What Are Some Of The Proven Ways To Prevent Hepatitis B
Healthcare providers stand by vaccination as a reliable prevention measure known to be effective to all age groups- adults, infants, and children. Therefore, close family members and sexual partners of infected persons must get tested and avail HBV vaccination to protect themselves. Medications have also been in use to prevent chronic HBV infection. Additionally, the power of vaccination of sexual partners and close family people cannot be overemphasized in aiding protection against the disease. Apart from vaccination, a few pointers to prevent hepatitis B Infection: Always make sure needles used for acupuncture, body piercing, tattoos, and ear piercing are sterile. Sanitary napkins and tampons need to be disposed of in a hygienic manner. Adopt effective hygiene upon exposure to contaminated blood like washing your hands well using soap. Avoid exposure of wounds to contamination. Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
What Is The Most Challenging Aspect Of Hepatitis B Infection
Hepatitis B can very easily escape diagnosis, as most victims do not know they are suffering can spread the disease. This is because symptoms are almost negligible during the onset of hepatitis B infection. Although the infection is treatable and largely preventable, yet early diagnosis can go a long way in the better prognosis of the condition. Further, even though there are good treatment options for hepatitis B, close to a million people with the infection do not make it.Asian countries portray a high prevalence of hepatitis B. This infection is very common among high-risk groups such as people with multiple sex partners, homosexuals, injection drug users or people staying lose to victims of Hepatitis B.
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
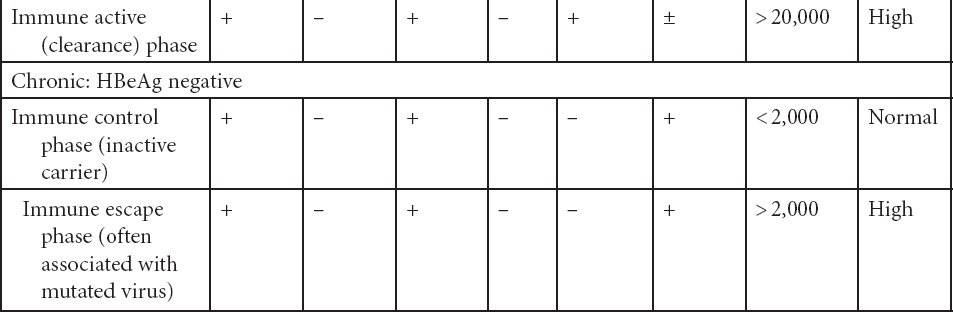
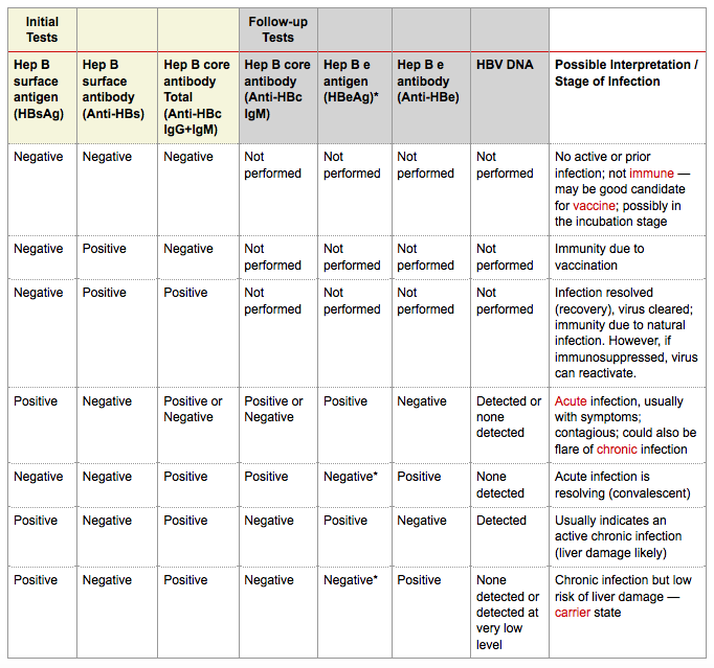
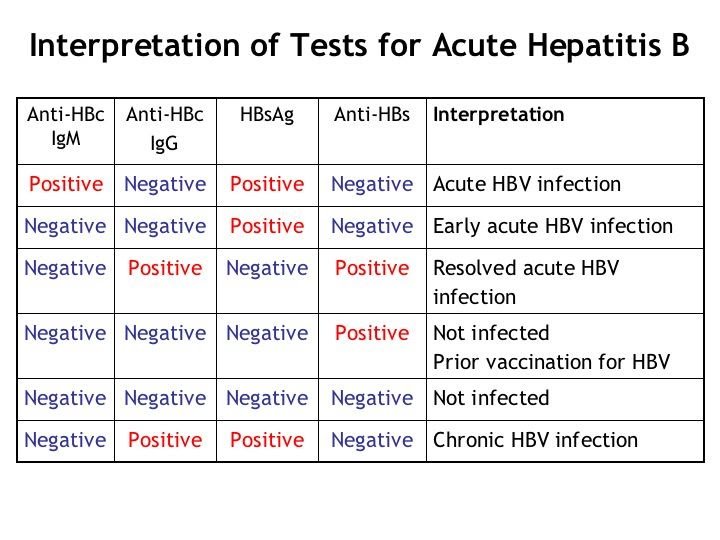
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
Also Check: New Drug To Cure Hepatitis C
Hbc Antibody Positive/hbs Antigen Negative/hbs Antibody Negative
The HBc antibody positive/HBs antigen negative serotype is further divided into naïve and occult types . However, since HBV reactivation is often observed in HBc antibody positive/HBs antigen negative cases, it may be preferable to divide HBc antibody positive/HBs antigen negative cases based on whether they are positive or negative for HBs antibodies. For HBc antibody positive patients, perhaps HBV reactivation is induced by rituximab. Although Hui et al reported a 3%-25% reactivation rate, prophylactic treatment may be desirable since the mortality is relatively high after reactivation occurs. In 2013, Huang et al conducted a randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effect of the prophylactic administration of entecavir on the frequency of HBV reactivation in HBc antibody positive patients. In their report, unlike in retrospective analyses, the prophylactic administration of entecavir was the most important factor, at least for HBc antibody positive patients. Furthermore, Seto et al recently reported frequent reactivation of HBV in patients with 10 mIU/mL HBs antibody prior to rituximab treatment. In HBc antibody positive patients, prophylactic treatment is necessary, at least for those who are antibody negative prior to rituximab treatment . We believe that the prophylactic administration of a nucleic acid analog is preferable in HBc antibody positive/HBs antigen negative/HBs antibody negative cases.
Epidemiology Of Hbv Reactivation
When combined with chemotherapy, the HBV reactivation rate during rituximab treatment has been reported to be 20%-55% overall and 3% in hepatitis B surface antigen negative patients. HBV reactivation can be caused by chemotherapy alone. However, rituximab more easily induces HBV reactivation independently upon combined treatment with chemotherapy or steroid treatment. The frequency of HBV reactivation is also higher with combination treatments including rituximab compared to chemotherapy alone or a combination chemotherapy and steroid treatment. Risk factors for HBV reactivation in patients receiving chemotherapy include being male, lack of HBs antibody, HBs antigen positivity, presence of a precore mutant, HBV-DNA level, anthracycline/steroid use, transplantation, second/third line treatment, youth, and the presence of lymphoma. However, when rituximab is used, the risk factors for HBV reactivation are narrowed to a lack of HBs antibody, youth, and being male. All the above reports are retrospective analyses of patients who were HBs antigen positive and who therefore were subject to prophylactic nucleoside analog therapy. In the future, patient groups must be identified who tend to experience reactivation even when receiving such therapy.
Read Also: How Did You Get Hepatitis C
Hbcab Or The Hepatitis B Core Antibody Test
The hepatitis B core antibody is produced by your immune system after infection by the hepatitis B virus, and it can persist for life. It is a sign that you either have an new, active hepatitis B infection or that you acquired hepatitis B in the past.
HBcAb is an immune system response to a protein in the core of the virus, and it is only present if you have been infected, rather than immunized against the virus. It is part of a routine screening panel of tests for hepatitis B. If your rest results turn out to be positive, your healthcare provider will order further tests to determine the stage of the infection, acute or chronic .
Also Known As: anti-HBc, HBcAb
Do I Really Need To Undergo This Test
Some of the overriding reasons your doctor has advised this test for you could be the following: Risk category of hepatitis B infection Suspicions of a liver infection Contact with infected people or contaminated fluids Symptoms of hepatitis B infection such as fever, abdominal pain, extreme tiredness, nausea, reduced appetite or discolored urine
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms To Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Core Total Antibodies With Reflex To Hepatitis B Core Antibody Igm Serum
Detection and differentiation between recent and past/resolved or chronic hepatitis B viral infection
Diagnosis of recent HBV infection during the “window period” when both hepatitis B surface antigen and antibodies to HBsAg are negative
This test is not useful for determining immunity to or recovery from hepatitis B viral infection.
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
Hepatitis B disease affects the liver and commonly spreads through body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Treatment Options
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B core antibodies appear shortly after the onset of symptoms of hepatitis B infection and soon after the appearance of hepatitis B surface antigen . Initially, anti-HBc Ab consist almost entirely of the IgM class, followed by appearance of anti-HBc IgG, for which there is no commercial diagnostic assay.
The anti-HBc total antibodies test, which detects both IgM and IgG antibodies, and the test for anti-HBc IgM antibodies may be the only markers of a recent hepatitis B infection detectable in the “window period.” The window period begins with the clearance of HBsAg and ends with the appearance of antibodies to hepatitis B surface antigen . Anti-HBc total Ab may be the only serologic marker remaining years after exposure to hepatitis B.
This assay is FDA-approved for in vitro diagnostic use and not for screening cell, tissue, and blood donors.
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
You May Like: Treatment To Cure Hepatitis C
Administration Of Nucleoside Analogs Upon Hbv Reactivation
We must evaluate whether to discontinue nucleoside analog administration in patients receiving those drugs that promote HBV reactivation. Since HBs antibody might become negative during rituximab treatment, discontinuation should be considered after the treatments completion. An additional problem exists with regard to determining the duration of the discontinuation period. Cases of HBV reactivation even after long periods of discontinuation have been documented. For example, even after HBs antibody became temporarily positive, it disappeared later and HBV reactivation was induced. If nucleoside analog treatment is given to HBs antibody negative patients who later become antibody positive, such treatment can be discontinued. On the other hand, HBV vaccination is unable to suppress HBV reactivation. If rituximab is administered continuously, HBs antibody may not be induced even after HBV vaccination. It is necessary to evaluate not only the induction of HBs antibody after HBV vaccination but also diseases that are appropriate for the discontinuation of nucleoside analog treatment. Based on the above discussion, Figure shows the modified guidelines from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare.
The review is summarized as schematics. The treatment direction described here is based on the assumption that all patients are screened in advance. HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B Core Antibody Blood Test Igm
A Hepatitis B Core Antibody Blood Test, IgM, measures HBcAb which is an antibody produced in response to the core-antigen, a component of the Hepatitis B virus.
Also Known As: Anti-HBc, IgM, Antibody to Hepatitis B Core Antigen, IgM, HBcAb, IgM.
Methodology: Immunochemiluminometric assay
Preparation: No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results: 1-2 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
Also Known As: Anti-HBc, IgM, Antibody to Hepatitis B Core Antigen, IgM, HBcAb, IgM.
Methodology: Immunoassay
Preparation: No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results: 1-2 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
Don’t Miss: What Does Hepatitis B Mean
What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
Read Also: Can You Catch Hepatitis C
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
You May Like: What To Do If You Have Hepatitis C
An Interesting Case Of Isolated False
He S. Yang
1Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, New York Presbyterian Hospital, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, USA
2Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, New York Presbyterian Hospital, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, USA
Abstract
1. Introduction
Here, we report a case of a female patient with persistent isolated HBsAg positivity with a lack of symptoms, other serological markers, risk factors, or vaccination to explain the positivity, highly suggestive of a false-positive result requiring thorough investigation to evaluate potential interferences.
2. Case Report
Upon further review of the patients history, no recognized, self-reported risk factors for viral hepatitis including unprotected sex, blood transfusions, tattoos, or intravenous drug abuse were reported. Furthermore, the patient denied personal or family history of liver disease or jaundice. Physical examination did not reveal stigmata of liver disease. Considering the patients low risk for blood-borne infections, it was suspected that the HBsAg and HIV screening results might be false positives due to an unknown interference with the analytical assays.
The patient was retested 3 months after her Mohs surgery. The HBsAg and HIV screening tests remained positive. This study has been approved by the institutional review board of Weill Cornell Medicine.
3. Discussion
Data Availability
Conflicts of Interest
Hepatitis B Core Ab Total Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Don’t Miss: What Does Hepatitis B Come From
What Are Some Of The Severe Complications Of Hepatitis B Infection
Chronic Hepatitis B infection in both children and adults can lead to health complications such as acute damage to liver cells, cirrhosis, and cancer. The virus can take as long as six months to be eliminated from the system, although in many cases, especially among new-borns, the infection continues to remain.
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to hepatitis B, your body mounts an immune reaction against it as an invader. This happens whether you are exposed due to blood or sexual contact or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The hepatitis B virus has proteins on its surface that cause your immune system to produce antibodies. With the vaccine, the sample contains the protein only and not the virus itself.
The first response your body will make when exposed to hepatitis B is to manufacture hepatitis B IgM antibodies. These early antibodies are produced to fight against several parts of the virus including its core. These antibodies are seen in the initial response, but they eventually fade away.
Your immune system then begins to produce IgG antibodies. It continues to produce these antibodies for the rest of your life. In this way, your immune system is always ready to attack hepatitis B virus when it is exposed to it.
Recommended Reading: Signs You Have Hepatitis B
What Do My Test Results Mean
Your age, gender, and medical history will also be factors that will come into play for the results of the test. Your healthcare provider is the best person who can help you with decoding your test results. If the result is Non-reactive or Negative, it indicates the absence of Hepatitis B core IgM antibodies in the blood. It means there is no recent or earlier HBV infection in the blood. If your test result is positive, it shows the presence of acute hepatitis B infection. The IgM anti-HBcshows up in the blood at about the same time symptoms manifest. The time taken to completely recover from this infection is about 06 months this also means that you will develop immunity from the HBV virus. Therefore, you will not contribute to the spread of the infection. Doctors recommend a followup of blood tests for hepatitis after 6 months. In case, you do not recover in 6months, then it is a far greater problem as the virus stays in the blood. It can damage the liver as well as spread the infection to others.
Being Tested For Hepatitis B Core Antibody
The hepatitis B core antibody test is part of a screening panel for hepatitis B, which also will include hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B surface antibody . These three tests look for acute and chronic infections.
Tests may be ordered if you have symptoms of hepatitis, such as jaundice , fever, fatigue, pale stools, dark urine, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. In this case, the hepatitis B core antibody IgM test may be used, as it shows an early stage of infection.
This test may be ordered if you are being screened for hepatitis B because you are donating blood or wish to become an organ donor. Hepatitis B can be transmitted by blood or through organ transplants, so donors are tested to prevent infecting recipients. It’s possible to have had the infection with only mild symptoms, so many people don’t realize they have had hepatitis B.
People who are part of populations at risk for hepatitis B infection will be screened. Screening is also often done for pregnant people, infants, people sharing a home with hepatitis B patients, people who may have been exposed by needlestick injuries or body fluids, and for people with HIV .
Recommended Reading: How Bad Is Hepatitis C