Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
Theres Reason For Hope With Hepatitis C
Unfortunately, even when people are diagnosed with hepatitis C, many dont do anything about it. According to a report published in May 2013 in the New England Journal of Medicine, only about a third of people with hepatitis C receive medical care for their condition.
Yet Singh says hes seeing more people with hepatitis C than ever before, as people are finding out that new treatment options often work well. New treatments for hepatitis C have been revolutionary, he says. Over 95 percent of patients can be cured with three months of treatment.
Newer antiviral drugs can clear the virus even in people who have had no luck on earlier medications. They also generally take less time to start working, cause fewer side effects, and can treat and even eliminate illnesses caused by hepatitis C.
The CDC recommends that all American adults over age 18 get screened at least once. Pregnant women should be tested during each pregnancy. People who inject drugs, share needles, or have received maintenance hemodialysis are also at risk. If you are in one of these higher risk groups, you should be tested routinely. Talk to your doctor.
If you do test positive and get treated, keep in mind that damage from liver cirrhosis usually cant be reversed, Singh says. Following treatment, youll be monitored closely for liver cancer and other health problems.
How Do You Treat Hepatitis C
People with acute infection do not always need treatment, because their immune system may clear hepatitis C on its own. If you test positive during the acute stage, your doctor may ask you to come back after a few months to re-test and to see if you need any treatment.
If people develop chronic infection, they will need treatment to help clear the virus. Where available, treatment with drugs called direct-acting antivirals can cure hepatitis in most cases. These are usually taken for 8-12 weeks. Your doctor will also check your liver for any damage.
If youve had hepatitis C in the past, youre not immune to future infections which means you can get it again. You can also still get other types of hepatitis, and having hepatitis C together with another type is more serious.
If youve already had hepatitis C, its advisable to have the vaccination against hepatitis A and B to protect your liver from further damage.
Whether you have symptoms or not, dont have sex until your healthcare professional says you can.
Also Check: How To Cure Hepatitis C Naturally
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
The new hepatitis C medicines have not been tested in pregnancy.
You should not become pregnant while taking treatment as it could be harmful to unborn babies.
If you’re pregnant, you must delay treatment until after your baby is born.
Speak to your doctor before starting hepatitis C treatment if you’re planning to become pregnant in the near future.
You’ll need to wait several weeks after treatment has ended before trying to get pregnant.
Women taking ribavirin should use contraception during treatment and for another 4 months after the end of treatment.
Men taking ribavirin should use a condom during treatment and for another 7 months after the end of treatment. This is because semen can contain ribavirin.
If you become pregnant during treatment, speak to your doctor as soon as possible to discuss your treatment options.
Hepatitis C Symptoms In Men
Hepatitis C symptoms in men are the same as in women. However, a 2014 study indicated that men may be less likely to clear the virus than women.
Hepatitis C in men may stay in their systems longer. It may also be more likely to cause symptoms in men compared to younger women.
Currently, there isnt a hepatitis C vaccine, though research is underway. However, avoiding contact with the blood of someone who has an HCV infection can help prevent you from acquiring the hepatitis C virus.
You can do this by:
- avoiding using someone elses razor, nail clippers, or toothbrush
- not sharing needles or syringes
- getting tattoos or piercings only at licensed facilities
- practicing safer sex with your partner by using condoms or other barrier methods
If you think you may have been exposed to HCV, its important to get tested as soon as possible.
Untreated chronic hepatitis C may eventually lead to complications, which can include severe scarring of the liver, which is called cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
Some people with hepatitis C may need a liver transplant.
If you believe you contracted HCV, the sooner you receive a hepatitis C diagnosis, the sooner your doctor can start a treatment plan to help you avoid complications.
You May Like: What Organ Does Hepatitis C Affect
How Often To Use
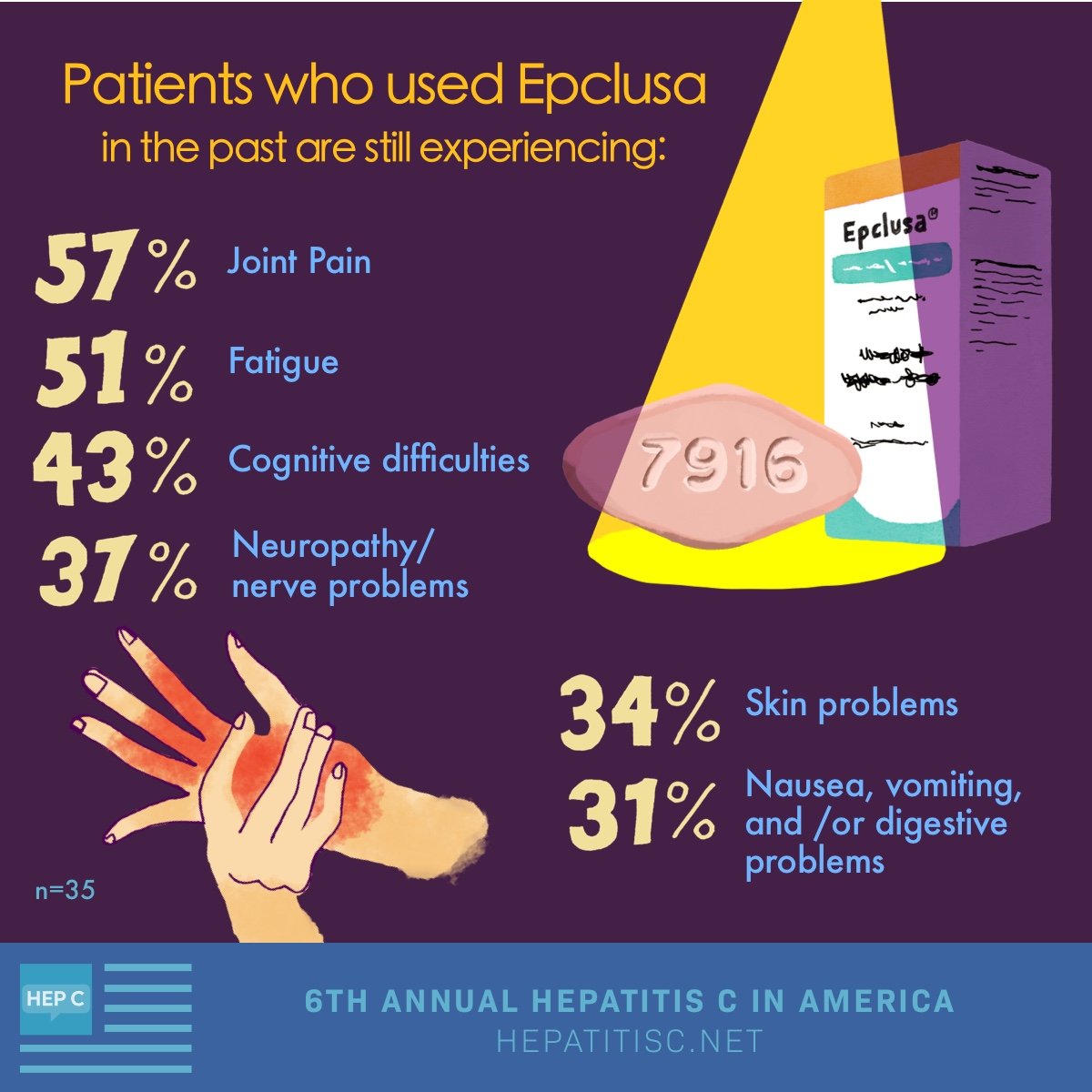
You may be wondering how long you have to take Epclusa to treat hepatitis C. Youll likely use the drug once daily for 12 weeks. This is the amount of time it takes for Epclusa to clear the hepatitis C virus from your body.
Its extremely important to not miss or skip doses of Epclusa. Missed or skipped doses can lower the level of the drug in your blood, which may cause Epclusa to work less well than usual. As a result, the drug may not clear the hepatitis C virus from your system.
To avoid missing a dose, try setting a reminder on your phone. If you do miss a dose of Epclusa, its important that you call your doctor right away. Theyll advise you on the best action for you to take.
Hepatitis C is an infection caused by the hepatitis C virus. The virus is transmitted through blood or body fluids, which can occur in several ways, including:
- sharing needles with a person who has the virus
- getting pricked by a needle that has the virus, which can be common in a healthcare setting
- having sex with someone who has the virus without using a condom or other barrier method
Once inside your body, hepatitis C virus attacks cells in your liver, causing inflammation.
How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis C To Others
If you have hepatitis C, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Tell your sex partner you have hepatitis C, and talk with your doctor about safe sex practices. In addition, you can protect others from infection by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care providers that you have hepatitis C. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.
Also Check: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
How To Know If Your Treatment Is Working
While you take any of these drugs, your doctor will keep close tabs on you. During office visits, they’ll check your overall health and ask about any side effects that you have and how you’re handling them.
During your treatment, you’ll also get blood tests. They measure your “viral load” — the amount of HCV that’s in your body.
Your treatment is a success if tests show that HCV is no longer in your blood 3 months after you stop taking the antiviral medicine. When you hit this milestone, it’s a good sign that you’ll stay virus-free.
What Are The Different Types Of Blood Tests How Often Should I Get These Tests Done
There are several different blood tests, or “labs” that your provider may order for you. The tests measure the amounts of various proteins and enzymes that the liver produces. This is a way of finding out how damaged the liver is. Your provider can determine how often each test needs to be done. Please see Understanding Lab Tests for more details about the tests you may have.
Recommended Reading: How Much Is Hepatitis A Vaccine
How Effective Is Treatment
Direct acting antivirals cure 9 out of 10 patients with hepatitis C.
Successful treatment does not give you any protection against another hepatitis C infection. You can still catch it again.
There’s no vaccine for hepatitis C.
If treatment does not work, it may be repeated, extended, or a different combination of medicines may be tried.
Your doctor or nurse will be able to advise you.
Tips And Remedies To Help With Side Effects
There are things you can do to ease many of the side effects from hepatitis C treatment.
Remember that these side effects will typically go away once you’re cured, so stick with your treatment. Work with your doctor on your treatment plan so that you can manage any problems and try to get the virus out of your body as soon as possible
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost Without Insurance
What Laboratory Tests Diagnose Hepatitis C
Laboratory blood tests will be done to evaluate the patient’s liver function and to look for hepatitis C antibodies . If these tests indicate that the person has hepatitis C, a hepatitis C “viral load” test will be done. This looks for genetic material from the hepatitis C virus and measures the quantity of hepatitis C virus that is circulating in the patient’s blood. This is helpful in determining if treatment is appropriate and to monitor the success of the treatment .
Individuals who had hepatitis C in the past and cleared the virus on their own will have a positive HCV antibody test, but there will be no hepatitis C virus genetic material in the blood. If a person is immunosuppressed due to an immunological condition, cancer chemotherapy, immunotherapy or HIV/AIDS, the test results may be different and need to be evaluated accordingly.
Why Should I Get Treated

Hepatitis C can be fatal when left untreated.
Untreated hepatitis C can lead to scarring of the liver known as cirrhosis.
A small number of people with cirrhosis will go on to get liver failure, the only treatment for which is a liver transplant. A small proportion of people with cirrhosis develop liver cancer.
Recommended Reading: Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis C
What Other Tests Diagnose Hepatitis C
Once the diagnosis of hepatitis C is established, other tests may be done to determine whether the patient has developed liver fibrosis or scarring . This can be done with a needle biopsy of the liver, and examining the biopsied liver tissue under the microscope. Liver biopsy is less commonly done today because noninvasive tests are more readily available, more easily accomplished and less costly.
Liver imaging can evaluate fibrosis using ultrasound and MRI scans. Additionally, calculations using a variety of blood tests also can predict the degree of inflammation and fibrosis present. Genotype testing will typically be done to determine what subtype of hepatitis C the patient has, as this will impact what drugs are used for treatment. Testing for other infections including HIV, hepatitis A, and hepatitis B is typically done to determine if the patient might have other conditions that could impact patient’s treatment and prognosis.
With the newest forms of antiviral treatment, the most common types of chronic hepatitis C can be cured in most individuals.
Who Can Be Treated For Hepatitis C
Treatment decisions should be made by both you and your provider. Current treatments for hepatitis C are very successful and can cure most people of the virus.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Antibody Negative Means
What Is Hepatitis C Infection How Many People Are Infected
Hepatitis C virus infection is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus . It is difficult for the human immune system to eliminate hepatitis C from the body, and infection with hepatitis C usually becomes chronic. Over decades, chronic infection with hepatitis C damages the liver and can cause liver failure. In the U.S., the CDC has estimated that approximately 41,200 new cases of hepatitis C occurred in 2016. When the virus first enters the body there usually are no symptoms, so this number is an estimate. About 75%-85% of newly infected people become chronically infected. In the U.S., more than 2 million people are estimated to be chronically infected with hepatitis C. Infection is most commonly detected among people who are 40 to 60 years of age, reflecting the high rates of infection in the 1970s and 1980s. There are 8,000 to 10,000 deaths each year in the U.S. related to hepatitis C infection. HCV infection is the leading cause of liver transplantation in the U.S. and is a risk factor for liver cancer. In 2016, 18,153 death certificates listed HCV as a contributing cause of death this is believed to be an underestimate.
Those who have cirrhosis from HCV also have a yearly risk of liver cancer of about 1%-5%.
Who Is At High Risk And Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C Infection
The U.S. Preventive Health Services task force recommends that all adults born between 1945 and 1965 be tested once routinely for hepatitis C, regardless of whether risk factors for hepatitis C are present. One-time testing also is recommended for:
- People who currently inject drugs or snort drugs, or ever did so, even once many years previously
- People with persistently elevated alanine aminotransferase level, a liver enzyme found in blood
- People who have HIV infection
- Children born to HCV- or HIV-infected mothers
- People who were ever on long-term hemodialysis
- People who got a tattoo in an unregulated setting, such as prison or by an unlicensed person
- People who received clotting factor produced before 1987
- People who received transfusions or organ transplants before July 1992, or who were notified that they received blood from a donor who later tested positive for hepatitis C infection
- Health care, emergency medical, and public safety workers after a needlestick, eye or mouth exposure to hepatitis C-infected blood
People who may have been exposed to hepatitis C in the previous 6 months should be tested for viral RNA load rather than anti-HCV antibody, because antibody may not be present for up to 12 weeks or longer after infection, although HCV RNA may be detectable in blood as soon as 2-3 weeks after infection.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C A Disease
Spread Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is spread through blood-to-blood contact when blood from a person with hepatitis C enters another persons bloodstream.
The most common way people become infected with hepatitis C in Australia is by sharing injecting equipment such as needles, syringes, spoons and tourniquets. It is possible to be infected with hepatitis C after only one risk event.
Hepatitis C may also be spread through:
- tattooing and body piercing with equipment that has not been properly cleaned, disinfected or sterilised such as backyard tattoos’. Registered parlours with appropriate infection control procedures are not a risk
- needlestick injuries in a healthcare setting
- receiving blood transfusions in Australia prior to 1990 before hepatitis C virus testing of blood donations was introduced
- medical procedures, blood transfusions or blood products and mass immunisation programs provided in a country other than Australia
- pregnancy or childbirth there is a 5% chance of a mother with chronic hepatitis C infection passing on the virus to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
Breastfeeding is safe, however if nipples are cracked or bleeding cease breastfeeding until they have healed.
Less likely possible routes of transmission of hepatitis C include:
Hepatitis C cannot be transmitted by:
- kissing
- sharing food, cups or cutlery
- shaking hands or day-to-day physical contact.
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis C
For people with hepatitis C, the goal of treatment with antiviral medication is to prevent the virus from replicating, or copying itself, and to eliminate the virus from the bloodstream. If the hepatitis C virus has been in the body for more than six months, the infection is considered chronic. Without treatment, most people with acute hepatitis C develop the chronic form of the disease.
Your doctor decides which antiviral medicationor combination of medicationsto prescribe based on the results of a blood test called a genotype test. There are six genotypes, or strains, of the hepatitis C virus, and people with certain genotypes respond more quickly to medical treatment.
For many years, the standard treatment for chronic hepatitis C consisted of the antiviral medications pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Ribavirin is taken by mouth every day, and interferon is an injection that you or a caregiver can administer once a week at home.
In 2013 and 2014, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a group of new medications for the treatment of hepatitis C. These medications, which include sofosbuvir, are very effective and have fewer side effects than older medications, particularly interferon.
Don’t Miss: Best Juice For Hepatitis B