Hepatitis A Vaccine Side Effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives difficult breathing swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
You should not receive a booster vaccine if you had a life threatening allergic reaction after the first shot.
Keep track of any and all side effects you have after receiving this vaccine. When you receive a booster dose, you will need to tell the doctor if the previous shot caused any side effects.
Becoming infected with hepatitis A is much more dangerous to your health than receiving this vaccine. However, like any medicine, this vaccine can cause side effects but the risk of serious side effects is extremely low.
-
extreme drowsiness, fainting or
-
high fever .
Common side effects may include:
-
low fever, general ill feeling
-
nausea, loss of appetite
-
headache or
-
swelling, tenderness, redness, warmth, or a hard lump where the shot was given.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report vaccine side effects to the US Department of Health and Human Services at 1-800-822-7967.
What Other Drugs Will Affect Havrix
Before receiving Havrix, tell the doctor about all other vaccines you have recently received.
Also tell the doctor if you have recently received drugs or treatments that can weaken the immune system, including:
-
an oral, nasal, inhaled, or injectable steroid medicine
-
medications to treat cancer, ppsoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, or other autoimmune disorders
-
radiation or
-
medicines to treat or prevent organ transplant rejection.
If you are using any of these medications, you may not be able to receive the vaccine, or may need to wait until the other treatments are finished.
This list is not complete. Other drugs may interact with hepatitis A vaccine, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Not all possible interactions are listed in this medication guide.
Vaccines For People Who Could Become Pregnant
Vaccination is important for everyone of reproductive age, whether planning a pregnancy or not.
During pregnancy, your immune system changes and this can put you at risk for a number of serious infectious diseases and complications. Your baby can also be affected by these infections, which can result in:
- birth defects
- miscarriage
- death
Since an unplanned pregnancy can happen, it’s important to keep your vaccinations up to date at all times. This will help protect you and your baby from certain infections that could cause serious complications. Talk to your health care provider about your vaccination status.
Learn more about vaccination and pregnancy.
Read Also: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Hepatic Formula Dry Dog Food
Vaccine For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Vaccine
It takes only a few shots to protect yourself and your loved ones against hepatitis B for a lifetime.
The hepatitis B vaccine is a safe and effective vaccine that is recommended for all infants at birth and for children up to 18 years. The hepatitis B vaccine is also recommended for adults living with diabetes and those at high risk for infection due to their jobs, lifestyle, living situations, or country of birth. Since everyone is at some risk, all adults should seriously consider getting the hepatitis B vaccine for a lifetime protection against a preventable chronic liver disease.
The hepatitis B vaccine is also known as the first anti-cancer vaccine because it prevents hepatitis B, the leading cause of liver cancer worldwide.
You cannot get hepatitis B from the vaccine. All hepatitis B vaccines that have been used since 1986 are made synthetically meaning the hepatitis B vaccines do not contain any blood products. Learn more.
If you have a current HBV infection or have recovered from a past HBV infection, the hepatitis B vaccine series will not benefit you or clear the virus. However, the vaccine can provide a lifetime of protection for loved ones who do not have hepatitis B and get the vaccine as soon as possible. Testing is the only way to know if you or your loved ones have a current infection or have recovered from a past infection.
Hepatitis B Vaccine Recommendations
Three-Dose Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule
Hepatitis A And International Travel
Who should receive protection against hepatitis A virus before travel?
All susceptible people traveling to or working in countries that have high or intermediate HAV endemicity are at increased risk for HAV infection. These travelers should be vaccinated or receive immune globulin before departure . For more information on international travel and hepatitis A, see CDCs travel page or ACIP updated recommendations on Prevention of Hepatitis A after Exposure to Hepatitis A Virus and in International Travelers.
How soon before international travel should the first dose of hepatitis A vaccine be given?
All unvaccinated people 12 months of age planning travel to an area with high or intermediate HAV endemicity should receive a single dose of vaccine as soon as travel is considered they should then complete the vaccine series with the appropriate dose and schedule. People traveling within 2 weeks should receive the initial dose of hepatitis A vaccine before departure and also simultaneously may be administered IG at a separate anatomic injection site for additional short-term protection . The hepatitis A vaccine series should be completed according to the routine schedule. Information on immune globulin dosing and additional information on hepatitis A vaccine and travel is available.
What should be done to protect international travelers < 6 months of age and other travelers unable to receive hepatitis A vaccine?
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva
Which Adults Need Hepatitis B Vaccine
- People whose sex partners have hepatitis B
- Any sexually active adult who is not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship
- Persons seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease
- Men who have sexual contact with other men
- Those with close household contact with an infected person
- Adults who share needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment
- Healthcare professionals
Hepatitis B is incurable. A safe, effective vaccine has been available since the 1980s. Vaccination can help protect individuals and contribute to the elimination of this highly infectious disease.
Guidance On Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization
Vaccine providers are asked to report, through local public health officials, any serious or unexpected adverse event temporally related to vaccination. An unexpected AEFI is an event that is not listed in available product information but may be due to the immunization, or a change in the frequency of a known AEFI.
Refer to Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization in Canada and Adverse events following immunization in Part 2 for additional information about AEFI reporting.
Also Check: Royal Canin Hepatic Wet Dog Food
Before Taking This Medicine
Hepatitis A pediatric vaccine will not protect against infection with hepatitis B, C, and E, or other viruses that affect the liver. It may also not protect against hepatitis A if you are already infected with the virus, even without showing symptoms.
You should not receive this vaccine if you have ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to any vaccine containing hepatitis A, or if you are allergic to neomycin.
Before receiving this vaccine, tell your doctor if you have:
-
an allergy to latex rubber or
-
a weak immune system .
You can still receive a vaccine if you have a minor cold. In the case of a more severe illness with a fever or any type of infection, wait until you get better before receiving this vaccine.
Vaccines may be harmful to an unborn baby and generally should not be given to a pregnant woman. However, not vaccinating the mother could be more harmful to the baby if the mother becomes infected with a disease that this vaccine could prevent. Your doctor will decide whether you should receive this vaccine, especially if you have a high risk of infection with hepatitis A.
It is not known if hepatitis A vaccine passes into breast milk or if it could harm a nursing baby. Tell your doctor if you are breast-feeding a baby.
Hepatitis A vaccine is not approved for use by anyone younger than 12 months old.
Hepatitis A And B: Diseases Of The Liver
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, most often caused by a viral infection. There are three common types of hepatitis caused by viruses: hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. Vaccines have been developed that protect people from contracting hepatitis A and B. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
Hepatitis A and hepatitis B can be spread from person to person, although in different ways. They have similar symptoms, which include abdominal pain, fever, fatigue, joint pain, and jaundice .
Over the last 20 years, there has been a 90% decrease in cases of hepatitis A and an 80% decrease in hepatitis B cases in the U.S. Health experts believe that immunization efforts have led to this drop in rates of infection.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Hepatitis Panel
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
Select Safety Information For Vaqta
Do not administer VAQTA® to individuals with a history of immediate and/or severe allergic or hypersensitivity reactions after a previous dose of any hepatitis A vaccine, or to individuals who have had an anaphylactic reaction to any component of VAQTA, including neomycin.
The vial stopper and the syringe plunger stopper and tip cap contain dry natural latex rubber that may cause allergic reactions in latex-sensitive individuals.
The most common local adverse reactions and systemic adverse events reported in different clinical trials across different age groups when VAQTA was administered alone or concomitantly were:
- Adults 19 years of age and older: injection-site pain, tenderness, or soreness , injection site warmth , and headache .
Hepatitis A virus has a relatively long incubation period . VAQTA may not prevent hepatitis A infection in individuals who have an unrecognized hepatitis A infection at the time of vaccination.
Immunocompromised persons, including individuals receiving immunosuppressive therapy, may have a diminished immune response to VAQTA and may not be protected against HAV infection after vaccination.
Vaccination with VAQTA may not result in a protective response in all susceptible vaccinees.
VAQTA may be administered concomitantly with Immune Globulin, human, using separate sites and syringes.
The total duration of the protective effect of VAQTA in healthy vaccinees is unknown at present.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Drinking After Someone
How Is Havrix Given
Havrix is given as an injection into a muscle. You will receive this injection in a doctor’s office or clinic setting.
You will most likely receive 2 separate injections of Havrix at 6 to 12 months apart, depending on your exposure or risk of infection.
To prevent hepatitis A while traveling, you should receive Havrix at least 2 weeks before your trip. Your healthcare provider will determine the best dosing schedule for your situation.
Your doctor may recommend treating fever and pain with an aspirin free pain reliever such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen when the shot is given and for the next 24 hours. Follow the label directions or your doctor’s instructions about how much of this medicine to use.
Recommended Adult Dosing Volume Of Monovalent Hepatitis B Vaccine

- Age 19 years and younger: Use 0.5 mL per dose .
- Age 20 years and older: 1.0 mL per dose .
For a one-page sheet reviewing the hepatitis B dosing schedule for children and adults, consult IACs Hepatitis A and B Vaccines: Be Sure Your Patients Get the Correct Dose. For complete dosing information, consult the ACIP hepatitis B vaccine recommendations for adults.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms To Hepatitis C
What To Do If You Miss A Scheduled Dose
The recommended schedule for the HBV vaccine follows a three-dose pattern, with all doses complete within 6 months. The good news is that if you miss a dose, you dont need to start the series of shots all over.
If you missed getting the second dose 1 month after the first, make an appointment as soon as possible. If you miss the third dose, you should also try to get it as quickly as possible. Keep in mind that the second and third doses
Why Do You Need A Hepatitis B Shot
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that cant be transferred person-to-person unless you have contact with an infected persons bodily fluids. Annual infection rates of HBV are going down in the United States thanks to vaccines. So you might be wondering if you or your child needs a shot to protect against hepatitis B.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatic Luciferase Expression
Routine Administration Schedule For Hepatitis B Vaccine In Adults
- The dosing schedule is 0, 1 to 2 months, and 4 to 6 months.
- There is some flexibility in the schedule, but be sure to keep in mind the minimum intervals between doses:
- At least four weeks between doses #1 and #2
- At least eight weeks between doses #2 and #3
- At least 16 weeks between doses #1 and #3
- If your patient falls behind on the hepatitis B vaccination schedule , continue vaccinating from where your patient left off. The series does NOT need to be restarted.
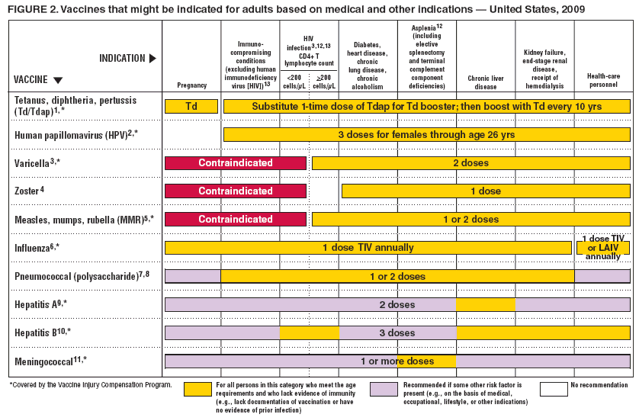
Measles Mumps And Rubella Vaccination
Routine vaccination
- No evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: 1 dose
- Evidence of immunity: Born before 1957 , documentation of receipt of MMR vaccine, laboratory evidence of immunity or disease
Special situations
- Pregnancy with no evidence of immunity to rubella: MMR contraindicated during pregnancy after pregnancy , 1 dose
- Nonpregnant women of childbearing age with no evidence of immunity to rubella: 1 dose
- HIV infection with CD4 count 200 cells/mm3 for at least 6 months and no evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: 2-dose series at least 4 weeks apart MMR contraindicated for HIV infection with CD4 count < 200 cells/mm3
- Severe immunocompromising conditions: MMR contraindicated
- Students in postsecondary educational institutions, international travelers, and household or close, personal contacts of immunocompromised persons with no evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: 2-dose series at least 4 weeks apart if previously did not receive any doses of MMR or 1 dose if previously received 1 dose MMR
- Health care personnel:
- Born in 1957 or later with no evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: 2-dose series at least 4 weeks apart for measles or mumps or at least 1 dose for rubella
- Born before 1957 with no evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: Consider 2-dose series at least 4 weeks apart for measles or mumps or 1 dose for rubella
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
How Hepatitis Is Spread
Hepatitis A: About 20,000 people in the U.S. contract hepatitis A each year. The hepatitis A virus is found in the stool of the infected person. It is spread through contaminated food or water or by certain types of sexual contact.
Children who get hepatitis A often don’t have symptoms, so they can have the virus and not know it. However, they can still spread it easily. Fortunately, children are now routinely vaccinated against hepatitis A.
Most people who get hepatitis A recover completely within two weeks to six months and don’t have any liver damage. In rare cases, hepatitis A can cause liver failure and even death in older adults or people with underlying liver disease.
Hepatitis B: Every year, about 40,000 people in the U.S. become infected with hepatitis B. Acute hepatitis lasts from a few weeks to several months. Many infected people are able to clear the virus and remain virus-free after the acute stage. However, for others, the virus remains in the body, and they develop chronic hepatitis B infection, which is a serious, lifelong condition. About 1.2 million people in the U.S. have chronic hepatitis B. Of these, 15% to 25% will develop more serious health problems, such as liver damage, cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer, and some people die as a result of hepatitis B-related disease.
Hepatitis B cannot be spread by contaminated water, food, cooking, or eating utensils, or by breastfeeding, coughing, sneezing, or close contact such as kissing and hugging.
When Do Adults Need Vaccines
Getting immunized is a lifelong, life-protecting job. Dont leave your healthcare providers officewithout making sure youve had all the vaccinations you need.
| If youve never had chickenpox or were vaccinated but received only 1 dose, talk to your healthcare provider to find out if you need this vaccine. |
| > > learn more |
Haemophilus influenzae
| Some adults with certain high-risk conditions need vaccination with Hib. Talk to your healthcare provider to find out if you need this vaccine. |
| > > learn more |
| You need this vaccine if you have a specific risk factor for hepatitis A infection or if you simply want to be protected from this disease. The vaccine is usually given in 2 doses, 6 to 18 months apart. |
| > > learn more |
| You need this vaccine if you have a specific risk factor for hepatitis B infection or if you simply want to be protected from this disease. The vaccine is given in 3 doses, usually over 6 months. |
| > > learn more |
| All men and women through age 26 years should receive this vaccine if they haven’t already received it. The vaccine can also be given to men and women through age 45 years. Check with your healthcare provider. The vaccine is given in 3 doses over 6 months. |
| You need a dose every year for your protection and for the protection of others around you. |
| > > learn more |
> > learn more:
| You need at least 1 dose of MMR if you were born in 1957 or later. Many people need a second dose. |
| > > learn more |
> > learn more:
Recommended Reading: How Do You Test For Hepatitis C