Additional Tests You Might Need
Once youve been diagnosed with Hepatitis C, your doctor will likely order a number of tests to find out about the health of your liver and decide on a treatment plan thats most appropriate for you.
Hepatitis C genotype
The Hepatitis C genotype refers to a specific strain or type of the Hepatitis C virus. There are six major types of Hepatitis C around the world: genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. In the United States, genotypes 1, 2, and 3 are common:
- Genotype 1: Most Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
- Genotype 2: About 10% of Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
- Genotype 3: About 6% of Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
The genotype of Hepatitis C does not change over time, so you only need to get tested once.
Genotype tests are done before a person starts treatment. Hepatitis C treatment works differently for different genotypes, so knowing your genotype helps your doctor choose the best treatment for you.
Testing for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B
Your doctor may test to see if your body is immune to Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B. If these tests show no prior exposure or protection, he or she will recommend that you be vaccinated against these two viruses to eliminate the chance of becoming infected.
Liver function tests or liver enzymes
- ALT
- AST
Liver function tests also include ALP and total bilirubin, among other things.
Tests to measure liver scarring or fibrosis
- Liver Biopsy
- Elastography
- Serum markers
Imaging tests
How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis C To Others
If you have hepatitis C, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Tell your sex partner you have hepatitis C, and talk with your doctor about safe sex practices. In addition, you can protect others from infection by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care providers that you have hepatitis C. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.
What Is Chronic Hepatitis C
Doctors refer to hepatitis C infections as either acute or chronic:
- An acute HCV infection is a short-term illness that clears within 6 months of when a person is exposed to the virus.
- A person who still has HCV after 6 months is said to have a chronic hepatitis C infection. This is a long-term illness, meaning the virus stays in the body and can cause lifelong illness. An estimated 3.2 million people in the U.S. have chronic HCV.
You May Like: How Much Does A Hepatitis C Test Cost
What Is Hepatitis C Infection How Many People Are Infected
Hepatitis C virus infection is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus . It is difficult for the human immune system to eliminate hepatitis C from the body, and infection with hepatitis C usually becomes chronic. Over decades, chronic infection with hepatitis C damages the liver and can cause liver failure. In the U.S., the CDC has estimated that approximately 41,200 new cases of hepatitis C occurred in 2016. When the virus first enters the body there usually are no symptoms, so this number is an estimate. About 75%-85% of newly infected people become chronically infected. In the U.S., more than 2 million people are estimated to be chronically infected with hepatitis C. Infection is most commonly detected among people who are 40 to 60 years of age, reflecting the high rates of infection in the 1970s and 1980s. There are 8,000 to 10,000 deaths each year in the U.S. related to hepatitis C infection. HCV infection is the leading cause of liver transplantation in the U.S. and is a risk factor for liver cancer. In 2016, 18,153 death certificates listed HCV as a contributing cause of death this is believed to be an underestimate.
Those who have cirrhosis from HCV also have a yearly risk of liver cancer of about 1%-5%.
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another person’s blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Read Also: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis C Untreated
Other Risks Can Include:
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another persons blood, such as razors, toothbrushes or nail clippers
- Inoculation practices involving multiple use needles or immunization air guns
- Exposure of broken skin to HCV infected blood
- HIV infected persons
People with current or past risk behaviors should consider HCV testing and consult with a physician. HCV testing is currently not available at most public health clinics in Missouri. For information about HCV testing that is available, call the HCV Program Coordinator at 573-751-6439.
How Common Is Hepatitis C
There are approximately 30,000 new cases of acute hepatitis C every year in the United States as estimated by the CDC. In 2015, it was estimated that approximately 3.5 million Americans were infected with hepatitis C.
On a global scale, the prevalence of hepatitis C is greatest in Central and East Asia, North Africa, and the Middle East. In 2016, it was estimated that 177 million people worldwide had antibodies to hepatitis C virus.
- exposure to other people who do or might have hepatitis C.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Ab W Refl To Hcv Rna Qn Pcr
How Is Monitoring Done After Treatment For Hepatitis C
Once patients successfully complete treatment, the viral load after treatment determines if there is an SVR or cure. If cure is achieved , no further additional testing is recommended unless the patient has cirrhosis. Those who are not cured will need continued monitoring for progression of liver disease and its complications.
While cure eliminates worsening of fibrosis by hepatitis C, complications may still affect those with cirrhosis. These individuals still need regular screening for liver cancer as well as monitoring for esophageal varices that may bleed.
Because hepatitis B co-infection may reactivate or worsen even after treatment for HCV, monitoring for hepatitis symptoms may be needed after the end of therapy.
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Don’t Miss: Is There A Home Test For Hepatitis C
Viral Superinfection In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C
In patients with chronic CHC a hepatic flare may also be the clinical manifestation of HAV, HBV, HBV plus HDV, HEV or CMV superinfection 1) or of lifestyle factors such as alcohol intake or the consumption of hepatotoxic drugs.
HAV superinfection in patients with CHC has been documented by several authors. Sagnelli et al described 21 patients with chronic hepatitis who developed hepatitis A, 13 with an underlying chronic HBV infection and 8 with a chronic HCV infection. In all cases HAV always had a self-limiting clinical course, associated with a marked inhibition of HBV and HCV genomes no patient had clinical, laboratory or ultrasound evidence of liver cirrhosis in this study and the underlying chronic hepatitis showed a regular clinical course. These data are in contrast with those from a previous study reporting a high rate of fulminant hepatitis due to acute hepatitis A occurring in patients with pre-existing chronic hepatitis, but are in complete agreement with those reported in numerous other studies.
Hepatic flares due to superinfections by other viruses such as HDV, heterologous HCV strains, HEV and CMV in patients with chronic hepatitis C have been poorly investigated.
There is little information on the outcome of chronic HCV infection after HBV/HDV superinfection. To this regard Deterding et al described a patient with chronic hepatitis C who cleared HCV infection during an acute self-limiting HBV/HDV superinfection.
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis
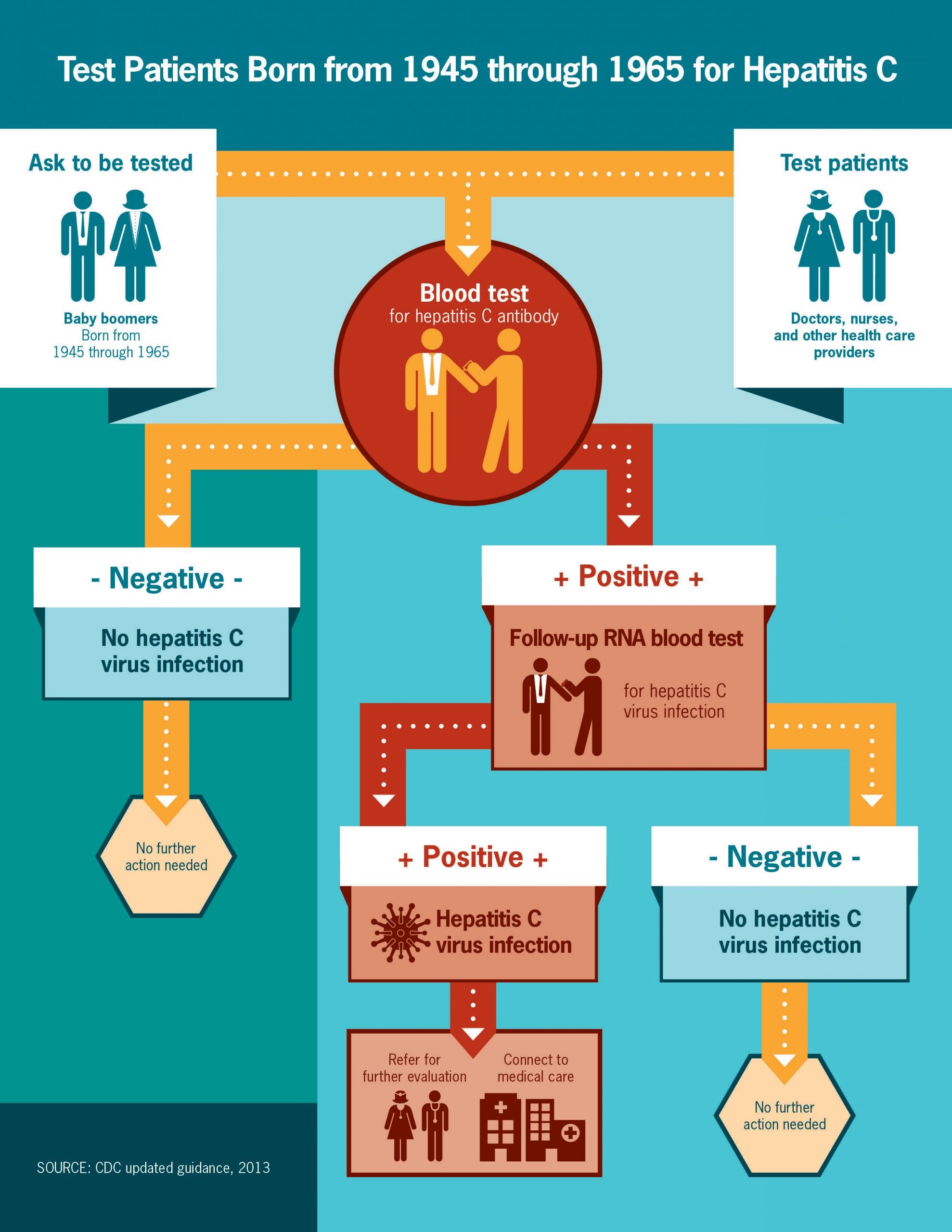
Tests To Diagnose Hepatitis C
How is Hepatitis C diagnosed?
There are two main blood tests typically used to diagnose Hepatitis C. First, youll have a screening test that shows if youve ever had Hepatitis C at some point in your life. If this test is positive, youll have a second test to see if you have Hepatitis C now. These blood tests are described below:
Hepatitis C antibody test
This is the screening test used by doctors to show whether or not you have ever been exposed to Hepatitis C at some time in your life, by detecting antibodies in your blood. Antibodies are substances your body makes to fight off all kinds of infections. If you were ever infected with Hepatitis C, your body would have made antibodies to fight the virus.
If the test result is:
- Negative, it means you have not been exposed to Hepatitis C and further testing is usually not needed.
- Positive, you have had Hepatitis C at some point. However, it does not tell you whether you have it now. Youll need to see your doctor for another test the Hepatitis C RNA test to determine if the virus is still active and present in your blood.
Hepatitis C RNA Qualitative Test
This test will determine whether or not you are currently infected with Hepatitis C. It is often called the PCR test because of the process used . It looks for the genetic material of the Hepatitis C virus in your blood.
If the test result is:
Hepatitis C RNA Quantitative Test
When To See A Doctor
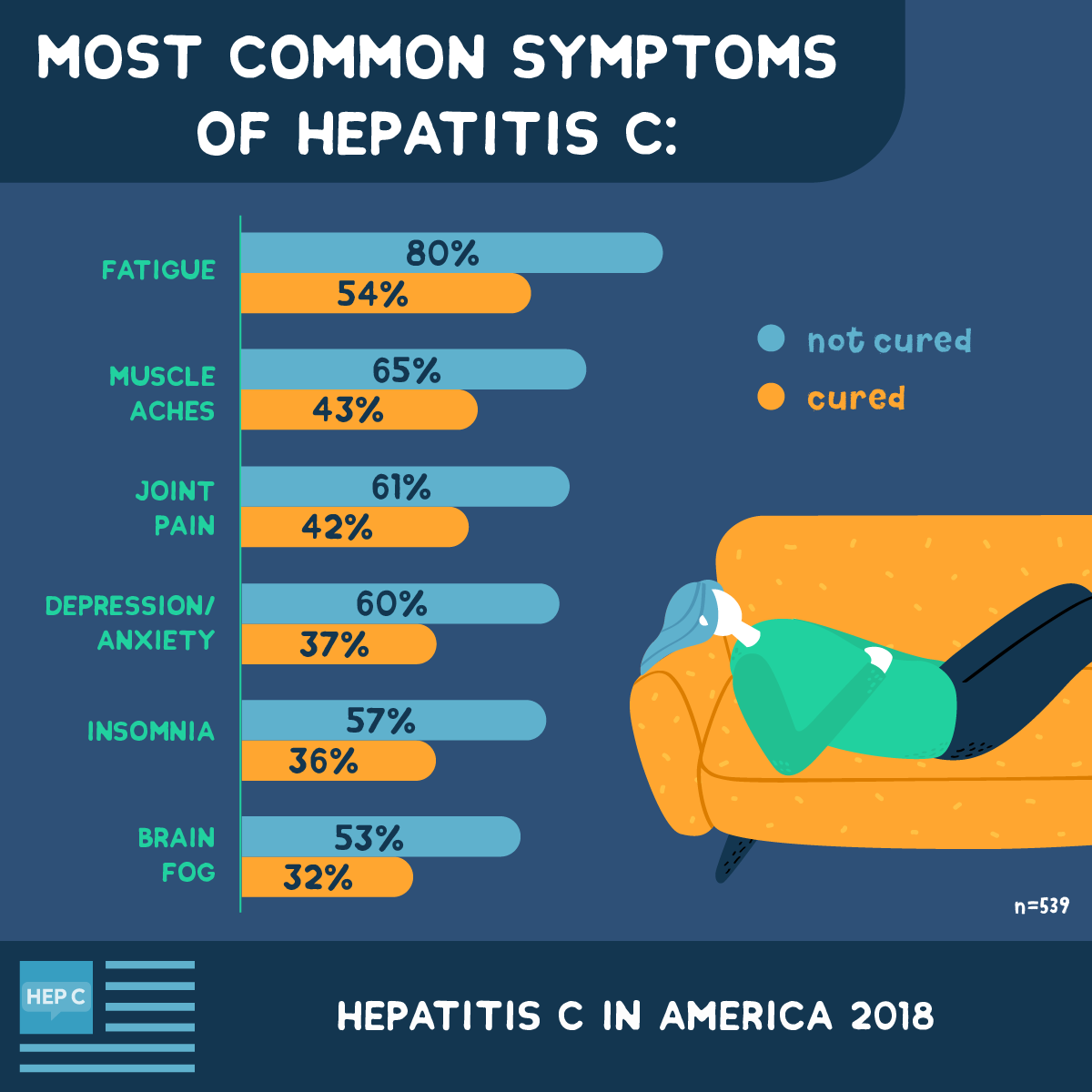
People should speak with a doctor if they suspect the following:
- They are at risk of contracting HCV.
- They need help with a substance use disorder that could expose them to HCV.
- They have recently undergone potential exposure to HCV.
- They are experiencing any symptoms of an HCV infection
Contracting HCV is preventable in many cases. Preventive measures include:
- not using illicit drugs, especially injectable substances
- taking care when undergoing body piercing or tattooing
- practicing sex with a condom
- not sharing personal items, such as razors or toothbrushes
- wearing gloves if you need to touch or handle another persons blood
When getting a piercing or tattoo, people should seek out a place that has a good reputation. It is vital to ask about the hygiene and sterilization practices at the facility before agreeing to the procedure.
You May Like: Can Chronic Hepatitis B Be Cured
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C spreads through contact with the blood of someone who has HCV. This contact may be through
- Sharing drug needles or other drug materials with someone who has HCV. In the United States, this is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.
- Getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on someone who has HCV. This can happen in health care settings.
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not sterilized after being used on someone who has HCV
- Having contact with the blood or open sores of someone who has HCV
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another person’s blood, such as razors or toothbrushes
- Being born to a mother with HCV
- Having unprotected sex with someone who has HCV
Before 1992, hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Since then, there has been routine testing of the U.S. blood supply for HCV. It is now very rare for someone to get HCV this way.
Recommended Reading: Best Medicine For Hepatitis B
What Laboratory Tests Diagnose Hepatitis C
Laboratory blood tests will be done to evaluate the patient’s liver function and to look for hepatitis C antibodies . If these tests indicate that the person has hepatitis C, a hepatitis C “viral load” test will be done. This looks for genetic material from the hepatitis C virus and measures the quantity of hepatitis C virus that is circulating in the patient’s blood. This is helpful in determining if treatment is appropriate and to monitor the success of the treatment .
Individuals who had hepatitis C in the past and cleared the virus on their own will have a positive HCV antibody test, but there will be no hepatitis C virus genetic material in the blood. If a person is immunosuppressed due to an immunological condition, cancer chemotherapy, immunotherapy or HIV/AIDS, the test results may be different and need to be evaluated accordingly.
What Is Hepatitis C Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, and hepatitis C is liver inflammation caused by the hepatitis C virus .
Journal of Clinical MicrobiologyJournal of Infectious Diseases
Though these genotypes appear to affect people similarly, they respond differently to treatments, and it’s possible to be infected with more than one HCV genotype at the same time.
Whatever the genotype, hepatitis C is considered either acute or chronic .
Read Also: Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
What Medications Cure Hepatitis C Infection
Interferons, for example, Roferon-A and Infergen, and pegylated interferons such as Peg-IntronT, Pegasys, were mainstays of treatment for years. Interferons produced sustained viral response of up to 15%. Later, peglatedll forms produced SVR of 50%-80%. These drugs were injected, had many adverse effects, required frequent monitoring, and were often combined with oral ribavirin, which caused anemia. Treatment durations ranged up to 48 weeks.
Direct-acting anti-viral agents are antiviral drugs that act directly on hepatitis C multiplication.
Also Check: How Much Is A Hepatitis C Test
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis C
In the United States, having been born between 1945 and 1965, and the use of illicit injection drugs are the two most common factors associated with hepatitis C. Other risk factors include
- having received blood transfusions prior to 1990,
- hemodialysis, and
- having greater than 10-lifetime sex partners.
Population studies show that hepatitis C is more common among males, non-Hispanic blacks, those with low income, and those with less than a high school education.
People who have HIV/AIDS have an increased risk for hepatitis C, because both these diseases are transmitted in the same ways, through blood and body fluids. If someone has both infections, that person is said to be co-infected with HIV and HCV.
Reactive Or Positive Hepatitis C Antibody Test
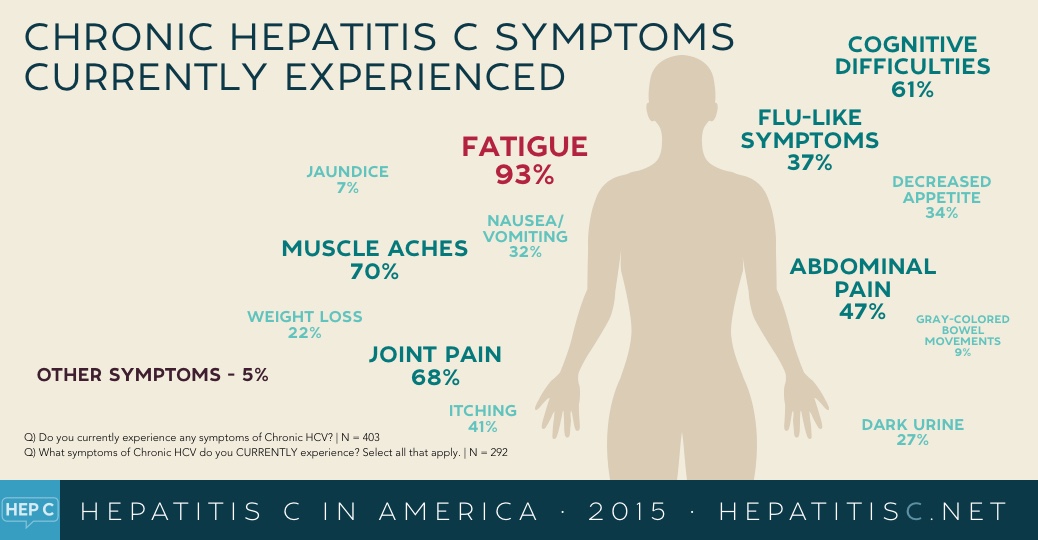
- A reactive or positive antibody test means that Hepatitis C antibodies were found in the blood and a person has been infected with the Hepatitis C virus at some point in time.
- Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true even if they have cleared the Hepatitis C virus.
- A reactive antibody test does not necessarily mean that you have Hepatitis C. A person will need an additional, follow-up test.
Persons for Whom HCV Testing Is Recommended
- Adults born from 1945 through 1965 should be tested once
- Those who:
- Ever injected drugs, including those who injected once or a few times many years ago
- Have certain medical conditions, including persons:
- who received clotting factor concentrates produced before 1987
- who were ever on long-term hemodialysis
- with persistently abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels
- who have HIV infection
Don’t Miss: Just Food For Dogs Hepatic