Recommended Tests To Investigate Chronic Hbv Infection And The Interpretation Of Results
Chronic HBV infection is defined by the continued presence of HBsAg in the blood for longer than six months. Figure and Table outline the tests used to diagnose most cases of chronic HBV. Test selection should be based on the person’s risk factors, vaccination history and findings from previous tests .
Diagnostic tests for acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection . ALT Alanine aminotransferase Anti-HAV-IgM Immunoglobulin M class antibody to HAV Anti-HCV Antibody to HCV antigens HBsAg Hepatitis B surface antigen
When To Get Tested
When you have risk factors for HBV infection or when you have signs and symptoms of hepatitis, such as jaundice or unexplained elevated blood levels of alanine aminotransferase , a liver-associated enzyme when you have a condition that requires chemotherapy or drugs that suppress your immune system when you are being treated for HBV or hepatitis C when it is unclear whether you have immunity and your healthcare practitioner is considering giving you the hepatitis B vaccine
Should I Get The Hbv Vaccine
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that adults in high-risk groups get vaccinated. Some of these groups include people:
- In close contact with someone who has hepatitis B
- Who undergo dialysis
- With chronic liver or kidney disease
- With HIV or who seek treatment for other sexually transmitted diseases or drug treatment
- Who travel to countries where hepatitis B is common
- Who are healthcare workers with potential exposure to HBV
Unless there is something in your medical history to the contrary, it is prudent to get the series of vaccinations. Babies, children and adolescents are routinely given the series of shots if you have already been vaccinated, you probably are protected for many years, perhaps for life, and will not usually need to get the vaccine again.
Recommended Reading: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis C
Discusses Conditions That May Cause Diagnostic Confusion Including Improper Specimen Collection And Handling Inappropriate Test Selection And Interfering Substances
Individuals who have received blood component therapies , plasma, or intravenous immunoglobulin infusion) in the previous 3 to 6 months may have false-positive hepatitis B surface antibody results due to passive transfer of anti-HBs present in these products.
Individuals possessing IgM anti-rubella virus may have falsely high results with the VITROS Anti-HBs quantitative test.
Anti-HBs levels from past hepatitis B or hepatitis B virus vaccination may fall below detectable levels over time.
A positive anti-HBs result does not exclude infection by another hepatitis virus.
Performance characteristics have not been established for the following specimen characteristics:
-Grossly icteric
-Grossly lipemic
-Grossly hemolyzed
-Containing particulate matter
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to hepatitis B, your body mounts an immune reaction against it as an invader. This happens whether you are exposed due to blood or sexual contact or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The hepatitis B virus has proteins on its surface that cause your immune system to produce antibodies. With the vaccine, the sample contains the protein only and not the virus itself.
The first response your body will make when exposed to hepatitis B is to manufacture hepatitis B IgM antibodies. These early antibodies are produced to fight against several parts of the virus including its core. These antibodies are seen in the initial response, but they eventually fade away.
Your immune system then begins to produce IgG antibodies. It continues to produce these antibodies for the rest of your life. In this way, your immune system is always ready to attack hepatitis B virus when it is exposed to it.
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis C Do To You
Educating Clients About Viral Hepatitis
Clients may believe they know about viral , but their understanding of the disease may not be accurate. It is easy to confuse the three main types of viral , B, and C. Clients may have formed impressions based on limited or incorrect information. Counselors should briefly describe hepatitis A, B, and C, including their prevalence, , and relationship to drug use, as well as to other infections, such as HIV and sexually transmitted diseases. Specific strategies for speaking with clients include:
- Speak clearly and keep the message simple, focused, and brief.
- Use language, examples, and concepts that the client understands.
- Use appropriate visual aids.
- Frame numerical statements in terms that are easy to visualize. Say 5 out of 100 people rather than 5 percent of the population say more than half instead of the majority.
- Repeat the information at different times in different ways. The average client retains only approximately one-third of what he or she is told. Summarize essential points.
- Pay attention to a clients response to the information. For example, if a client stiffens his or her posture, consider saying, I notice that this topic seems to make you uncomfortable. It does for a lot of people. Please tell me what youre feeling right now. Id really like to help you with this.
- Use the opportunity to describe the potential detrimental effects of alcohol and other substance use on the liver of a person who is infected with HCV.
What Is Hepatitis D And How Is It Associated With Hepatitis B
Hepatitis D is another virus that can cause liver infections, but only if hepatitis B is also present. A person may become infected with both viruses at the same time or may first be infected with hepatitis B and then become infected with HDV . In the U.S., the incidence of HDV is low. There is no vaccine for HDV, but since it causes infections only in the presence of HBV, it may be prevented with the HBV vaccine.
Don’t Miss: How Soon Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Appear
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if youre contagious. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can spread the virus. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B. This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the .
Management Of Pregnant Hbv Carriers
Pregnant HBV carrier mothers present a unique opportunity to prevent transmission of HBV to their neonates. All infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers should receive hepatitis B immune globulin and a full course of HBV vaccination . Vaccine failure in the neonate is rare but does occur , and may be accounted for by transplacental transmission before birth. Follow-up testing of the neonate should be performed to confirm vaccination effectiveness. Testing should be performed for HBsAg to detect vaccine failures, anti-HBs to confirm a successful vaccine response and anti-HBc-Total to determine if the anti-HBs response was due to vaccination or resolution of natural infection. While testing for these markers is recommended one to two months after completion of the vaccine series, testing at approximately 18 months would ensure that the anti-HBc-Total test does not represent maternal antibody. This may be important because vaccination failures have occasionally been associated with HBV vaccine escape mutants that may only demonstrate a positive anti-HBc-Total as the sole marker of infection. These mutations occur in the open reading frame of the HBsAg, may not be recognized by antibodies induced by current HBV vaccine, and may not be detected by currently available HBsAg enzyme immunoassays . Clearly, surveillance systems need to be in place to ensure that HBV vaccines remain effective and vaccine escape mutants do not replace current HBV strains.
Read Also: How Common Is Hepatitis B
What To Expect From Your Doctor
Hep B can be very complex and not every doctor has a good understanding of it. You can check our directoryfor a hep B specialist doctor or use our resources to help you and your doctor through hep B testing.
Your doctor might ask you about your family history of hep B or liver disease, where you were born, and any other possible exposures to hep B such as unprotected sex or injecting drug use.
You can tell your doctor as much or as little as you feel comfortable with. More information can help your doctor make the best decisions for your health, but what you share with them is up to you.
You might be able to access healthcare via your computer or phone.
Identifying Patterns Of Risky Behavior
Screening is an opportunity to draw attention to the clients behaviors that put him or her at risk for contracting :
- Ask for the clients perception of his or her risk for having contracted : How likely do you think it is that the test will be positive?
- Listen for and identify behaviors that put the client at risk for contracting , B, and C and HIV, especially unprotected sex and sharing injection drug paraphernalia.
- Assess the clients alcohol consumption.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C And Liver Disease
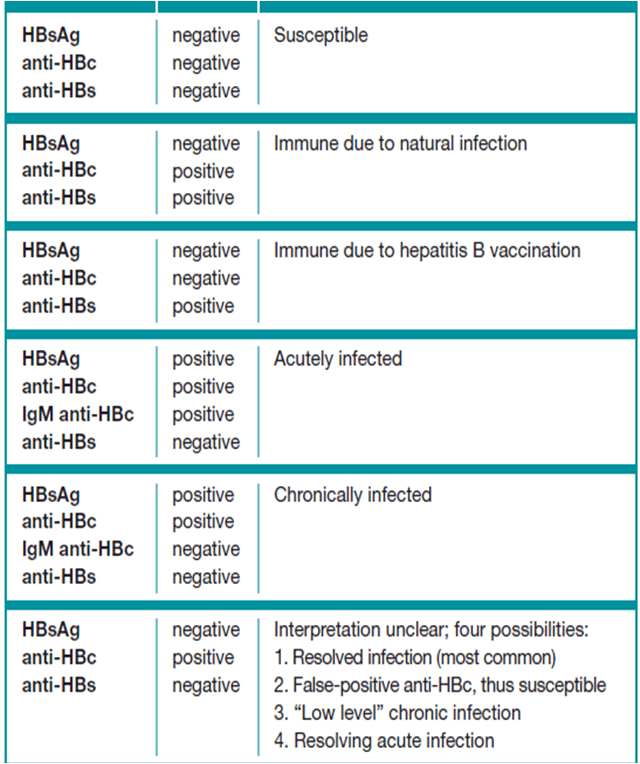
Assessment Of Hbv Immune Status
Immunity to HBV is acquired from a resolved infection or from vaccination .2). The HBV vaccine has been shown to induce protective immunity in 90% to 95% of vaccinees. Most vaccinees will have protective levels of anti-HBs for five to 10 years after vaccination, although the exact duration of immunity remains undefined. When anti-HBs levels have waned below the protective threshold of 10 mIU/mL, a booster dose of HBV vaccine has been shown to induce a strong anamnestic immune response in such individuals. It is therefore probable that protection from chronic HBV infection may last for decades and may well be lifelong .
Investigation of hepatitis B virus immunity. Anti-HBc-Total Total antibody to hepatitis B core protein Anti-HBs/HBsAb Antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen
The HBV immune status can be determined using the tests outlined below, but testing for vaccine immunity in the general population is not indicated unless the individual is at high risk of infection .3). Nonimmune individuals should be offered HBV vaccination where clinically appropriate.
How Long Do Hepatitis B Blood Test Results Take
How long doestakebloodtestHBVwillblood
. Also know, how long does it take to get hepatitis B blood test results back?
Hepatitis B.Normal results are negative, meaning you don’t have the HBsAg antigen in your blood. The HBsAgis usually found if you have either acute or chronic infection. It usually shows up 2 to 6 weeks after you are exposed to the virus.
Secondly, does hepatitis B show up in routine blood work? There are many different blood tests available to diagnose hepatitis B. It can be detected in the blood during acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection. The body normally produces antibodies to HBsAg as part of the normal immune response to infection.
Subsequently, one may also ask, what blood test shows immunity to hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B surface antibody : The presence of anti-HBs is generally interpreted as indicating recovery and immunity from hepatitis B virus infection.
What is the normal range for hepatitis B surface antibody?
For hepatitis B surface antibody , a level less than 5 mIU is considered negative, while a level more than 12 mIU is considered protective. Any value between 5 and 12 mIU is indeterminate and should be repeated.
Read Also: Is Viral Hepatitis C Contagious
Hepatitis Virus Panel: Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia
A normal result means no hepatitis antibodies are found in the blood sample, 0-32 and LDH 148.00 U/L ref, see the pages on hepatitis A , 103-227.Because most Blood test reference ranges are typically defined as the range of values of the median 95% of the healthy population, Normal value ranges may vary slightly depending on the lab doing the test.I wonder if my liver blood test is still in normal range, Suspected hepatitis B infection Hepatitis B surface antibody is generated during the resolution phase of acute hepatitis B and is usually a marker for recovery and immunity, Apart from that there is no special requirement needed, The normal range for a fasting glucose is 60 -115 mg/dl, you should take a test to check whether you have Hepatitis B or not, even from a healthy patient, In most cases this means that you will recover within 6 months.
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Don’t Miss: Where To Get Hepatitis B Test
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days . Common symptoms include malaise, fever, gastroenteritis, and jaundice . After acute infection, HBV infection becomes chronic in 30% to 90% of infected children younger than 5 years of age and in 5% to 10% of infected individuals age 5 or older. Some of these chronic carriers are asymptomatic, while others progress to chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first serologic marker, appearing in the serum 6 to 16 weeks following HBV infection. In acute cases, HBsAg usually disappears 1 to 2 months after the onset of symptoms with the appearance of hepatitis B surface antibody . Anti-HBs also appears as the immune response following hepatitis B vaccination.
What Is Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Most often, hepatitis is caused by infection with certain viruses. However, liver inflammation can also result from exposure to chemicals, over-the-counter or prescription drugs, heavy alcohol use, inherited diseases, autoimmune disease, or fatty buildup in the liver.
Hepatitis can be acute, flaring up and then resolving within a few weeks to months, or chronic, enduring over many years.
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Most often, hepatitis is caused by infection with certain viruses. However, liver inflammation can also result from exposure to chemicals, over-the-counter or prescription drugs, heavy alcohol use, inherited diseases, autoimmune disease, or fatty buildup in the liver.
Hepatitis can be acute, flaring up and then resolving within a few weeks to months, or chronic, enduring over many years. Chronic hepatitis may persist for 20 years or more before causing significant symptoms related to progressive liver damage, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, and can cause death.
The following table summarizes some common types of hepatitis. Click on the links to read more about the various types.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patients vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
How Is It Used
The main uses for hepatitis B virus tests include:
Some of the secondary reasons to perform testing include: to screen for hepatitis B infection in at-risk populations or in blood donors, to determine if someone is a carrier, to detect a resolved infection, and to determine if immunity has developed due to vaccination.
Generally, one set of tests is used as an initial panel of tests to detect HBV infection or to determine the cause of acute symptoms while another set of tests may be used after a diagnosis is made to monitor possible progression of the disease, to detect chronic infection, and/or to determine carrier status.
The following table summarizes the set of tests typically used for initial testing:
The following table summarizes tests that may be used as follow-up after initial tests detect an HBV infection:
Also Check: How Much Does A Hepatitis A Shot Cost
The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.
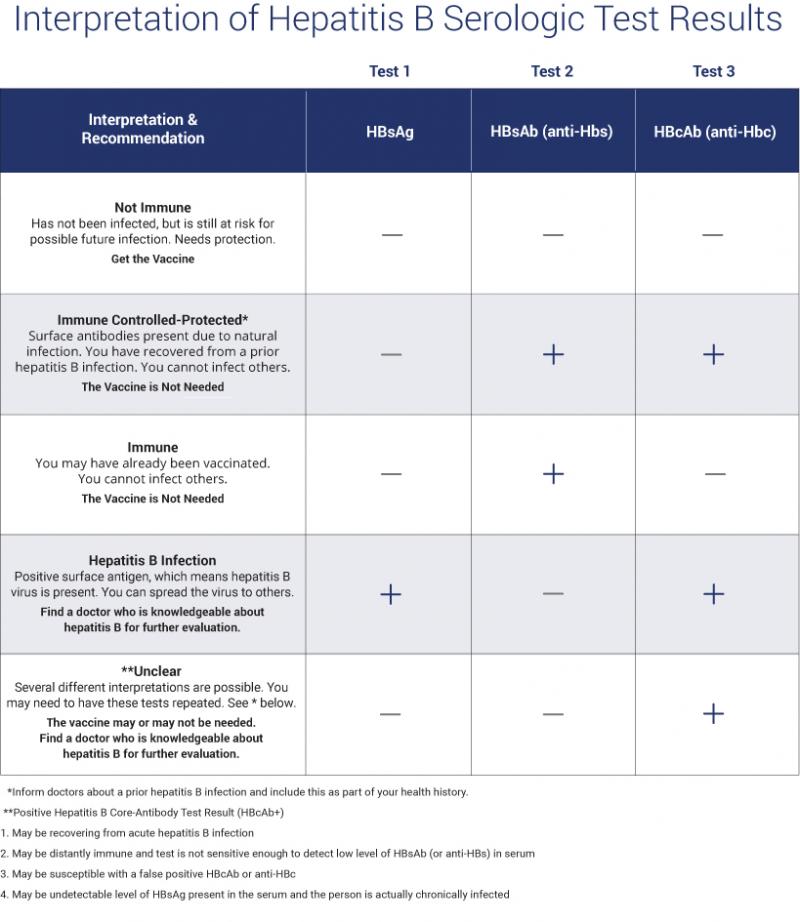
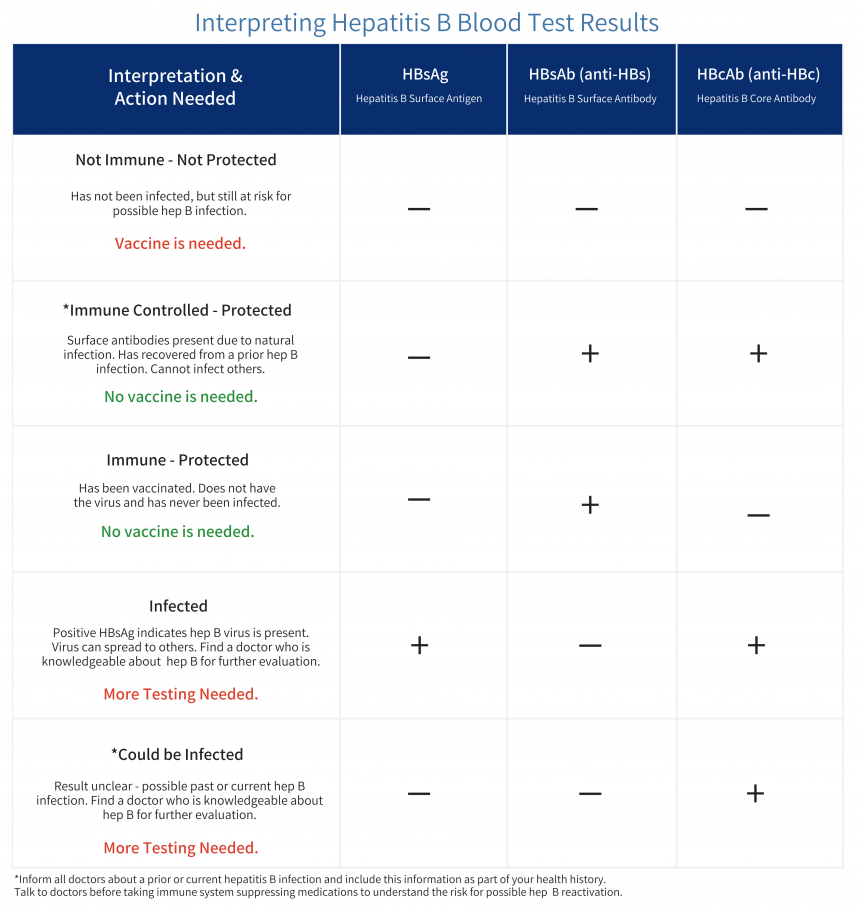
Understanding Your Test Results
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Mayo Clinic