Current Therapy Related Information
In recent years, direct-acting antiviral agents become available to treat patients with hepatitis C, offering the advantage of higher efficacy rates and reduced side effects compared with the former standard therapy, pegylated interferon plus ribavirin for up to 48 weeks. Several all-oral treatments for have been approved, both federally and provincially. Interferon-free treatment options include sofosbuvir/ledipasvir , ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir + dasabuvir , sofosbuvir/velpatasvir , grazoprevir/elbasvir , and ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir . They offer patients a low pill burden, few side effects, a shorter treatment length , and efficacy rates of 90% or higher.
Currently, the biggest barrier to treatment with the new combinations is their high cost, and treatment rates remain low. Accessing treatments may be challenging, particularly for patients with multiple barriers or minimal liver damage. Patients in rural and remote areas, in particular, may have difficulty in accessing a hepatitis specialist.
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
Should pregnant women be tested for HCV antibodies?
Yes. All pregnant women should be screened for anti-HCV during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is < 0.1% . Pregnant women with known risk factors should be tested during each pregnancy, regardless of setting prevalence. Any pregnant women testing positive for anti-HCV should receive a PCR test for HCV RNA to determine current infection status.
Can a mother with hepatitis C infect her infant during birth?
The overall risk of an infected mother transmitting HCV to her infant is approximately 4%8% per pregnancy . Transmission occurs during pregnancy or childbirth, and no prophylaxis is available to protect the newborn from infection. The risk is significantly higher if the mother has a high HCV viral load, or is coinfected with HIV with which the rate of transmission ranges from 8%15% . Most infants infected with HCV at birth have no symptoms.
Should a woman with hepatitis C be advised against breastfeeding?
When should children born to HCV-infected mothers be tested to see if they were infected at birth?
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Are pregnant
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have HIV
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
Read Also: How To Find Out If You Have Hepatitis
Most Read Local Stories
Garon died a week after his doctor told him a University of Washington Medical Center committee had again denied him a spot on the liver transplant list.
He said Im going to die with such conviction, Garon told an AP reporter at the time. Im not angry, Im not mad, Im just confused.
Garon believes he contracted hepatitis C by sharing needles with speed freaks as a teenager. In recent years, he said, pot has been the only drug hes used. In December, he was arrested for growing marijuana.
He had been in the hospice for two months and previously was rejected for a transplant at Harborview Medical Center.
Harborview said he would be considered if he avoided pot for six months and the university hospital offered to reconsider if he enrolled in a 60-day drug treatment program, but doctors said his liver disease was too advanced for him to last that long. The university hospital committee agreed to reconsider anyway, then denied him again.
In a May 1 story about the death of Timothy Garon, The Associated Press reported erroneously that a doctor had told Garon the previous week that he had been denied placement on a liver-transplant list due to his use of medical marijuana. According to Garons family and lawyer, the doctor did not give a reason for the denial.
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatments For Hepatitis C Infection
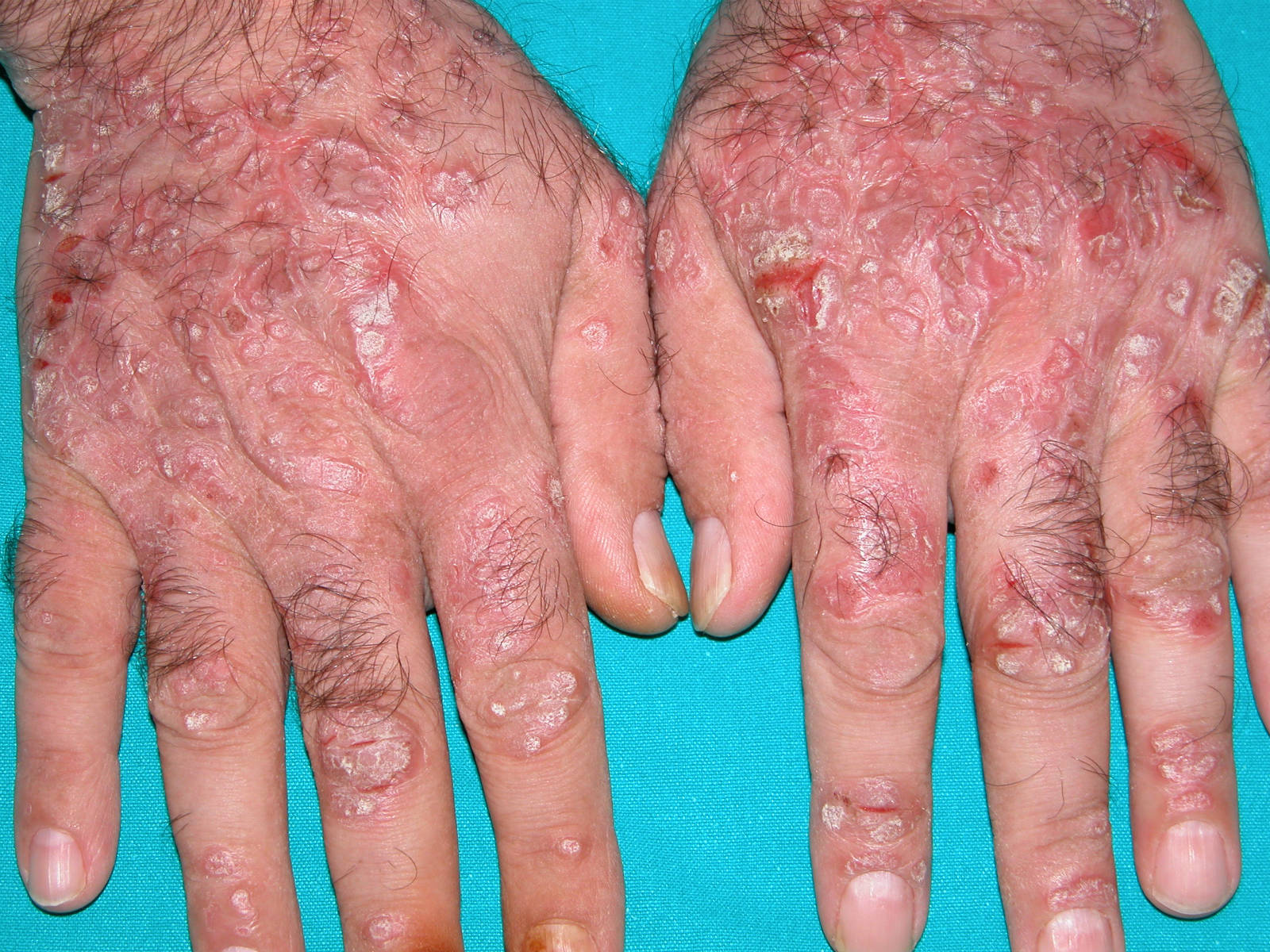
Side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon
- The most common side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon include fever, flu-like symptoms, and depression. Patients must be monitored closely for depression. Risk of suicide is a reason to avoid interferons.
- Interferons also reduce white blood cell and/or red blood cell counts . This may cause increased susceptibility to infection. Interferons also increase the risk of certain cancers. Death rarely occurs as a result of therapy, but may occur from progression of liver failure in patients with advanced cirrhosis.
Side effects of ribavirin
- Ribavirin most commonly causes anemia due to destruction of red blood cells . This can be severe enough that people with heart disease may suffer a heart attack from insufficient blood flow, so people with heart disease should not receive this drug. Anemia improves with a reduction in the dose of ribavirin. Injected growth factor that stimulates the production of red blood cells often is used to improve the anemia associated with ribavirin. Ribavirin also accumulates in the testicles and ovaries and causes birth defects in animals. Although no birth defects have been reported in humans, both men and women should use contraceptive measures to avoid pregnancy during and for at least six months after ribavirin treatment.
Side effects of DAAs
- The most common and significant side effects of boceprevir , sofosbuvir , and ledipasvir/sofosbuvir include
- fatigue ,
Read Also: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B
What Laboratory Tests Diagnose Hepatitis C
Laboratory blood tests will be done to evaluate the patient’s liver function and to look for hepatitis C antibodies . If these tests indicate that the person has hepatitis C, a hepatitis C “viral load” test will be done. This looks for genetic material from the hepatitis C virus and measures the quantity of hepatitis C virus that is circulating in the patient’s blood. This is helpful in determining if treatment is appropriate and to monitor the success of the treatment .
Individuals who had hepatitis C in the past and cleared the virus on their own will have a positive HCV antibody test, but there will be no hepatitis C virus genetic material in the blood. If a person is immunosuppressed due to an immunological condition, cancer chemotherapy, immunotherapy or HIV/AIDS, the test results may be different and need to be evaluated accordingly.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Virus
Symptoms for HCV may not appear for 20 to 30 years, and that is why it is so important to get tested. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control now recommends that all adults 18 years and older are tested at least once for HCV. Some high risk groups may need more frequent testing, and all pregnant women should be tested during every pregnancy.
HCV can actually clear itself from the body in about 15% of people, but most people become infected with the virus chronically.
Early symptoms of acute HCV occur within 1 to 3 months and may last several weeks. These may include:
- yellow-colored skin or eye sclera
- weakness
- nausea and stomach pain
- joint or muscle pain
Chronic, long-term symptoms of HCV can include weight loss, fluid build-up and swelling, poor appetite, fatigue, easy bruising and bleeding, itchy skin, jaundice, dark-colored urine, confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech , and spider-like blood vessels on the skin .
Read Also: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Blood And Vessel Problems
People with hepatitis C often get a condition called cryoglobulinemia. This happens when certain proteins in your blood stick together in cold weather. They can build up in vessels and block blood flow, which causes swelling and damage. The condition can affect your skin, organs, nerves, and joints.
Hepatitis C also can cause problems with blood itself. You may not make enough white blood cells, which fight infections, or platelets, which help your blood clot.
The infection can also make you bruise easily or get red or purple spots under your skin. Those are signs of a bleeding disorder called immune thrombocytopenic purpura.
What Drugs Treat And Cure Hepatitis C
The treatment of chronic hepatitis C has gone through several generations of medications. Not long ago, treatment was limited to interferon alpha-2b or pegylated interferon alpha-2b , and ribavirin . Interferon and pegylated interferon need to be injected under the skin , while ribavirin is taken by mouth. This combination therapy is infrequently used today, being recommended for only the least common genotypes of hepatitis C virus .
Since 2010, direct-acting antiviral drugs have been in use. The second generation of antivirals for HCV was the protease inhibitors telaprevir and boceprevir , both taken by mouth. These were used in combination with the earlier drugs to increase effectiveness . These drugs are also no longer in common use, and have been replaced by better options.
As more has been learned about how hepatitis C virus multiplies within the liver cells, new drugs continue to be developed to interfere with this multiplication at different stages. As such, we no longer think in terms of generations of drugs, but rather categories of action. Research and development of these direct-acting antivirals continue, with new agents coming to market every few months. Each category is improved and expanded by the addition of new drugs, which are safer and more effective.
Currently available and commonly used direct-acting antiviral drugs include:
- simeprevir
- Muscle aches
Recommended Reading: How Much Does A Hepatitis A Shot Cost
Hepatitis C Symptoms & Treatments
Hepatitis is a group of viruses that causes liver inflammation and damage. The hepatitis C virus is transmitted from one person to another in blood or other body fluids, such as semen and vaginal secretions.
Hepatitis C is the most common cause of viral hepatitis and one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease in the United States. The majority of people infected with hepatitis C develop chronic hepatitis C, however, most remain without symptoms.
While there is still no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C, there are now medications that can cure most cases of chronic HCV. These oral medications are taken every day for two to six months.
The first of a group of oral medications to significantly boost the cure rate for hepatitis C were approved by the FDA in 2013 and 2014. Until then, treatment to control chronic HCV required weekly injections and oral medications that many people couldnt tolerate because of other health problems or unacceptable side effects.
Symptoms for hepatitis C can take decades to develop. Because of this, approximately half of those with HCV don’t know they’re infected. Thats why the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that everyone at risk for hepatitis C be screened for the infection.
The hepatitis C virus is transmitted from person to person through blood, semen, vaginal secretions, or other body fluids. Risk factors for developing hepatitis C include:
- Dark urine
Hepatitis C And Liver Transplantation
Some people with advanced hepatitis C infection and severe liver damage undergo a liver transplant, but that doesn’t eradicate the infection. Patients with active infection at the time of the transplant will develop hepatitis C in the new liver. Sometimes the infection recurs even when patients are on antiviral treatment. Those who have achieved sustained virologic response – meaning no detectable virus in the blood 6 months after treatment – have a very low risk of developing hepatitis C infection in the new liver.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted Cdc
When To Seek Medical Advice
See your GP if you persistently have any of the later symptoms above, or if they keep returning. They may recommend having a blood test that can check for hepatitis C.
Read more about diagnosing hepatitis C.
None of the symptoms above mean you definitely have hepatitis C, but it’s important to get them checked out.
You should also speak to your GP about getting tested if there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you don’t have any symptoms. This particularly includes people who inject drugs or have done so in the past.
Read about the causes of hepatitis C for more information about who’s at risk of having the infection.
Page last reviewed: 21 June 2018 Next review due: 21 June 2021
Notes Comments And Feedback

Despite our very best efforts to allow anybody to adjust the website to their needs, there may still be pages or sections that are not fully accessible, are in the process of becoming accessible, or are lacking an adequate technological solution to make them accessible. Still, we are continually improving our accessibility, adding, updating and improving its options and features, and developing and adopting new technologies. All this is meant to reach the optimal level of accessibility, following technological advancements. For any assistance, please reach out to
Don’t Miss: How Does A Person Contract Hepatitis
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
Blood tests for hepatitis C
There are several blood tests for the diagnosis of hepatitis C infection. Blood can be tested for antibody to hepatitis C . It takes about 8-12 weeks on average, and up to 6 months, for antibodies to develop after the initial infection with hepatitis C, so screening for antibodies may miss a few newly infected individuals. Having antibodies is not an absolute indication of active, multiplying hepatitis C virus, but if the antibody test is positive , the statistical probability of active infection is greater than 99%.
Several tests are available to measure the amount of hepatitis C virus in a person’s blood . The hepatitis C virus’s RNA can be identified by a type of test called polymerase chain reaction that detects circulating virus in the blood as early as 2-3 weeks after infection, so it can be used to detect suspected acute infection with hepatitis C early infection. It also is used to determine whether active hepatitis is present in someone who has antibodies to hepatitis C, and to follow the viral load during treatment.
Blood tests are also performed to identify the genotypes of HCV. Genotypes respond differently to different treatment, so this information is important in selection of the most appropriate treatment regimen.
Estimation of liver fibrosis using blood tests also is quite reliable in diagnosing clinically significant scarring these include FIB-4, FibroSure, Fibrotest, and aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index .
Preventing The Spread Of Hepatitis C
There is no vaccine available to prevent a person from being infected with hepatitis C. Recommended behaviours to prevent the spread of the virus include:
- Always use sterile injecting equipment. This can be accessed from your local needle and syringe program service.
- Avoid sharing personal items such as toothbrushes, razors, nail files or nail scissors, which can draw blood.
- If you are involved in body piercing, tattooing, electrolysis or acupuncture, always ensure that any instrument that pierces the skin is either single use or has been cleaned, disinfected and sterilised since it was last used.
- If you are a healthcare worker, follow standard precautions at all times.
- Wherever possible, wear single-use gloves if you give someone first aid or clean up blood or body fluids.
- Although hepatitis C is not generally considered to be a sexually transmissible infection in Australia, you may wish to consider safe sex practices if blood is going to be present, or if your partner has HIV infection. You may wish to further discuss this issue and personal risks with your doctor.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis C Go Away On Its Own
Chronic Hepatitis C Symptoms
If you donât get diagnosed and treated, you could have the disease for years and not know it. Doctors call this the chronic form, because it lasts a long time. Some people who’ve had it for a while get scarring of the liver, which is called cirrhosis. or liver cancer.
In addition to the above symptoms, signs that your liver isnât working the way it should include:
- Ascites — fluid buildup in your belly
- Easy bleeding
- Hepatic encephalopathy — confusion, drowsiness, and slurred speech
- Jaundice of the skin
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people who contract hepatitis C do not have any symptoms, especially in the early stages. However, some people do develop early symptoms, which may include:
- Painful joints
- Rash
- Swelling
But 3 out of 4 cases result in a chronic infection. In these people, symptoms may develop years, even decades later, when liver damage occurs. Others develop symptoms from 2 weeks to 6 months after infection. The average time to develop symptoms is 6 to 7 weeks after acquiring the virus. Those newly infected with hepatitis C may experience mild-to-severe fever, fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, joint pain, dark urine, clay-colored stool, and yellowing of the skin . A person who has hepatitis C infection but isn’t exhibiting any symptoms can still pass the virus on to others.
Recommended Reading: Home Remedies For Hepatitis C In Urdu
Symptoms Of Hcv Infection
About 70 to 80 percent of individuals who contract HCV show no symptoms of acute hepatitis. When present, symptoms of acute illness may include fever, malaise, nausea, jaundice, arthralgia , dark urine, pale stools, and abdominal pain. Acute symptoms typically subside within several weeks. In very rare instances, primarily when another chronic liver disease is present, acute illness culminates in fulminant hepatic failure.
In roughly 70 to 90 percent of persons infected with HCV, the virus persists in the liver following the acute phase of infection. In the majority of cases, chronic infection is asymptomatic for decades. The infection may be noticed only after routine blood tests reveal elevated levels of liver enzymes, by which time liver function has begun to decline. Symptomatic patients may experience fatigue, nausea, anorexia, myalgia , arthralgia, weakness, and weight loss. Complications arising from chronic HCV infection include cirrhosis , liver failure, and liver cancer.