Study Design And Population
This nationwide cohort study included patients infected with a nonepidemic HCV genotype treated with an interferon-free DAA regimen. Nonepidemic HCV genotypes were defined as genotypes and subtypes other than 1a/1b/2a/2b/3a/4a/4d. All laboratories performing HCV genotyping in the Netherlands were approached. All but 1 participated in the study: the Amsterdam University Medical Centers Sanquin Diagnostics, Amsterdam UMC Groningen, Groningen LUMC, Leiden Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam and Maastricht UMC, Maastricht.
Treatment With Sof + Dcv
SOF + DCV had been administered to 193/316 patients among whom 123 also received RBV. Treatment duration was short in 119/193 and long in 74/193 patients .
In the mITT group, SVR12 was obtained in 177/193 of those treated with SOF + DCV +/-RBV. SVR12 rates did not differ between those who received shorter versus longer treatment duration and 66/74 respectively. Nor did it differ between those who did and did not receive RBV versus 62/70 , respectively). However, among those who received short treatment there was a trend towards higher SVR12 rates in patients who received RBV compared with those who did not and 33/38 respectively p = 0.055). In further bivariate analyses, SVR12 was independent of age, gender, treatment experience, the presence of cirrhosis, the presence of decompensated liver disease and liver elasticity.
SOF+DCV was administered to 20 patients with Child Pugh B or C and SVR was achieved in 17 of these. Treatment duration was 24 weeks in 15 and 1216 weeks in 5 patients. RBV was administered to 12 patients.
Treatment Of Hcv Genotype 3 With Compensated Cirrhosis: Sofosbuvir Plus Ribavirin
SOF plus RBV for 12 weeks is not recommended for treatment of cirrhotic patients with HCV genotype 3 infections. The overall SVR rates in naive cirrhotic patients treated for 12 weeks ranged from 21 to 34% . Two trials found that SOF plus RBV for 12 weeks for naive patients with cirrhosis resulted in SVR rates of 21% and 34% .
Extending the treatment with SOF plus RBV in this population improved the SVR rates . The Boson study included 21 naive patients with cirrhosis treated with SOF plus RBV for 16 weeks and 12 achieved SVR . Extending the treatment for 24 weeks in this population improved the SVR rates from 82 to 92% . In the Boson study, among 22 naive patients with cirrhosis treated with SOF plus RBV for 24 weeks, 18 achieved SVR . In the Valence study, 12 of 13 patients achieved SVR . SOF plus RBV for 24 weeks is recommended by EASL for treatment-naive patients with cirrhosis and by AASLD as an alternative regimen for treatment-naive patients with HCV genotype 3 infection who are IFN-ineligible .
Among treatment-experienced patients with cirrhosis and HCV genotype 3 infection treated with SOF plus RBV for 12 weeks, the SVR rates are around 20%, similar to those observed in naive patients . Only one study, the Fusion trial, assessed SOF plus RBV for 12 weeks in treatment-experienced patients with cirrhosis, including 26 patients, and only 20% achieved SVR .
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A Shots At Costco
Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes
An important variable for all patients with chronic hepatitis C virus is the”genotype” of HCV with which they are infected. This is the strain of the virus towhich they were exposed when they were infected, often many years prior to theirevaluation, and it is determined by a simple blood test. Genotypes of HCV aregenetically distinct groups of the virus that have arisen during its evolution. Approximately 75% of Americans with HCV have genotype 1 of the virus, and 20-25% have genotypes 2 or 3, with small numbers ofpatients infected with genotypes 4, 5, or 6. Most patients with HCVare found to have only one principal genotype, rather than multiple genotypes. Genotype 4 is much more common in Africathan in many other parts of the world, genotype 6 is common in Southeast Asia, andeach area of the world has its own distribution of genotypes.
Hepatitis C Cure Rate Tops 90% In Hard
The sofosbuvir-based therapy was reviewed in a real-life Scandinavian study
Hepatitis C patients with hard-to-treat genotype 3 showed sustained virologic response of greater than 90% in a real-life study of a therapy based on the direct-acting antiviral drug sofosbuvir
HCV genotype 3 has been linked to increased risk of developing cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma compared to other versions of the virus, previous studies have found.
Chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 3 infection with advanced liver disease has emerged as the most challenging to treat, researchers led by Olav Dalgard , MD, Ph.D. at Akershus University Hospital in Oslo, Norway noted in their study.
The research team from Norway, Denmark, Finland and Sweden chose patients from those four countries for the retrospective cohort study. About 100,00 people in Scandinavia are infected with HCV and half of them have genotype 3, according to the paper.
Genotype 3 is common all over Scandinavia and in the UK, Dalgard told MD Magazine in an email. We dont know why, but genotype 3 has its origin in South Asia and both the UK and Norway and Denmark have large immigrant populations from Pakistan.
Only a few studies have reported the effect of sofosbuvir-based treatment in genotype 3 patients with advanced liver disease in a real-life setting, the authors said.
Recommended Reading: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Why Do People Have Different Genotypes
A person of any racial or ethnic group can carry any genotype or subtype. However, some may be more prevalent in some racial or ethnic groups than others. In the United States, over 90% of African Americans, compared to 67% of Caucasians, carry genotype 1.
People who travel between regions where different genotypes are more common can be exposed to different HCV genotypes, leading to a mixed infection. HCV is transmitted through contact with blood, such as through contaminated blood products or medical equipment, blood transfusions, kidney dialysis, or the sharing of drug injection equipment, such as syringes, or non-injection equipment, such as pipes, spoons, cotton balls, or straws for snorting drugs.
Medications Used To Treat Hepatitis C
The HCV Medications section on this website provides detailed information for each of the Food and Drug Administration -approved medications listed in the treatment recommendations, including links to the full prescribing information and to patient assistance programs. The DAAs exert their action at specific steps in the HCV life cycle. There are three major classes of DAA medications: nonstructural proteins 3/4A protease inhibitors, NS5A inhibitors, and NS5B polymerase inhibitors the NS5B polymerase inhibitors include the nucleoside analogs and nonnucleoside analogs. Adherence with the treatment regimen is of paramount importance. Thus, individuals should receive detailed counseling regarding the importance of adherence prior to starting therapy, as well as intensive monitoring and follow-up during therapy.
Also Check: Just Food For Dogs Hepatic
Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 3
Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by hepatitis c, a blood-borne virus transmitted through direct contact with infected blood. It causes inflammation of the liver, which leads to diminished liver function or liver failure.
The infection is less likely to exhibit symptoms until the liver gets damaged, which may take several years.
In chronic HCV patients, the infection leads to scarring and poor liver function, leading to complications, including jaundice, fluid accumulation in the abdomen, bleeding and liver cancer.
Genotype 3 is the most treatment-resistant and aggressive hepatitis C that affects 12% of chronic HCV patients in the US.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions estimates, HCV affects 2.7 million Americans and approximately 170 million people worldwide.
Retreatment Of Persons With Prior Peginterferon And Ribavirin Failure
The latest version of the AASLD-IDSA HCV Guidance no longer provides specific recommendations for retreatment of persons with a history of peginterferon plus ribavirin therapy, with or without an earlier generation direct-acting antiviral agent . The AASLD-IDSA HCV Guidance notes that these individuals respond to retreatment similar to treatment-naïve persons, thus implying the treatment approach should be the same as with treatment-naïve individuals. Although the pool of persons with a history of failure with a peginterferon-based regimen who need retreatment is small and diminishing, there are some individuals with this treatment history who need retreatment and may require special consideration that differs from that of treatment-naïve individuals. The following outlines a few of these key considerations based on available data and previous guidance that should be noted when retreating an individual with a history of prior treatment failure with peginterferon plus ribavirin, with or without an earlier generation DAA . Note that except for the 8-week option of glecaprevir-pibrentasvir , when retreating these individuals with first-line DAA combinations that have pangenotypic activity , the treatment will be the same as their treatment-naïve counterparts.
Also Check: Hepatitis C And Liver Disease
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
The new hepatitis C medicines have not been tested in pregnancy.
You should not become pregnant while taking treatment as it could be harmful to unborn babies.
If you’re pregnant, you must delay treatment until after your baby is born.
Speak to your doctor before starting hepatitis C treatment if you’re planning to become pregnant in the near future.
You’ll need to wait several weeks after treatment has ended before trying to get pregnant.
Women taking ribavirin should use contraception during treatment and for another 4 months after the end of treatment.
Men taking ribavirin should use a condom during treatment and for another 7 months after the end of treatment. This is because semen can contain ribavirin.
If you become pregnant during treatment, speak to your doctor as soon as possible to discuss your treatment options.
Treatment Of Hcv Genotype 3 Infection In Non
The combination of SOF plus RBV for 24 weeks was the first interferon-free therapy for patients with HCV genotype 3 infection approved by the FDA. International guidelines differ regarding the recommendations for this regimen. EASL guidelines do not recommend this therapeutic regimen for treatment-experienced cirrhotic patients. On the other hand, AASLD recommends SOF plus RBV as an alternative regimen for patients without cirrhosis with previous PegIFN/RBV failure or treatment-naive patients who are IFN-ineligible .
In naive non-cirrhotic patients with HCV genotype 3 infection, SOF plus RBV for 12 weeks resulted in an overall SVR of 61-68%. However, extending the treatment to 24 weeks led to an approximate 30% increase in SVR rates, ranging from 90 to 96% .
Two large clinical trials evaluated the efficacy of SOF plus RBV for 12 weeks in naive, non-cirrhotic patients infected with HCV genotype 3. The Fission trial included 145 patients, but only 89 achieved SVR . The Positron trial included 84 naive patients who were interferon-ineligible or intolerant, of which 57 reached SVR . The Boson clinical trial found higher SVR among naive and non-cirrhotic patients treated with SOF plus RBV for 16 weeks. Among 70 patients treated, 58 achieved SVR . Another arm of this study evaluated 72 naive non-cirrhotic patients treated for 24 weeks, with an overall SVR of 90% . SOF plus RBV for 24 weeks was also used in the Valence trial, which included 92 patients and 87 achieved SVR .
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Immunity
How Effective Is Treatment
Direct acting antivirals cure 9 out of 10 patients with hepatitis C.
Successful treatment does not give you any protection against another hepatitis C infection. You can still catch it again.
There’s no vaccine for hepatitis C.
If treatment does not work, it may be repeated, extended, or a different combination of medicines may be tried.
Your doctor or nurse will be able to advise you.
Which Treatment Works For Each Genotype
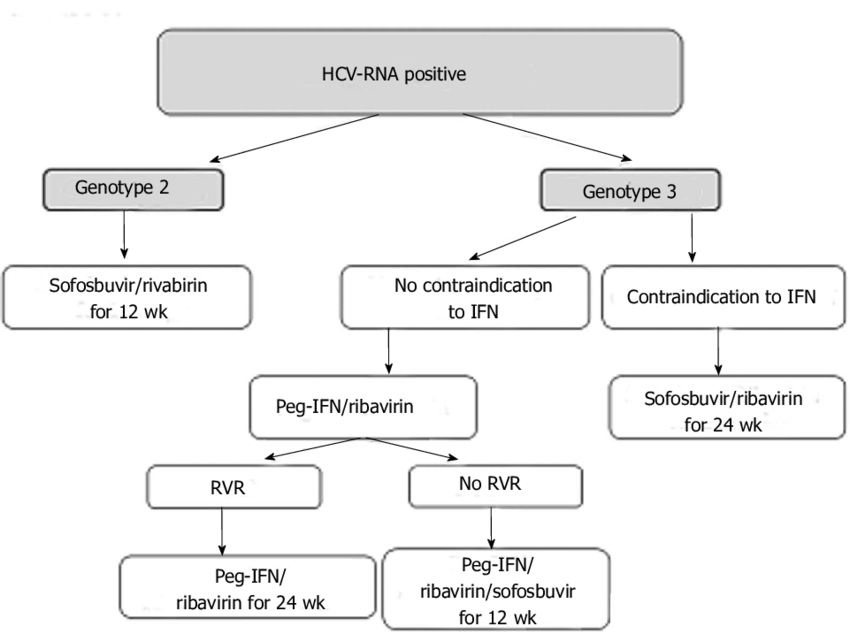
- All Genotypes: see Epclusa fact sheet
- Genotypes 1 through 4: see Sovaldi, Viekira XR and Technivie, Harvoni, Olysio fact sheets
- Genotypes 1 or 4: see Zepatier fact sheet
- Genotypes 2 or 3: see Sovaldi, Daklinza fact sheets
- Genotype 6: see Harvoni fact sheets
Ribavirin causes birth defects and miscarriage. HCV treatment regimens that include RBV should not be used by pregnant women or by male partners of pregnant women. RBV stays in a persons body for months, so women and their male partners should avoid pregnancy until six months after stopping it .
This fact sheet is current as of December 2016. It is recommended to be read alongside the Adherence and HCV Diagnostics fact sheets. Always check for updated information.
Don’t Miss: What Do You Do If You Have Hepatitis C
Hyperlipidemia Diabetes Mellitus Or Ir
Lipid metabolism is intimately involved in the molecular mechanisms of the HCV infectious cycle. HCV replication influences and depends upon cholesterol uptake and efflux through different lipoprotein receptors during its entry into the hosts cells . Very low-density lipoprotein-associated proteins, including apolipoprotein B, apoE and microsomal triglyceride transfer proteins, have been shown to play a crucial role in the formation of infectious HCV particles, especially pertaining to genotype 3 . HCV can bind low-density lipoprotein receptors and lead to intracellular lipid deposition . Patients infected with genotype 3 tend to have hypocholesterolemia and hypobetalipoproteinemia, which may account for the direct effect of the virus on lipid metabolism . It appears that HCV-3 also selectively interferes with the late cholesterol pathway, a phenomenon that appears to disappear with SVR . Interestingly, high LDL levels tends to predict SVR in patients treated with interferon and ribavirin . Since LDL receptors are involved in HCV entry into hepatocytes, higher LDL levels may decrease the number of LDL receptors on the cell membrane, thus decreasing cellular infectivity .
Do Genotypes Change Over Time
A viruss genotype usually stays the same. Genetic changes, or mutations, can occur at random or in response to the environment. Some mutations are harmless, but others can affect how well a patient responds to treatment. New HCV treatments include more than one drug to prevent drug resistance from happening by targeting more than one step in the virus life cycle. However, if patients miss treatment doses, this can lead to genetic mutations, which cause resistance to HCV treatment .
HARDER TO TREAT GENOTYPE 3
Genotype 3 is the second most common HCV subtype in the world, particularly in Northern Europe, South Asia, and Southeast Asia. It can pose more difficult health problems for people with HCV, including more rapid progression of liver disease, increased rates of steatosis , and a higher risk for cancer . Genotype 3 has been associated with unique characteristics, such as how it creates resistance to insulin and how it causes the liver to break down fats, which make it harder to treat with DAAs.
People infected with genotype 3 are the most challenging to treat if they:
- have previously tried treatment
- have cirrhosis, and
- have , which is a life-threatening condition leading to liver failure.
Genotype 3 often requires longer treatment and does not achieve strong cure rates. There are lower cure rates in patients with cirrhosis.
Also Check: Treatment To Cure Hepatitis C
Genotype Table: Recommended Treatments For Hepatitis C Genotypes 1 2 3456
| Generic Brand Name | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis c Genotype 1, 4, 5, 6 treatment. It is mainly used to treat Hep C | A combination pill taken once a day. Its usually taken for 12-24 weeks, and sometimes only 8 weeks. | Major side effects are rare. | Natco, Hetero, Mylan, Zydus Cadila, Dr. Reddy | ||
| Hepcinat, Sofovir, Myhep, Sovihep, Resof | 400 mg Sofosbuvir | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 | 1 Sofosbuvir pill and 1 Daclatasvir pill once a day for 12 weeks. Sometimes used with Ribavirin. | Major side effects are rare. | Natco, Hetero, Mylan, Zydus Cadila, Dr. Reddy |
Sofosbuvir Plus Pegylated Interferon/ribavirin
The combination of SOF plus PegIFN/RBV for 12 weeks is the only interferon based therapy recommended by the EASL and AASLD guidelines for the treatment of HCV genotype 3 infection .
In naive non-cirrhotic patients, SOF plus PegIFN/RBV for 12 weeks resulted in an overall SVR of 92-100% . However, efficacy data is scarce: few patients were included in clinical trials and only three studies evaluated the SVR rates in this population. The phase II study included 25 naive non-cirrhotic patients treated with SOF plus PegIFN/RBV for 12 weeks, reaching an overall SVR rate of 92%, but no SVR data according to specific genotype is available 70033-1.). Another phase II study included 17 patients treated with SOF plus PegIFN/RBV for either 12 or 8 weeks and the overall SVR rate was 100% in both arms . The Boson phase III study included 71 naive non-cirrhotic patients with HCV genotype 3 infection treated with SOF plus PegIFN/RBV for 12 weeks, achieving an overall SVR rate of 96% .
In non-cirrhotic patients, including naive and with previous failure to PegIFN/RBV, SOF plus PegIFN/RBV for 12 weeks resulted in high SVR rates . It must be noted that non-significant differences in SVR rates were observed among naive and treatment-experienced patients, but these data need to be cautiously analyzed, since only small cohorts were included in the studies.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis Ca Sexually Transmitted Disease
Sofosbuvir Plus Daclatasvir With Or Without Rbv
The combination SOF plus DCV for 12 weeks is recommended by EASL and AASLD for the treatment of patients with HCV genotype 3 infection . In non-cirrhotic patients with HCV genotype 3 infection, whether naive or treatment-experienced, SOF plus DCV with or without RBV for 12 or 24 weeks resulted in an overall SVR of 80100% .
Among naive or treatment-experienced patients without cirrhosis, treatment with SOF plus DCV for 12 weeks resulted in an overall SVR of 9497% . Two studies evaluated SOF plus DCV for 12 weeks in naive or treatment-experienced non-cirrhotic patients with HCV genotype 3 infection . ALLY-3, a phase III clinical trial, included 75 naive and 34 previously treatment-experienced patients and SVR rates were, respectively, 97% and 94% . An observational study included 25 naive and treatment-experienced patients, 24 of whom achieved SVR .
A single study, ALLY-3+, evaluated the addition of RBV to SOF plus DCV for 12 or 16 weeks for HCV genotype 3 naive or treatment-experienced patients without cirrhosis, including 14 patients with advanced fibrosis, but without cirrhosis. Six patients were treated for 12 weeks and 8 patients were treated for 16 weeks with SOF plus DCV and RBV, with all of them achieving SVR12 in both the 12- and 16-week treatment arms plus sofosbuvir plus ribavirin for 12 or 16 weeks in HCV genotype 3-infected patients with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis: The ALLY-3+ phase 3 study. AASLD Liver Meeting 2015. San Francisco, November 1317, 2015.).