Is Mild Hepatomegaly Dangerous
The extent to which a slightly enlarged liver is dangerous depends on the reason for the enlargement.
For people with NAFLD, a slightly enlarged liver is unlikely to pose a major threat to health. However, it could be an indication that a person should consider making some lifestyle changes.
That said, certain conditions can cause a slightly enlarged liver to become a significantly enlarged and damaged liver without treatment. Such conditions include:
- alcohol use disorder
- hepatitis B, C, and D
- cancer
In general, mild hepatomegaly indicates that it is time to visit a doctor for a full physical evaluation.
Hepatomegaly usually does not cause any symptoms. In fact, the liver conditions that lead to hepatomegaly can progress significantly without causing any symptoms at all.
Because of this, a person should see a doctor if they:
- experience any symptoms of an enlarged liver
- develop any other symptoms of liver disease
- have any conditions that increase their risk of developing liver disease
The outlook for people with hepatomegaly depends on the cause of the hepatomegaly and the extent of the liver damage.
People with hepatitis A and acute hepatitis B usually recover without treatment.
People with the early stages of NAFLD may also have a positive outlook. A mildly damaged liver can often repair itself if a person makes the necessary lifestyle changes early on.
People who have other forms of liver damage will need to ask their doctor about their individual outlook.
Nafld And Alcoholic Liver Disease
It is often stated in the literature that NASH is histologically identical to ASH, but is that really true? There are several lesions of alcoholic liver disease that, to date, are not known in NAFLD, including sclerosing hyaline necrosis, the veno-occlusive lesion first described by Goodman and Ishak, and alcoholic foamy degeneration. On the other hand, there are several biopsies of fatty liver disease for which the pathologist cannot be sure of the true etiology of liver disease, and cases in which obesity, diabetes and alcohol are all likely contributing factors . In addition, most of the standard literature in liver pathology notes that Mallory hyaline and neutrophilic infiltrates may be more prominent in ALD.
Figure 4
Sclerosing hyaline necrosis. The terminal hepatic venule is obliterated and only visualized on special stains, which may highlight the remnants of the vein wall. Many of the surrounding hepatocytes have undergone necrosis, and several of the remaining hepatocytes are ballooned and/or have Mallory’s hyaline with surrounding neutrophils, a lesion known as satellitosis.
Is Mild Hepatomegaly Serious
Rather than a disease in itself, hepatomegaly is a symptom or complication of other liver conditions, some of them life-threatening. For this reason, hepatomegaly is something to take seriously, as it points to an underlying problem that could be quite serious. Liver disease can develop for years with no overt symptoms at all.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
What Are The Stages Of Liver Fibrosis
There are several different scales of liver fibrosis staging, where a doctor determines the degree of liver damage. Since staging can be subjective, each scale has its own limitations. One doctor may think a liver is slightly more scarred than another. However, doctors will usually assign a stage to liver fibrosis because it helps the patient and other doctors understand the degree to which a persons liver is affected.
One of the more popular scoring systems is the METAVIR scoring system. This system assigns a score for activity or the prediction of how fibrosis is progressing, and for the fibrosis level itself. Doctors can usually assign this score only after taking a biopsy or tissue sample of a piece of the liver. The activity grades range from A0 to A3:
- A0: no activity
- F4: cirrhosis
Therefore, a person with the most severe disease form would have an A3, F4 METAVIR score.
Another scoring system is Batts and Ludwig, which grades fibrosis on a scale of grade 1 to grade 4, with grade 4 being the most severe. The International Association of the Study of the Liver also has a scoring system with four categories that range from minimal chronic hepatitis to severe chronic hepatitis.
Doctors dont often diagnose liver fibrosis in its mild to moderate stages. This is because liver fibrosis doesnt usually cause symptoms until more of the liver is damaged.
When a person does progress in their liver disease, they may experience symptoms that include:
- appetite loss
Ultrasonography Ct Scanning And Mri
Noninvasive studies such as ultrasonography , computed tomography scanning, and magnetic resonance imaging are useful in helping to establish a diagnosis of steatosis, as well as in finding evidence for portal hypertension these imaging tests are also helpful in ruling out biliary dilation in patients with a cholestatic pattern of liver test result abnormalities.
However, these imaging modalities can neither define the cause of steatosis nor reliably distinguish between benign steatosis and steatohepatitis. Benign steatosis may be focal or diffuse, whereas steatohepatitis is usually diffuse.
In patients with alcoholic steatosis, the liver appears diffusely echogenic on US. In patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , the liver is hyperechogenic or bright. Steatosis is detected only when substantial fatty change is present. Studies in patients who are about to undergo gastric bypass surgery indicate that US has a 93% predictive value for NAFLD, with an accuracy of 76%. Patients with steatosis on US have a higher incidence of coronary artery disease and should undergo cardiac evaluation if suspicious symptoms are present.
The mean CT count is lower in the liver than in the spleen. CT scans may be used to monitor the course of the disease on successive scans. Focal fatty lesions may be identified by dual-energy CT scans that demonstrate increased attenuation with increasing energy.
Recommended Reading: Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Pathogenesis Of Steatosis In Chronic Hepatitis C
IR emerges as a very important host factor, mainly because it has been related to steatosis development, fibrosis progression and non-response to peg-interferon plus ribavirin. HCV directly associates with IR independent of the visceral fat area in non-obese and non-diabetic patients. HCV is directly associated with IR in a dose-dependent manner, independent of the visceral adipose tissue area.
Factors associated with steatosis in chronic hepatitis C are: viral factor host factors , and drug therapy . The mechanisms underlying the development of parenchymal steatosis in HCV infection are not exactly known.
The first mechanism supposes that HCV core protein may block assembly of Apo-A1-A2 with TAG. This will result in decreased export of TAG bound to apolipoprotein- as VLDL out of hepatocyte, which is corrected by antiviral therapy. Others propose that the core protein induces oxidative stress within the mitochondria that contributes to lipid accumulation. Though the exact mechanism remains elusive, it seems that HCV itself can directly induce steatosis in genotype 3 by the cytopathic effect of high titer of intracytoplasmic negative strand HCV RNA.
The main deleterious effect of IR in chronic hepatitis C is the ability to promote fibrosis progression. High serum glucose levels have been found associated with an increased rate of fibrosis progression, even greater than overweight.
Lose Weight If Needed
Losing weight can help you reverse fatty liver disease. When you lose fatty tissue, this also means that you are losing fat from your liver.
To facilitate weight loss, aim to create a calorie deficit, meaning you are burning more energy than you consume. Eating healthy foods, controlling portion sizes, and exercising help encourage weight loss.
Make sure that you follow a balanced diet to lose weight, instead of following extreme diet plans. In addition to losing fat, its essential to also maintain muscle mass.
You May Like: How Contagious Is Hepatitis C
Symptoms And Treatments For High Iron
Overview of High Iron High iron, a condition known as hemochromatosis, is when the body absorbs too much iron from the foods. The excess iron usually accumulates in the organs, including the liver, heart, and pancreas. When iron stores overtime in these vital organs, it can lead to life-threatening conditions, …
Liver Biopsy And Histopathologic Examination
Liver biopsy and histopathologic examination are important components of the diagnostic evaluation in patients with suspected alcoholic liver disease . They are the most sensitive and specific means of evaluating the degree of liver cell injury and hepatic fibrosis. Several reasons justify obtaining a liver biopsy in patients with ALD, including the following:
-
Confirming the diagnosis
-
Excluding other unsuspected causes of liver disease
-
Assessing the extent of liver damage
-
Defining the prognosis
In making the decision on whether to perform a biopsy, it is important to consider the strength of the clinical diagnosis and the role that the biopsy findings would have in guiding therapeutic options. For patients who are unlikely to receive specific treatments or who have conditions that make a biopsy unsafe, the 2018 ALD guideline recommends including procedure risk in the biopsy decision.
A liver biopsy and histopathologic examination are required to establish the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease . The diagnosis should be considered in all patients with unexplained elevations in serum aminotransferases . It should also be considered in patients with NAFLD who are at increased risk of having steatohepatitis and/or advanced fibrosis. The Brunt classification is the standard used to report NAFLD and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis biopsy specimens.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms To Hepatitis C
Progression Of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease can progress and develop into more severe forms of liver disease. The first step in the progression of fatty liver disease is nonalcoholic steatohepatitis . Steatohepatitis indicates that fatty liver disease is now causing inflammation within your liver. If your liver is inflamed, this means that the livers cellular processes are not operating as smoothly as usual. The tissues are irritated, and liver processes are essentially clogged.
The progression of liver steatosis tends to be more rapid if you also have other conditions like hepatitis C or iron deposition in the liver.
What is the NASH liver disease life expectancy? Generally, if diet and lifestyle changes are made and recommended medical interventions are followed, an individual with NASH can live a long healthy life.
If NASH is left untreated, it can lead to liver fibrosis, also known as hepatic fibrosis. Fibrosis describes the development of scar tissue in the liver. Over time, fibrosis can lead to liver cirrhosis. Liver cirrhosis describes the significant scarring of the liver and impeded liver functions. Over time, liver cirrhosis can lead to liver cancer or liver failure.
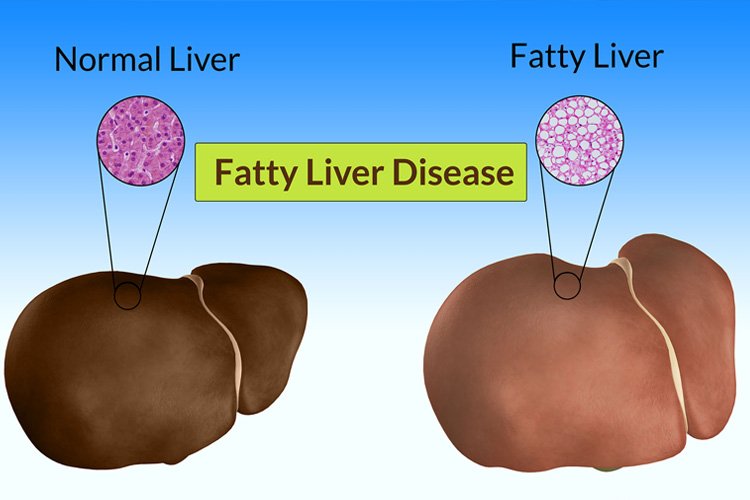
What Is Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
NAFLD is a type of fatty liver disease that is not related to heavy alcohol use. There are two kinds:
- Simple fatty liver, in which you have fat in your liver but little or no inflammation or liver cell damage. Simple fatty liver typically does not get bad enough to cause liver damage or complications.
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis , in which you have inflammation and liver cell damage, as well as fat in your liver. Inflammation and liver cell damage can cause fibrosis, or scarring, of the liver. NASH may lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Also Check: My Husband Has Hepatitis A Can I Get It
Causes Of Fatty Liver Disease
Eating excess calories causes fat to build up in the liver. When the liver does not process and break down fats as it normally should, too much fat will accumulate. People tend to develop fatty liver if they have certain other conditions, such as obesity, diabetes or high triglycerides.Alcohol abuse, rapid weight loss and malnutrition may also lead to fatty liver. However, some people develop fatty liver even if they have none of these conditions.
Measurements And Definitions Of Laboratory Parameters
A total of 5ml of venous blood sample was collected from each patient who had been fastened for at least 8h before 18F-FDG PET/CT scanning and used for determination of 1) alanine aminotransferase , aspartate aminotransferase , total cholesterol , triglyceride , high-density lipoprotein cholesterol , low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and fasting blood glucose using Hitachi 7600120 automatic biochemical analyzer, 2) thyroid stimulating hormone and fasting insulin levels using Roche Cobas 8000 automatic electrochemical immunoassay analyzer, and 3) fasting glycosylated hemoglobin using high-pressure liquid phase method on Bio-Rad D-10 Hemoglobin Analyzer. Patients with ALT 50u/L were considered to have abnormal liver function. Patients who had been diagnosed as diabetes or who had fasting blood glucose 7.0mmol/L or HbA1c6.5% were diagnosed as diabetes according to the 2017 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes issued by American Diabetes Association . According to the guidelines , patients who met at least one of the following criteria: serum TC6.22mmol/L, serum TG2.26mmol/L, serum HDL-C< 1.04mmol/L and serum LDL-C4.14mmol/L were diagnosed as dyslipidemia. The homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance index was calculated according to the following formula : fasting insulin ×fasting glucose /405. HOMA-IR> 2.5 was defined as insulin resistance .
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Advanced Hepatitis C
Can Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Cause Complications
The main risk of NAFLD is cirrhosis, which can limit your livers ability to do its job. Once youve been diagnosed with cirrhosis, it cant be reversed, but there are treatment options that can slow it down, or stop it.
If cirrhosis is not slowed or stopped, it can result in liver failure, which means your liver can no longer do its job. This may mean youll need a liver transplant.
Liver cancer is another possible complication of untreated cirrhosis.
There is no specific medication or procedure to treat NAFLD. Instead, your doctor will most likely recommend several important lifestyle changes. These include:
- losing weight
- eating a nutrient-dense diet full of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains
- limiting your intake of unhealthy fats and added sugars
- increasing physical activity
- managing your cholesterol and blood glucose levels
- avoiding alcohol
What Causes Fatty Liver Disease
Some people get fatty liver disease without having any pre-existing conditions. But these risk factors make you more likely to develop it:
- Having Type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Having metabolic syndrome .
- Taking certain prescription medications, such as amiodarone , diltiazem , tamoxifen or steroids.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatic Flexure Cancer
Expression Of The Fatty Liver Disease Gene Depends On Environment
Your DNA an abbreviation short for deoxyribonucleic acid is a code that makes you human and determines your individual traits. Some traits, such as eye color, are influenced by just two genes and based on your inherited genes, will remain set in stone for your lifetime.
Other traits, such as personality, are much more complex and described as polygenic traits since they are influenced by a large number of different genes. An individuals personality like introversion or open-mindedness is highly influenced by both genes and the environment. For example, a naturally introverted child may become more extroverted over time in response to positive experiences with family and peers.
The expression of the genes contributing to fatty liver disease is comparable to more complex traits, like personality. Inheriting certain forms of the gene may predispose you to fatty liver disease under certain environmental conditions.
Role Of Fatty Acid Oxidation In Hepatic Steatosis
Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. Short- and medium-chain fatty acids traverse the plasma membrane passively while long-chain fatty acids require membrane transporters . LCFAs are acylated in the cytosol and then enter the mitochondria, helped by the carnitine acyl-transferases CPT1 and CPT2. The -oxidation of acyl-coenzyme A takes place in the mitochondria and consists of 4 reactions, with the last 3 catalyzed by the mitochondrial trifunctional protein. -Oxidation spiral leads to the formation of acetyl-CoA, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide , and flavin adenine dinucleotide from each oxidation cycle. NADH and FADH2 are used by the mitochondrial respiratory chain to generate adenosine triphosphate.
Studies from our group at the University of Missouri document a role for mitochondrial dysfunction in the development of steatosis. Mice heterozygous for MTP that were fed a low-fat chow diet developed insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in parallel by 9 months of age. This primary defect in mitochondrial -oxidation also causes hepatic insulin resistance, which is selective to impairments in hepatic glycogen metabolism and independent from factors that are known to cause hepatic insulin resistance, such as diacylglyceride and ceramide accumulation in the liver.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Sexually
Fate Of Fatty Acids In The Liver
In the fasting state, adipocyte TAG is hydrolyzed to release FFAs, which are transported to the liver where they can serve as substrates for mitochondrial -oxidation. -oxidation of fatty acids is a major source of energy needed to maintain liver viability during fasting. It is also the source of the ketone bodies, acetoacetate and acetone. These are released into the blood and are essential fuel sources for peripheral tissues, when glucose is in short supply. Defects in hepatic -oxidation cause microvesicular steatosis of the liver, increase in oxidative stress due to extramitochondrial oxidative stress. ROS and peroxidation products lead to cytotoxic events, release of proinflammatory cytokines and activation of hepatic stellate cells and fibrosis.
Living With Fatty Liver Disease
If you are living with fatty liver disease, learn as much as you can about your condition and work closely with your medical team. Since many medications can harm your liver, always let all your health care providers know about any medications you are taking. These include OTC drugs, dietary supplements, and vitamins. Other ways to manage fatty liver disease include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and continuing to avoid alcohol.
Recommended Reading: Is There Immunization For Hepatitis C
Greens To Prevent Fat Buildup
Compounds found in spinach and other leafy greens may help fight fatty liver disease.
A 2021 study found that eating spinach specifically lowered the risk of NAFLD, possibly due to the nitrate and distinct polyphenols found in the leafy green. Interestingly enough, the study focused on raw spinach, as cooked spinach did not have the same strong results. This could be because cooking spinach may result in lowered polyphenolic content and antioxidant activity.