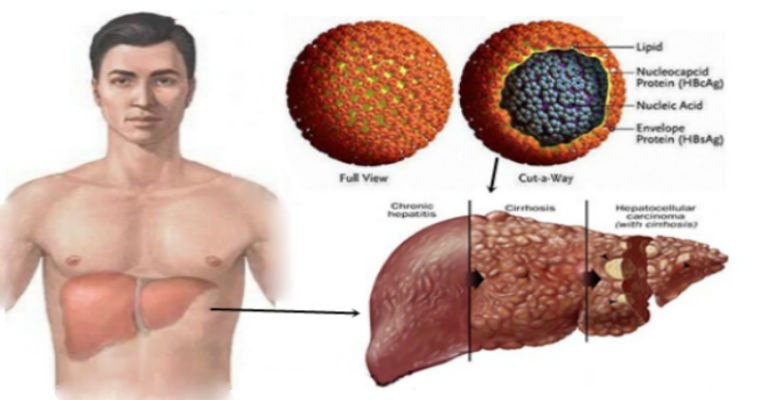
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
The virus that causes hepatitis B lives in blood, semen, and other fluids in your body. You usually get it by having sex with someone who’s infected.
You also can get it if you:
- Have direct contact with infected blood or the body fluids of someone who’s got the disease, for instance by using the same razor or toothbrush as someone who has hepatitis B, or touching the open sores of somebody who’s infected.
- If you’re pregnant and you’ve got hepatitis B, you could give the disease to your unborn child. If you deliver a baby who’s got it, they need to get treatment in the first 12 hours after birth.
Whats The Difference Between Hepatitis A B And C
Chronic Illness, Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Hepatology, Liver Health
Youve probably seen stories in the news about hepatitis A outbreaks linked to infected restaurant workers, or how a rising rate of hepatitis C infections is causing increased health care costs.
But you might not know the difference between hepatitis A, B and C, or why you should be concerned about them.
Heres why: Hepatitis, or inflammation of the liver, affects more than 50,000 new people each year and is a leading cause of liver cancer and liver transplants. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates as many as 6 million people in the U.S. are living with hepatitis.
Having hepatitis can be dangerous and uncomfortable. Symptoms are similar for hepatitis A, B and C and may include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, gray-colored stools, joint pain and jaundice . Even worse, chronic hepatitis often has no symptoms, and people dont know theyre infected until they get very sick.
Michael Fried, MD, director of the UNC Liver Center, explains the difference between the types of hepatitis and how to protect yourself.
What If You Test Positive For Hepatitis
If testing discloses that you have viral hepatitis there are steps to prevent your passing the viruses to family and friends. Washing the hands helps prevent transmission of hepatitis A. Not sharing needles, razors, nail clippers, or toothbrushes also will reduce transmission of viral hepatitis. Everyone should be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
You May Like: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
What Are The Risk Factors
Some people are at an increased risk for contracting HAV, including:
- people traveling to areas of the world where hepatitis A is common
- men who have sex with men
- people who use injectable or noninjectable drugs
- caregivers for those who have hepatitis A
- people who are experiencing homelessness
- people living with a child whos been adopted from an area where hepatitis A is common
Are Test Results Accurate
Although an acute viral hepatitis panel is a standard panel used to detect evidence of viral hepatitis, in many cases it provides only preliminary results. For patients who have abnormal results on the hepatitis B or C portions of this panel, additional testing is necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B
Key Points About Hepatitis In Children
-
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. It can damage and destroy liver cells.
-
Hepatitis in children can be caused by many things. Your child can get hepatitis by being exposed to a virus that causes it.
-
There are 5 main types of the hepatitis virus: A, B, C, D, and E.
-
The most common symptoms of hepatitis include a yellowish color to the skin and whites of the eyes and flu-like symptoms.
-
Some children don’t have any symptoms.
-
Getting vaccinated and having good hygiene can prevent hepatitis.
Do You Need Vaccinations Before Traveling Abroad
The CDC divides travel vaccinations into three categories: 1) routine, 2) recommended, and 3) required. The only vaccine classified as “required” by International Health Regulations is the yellow fever vaccination for travel to certain countries in sub-Saharan Africa and tropical South America.
“Routine” vaccinations are those that are normally administered, usually during childhood, in the United States. These include immunizations against:
- tetanus
Don’t Miss: Treatment For Liver Cirrhosis Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B: How Does It Spread
You can get it through contact with the blood or body fluids of an infected person. In the U.S., it’s most often spread through unprotected sex. It’s also possible to get hepatitis B by sharing an infected person’s needles, razors, or toothbrush. And an infected mother can pass the virus to their baby during childbirth. Hepatitis B is not spread by hugging, sharing food, or coughing.
How Do You Treat Hepatitis B
Like hepatitis A, medical treatment for acute hepatitis B is focused on getting plenty of rest and fluids and eating a healthy diet, although sometimes antiviral drugs are recommended for severe cases to help prevent liver failure. Patients with chronic hepatitis B may be given an oral antiviral drug to control the viral infection and minimize liver damage. These drugs are effective, but they rarely cure chronic hepatitis B. Therefore, these medications often have to be taken for life.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis B Come From
What Is The Treatment For Viral Hepatitis
Treatment of acute viral hepatitis and chronic viral hepatitis are different. Treatment of acute viral hepatitis involves resting, relieving symptoms, and maintaining an adequate intake of fluids. Treatment of chronic viral hepatitis involves medications to eradicate the virus and taking measures to prevent further liver damage.
Acute hepatitis
In patients with acute viral hepatitis, the initial treatment consists of relieving the symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain . Careful attention should be given to medications or compounds, which can have adverse effects in patients with abnormal liver function . Only those medications that are considered necessary should be administered since the impaired liver is not able to eliminate drugs normally, and drugs may accumulate in the blood and reach toxic levels. Moreover, sedatives and “tranquilizers” are avoided because they may accentuate the effects of liver failure on the brain and cause lethargy and coma. The patient must abstain from drinking alcohol since alcohol is toxic to the liver. It occasionally is necessary to provide intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration caused by vomiting. Patients with severe nausea and/or vomiting may need to be hospitalized for treatment and intravenous fluids.
Chronic hepatitis
Medications for chronic hepatitis C infection include:
- oral daclatasvir
Medications for chronic hepatitis B infection include:
- oral entecavir
- oral tenofovir
Fulminant hepatitis
What Happens During A Hepatitis Panel
A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out. This usually takes less than five minutes.
You may also be able to use an at-home kit to test for hepatitis. While instructions may vary between brands, your kit will include a device to prick your finger . Youll use this device to collect a drop of blood for testing. For more information on at-home testing for hepatitis, talk to your health care provider.
Don’t Miss: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis B
Although unprotected sex is the most common way of becoming infected with hepatitis B, infection is more likely for people who have multiple sex partners. Shared needles also are an important means of spreading hepatitis B. Other risk factors are being a health care worker, but infection usually is related to needle sticks. There also is a risk of becoming infected by living with someone who has chronic hepatitis B, in part due to sexual transmission.
What Does The Test Measure
An acute viral hepatitis panel includes several tests that measure antigens and antibodies. Antigens are foreign substances such as proteins of the virus itself, while antibodies are substances produced by the immune system in response to the viral infection.
An acute viral hepatitis panel tests for antigens and/or antibodies of hepatitis A, B, and C:
Recommended Reading: How To Find Out If You Have Hepatitis
Can Hepatitis B And C Be Prevented
Today, all babies get vaccinated against the hepatitis B virus in a series of three shots over a 6-month period. Doctors also recommend “catch-up” vaccination for all kids and teens younger than 19 years old who didn’t get the vaccine as babies or didn’t get all three doses.
Unfortunately, there’s no vaccine for hep C yet.
Chronic Hepatitis B Treatment
For hepatitis B, treatment is aimed at controlling the virus and preventing damage to the liver. Antiviral medications are available that will benefit most people, but the medications need to be chosen carefully, and the treatment needs to be monitored in order to assure successful treatment and to prevent or treat medication-related side effects. For some individuals, the risks of treatment may not be justified.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Who’s Most At Risk Of Hepatitis B
People at highest risk of hepatitis B include:
- people born or brought up in a country where the infection is common
- babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B
- people who have ever injected drugs
- anyone who has had unprotected sex, including anal or oral sex particularly people who have had multiple sexual partners, people who have had sex with someone in or from a high-risk area, men who have sex with men, and commercial sex workers
- close contacts, such as family members, of someone with a long-term hepatitis B infection
The risk of getting hepatitis B for travellers going to places where the infection is common is generally considered to be low if these activities are avoided.
Your GP can arrange for you to have a blood test to check for hepatitis B and have the hepatitis B vaccination if you’re at a high risk.
How Much Does The Test Cost
Several factors affect the cost of an acute viral hepatitis panel, including where the test is conducted, if any other tests or procedures are being performed at the same time, and whether or not the patient has health insurance that covers testing.
In addition to the panel itself, costs may include technician fees for collecting a blood sample and an additional charge for the office visit. These costs may be covered by health insurance if the acute viral antibody test is prescribed by a doctor. Patients with health insurance may still be responsible for copays, deductibles, and other charges.
Read Also: Fast Track Hepatitis B Vaccine In Houston Tx
How Hepatitis B Is Spread
Hepatitis B can be spread by:
- a mother to her newborn baby, particularly in countries where the infection is common all pregnant women in the UK are offered screening for hepatitis B babies of infected mothers are vaccinated immediately after birth to help prevent infection
- injecting drugs and sharing needles and other drug equipment, such as spoons and filters
- having sex with an infected person without using a condom
- having a tattoo, body piercing, or medical or dental treatment in an unhygienic environment with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country where blood is not tested for hepatitis B all blood donations in the UK are now tested for the infection
- sharing toothbrushes or razors contaminated with infected blood
- the skin being accidentally punctured by a used needle this is mainly a risk for healthcare workers
- the blood of someone with hepatitis B getting into an open wound, cut or scratch in rare cases, being bitten by someone with hepatitis B can also spread the infection
Hepatitis B is not spread by kissing, holding hands, hugging, coughing, sneezing or sharing crockery and utensils.
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis B
The goal of treating chronic hepatitis B is to control the virus and keep it from damaging the liver. This begins with regular monitoring for signs of liver disease. Antiviral medications may help, but not everyone can take them or needs to be on medication. Be sure to discuss the risks and benefits of antiviral therapy with your doctor.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
What Is Acute Fulminant Hepatitis
Rarely, individuals with acute infections with HAV and HBV develop severe inflammation, and the liver fails . These patients are extremely ill with the symptoms of acute hepatitis already described and the additional problems of confusion or coma , as well as bruising or bleeding . In fact, up to 80% of people with acute fulminant hepatitis can die within days to weeks therefore, it is fortunate that acute fulminant hepatitis is rare. For example, less than 0.5% of adults with acute infection with HBV will develop acute fulminant hepatitis. This is even less common with HCV alone, although it becomes more frequent when both HBV and HCV are present together.
What Do Doctors Do

A doctor who thinks someone may have hepatitis may ask questions like these:
- Has the person been around anyone who works in health care or childcare?
- Did the person stick himself or herself with a dirty needle or get a tattoo with a dirty needle?
- Did the person have contact with the bodily fluids of someone who has hepatitis?
- Did the person have a blood transfusion as a baby?
- Have any of the person’s family members had hepatitis?
- Could the person have eaten food that was contaminated with hepatitis A?
The doctor can order a blood test to see if someone has hepatitis and which type, then help the person get the right care.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis A: Who Is At Risk
A prime risk factor for hepatitis A is traveling to or living in a country with high infection rates. You can check the CDC’s travel advisories to learn about recent outbreaks. Eating raw foods or drinking tap water can raise your risk while traveling. Children who attend daycare centers also have a higher risk of getting hepatitis A.
How Do Health Care Providers Test For Hepatitis B
Testing for Hepatitis B involves the measurement of several Hepatitis B virus -specific antigens and antibodies. Different serologic markers or combinations of markers are used to identify different phases of HBV infection. They can determine whether a patient has acute or chronic HBV infection, is immune to HBV due to prior infection or vaccination, or is susceptible to infection.
Getting tested is the only way to know if you have Hepatitis B. CDCs Hepatitis B screening recommendations call for:
- People born in countries with moderate or high prevalence of Hepatitis B
- People born in the U.S. not vaccinated as infants whose parents were born in regions with high rates of Hepatitis B
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household and sexual contacts of Hepatitis B infected people
- People requiring immunosuppressive therapy
- People with end-stage renal disease
- Blood and tissue donors
You May Like: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B Virus
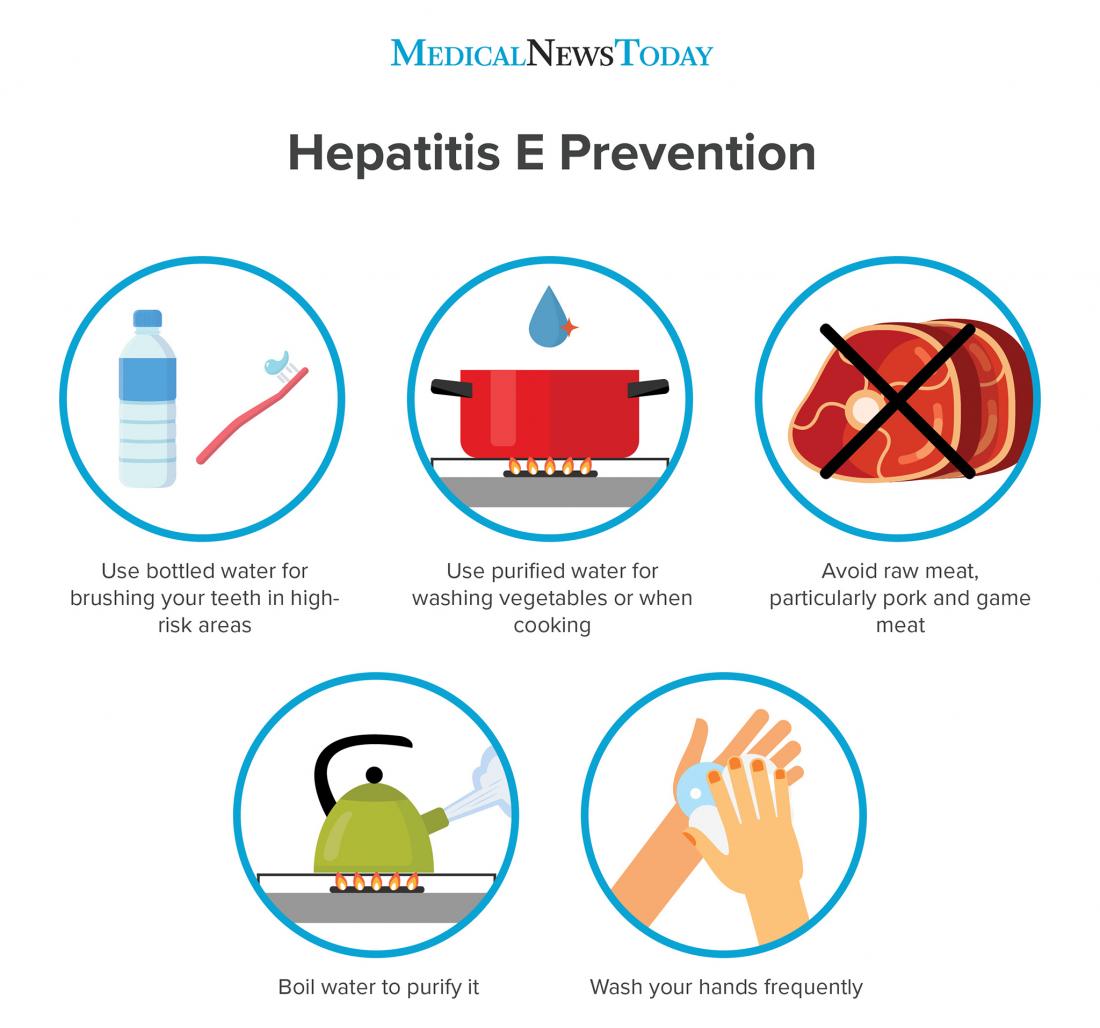
How Is Hepatitis A Transmitted
Hepatitis A is transmitted when a person ingests fecal matter from contact with objects, food or drinks contaminated by small undetected amounts of stool from an infected person.
Hepatitis A can also spread from close personal contact with an infected person such as through sex or caring for someone who is ill.
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
Each type of hepatitis is treated differently.
Hepatitis A often goes away on its own and home treatment is all that is needed to help the liver recover, such as:
- Rest
- Avoiding alcohol
- Avoiding certain medicines that can be harmful to the liver
Hepatitis B often goes away on its own in about 6 months, and can also be treated at home with the above remedies. Other treatments for hepatitis B include:
- Antiviral medications
- Liver transplant in severe cases
Treatment for hepatitis C is effective on certain forms of the hepatitis C virus. The choice of medications depends on the type of hepatitis C you have, whether you have been treated for the illness before, how much liver damage has occurred, any other underlying medical issues, and other medicines you take. Treatment for hepatitis C usually involves 8 to 12 weeks of oral antiviral medications, such as:
- Elbasvir-grazoprevir
Also Check: How Does Hepatitis C Affect The Liver
What Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis
Patients infected with HBV and HCV can develop chronic hepatitis. Doctors define chronic hepatitis as hepatitis that lasts longer than 6 months. In chronic hepatitis, the viruses live and multiply in the liver for years or decades. For unknown reasons, these patients’ immune systems are unable to eradicate the viruses, and the viruses cause chronic inflammation of the liver. Chronic hepatitis can lead to the development over time of extensive liver scarring , liver failure, and liver cancer. Liver failure from chronic hepatitis C infection is the most common reason for liver transplantation in the U.S. Patients with chronic viral hepatitis can transmit the infection to others with blood or body fluids as well as infrequently by transmission from mother to newborn.
Groups At High Risk Of Hep B Transmission
Hep B can only be passed on through blood-to-blood contact, unprotected sex or during birth so you might be at risk of having hep B if you:
- have moved to Australia from a country where hep C is widespread
- were born to a mother who was hep B positive during her pregnancy
- live or have lived with someone with hep B
- have or have had a sexual partner who has hep B
- have ever injected drugs or steroids
- are in prison or have ever been in prison
- have had blood transfusions, blood products or organ transplant in Australia before February 1990
- are of Aboriginal ancestry
- have had unsterile cosmetic or medical procedures.
- have had unsterile tattooing or piercing
- have ever taken part in unsterile traditional practices such as traditional tattooing, circumcision, initiation rituals involving blood, and scarification
- do not meet the above profiles but have abnormal liver function tests or experience hep B symptoms
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis C Spread