Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Igg
Test Number: 3611850 Test Description
The reported index results are traceable to the World Health Organization Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin 1st International Reference Preparation. An Index value of 1.00 is equivalent to 10mIU/mL of HBsAb. The CDC guidelines indicate that an accepted criteria for immunity to HBV is HBsAb activity of > /= 10mIU/mL :1-26) or an index value of > /= 1.00. The system reports the HBsAb antibody activity as reactive or non-reactive along with the Index value.
Reactive > /= 1.00 Index Value or > /= 10 mIU/mL Have Protective Immunity < 1.00 Index Value or < 10 mIU/mL Does Not Have Protective Immunity) Test Notes It should be noted that the assay performance characteristics of the HBsAb assay has not been established for either immunocompromised, immunosuppressed patients or on cord blood specimens from neonates, infants, or children less than 12 years age.
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Qualitative
Presence of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen is used to determine immune status to HBV or disease progression in individuals infected with HBV. Anti-HBs levels can be measured to determine if vaccination is needed, or following a vaccination regimen, to determine if protective immunity has been achieved.
â Anti-HBs usually can be detected several weeks to several months after HBsAg is no longer found, and it may persist for many years or for life after acute infection has been resolved.
â It may disappear in some patients, with only antibody to core remaining.
â People with this antibody are not overtly infectious.
â Presence of the antibody without the presence of the antigen is evidence for immunity from reinfection, with virus of the same subtype.
What is the Hepatitis B virus?
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days .
What are common symptoms?
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patientâs vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
You May Like: How Does One Contact Hepatitis C
What Is The Difference Between The Hepatitis B Surface Antigen And The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The basic blood test for hepatitis B consists of three screening tests: a hepatitis B surface antigen test, which determines whether a person currently has the infection a hepatitis B core antibody test, which determines whether a person has ever been infected and a hepatitis B surface antibody test, which determines
Diagnosis Of Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
HBsAg is the first serologic marker to appear and may be detected within 1 to 2 weeks after exposure. It precedes the development of symptoms by an average of 4 weeks.104 The presence of HBsAg indicates ongoing infection. Qualitative but not quantitative methods are used by most clinical laboratories because the amount of antigen does not correlate with disease activity or with the presence of an acute or chronic infection.26 Some symptomatic patients may have self-limited, acute HBV infection without detectable HBsAg. These patients, up to 9% in some studies, have other detectable markers of infection.104 HBeAg appears virtually simultaneously, peaks, and then declines in parallel with HBsAg. It usually disappears before HBsAg. Adult patients who remain persistently positive for HBeAg for more than 10 weeks are likely to become chronically infected. HBeAg indicates a high level of viral replication and infectivity. Most patients with nondetectable HBeAg have resolving, minimal, or no active liver disease.26 Pre-core mutants of HBV do not express HBeAg they may be responsible for a more severe course and, in some cases, fulminant disease. Serum aminotransferase levels become raised but are nonspecific. They begin to increase just before the development of symptoms and then peak , with the development of jaundice.
Howard C. Thomas, Jennifer A. Waters, in, 1998
Recommended Reading: Can You Have Hepatitis C And Not Know It
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Home Test Kit
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to HBV, your body mounts an immune defense to specifically target and neutralize the invader. Unlike innate immunity which mounts a generalized defense against all invaders, this type of immunity is disease-specific.
This immune response occurs whether you are exposed to HBV through blood or sexual contact, or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The virus has proteins on its surface, called antigens, that serve as unique identification tags. When HBV enters the body, the immune system “encodes” antibodies specific to these antigens so that it can recognize and attack the virus should it appear again.
There are two types of antibodies produced in response to the virus:
- Immunoglobulin M is the antibody that mounts the initial attack but eventually fades away.
- Immunoglobulin G is the antibody that provides long-lasting immune protection against HBV. The immunity can last for many years, but it gradually wanes over time.
Addressing Hepatitis For The First Time
It is crucial that a treatment counselor or health professional use a nonjudgmental and compassionate tone. Clients need to feel comfortable disclosing information about their health and risky behaviors. The following strategies can help initiate the conversation:
- Display posters, literature, or other -related items that could help prompt the client to ask questions about hepatitis. .
- Assess clients ability to discuss , based on their degree of openness in the counseling session, the amount of detail they provide in their responses, and the length of the therapeutic relationship.
- Raise the subject in a way that avoids making clients feel defensive or afraid. Consider introducing the subject by making parallels with other conditions that have been discussed. Say, for example, You said you were tested for HIV several times. Were you ever tested for viral ? or You mentioned that your friend is sick with HIV. Have you been tested for HCV or HIV? Tell me about those tests.
- Be patient and allow time for multiple, short conversations about the subject. This might ease feelings of fear, anxiety, or shame.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis And What Causes It
False Positive Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Due To Recent
Hepatitis B is the most common viral hepatitis, potentially life threatening, with long term complications. Currently, vaccine is the most effective tool against hepatitis B infection. It is worthwhile mentioning that due to rampant use of hepatitis B vaccine , there have been concerns about hepatitis B surface antigen reactivity.
What Does It Mean When Hepatitis Is Reactive
A reactive or positive antibody test means you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time. Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true if they have cleared the virus, have been cured, or still have the virus in their blood.
What does it mean if hepatitis B surface antibody is non reactive?
Normal results are negative or nonreactive, meaning that no hepatitis B surface antigen was found. If your test is positive or reactive, it may mean you are actively infected with HBV. In most cases this means that you will recover within 6 months.
What is the difference between Hep B surface antigen and antibody?
The basic blood test for hepatitis B consists of three screening tests: a hepatitis B surface antigen test, which determines whether a person currently has the infection a hepatitis B core antibody test, which determines whether a person has ever been infected and a hepatitis B surface antibody test, which determines
You May Like: Do I Have Hepatitis B
Question 3 How Is The Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test Performed
An immunometric technique is used. The anti-HBs binds to HBsAg ad and ay subtypes, which are coated on the test wells. Binding of a horseradish peroxidase-labeled HBsAg conjugate to the anti-HBs completes the sandwich formation. Unbound materials are then washed away. In the next step, the horseradish peroxidase catalyzes oxidation of a luminogenic substrate, producing light. Light signals are detected and quantified. Intensity of the light is proportional to the amount of anti-HBs present in the patient sample. The result is standardized to an international unit system and reported as milliinternational units per milliliter .
Read Also: Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive Treatment
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Health Streets Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test checks for a current infection of the hepatitis B virus. If the test is positive, then the person can be contagious to others.
Online registration is simple. You choose the lab location based on ZIP code during registration. An authorization barcode is instantly emailed to you and texted directly to the phone of the person being tested. A map of the clinic location will accompany the barcode. The registrant can then walk into the testing facility and show the barcode along with photo ID. Results are fast and stored securely online. Individuals and employers can register online or call to order tests.
Recommended Reading: Hepatic Porphyrias Diagnosis And Management
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Identifying Patterns Of Risky Behavior

Screening is an opportunity to draw attention to the clients behaviors that put him or her at risk for contracting :
- Ask for the clients perception of his or her risk for having contracted : How likely do you think it is that the test will be positive?
- Listen for and identify behaviors that put the client at risk for contracting , B, and C and HIV, especially unprotected sex and sharing injection drug paraphernalia.
- Assess the clients alcohol consumption.
Don’t Miss: What Type Of Hepatitis Is Curable
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood and sexual fluids. This can most commonly occur in the following ways:
Direct contact with infected blood
From an infected pregnant person to their newborn during pregnancy and childbirth
Needles and other medical/dental equipments or procedures that are contaminated or not sterile
Unprotected sex
Use of illegal or street drugs
Body piercing, tattooing, acupuncture and even nail salons are other potential routes of infection unless sterile needles and equipment are used. In addition, sharing sharp instruments such as razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, earrings and body jewelry can be a source of infection.
Hepatitis B is NOT transmitted casually. It cannot be spread through toilet seats, doorknobs, sneezing, coughing, hugging or eating meals with someone who is infected with hepatitis B.
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
The hepatitis B surface antibody test , looks for antibodies that your immune system makes in response to the surface protein of the hepatitis B virus. The hepatitis B surface antibody is also referred to as anti-HBs and should not be confused with HBsAg, which stands for hepatitis B surface antigen.
Read Also: Hepatitis B E Antibody Reactive Means
Hepatitis B Core Igm Antibody
Order Name:HEP BCOR M Recent onset of hepatitis B infection. No evidence of recent hepatitis B infection. Indicates that test should be repeated in 1-2 weeks. Test Notes It should be noted that the assay performance characteristics of the IgM anti-HEP B core assay have not been established for either immunocompromised, immunosuppressed patients or on cord blood, neonatal specimens, infants or children less than 12 years age.
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After three intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Titer Labcorp Cost
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Non Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
Reactivation Risk In Anti
Table 1 American Gastroenterological Association classification of reactivation risk in HBsAg/anti-HBc patients Full size table
The risk of HBV reactivation can be assessed based on positivity for HBV serum biomarkers and the type, duration, combination of agents, and dosing of immunosuppressive or chemotherapeutic agents . HBV reactivation risk can be as high as 4070% in anti-HBc-only, patients who are undergoing chemotherapy with B cell depleting antibodies like rituximab .
Noting that reactivation after immunosuppressive therapy is associated with significant morbidity and mortality, the AGA recommends antiviral prophylaxis for patients classified as at either moderate or high risk for reactivation for low-risk patients, there is no prophylaxis recommendation monitoring is per provider preference but seemingly sufficient . Entecavir and tenofovir prodrugs should be used as first-line prophylaxis or therapy due to their stronger antiviral potency and high threshold for resistance.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine For Newborns
How The Test Is Performed
Blood is most often drawn from a vein from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. The site is cleaned with germ-killing medicine . The health care provider wraps an elastic band around the upper arm to apply pressure to the area and make the vein swell with blood.
Next, the provider gently inserts a needle into the vein. The blood collects into an airtight tube attached to the needle. The elastic band is removed from your arm. Once the blood has been collected, the needle is removed. The puncture site is covered to stop any bleeding.
In infants or young children, a sharp tool called a lancet may be used to puncture the skin and make it bleed. The blood collects into a small glass tube, or onto a slide or test strip. A bandage may be placed over the area if there is any bleeding.
The blood sample is sent to a lab to be examined. Blood tests are used to check for antibodies to each of the hepatitis viruses.
Read Also: How Long Does Hepatitis B Vaccine Last
What Abnormal Results Mean
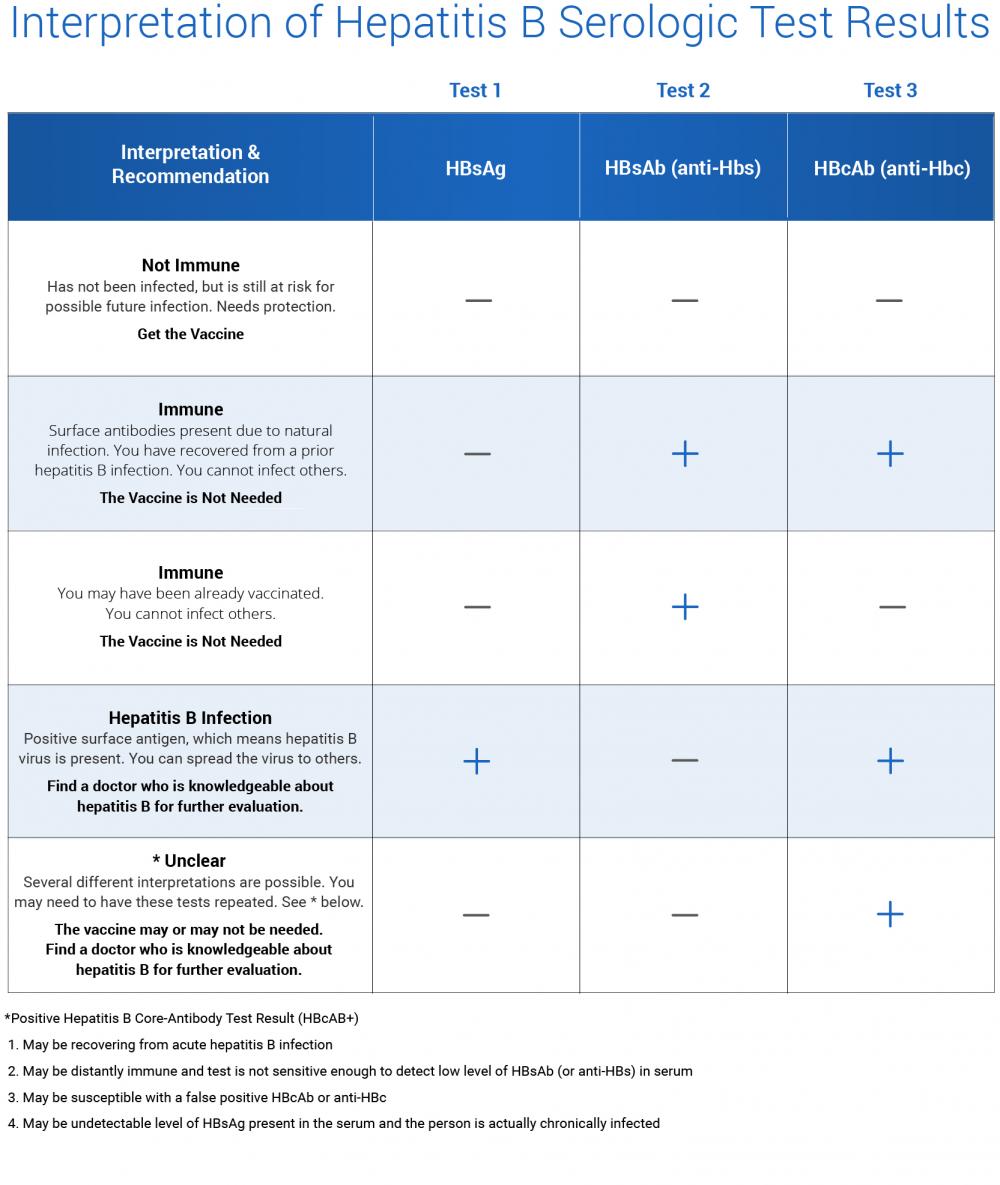
There are different tests for hepatitis A and hepatitis B. A positive test is considered abnormal.
A positive test may mean:
- You currently have a hepatitis infection. This may be a new infection , or it may be an infection that you have had for a long time .
- You had a hepatitis infection in the past, but you no longer have the infection and cant spread it to others.
Hepatitis A test results:
- IgM anti-hepatitis A virus antibodies, you have had a recent infection with hepatitis A
- Total antibodies to hepatitis A, you have a previous or past infection, or immunity to hepatitis A
Hepatitis B test results:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen : you have an active hepatitis B infection, either recent or chronic
- Antibody to hepatitis B core antigen , you have a recent or past hepatitis B infection
- Antibody to HBsAg : you have a past hepatitis B infection or you have received the hepatitis B vaccine and are unlikely to become infected
- Hepatitis B type e antigen : you have a chronic hepatitis B infection and you are more likely to spread the infection to others through sexual contact or by sharing needles
Antibodies to hepatitis C can most often be detected 4 to 10 weeks after you get the infection. Other types of tests may be done to decide on treatment and monitor the hepatitis C infection.
Also Check: Can You Spread Hepatitis C
Read Also: Can You Drink Alcohol If You Have Hepatitis C
What Does Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Ql Reactive Mean
If this test is positive or reactive, then your immune system has successfully developed a protective antibody against the hepatitis B virus. This will provide long-term protection against future hepatitis B infection. Someone who is HBsAb+ is not infected and cannot pass the virus to others.
Can reactive hepatitis B be cured?
Most adults with hepatitis B recover fully, even if their signs and symptoms are severe. Infants and children are more likely to develop a chronic hepatitis B infection. A vaccine can prevent hepatitis B, but theres no cure if you have the condition.
What is the normal level for Hep B surface AB?
For hepatitis B surface antibody , a level less than 5 mIU is considered negative, while a level more than 12 mIU is considered protective. Any value between 5 and 12 mIU is indeterminate and should be repeated.