What Does The Test Measure
An acute viral hepatitis panel includes several tests that measure antigens and antibodies. Antigens are foreign substances such as proteins of the virus itself, while antibodies are substances produced by the immune system in response to the viral infection.
An acute viral hepatitis panel tests for antigens and/or antibodies of hepatitis A, B, and C:
What Is Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis A virus . In the USA, hepatitis A infections have declined by 90% since the hepatitis A vaccine first became available in 1995. Still, there are cases of hepatitis A reported to the San Francisco Department of Public Health every year among San Francisco residents. Hepatitis A is still common in Latin America, Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and eastern Europe.
How Is Hepatitis A Spread
Hepatitis A
The hepatitis A virus is usually spread by putting something in your mouth that is contaminated with the virus. The virus is found in the stool of people with hepatitis A and is spread when someone’s stool accidentally contaminates food or water. This can happen when an infected person does not adequately wash their hands after using the bathroom then touches other things such as food. When other people eat that food, they can get infected with hepatitis A. Usually the transmission is between people in very close personal contact.
Foods themselves can be contaminated with hepatitis A virus, such as raw oysters harvested from sewage-contaminated water. When people eat food contaminated with hepatitis A virus, they can get infected with the virus.
Hepatitis A is usually spread through:
- household contact with an infected person
- sexual contact with an infected person
- eating or drinking contaminated food or water
- sharing eating utensils that are contaminated
- touching contaminated surfaces and then placing your hands near or in the mouth
Don’t Miss: Liver Disease Caused By Hepatitis C
Hev Infection In Developed Countries
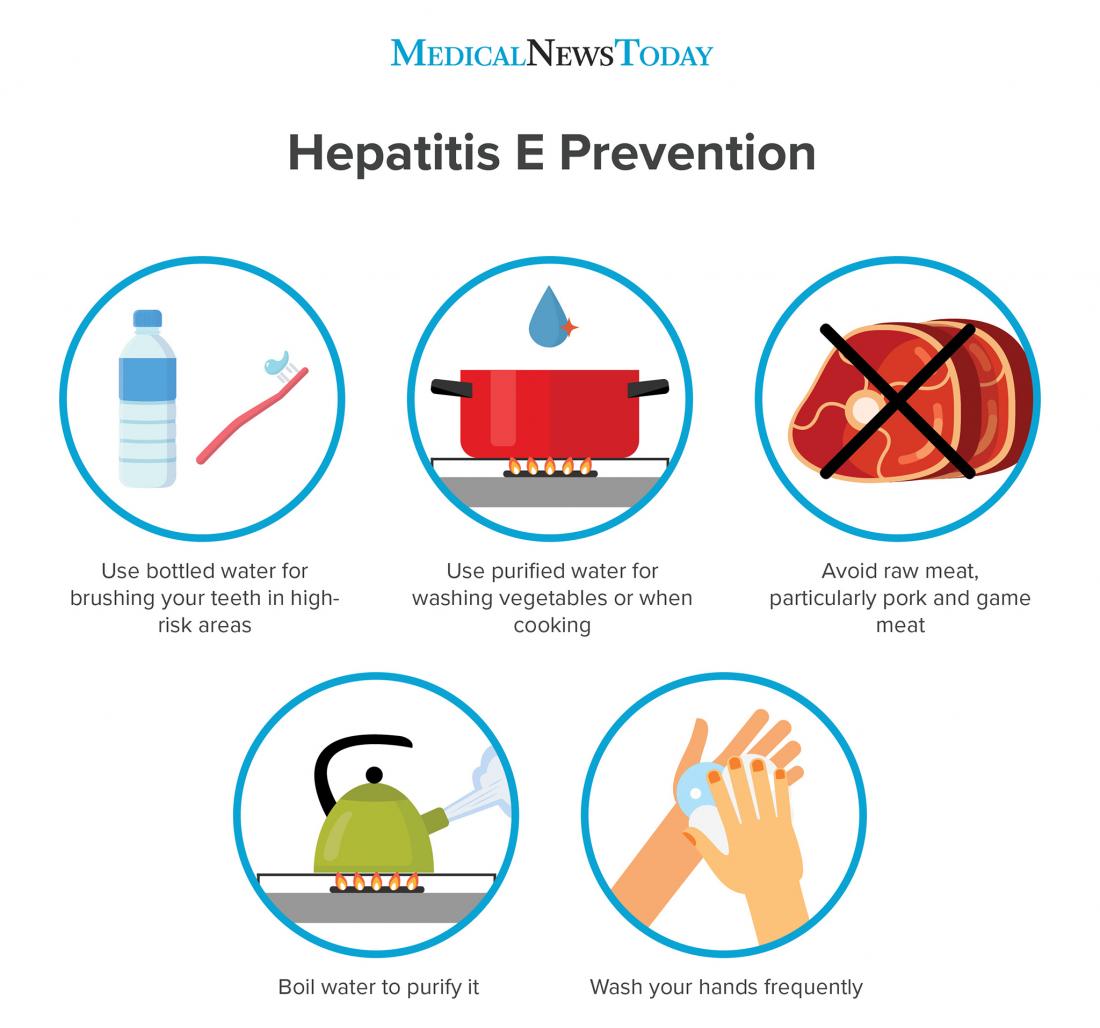
Over the last 15 years, it has become evident that hepatitis E is not a disease confined to developing countries or travelers returning from such locations. Numerous studies show that autochthonous hepatitis E is a problem across Europe, North America, New Zealand, and Japan . In contrast to the case in developing countries, autochthonous hepatitis E is a zoonotic infection caused by HEV genotypes 3 and 4, and an important route of infection is by consumption of uncooked or poorly cooked pork or game meat .
In developed countries, anti-HEV IgG seroprevalence studies are problematic . Many of the earlier studies showed very low seroprevalences, in the 1 to 2% range . Most of these studies used anti-HEV assays of poor sensitivity and almost certainly significantly underestimated the true seroprevalence .
Are Test Results Accurate
Although an acute viral hepatitis panel is a standard panel used to detect evidence of viral hepatitis, in many cases it provides only preliminary results. For patients who have abnormal results on the hepatitis B or C portions of this panel, additional testing is necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Can It Be Cured
When Will Symptoms Appear After You Have Been Exposed To Hav
It generally takes about 4 weeks for symptoms to appear, but they can start at 2 weeks or they can start up to 8 weeks after you have been exposed. You probably wont get every symptom immediately, but they tend to emerge over days.
Also, you can have no symptoms and have the virus and be contagious. Children especially may be free of symptoms despite being infected.
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
The following questions about the results of an acute viral antibody panel may be helpful to review with a doctor:
- What tests were included in this panel?
- What was my test result?
- Do I have a hepatitis infection, and if so, which type?
- Would I benefit from hepatitis vaccination?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my test result?
Don’t Miss: How Can Hepatitis B Be Transmitted
Virus Biology Reservoir And Transmission
HEV is a nonenveloped virus with an icosahedral capsid and a size of 27 to 34 nm. The virus has a positive-sense, single-stranded, 7.2-kb RNA genome which is capped and polyadenylated at the 5 and 3 termini, respectively . The HEV genome contains three open reading frames . ORF1 encodes a protein of 1,693 amino acids containing functional domains present in the nonstructural proteins of other positive-strand RNA viruses . These functional domains include methyltransferase, cysteine protease, RNA helicase, and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase domains. ORF2 encodes the viral capsid protein of 660 amino acids that is responsible for virion assembly , interaction with target cells , and immunogenicity . The ORF2 protein consists of three linear domains: the shell domain , the middle domain , and the protruding domain , harboring the neutralizing epitope . ORF3, which overlaps ORF2, encodes a small protein of 113 or 114 amino acids that is involved in virion morphogenesis and release .
HEV replicates in the cytoplasm, with a subgenomic RNA producing the ORF2 and ORF3 proteins and the full genomic RNA encoding nonstructural proteins and serving as a template for replication . Current data suggest that the ORF1 protein is not subjected to proteolytic processing . HEV replicates in hepatocytes but also in the small intestine, colon, and lymph nodes, as demonstrated by detection of negative-sense RNA intermediates .
Hepatitis E virus genome.
Who Is At Risk Of Hepatitis A
Anyone can get hepatitis A if they have not beenvaccinated. In the U.S., you are at a higher risk if you:
- Use illegal drugs, whether injected or not
- Live with someone who has hepatitis A
- Have bleeding problems and take clotting factors
- Have oral-anal sexual contact with someone who has hepatitis A
- Travel to areas that have high rates of hepatitis A
Travel to Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe,or Central and South America,including Mexico, increases the riskof getting hepatitis A.
Also Check: Causes And Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Who Gets Hepatitis A
Anyone can get hepatitis A, but certain persons are at increased risk of infection, including:
- Children and adults living in areas with increased rates of hepatitis
- Persons traveling to countries where hepatitis A is common
- Men who have sex with men
- Injecting and non-injecting drug users
- Sexual contacts of infected persons
- Household contacts of infected persons
Hepatitis A Outbreak: How Does A Virus Get Into Strawberries
09 September 2016
Nearly 90 people in seven states have become sick in an outbreak of hepatitis A linked to frozen strawberries imported from Egypt, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. But how does the hepatitis A virus get into strawberries?
Berries of all types are actually a common conduit for viruses, said Benjamin Chapman, a food-safety specialist and an associate professor at North Carolina State University. Over the past decade, there have been several virus outbreaks linked to imported berries, he said.
One of the reasons for this is that berries are very delicate, and so unlike other, hardier fruits and vegetables, berries need to be harvested by hand, Chapman told Live Science.
Tomatoes, for example, are machine-harvested, so no hands touch them, he said. But berries are too fragile for machines, so each berry is handpicked, he said.
Because hepatitis A is spread through the “fecal-to-oral route,” if workers picking berries were infected with hepatitis A and had not properly washed their hands, they could transfer the virus from their hands to the berry, Chapman said. In parts of the world where hepatitis A is more common, this is definitely a risk, he added.
It’s more likely, however, that the water used to irrigate the strawberries was the source of the virus in this outbreak, Chapman said. And, yes, because of that fecal-to-oral route, that means sewage-contaminated water.
Recommended Reading: Rash Caused By Hepatitis C
How Can I Keep From Getting This Disease
Wash your hands with soap and warm water before and after cooking, after using the bathroom, and after changing diapers.
Before you travel outside the United States, ask your doctor if you should get a hepatitis A shot. You also should get the shot if you use illegal drugs, have anal sex, received clotting factor concentrates, or have liver disease. Children younger than one year should not get the shot.
If you come into contact with someone who has hepatitis A and you have never had the disease or had a hepatitis A shot, you should see your doctor right away. He or she will give you a shot that can help keep you from getting sick.
Who Should Obtain The Hepatitis A Vaccine

Hepatitis A vaccine is recommended for the following persons:
- Travelers to areas with increased rates of hepatitis A
- Men who have sex with men
- Injecting and non-injecting drug users
- Persons with clotting-factor disorders
- Persons with chronic liver disease
- All children aged 12-23 months children not fully vaccinated by age two
The hepatitis A vaccine may also be used in certain outbreak situations where ongoing transmission is occurring. Although studies of certain occupational groups have not shown an increased risk, such people may consider vaccination if they wish to further reduce their risk or are in communities where ongoing outbreaks are occurring.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take To Cure Hepatitis C
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread by coming in contact with thehepatitis A virus. This includes:
- Contact with any person infected with the hepatitis A virus
- Sexual contact with an infected person
- Touching contaminated surfaces and then placing your hands near or in your mouth
- Sharing eating utensils that have virus on them
- Eating food or drinking water that has been contaminated by feces that contain the virus. The food and drinks most likely to be contaminated are:
- Fruits
- Ice
- Water
In the United States, chlorine in the water kills hepatitisA virus. But infected food workers can still spreadhepatitis A directly to food. This occurs when hands arenot washed or cleaned before food is handled.
Infected people can spread the virus to others a few weeks before they begin to feel bad.
Chronic Hev Infection In Solid Organ Transplant Patients
An increasing number of recent studies have shown that HEV can cause chronic infection that can rapidly result in cirrhosis . Although the majority of chronic HEV cases are diagnosed in the transplant population , several chronic cases have also been observed in patients coinfected by HIV and in hematological patients treated with anticancer chemotherapy . All chronic HEV cases were observed in patients infected by HEV genotype 3. No case of chronic HEV genotype 1, 2, or 4 infection has been described. All chronic cases have been autochthonous and have not been associated with travel. A diagnosis of chronic hepatitis used to be considered when persisting HEV replication lasted for at least 6 months. However, very recently, in the setting of organ transplantation, it was observed that no spontaneous clearance of HEV occurs between 3 and 6 months after an acute infection. This suggests that chronic HEV infection should be considered when HEV replication persists for more than 3 months .
Adult SOT patients.
HEV transmission in SOT patients.
Prevalence and incidence.
You May Like: Can You Cure Hepatitis A
Who Should Receive The Hepatitis A Vaccine
In general, CDC recommends the following groups be vaccinated for hepatitis A:
- All children at age 1 year
- Travelers to countries that have high rates of hepatitis A
- Family members and caregivers of recent adoptees from countries where hepatitis A is common
- Men who have unprotected sexual contact with other men
- Users of injection and illegal drugs
- People with chronic liver diseases, hepatitis B, or hepatitis C
- People who are treated with clotting-factor concentrates
- People who work with hepatitis A infected animals or in a hepatitis A research laboratory
Hev Infection In Patients With Preexisting Liver Disease
Patients with underlying chronic liver disease who develop hepatitis E have a poor prognosis, as they frequently develop acute or subacute liver failure. In a study of a large cohort of patients in India with decompensated chronic liver disease, patients who had decompensation because of acute hepatitis E virus infection had a significantly worse prognosis than patients who had decompensation due to another cause . The 12-month mortality in the cohort with hepatitis E virus infection was 70%. In developed countries, smaller studies have also shown a poor prognosis for patients with underlying chronic liver disease , but it is not clear how frequently this occurs, as such patients are currently not routinely tested for evidence of infection with HEV. However, two studies show that there is a strong relationship between deaths from decompensated chronic liver disease and pork consumption in developed countries . The reason for this observation is uncertain, but it might be explained by unrecognized infection with HEV. Studies to address this hypothesis are ongoing, and the results are awaited with interest.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex
Treatment And Prevention Of Hepatitis A
Because hepatitis A virus infections can have serious health consequences, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends providing post-exposure prophylaxis for unvaccinated people who have consumed any contaminated food or water within two weeks of exposure.
PEP consists of:
- Hepatitis A vaccine for people between the ages of 1 and 40 years
- Hepatitis A virus-specific immunoglobulin for people outside of this age range, but the hepatitis A vaccine can be substituted if IG is not available.
- Those with evidence of previous vaccination or who can confirm previous hepatitis A illness do not require PEP.
If you are unsure if you have been vaccinated against hepatitis A, contact your health professional to check your immunization records. If you have been vaccinated, no further action is needed. If you have never received the hepatitis A vaccine, getting a single dose within two weeks of exposure can protect against illness. If you are unable to determine whether you have already been vaccinated, receiving an additional dose of vaccine is not harmful if you have already been vaccinated.
How Is Hepatitis A Infection Prevented
Vaccination
- The hepatitis A vaccine offers excellent protection against HAV. The vaccine is safe and highly effective. Vaccination consists of 2 doses of vaccine spaced 6-12 months apart. Protection starts 1-2 weeks after the first dose of vaccine, and lasts for 20 years to life after 2 doses.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children should receive hepatitis A vaccine starting at 1 year of age .
- The CDC recommends hepatitis A vaccine for all persons traveling to countries where HAV is common . For infants that will be traveling internationally, an early dose of Hepatitis A vaccine can be given at age 6-11 months.
Natural Immunity
- People who have hepatitis A infection become immune to HAV for the rest of their lives once they recover. They cannot get hepatitis A twice.
- The blood test for immunity to hepatitis A is called the Hepatitis A Total Antibody test. People who have had hepatitis A and those who have received hepatitis A vaccine show positive antibodies to hepatitis A on this test for the rest of their life.
Healthy Habits
- Good personal hygiene and proper sanitation help prevent the spread of the HAV virus. Always wash your hands with soap and water after using the bathroom, changing a diaper, and before preparing, serving, or eating food.
- Alcohol-based hand sanitizers do not kill the hepatitis A virus
After Exposure to HAV
Recommended Reading: How To Contract Hepatitis B And C
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis A
There is a vaccine, made from an inactivateddeadvirus to prevent hepatitis A. If you are not sure you have had the vaccine, you can ask your doctor to test you to see if you have been vaccinated.
You can also practice good hand washing hygiene. Make sure you use soap and warm water to wash your hands for at least 15 to 30 seconds after you use the toilet, change diapers, and before and after touching food.
If you are traveling in another country, especially a developing country, drink only bottled water and use only bottled water to brush your teeth, wash your produce, and freeze for ice cubes.
Why Isn’t Hepatitis A Vaccine Required For Food Service Workers

While food service employers can offer hepatitis A vaccine to their employees if they wish, most public health authorities prefer not to make it mandatory for the following reasons:
- There is no evidence that food service workers are at any greater risk of acquiring hepatitis A than are people in other occupations.
- Only 2-3 percent of all hepatitis A cases are acquired through restaurant food.
- Employee turnover in some segments of the food service industry is high, making it impractical to vaccinate staff.
- Emphasis on careful hand washing, use of disposable gloves and not working when ill are measures that can greatly minimize the risk of spreading hepatitis A and a number of other infections.
- Hepatitis A vaccine would be strongly recommended for food service workers in a county or region where a community-wide outbreak has been recognized.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
What Is Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E, also called enteric hepatitis , is similar to hepatitis A, and more prevalent in Asia and Africa. It is also transmitted through the fecal-oral route. It is generally not fatal, though it is more serious in women during pregnancy and can cause fetal complications. Most patients with hepatitis E recover completely.
How Is Hepatitis A Transmitted
HAV is highly contagious. It is spread primarily when a person ingests the virus from food, drinks, or objects that have been contaminated by small amounts of stool from an infected person sex with an infected person, particularly if it involves anal-oral contact and through injection drug use. In crowded, unsanitary conditions, HAV can be spread quickly and cause outbreaks by exposure to contaminated water or food .
You May Like: Medication For Hepatitis C Cure