Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
- Description
-
The Quantitative detection Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody in human sera using the FDA approved Abbott ARCHITECT AUSAB-DIL test two-step chemiluminescent immunoassay.
In the first step, sample, assay diluent, and recombinant Hepatitis B surface Antigen coated paramagnetic microparticles are combined. Anti-HBs present in the sample binds to the rHBsAg coated microparticles. In the second step, rHBsAg acridinium-labeled conjugate is added, which binds to IgG anti-HBs. Then pre-trigger and trigger solutions are added to the reaction mixture. The resulting chemiluminescent reaction is measured as relative light units .
A direct relationship exists between the amount of anti-HBs in the sample and the RLUs. The concentration of anti-HBs in the sample is determined using an active ARCHITECT AUSAB calibration curve. Results are reported as mIU/mL.
For Batteries containing HBSAb see:
Hepatitis B Antibodies , Quantitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody and Hepatitis B virus Core IgG and IgM antibodies
Hepatitis B Battery , Quantitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody , Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface Antigen and Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Core IgG and IgM antibodies
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen & Antibody , Quantitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface IgG antibody and Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus Surface Antigen
- Synonyms
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
Patients may find it helpful to ask questions about their hepatitis B test results. Questions that may be helpful include:
- What was my test result?
- Do I have an acute or chronic hepatitis B infection?
- Does the test result suggest that I have immunity for hepatitis B?
- Would I benefit from hepatitis B vaccination?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my hepatitis B test results?
Recommended Reading: What Can Hepatitis C Do To You
What Is The Difference Between The Hepatitis B Surface Antigen And The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The basic blood test for hepatitis B consists of three screening tests: a hepatitis B surface antigen test, which determines whether a person currently has the infection a hepatitis B core antibody test, which determines whether a person has ever been infected and a hepatitis B surface antibody test, which determines
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
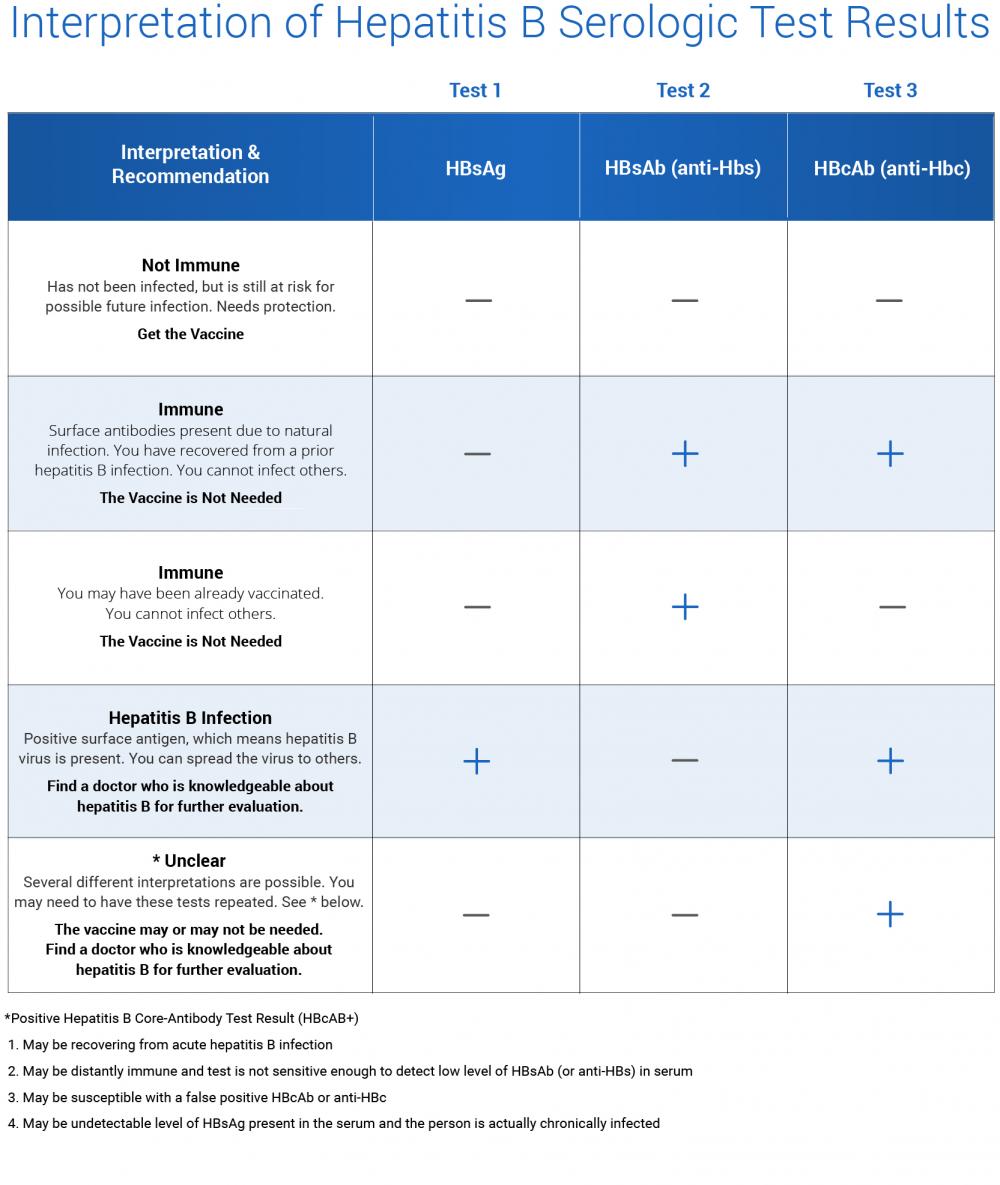
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Recommended Reading: How Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted Sexually
Read Also: Final Stage Of Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to HBV, your body mounts an immune defense to specifically target and neutralize the invader. Unlike innate immunity which mounts a generalized defense against all invaders, this type of immunity is disease-specific.
This immune response occurs whether you are exposed to HBV through blood or sexual contact, or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The virus has proteins on its surface, called antigens, that serve as unique identification tags. When HBV enters the body, the immune system “encodes” antibodies specific to these antigens so that it can recognize and attack the virus should it appear again.
There are two types of antibodies produced in response to the virus:
- Immunoglobulin M is the antibody that mounts the initial attack but eventually fades away.
- Immunoglobulin G is the antibody that provides long-lasting immune protection against HBV. The immunity can last for many years, but it gradually wanes over time.
Whats The Hepatitis B Titer Test Used For
A hepatitis B titer test measures antibodies in your blood to see if youre immune either due to vaccination or previous infection.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that targets your liver. It can be transmitted by coming into contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person. A person with the virus can also infect their child during birth.
Hepatitis B can develop into a chronic infection. Chronic infection occurs when your body cant fight off the virus within six months. Chronic hepatitis B infections most commonly develop less than six years old, especially in infants.
Hepatitis B titer tests can be used to evaluate:
- whether a high-risk person is immune to hepatitis B
- whether hepatitis B immunoglobulin is needed after a needle prick
- men who have sex with men
- people born in countries with a hepatitis B prevalence greater than 2 percent
- people born in the United States not vaccinated as children and with parents born in regions with more than 8 percent hepatitis B prevalence
You may need your titer test results as proof of hepatitis B immunity in order to get into healthcare programs at many schools for example, the nursing program at Lone Star College. In the United States, employers are not allowed to withdraw a job offer if they learn you have hepatitis B.
Don’t Miss: I Have Hepatitis B What Should I Do
Screening Tests For Hepatitis B
Your blood may be screened for HBV for many different reasons. The three tests generally include HBsAg, antibody to HBsAg, and antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. This allows the healthcare provider to know whether you could benefit from vaccination, or if you have active or chronic hepatitis B and need counseling, care, or treatment.
You may be routinely screened if you are pregnant, are donating blood or tissue, need immunosuppressive therapy, or have end-stage renal disease. You will also be screened if you are in groups that are at higher risk for HBV.
Question 1 What Is The Clinical Indication For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitation
Hepatitis B surface antibody quantitation is used to determine hepatitis B immune status, ie, to determine if the patient has developed immunity against the hepatitis B virus. Such immunity may develop following exposure to the hepatitis B virus or its vaccine.
Patients at higher risk of exposure to the virus include:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected persons
- People with more than 1 sex partner in the last 6 months
- People with a history of sexually transmitted infection
- Men who have sex with men
- Injection drug users
- Household contacts of an infected person
- Healthcare and safety workers who have contact with blood and body fluids
- People who have lived or traveled in an area in which hepatitis B is common
- People who live or work in a prison
Testing is not recommended routinely following vaccination. It is advised only for people whose subsequent clinical management depends on knowledge of their immune status. These people include:
- Chronic hemodialysis patients
- Immunocompromised people, including those with HIV infection, hematopoietic stem-cell transplant recipients, and people receiving chemotherapy
- Infants born to women who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Sex partners of people who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Healthcare and public safety workers who have contact with blood or body fluids
Recommended Reading: What Type Of Virus Is Hepatitis C
Demographic Characteristics And Clinical Status
The analytic samples drawn from 294 patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus at baseline, comprised 23 cases and 311 matched controls Table shows their demographic and clinical characteristics. Mean age and rheumatic disease types were similar between case and control groups. No patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus had detectable HBV DNA at enrolment. Compared with controls, cases had lower baseline serum anti-HBs titers, more prevalent comorbidities , and relatively higher accumulated doses of sulfasalazine, leflunomide, and prednisolone. Most people in both groups used anti-TNF agents . No study subjects were kidney transplant recipients.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of cases and controls treated with biologic DMARDs
No cases had clinical HBV reactivation during follow-up , and no cases developed alanine transaminase elevation, or received any anti-viral treatment during median follow-up of 30months after anti-HBs loss. Only one of the 16/23 cases whose serum HBV DNA was monitored after anti-HBs loss ever had a detectable viral load , which was observed only once, with no recurrence as of August 2020.
Sequence Following An Initial Negative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
As you obtain documentation, please submit documentation of each step to CastleBranch
- Initial Hepatitis B titer negative for immunity
- Receive Hepatitis B challenge dose/booster
- Repeat Hepatitis B titer 4-6 weeks after challenge/booster vaccine
Don’t Miss: What Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis C
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patients vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Clinical Information Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test

Hepatitis B e antigen is a small polypeptide that exists in a free form in the serum of individuals during the early phase of hepatitis B infection, soon after hepatitis B surface antigen becomes detectable. Serum levels of both HBeAg and HBsAg rise rapidly during the period of viral replication. The presence of HBeAg in serum correlates with hepatitis B virus infectivity, the number of infectious virions, and the presence of HBV core antigen in the infected hepatocytes.
During recovery from acute hepatitis B, HBeAg level declines and becomes undetectable in the serum, while hepatitis B e antibody appears and becomes detectable in the serum. Anti-HBe usually remains detectable for many years after recovery from acute HBV infection.
In HBV carriers and patients with chronic hepatitis B, positive HBeAg results usually indicate presence of active HBV replication and high infectivity. A negative HBeAg result indicates very minimal or no HBV replication. Positive anti-HBe results usually indicate inactivity of the virus and low infectivity. Positive anti-HBe results in the presence of detectable HBV DNA in serum also indicate active viral replication in these patients.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Transmission Routes Cdc
You May Like: Hepatitis C Can It Be Cured
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days . Common symptoms include malaise, fever, gastroenteritis, and jaundice . After acute infection, HBV infection becomes chronic in 30% to 90% of infected children younger than 5 years of age and in 5% to 10% of infected individuals age 5 or older. Some of these chronic carriers are asymptomatic, while others progress to chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first serologic marker, appearing in the serum 6 to 16 weeks following HBV infection. In acute cases, HBsAg usually disappears 1 to 2 months after the onset of symptoms with the appearance of hepatitis B surface antibody . Anti-HBs also appears as the immune response following hepatitis B vaccination.
Recommended Reading: Most Common Way To Get Hepatitis C
What Is The Most Challenging Aspect Of Hepatitis B Infection
Hepatitis B can very easily escape diagnosis, as most victims do not know they are suffering can spread the disease. This is because symptoms are almost negligible during the onset of hepatitis B infection. Although the infection is treatable and largely preventable, yet early diagnosis can go a long way in the better prognosis of the condition. Further, even though there are good treatment options for hepatitis B, close to a million people with the infection do not make it.Asian countries portray a high prevalence of hepatitis B. This infection is very common among high-risk groups such as people with multiple sex partners, homosexuals, injection drug users or people staying lose to victims of Hepatitis B.
Also Check: Hepatitis C How Is It Contracted
We Implement Proven Measures To Keep Your Data Safe
At HealthMatters, we’re committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We’ve put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
Popular search
Discusses Conditions That May Cause Diagnostic Confusion Including Improper Specimen Collection And Handling Inappropriate Test Selection And Interfering Substances
Individuals who have received blood component therapies , plasma, or intravenous immunoglobulin infusion) in the previous 3 to 6 months may have false-positive hepatitis B surface antibody results due to passive transfer of anti-HBs present in these products.
Individuals possessing IgM anti-rubella virus may have falsely high results with the VITROS Anti-HBs quantitative test.
Anti-HBs levels from past hepatitis B or hepatitis B virus vaccination may fall below detectable levels over time.
A positive anti-HBs result does not exclude infection by another hepatitis virus.
Performance characteristics have not been established for the following specimen characteristics:
-Grossly icteric
-Grossly hemolyzed
-Containing particulate matter
You May Like: What Are The Signs Of Having Hepatitis C
Understanding Of Lab Tests Results
Please visit the site associated with The American Association for Clinical Chemistry for better understanding of tests. There you will find the most detailed and full information regarding lab tests. In common questions tab you will find answers on the most common questions.
In addition, you can use a special form to ask the question. It is useful, if there is no answer on your question on the web site. A laboratory scientist will answer your question. It is a part of voluntary service provided by the American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science.
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Immunity Quantitative
CPT Code: 86317Includes: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Immunity, QuantitativeABN Requirement: No Alternative: EDTA tube
Collection:
Transport: Store specimen at 2°C to 8°C after collection and ship the same day per packaging instructions included with the provided shipping box.
Stability:
Ambient : 5 daysRefrigerated : 14 daysFrozen : 30 days
Causes for Rejection: Improper labeling samples not stored properly samples older than stability limits gross hemolysis gross lipemia
Methodology: Immunoassay
Turn Around Time: 1 to 3 days
Reference Range: 10 mIU/mL
Clinical Significance: This assay is used to determine immune status for Hepatitis B as 10 mIU/mL as per CDC Guidelines.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Treatment In Homeopathy
Question 5 What Is The Natural History Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibody During Acute Hepatitis B Infection And Convalescence
HBsAg can be detected in the blood 4 to 10 weeks after exposure. This corresponds to onset of symptoms and viremia detectable by nucleic acid amplification methods. Most hepatitis B infections are self-limited and are associated with disappearance of HBsAg within 4 weeks of onset of symptoms. The anti-HBs then appears and increases to a plateau level that persists indefinitely.2
Diagnosis Of Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
HBsAg is the first serologic marker to appear and may be detected within 1 to 2 weeks after exposure. It precedes the development of symptoms by an average of 4 weeks.104 The presence of HBsAg indicates ongoing infection. Qualitative but not quantitative methods are used by most clinical laboratories because the amount of antigen does not correlate with disease activity or with the presence of an acute or chronic infection.26 Some symptomatic patients may have self-limited, acute HBV infection without detectable HBsAg. These patients, up to 9% in some studies, have other detectable markers of infection.104 HBeAg appears virtually simultaneously, peaks, and then declines in parallel with HBsAg. It usually disappears before HBsAg. Adult patients who remain persistently positive for HBeAg for more than 10 weeks are likely to become chronically infected. HBeAg indicates a high level of viral replication and infectivity. Most patients with nondetectable HBeAg have resolving, minimal, or no active liver disease.26 Pre-core mutants of HBV do not express HBeAg they may be responsible for a more severe course and, in some cases, fulminant disease. Serum aminotransferase levels become raised but are nonspecific. They begin to increase just before the development of symptoms and then peak , with the development of jaundice.
Howard C. Thomas, Jennifer A. Waters, in, 1998
Recommended Reading: Can You Have Hepatitis C And Not Know It
Recommended Reading: How Often Does Hepatitis B Vaccine Need To Be Given