testing those with ongoing risk.
Reactive Or Positive Hepatitis C Antibody Test
- A reactive or positive antibody test means that Hepatitis C antibodies were found in the blood and a person has been infected with the Hepatitis C virus at some point in time.
- Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true even if they have cleared the Hepatitis C virus.
- A reactive antibody test does not necessarily mean that you have Hepatitis C. A person will need an additional, follow-up test.
Persons for Whom HCV Testing Is Recommended
- Adults born from 1945 through 1965 should be tested once
- Those who:
- Ever injected drugs, including those who injected once or a few times many years ago
- Have certain medical conditions, including persons:
- who received clotting factor concentrates produced before 1987
- who were ever on long-term hemodialysis
- with persistently abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels
- who have HIV infection
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis C From