Other Hepatitis C Tests
After an individual has received a reactive or positive result from a hepatitis C antibody test, they will need to have two follow-up tests.
The first test checks to see whether a person still has the virus the other measures the amount of the virus in the blood.
The first test is the hep C RNA qualitative test, also known as the PCR test. A positive result means that a person has the hepatitis C virus. A negative result means that the body has cleared the virus without treatment.
The second test is the hep C RNA quantitative test. The result of this test is given as a number rather than a positive or negative. This is because the test compares the amount of the virus in the body before, during, and after treatment.
The number given as a result of this test is known as the viral load. The lower amount of the hepatitis C virus in the blood, the better the chances that a person can eliminate the virus from their body.
After hepatitis C virus is diagnosed, other tests may be needed:
Certain behaviors, experiences, and medical procedures increase the risk of getting the hepatitis C virus, which is transmitted by contact with blood.
The following are risk factors for contracting the virus:
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advise all baby boomers get tested for hepatitis C. Baby boomers are people born between 1945 and 1965. They are five times more likely to have the virus than other adults.
Treatment For Hcv Infection
Treatment for HCV infection is available. The role of treatment in acute infection is being evaluated and currently the existing data shows that response to 6 months of standard therapy with interferon in terms of absence of HCV RNA from serum is excellent and progression to chronicity is reduced. The recommended treatment for chronic HCV infection is a combination of a pegylated IFN alpha and ribavirin. The treatment duration depends on the genotype of the virus and it has two goals. The first is to achieve sustained eradication of HCV, that is, sustained virologic response , which is defined as the persistent absence of HCV RNA in serum for 6 months or more after completing antiviral treatment. The second goal is to prevent progression to cirrhosis, HCC, and decompensated liver disease requiring liver transplantation.
What To Think About
- There is no vaccine to prevent infections with the hepatitis C virus.
- All donated blood and organs are tested for hepatitis C before being used.
- Other tests that show how well the liver is working are usually done if your doctor thinks you may have hepatitis C. These may include blood tests for bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, alanine aminotransferase, and aspartate aminotransferase.
- Aspartate Aminotransferase
You May Like: Hepatitis C Can You Get Rid Of It
What Do The Results Mean
There are two results from a hepatitis C antibody test.
- A non-reactive or negative test result means that the person does not have the virus. The exception is if someone has come into contact with the virus recently, such as through contaminated blood. If this is the case, they will need to have another test.
- A reactive or positive test result means that the person has had the virus at some point but does not mean that they still have it. Further tests will be needed to check whether the virus is still active in the body and if treatment will be required.
Once diagnosed with hepatitis C, a person will need to undergo a series of different tests to see how the virus has affected their body.
These tests will check for any liver damage, identify how well the liver is working, and help a healthcare professional to decide on treatment.
Hepatitis C is treated with medication known as an antiviral. It gets this name because it aims to clear the virus out of the body.
Another aim of the medication is to slow down damage to the liver. It may also reduce the chance of a person getting liver cancer or developing serious liver scarring, known as cirrhosis.
A person with hepatitis C will require regular testing during treatment to see how well the medication is working. Keeping healthy, getting enough sleep, and avoiding drugs and alcohol can help treatment to work.
Hcv Core Antigen Detection
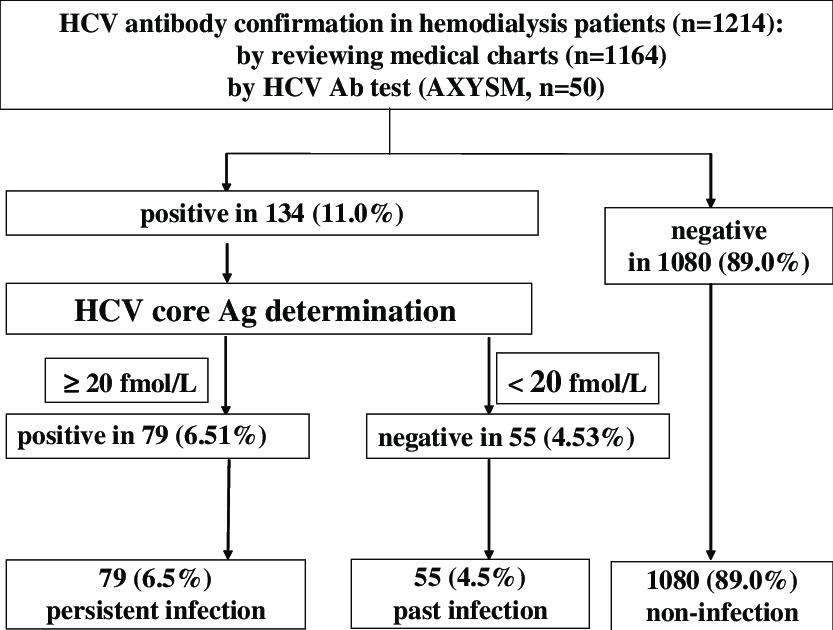
During the past decade, several assays for the detection of the core antigen of HCV by ELISA or CLIA have been developed. These assays were envisioned as alternatives to NAT to be used in resource-limited settings, where molecular laboratory services are either not available or not widely utilized owing to cost issues. Since these assays are either ELISA or CLIA based, they are user friendly, require less technical expertise and are less expensive compared to molecular techniques. Evaluations in transfusion settings have shown that the HCVcore Ag assay detects HCV infection as effective as NAT, about 40-50 days earlier than the current third generation anti-HCV screening assays. HCV core antigen levels closely follow HCV RNA dynamics, and allow clinical monitoring of a patient’s therapy, independently of HCV genotype. The major limitation of the HCV core Ag assay is its lower sensitivity limiting its utility. A new generation CLIA based quantitative test with sensitivity comparable to that of end point PCR but less than that of real time RT-PCR has been reported.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms To Hepatitis C
What If You Lost Your Hepatitis B Immunity
There is a reason that they dont recommend testing more than one to two months after your last dose of hepatitis B vaccine.
Studies indicate that immunologic memory remains intact for at least 20 years and confers protection against clinical illness and chronic HBV infection, even though anti-HBs levels that once measured adequate might become low or decline below detectable levels. If one is challenged with HBV, people whose immune systems are competent will mount an anamnestic response and develop protective anti-HBs.
Immunization Action Coalition on Hepatitis B Questions
It is known that anti-HBs levels can decrease over time.
Fortunately, this does not lead to waning immunity in typical circumstances. Because of an anamnestic response, the hepatitis B vaccine provides long lasting protection, even if your antibody levels appear to have dropped.
Is It Safe To Take Aspirin Or Tylenol If I Have Hepatitis C
Tylenol is an over-the-counter pain killer. It can be harmful in high doses. If you have hepatitis or liver disease, then you can take Tylenol, but no more than 2,000 mg total over 24 hours. In general, this could be one 500 mg tablet every 6 hours, at the most. Acetaminophen is also included as an ingredient in some opiate medications and in some over-the-counter cold/flu medications, so please be aware of the dose of acetaminophen you may be taking from some combination medicines.
Aspirin, ibuprofen , naproxen , and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , can be harmful if you have cirrhosis. They are safe in hepatitis patients who do not have cirrhosis. But, if a patient has cirrhosis, then NSAIDs cannot be taken at all. If you are not sure, always check with your provider.
Also Check: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B Virus
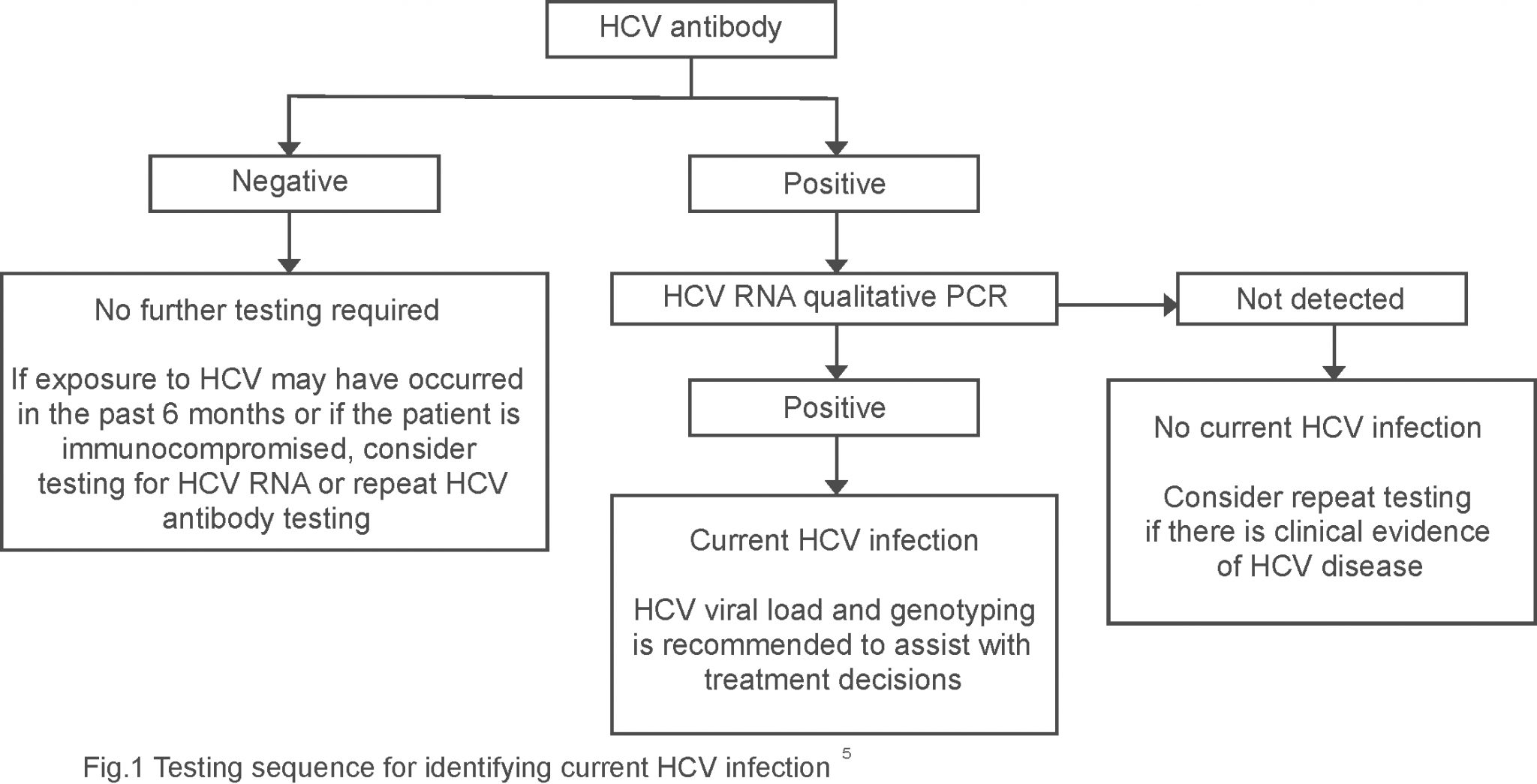
What Are The Tests For Hepatitis C
There are two blood tests needed to diagnose hepatitis C:
The antibody test–called HCV antibody, HCV Ab, or anti-HCV–is done first. If this test is positive, it means that you have been infected with hepatitis C at some point in the past. If your antibody test is negative, then you have never been infected with hepatitis C if you were infected within the past month or so, the test may not be accurate you may needed to be retested at a later date.
However, a positive antibody test does not tell you if you still have hepatitis C. For that, you need to have a HCV RNA test, which determines whether the virus itself is in the bloodstream.
If any RNA is present in the blood after 6 months from time of infection, then you have chronic hepatitis C.
If no RNA is detected in the blood after 6 months, you no longer have hepatitis C.
Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
A positive result indicates the presence of hepatitis C virus -specific IgG antibodies due to past or chronic hepatitis C. Past HCV infection can be distinguished from chronic HCV infection only by direct detection of HCV RNA using molecular test methods eg, HCVQN / Hepatitis C Virus RNA Detection and Quantification by Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR , Serum. HCV RNA is present in acute or chronic hepatitis C but not in past HCV infection.
A negative result indicates the absence of HCV-specific IgG antibodies. A reactive HCV antibody screening test result with a negative HCV antibody confirmatory result indicates a probable false-reactive screening test result.
An indeterminate result indicates that HCV-specific IgG antibodies may or may not be present. Indeterminate results should be interpreted along with patient’s risk factors for HCV infection and clinical findings. Individuals at risk for HCV infection with indeterminate results should be retested with an HCV antibody confirmatory test in 1 to 2 months to determine the definitive HCV antibody status. Molecular tests to detect HCV RNA may be necessary to determine HCV infection status in those at-risk immunocompromised patients with indeterminate HCV antibody confirmatory test results due to delayed appearance of fully complement of HCV-specific antibodies.
Don’t Miss: What Does It Mean If You Have Hepatitis C Antibodies
Who Can Be Treated For Hepatitis C
Treatment decisions should be made by both you and your provider. Current treatments for hepatitis C are very successful and can cure most people of the virus.
Can I Get Reinfected With Hepatitis C
If you become infected with hepatitis C infection and then clear the virus , yes, it is possible for you to become infected again.
The chance of another infection with hepatitis C is much, much less than the chance of a first-time infection, but it is not impossible. It has happened in people who continue to use injection drugs, and some studies suggest that it happens even more often in people who are also HIV positive.
In other words, having had hepatitis C once does not make you “immune” to getting hepatitis C again.
The best way to avoid reinfection is to reduce risky behaviors that can result in exposure to the hepatitis C virus: Do not use injection drugs, do not share needles for any reason, avoid blood-to-blood exposures with others, and use condoms if you are sexually active with a new partner or with a partner who has used injection drugs.
The research in this area is ongoing, and we will continue to learn more about this very important topic. But for now, preventing re-exposure to the hepatitis C virus is the only sure way of avoiding infection and reinfection with hepatitis C.
You May Like: What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis
Blood Transfusion Issues And Donor Counseling
Guidelines for donor notification for donors positive for transfusion transmissible infections are outlined in An Action Plan for Blood Safety by National AIDS Control Organization 2004. A blood donor is offered an option to know his TTI status at the time of registration for blood donation after due counseling and give consent for the same.
Notifying donors regarding a single positive screening test is fraught with the risk of causing undue anxiety and stress to a donor. If a screening test is positive, the blood unit should be immediately discarded. Presently there are no guidelines regarding confirming the test results before informing the donor. In case of samples with low S/CO and grey zone samples, a retesting of the donor samples using a different assay would be imperative before notifying the donor. There are clear cut guidelines regarding donor notification and referral for HIV positive blood donors with integrated counseling and testing centers available for the same. Donors who are positive for viral hepatitis markers have to be counseled by blood bank staff. An algorithm for donor counseling for HCV positive donors is outlined in .
Algorithm for donor counseling for HCV positive donors
Why It Is Done
You may need these tests if:
- You have symptoms of hepatitis.
- You may have been exposed to the virus. You are more likely to have been exposed to the virus if you inject drugs or are exposed to body fluids .
- You’ve had other tests that show you have liver problems.
- You are 18 to 79 years old.
- You have an HIV infection.
The tests also are done to help your doctor decide about your treatment and see how well it works.
You May Like: Colloidal Silver And Hepatitis C
How Common Is Hepatitis C
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention think that 2.4 million Americans are infected with HCV. It is the most common infection carried by blood in the United States. Veterans have higher rates of hepatitis C than the rest of the country so it is especially important to discuss hepatitis C testing with your provider if you are a Veteran. But, Veterans are not the only ones with high rates of hepatitis C. Baby boomers have higher rates of hepatitis C than people in other age groups in the country as well. Often, people infected with hepatitis C are not aware of their infection because they have no symptoms and they do not feel ill so getting tested if you are at higher risk is important step.
How Do I Tell Someone I Have Hepatitis C
Informing someone that you have hepatitis C can be hard. Most people know little about this disease. You can start with how you found out about your diagnosis. It helps to be prepared with educational materials on HCV, and to be aware of the ways that people can and cannot be infected. For example, it is very rare for HCV to be transmitted during sex. Be sure to tell anyone who may be directly affected, such as:
You may want to encourage others to be tested for HCV if they have similar risk factors.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Contagious Through Urine
How Could A Person Have Been Exposed To Hepatitis C
HCV is spread primarily by direct contact with human blood. For example, you may have gotten infected with HCV if:
-
You ever injected street drugs, that may have had someone else’s blood that contained HCV on them. With the opioid crisis we are facing, we are now seeing increased rates of new hepatitis C infection.
-
You received blood, blood products, or solid organs from a donor whose blood contained HCV.
-
You were ever on long-term kidney dialysis as you may have unknowingly shared supplies/equipment that had someone else’s blood on them.
-
You were ever a healthcare worker and had frequent contact with blood on the job, especially accidental needlesticks.
-
Your mother had hepatitis C at the time she gave birth to you. During the birth her blood may have gotten into your body.
-
You ever had sex with a person infected with HCV.
-
You lived with someone who was infected with HCV and shared items such as razors or toothbrushes that might have had his/her blood on them.
Are There Home Tests For Hepatitis C
Yes. For example, the OraQuick HCV Rapid Antibody Test was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2011 for at-home screening for HCV for people showing signs or symptoms of HCV infection or who are at high risk for infection.It involves taking a sample of blood from a fingertip, mixing it with a special solution, and then using a device similar to a pregnancy test stick that detects the presence of HCV antibodies. The test is 98% accurate.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva
When Should I Get Hepatitis C Testing
When used for early detection in patients without symptoms of hepatitis C, screening is recommended at least once for all adults aged 18 years or older, except in locations with very low prevalence of HCV. Screening is also recommended during pregnancy and for patients of any age with risk factors for HCV infection. In patients with risk factors, periodic screening is recommended for as long as risk factors persist.
Risk factors for HCV include:
- Current or past injectable drug use
- Having a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- Receiving kidney dialysis
- Pain in the abdomen or joints
- Nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite
- Jaundice or yellowish skin and eyes
Hepatitis C testing may also be performed when liver tests are abnormal or when diagnosing the cause of existing liver damage.
Did Your Hepatitis B Antibody Test Come Back Negative
Three doses of the hepatitis B vaccines have been shown to provide long lasting protection in most people.
Do you need to get your titers checked to make sure you are immune?
Usually not. Simply being fully vaccinated with the vaccine is good enough evidence that you are immune in most, but not all circumstances.
A few circumstances in which you might need to be tested can include:
- a baby who was born to a HBsAg mother
- being a healthcare worker who has a job and who is in a work setting that puts them at higher risk for exposure to blood or body fluids from patients who are positive for HBsAg
- being immunocompromised, so you are not sure if the vaccine is going to work, or patients requiring chronic dialysis
- someone who has sex or shares needles with a person who has a chronic hepatitis B infection
The screening test for vaccine immunity that is done checks the persons level of anti-HBs . It should be done one to two months after your last dose of hepatitis B vaccine, but not later.
Persons determined to have anti-HBs concentrations of 10 mIU/mL after receipt of the primary vaccine series are considered immune, and the result should be documented. Immunocompetent persons have long-term protection and do not need further periodic testing to assess anti-HBs levels.
CDC on Immunization of Health-Care Personnel
You May Like: How Can You Transmit Hepatitis C