Considerations For Hepatitis C Cases Who Were Transplant Recipients
With the availability of curative treatment for HCV infection, an increasing number of transplant recipients are receiving organs from anti-HCV and HCV-RNA positive donors . This can result in transmission of hepatitis C to the recipient, which is then treated with DAA agents . In some jurisdictions, these expected donor-derived HCV transmissions might represent a significant proportion of new acute HCV infections therefore, jurisdictions are encouraged to reach out to transplant facilities and discuss public health reporting of expected donor-derived HCV infections.
A listing of transplant facilities in the United States, including facility location and phone number, can be found on the OPTN websiteexternal icon . As these patients are already linked to testing and treatment, the infections should be notified to CDC as new acute cases. However, the jurisdiction need not investigate beyond indicating that the infection was donor-derived.
Typically, there are two outstanding questions that only the public health jurisdiction can answer: 1) Did the recipient have any behavioral or other risks for hepatitis C and 2) Does the jurisdiction have any ongoing investigations of health care-associated hepatitis C that might be related to this investigation?
Table 4-3. Considerations for hepatitis C cases who were organ transplant recipients*
| Organ Recipient Pre-transplant |
|---|
Can Hcv Infection Be Prevented
The best protection against HCV is to never inject drugs. If you do inject drugs, always use new, sterile needles, and do not reuse or share needles, syringes, or other injection drug equipment.
People, including people with HIV, can also take the following steps to reduce their risk of HCV infection:
- Do not share toothbrushes, razors, or other personal items that may come in contact with another personâs blood.
- If you get a tattoo or body piercing, make sure the instruments used are sterile.
- Use condoms during sex. The risk of HCV infection through sexual contact is low, but the risk increases in people with HIV. Condoms also reduce the risk of HIV transmission and infection with other sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea and syphilis.
Wisconsin Hepatitis C Program
The Wisconsin Hepatitis C Program is the lead agency in Wisconsin responsible for coordinating the state’s public health activities focused on the prevention, detection, and treatment of hepatitis C.
COVID-19 impact on people with hepatitis C
Learn how the Hepatitis C Program is impacted by COVID-19.
Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus . Hepatitis C is spread through contact with blood from an infected person. Today, most people become infected with the hepatitis C virus by sharing needles or other equipment used to prepare and inject drugs. For some people, hepatitis C is a short-term illness, but for more than half of people with the hepatitis C virus, it becomes a long-term, chronic infection. People with chronic hepatitis C can often have no symptoms and dont feel sick. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. The best way to prevent hepatitis C is by avoiding behaviors that can spread the disease, especially injecting drugs. Getting tested for hepatitis C is important, because treatments can cure most people with hepatitis C in 8 to 12 weeks..
Read Also: Hepatitis C Treatment Guidelines 2017
How Does Hcv Spread From Person To Person
HCV is spread mainly through contact with the blood of a person who has HCV. In the United States, HCV is spread mainly by sharing needles or other injection drug equipment with someone who has HCV. HCV can also be spread through sexual contact. While the risk of transmission through sexual contact is low, the risk is increased in people with HIV.
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
Read Also: How Did You Get Hepatitis C
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
Should pregnant women be tested for HCV antibodies?
Yes. All pregnant women should be screened for anti-HCV during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is < 0.1% . Pregnant women with known risk factors should be tested during each pregnancy, regardless of setting prevalence. Any pregnant women testing positive for anti-HCV should receive a PCR test for HCV RNA to determine current infection status.
Can a mother with hepatitis C infect her infant during birth?
The overall risk of an infected mother transmitting HCV to her infant is approximately 4%8% per pregnancy . Transmission occurs during pregnancy or childbirth, and no prophylaxis is available to protect the newborn from infection. The risk is significantly higher if the mother has a high HCV viral load, or is coinfected with HIV with which the rate of transmission ranges from 8%15% . Most infants infected with HCV at birth have no symptoms.
Should a woman with hepatitis C be advised against breastfeeding?
When should children born to HCV-infected mothers be tested to see if they were infected at birth?
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
You May Like: Daa Drugs For Hepatitis C
Should People With Hiv Get Tested For Hcv
Every person who has HIV should get tested for HCV. Usually, a person will first get an HCV antibody test. This test checks for HCV antibodies in the blood. HCV antibodies are disease-fighting proteins that the body produces in response to HCV infection.
A positive result on an HCV antibody test means that the person has been exposed to HCV at some point in their life. However, a positive antibody test does not necessarily mean the person has HCV. For this reason, a positive result on an HCV antibody test must be confirmed by a second test. This follow-up test checks to see if HCV is present in the personâs blood. A positive result on this test confirms that a person has HCV.
How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis C To Others
If you have hepatitis C, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Tell your sex partner you have hepatitis C, and talk with your doctor about safe sex practices. In addition, you can protect others from infection by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care providers that you have hepatitis C. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.
Don’t Miss: Hep C Without Hepatic Coma
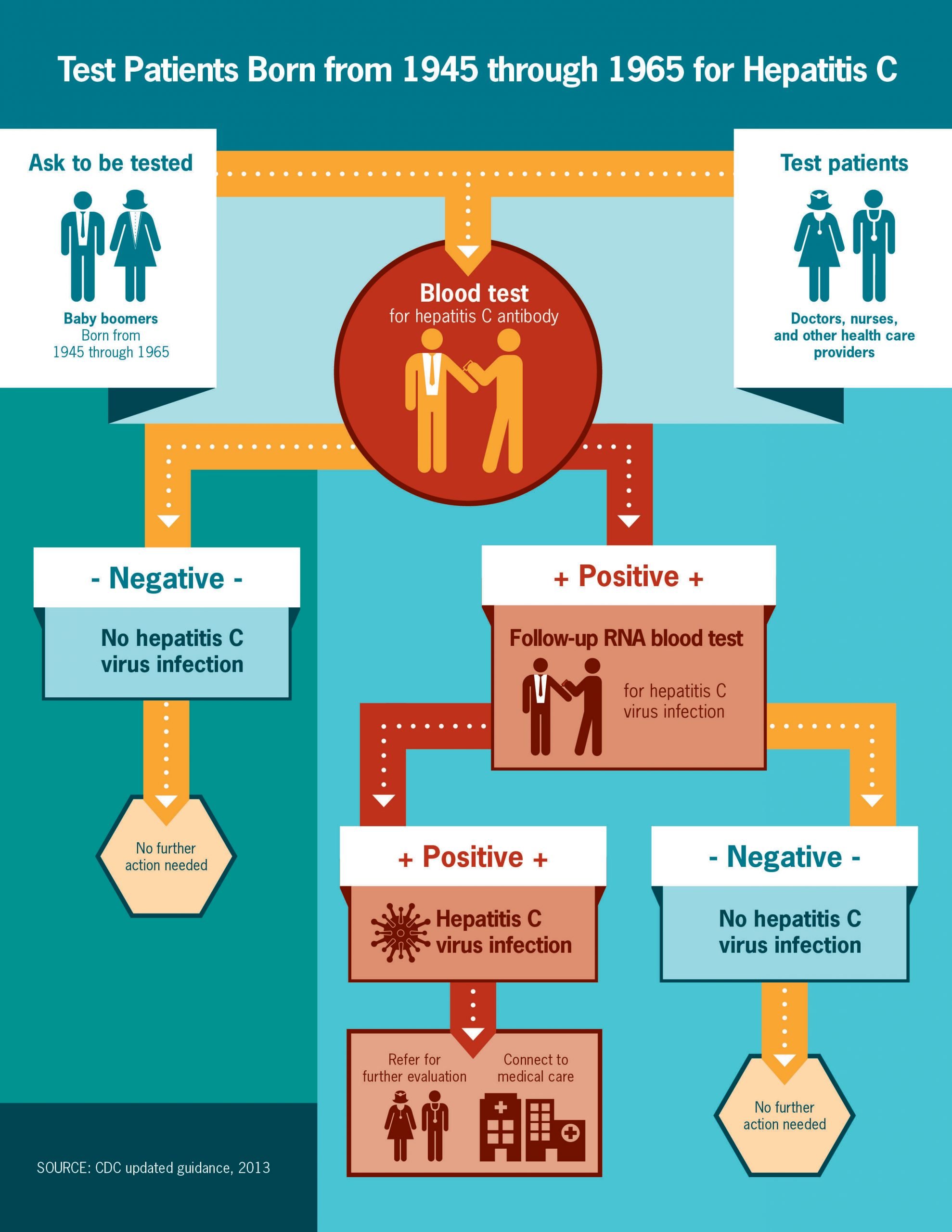
Who Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C
- All people born between 1945 and 1965
- Anyone who has ever injected drugs, even if once or many years ago
- People with HIV infection
- People who had a blood transfusion organ transplantation before 1992
- People who have been exposed to blood on the job through a needle stick or other injury
- People receiving hemodialysis
- People who have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Also Check: What Vitamins Are Good For Hepatitis B
Why Test All Your Adult Patients
- New cases of hepatitis C are on the rise, particularly among reproductive age adults. Rates of new HCV infections increased by more than 60% from 2015 to 2019. And in 2019, more than 63% of HCV infections occurred among adults 20-39 years of age.
- Your patients arent aware of their risk. Almost half of people with hepatitis C are unaware of their infection. Testing is the first step to accessing curative treatment. Without treatment, approximately 15-20% of adults with chronic HCV infection will develop progressive liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
- Hepatitis C can be cured. Over 90 percent of people infected with HCV can be cured with 8-12 weeks of oral therapy. Treatment of hepatitis C is associated with reductions in mortality among persons with chronic hepatitis C.
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis C

Doctors usually recommend one-time screening of all adults ages 18 to 79 for hepatitis C. Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis C. Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have hepatitis C. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis C before it causes serious health problems.
Recommended Reading: Natural Remedies For Hepatitis C
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Many adults have few or no symptoms. When symptoms occur, they can include tiredness, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, stomach ache, and muscle or joint pain. Urine may become darker in color, and then jaundice may appear. Years later, cirrhosis may occur in some who are infected, when scar tissue replaces healthy liver cells.
Case Reporting And National Notification
Cases of acute, chronic, and perinatal hepatitis C and hepatitis C during pregnancy should be reported to HDs as specified by state, territorial, or local regulations. Acute, chronic, and perinatal hepatitis C are nationally notifiable conditions . Hepatitis C cases are identified using an event code corresponding to the hepatitis C condition . Data are sent weekly or more frequently, depending on the infrastructure of the jurisdiction sending the data. Cases might be re-classified or removed as needed after the initial transmission to CDC, as long as the changes occur before surveillance data are finalized each year.
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis B And C Transmitted
Where Can You Get More Information
Your doctor, nurse, or health care clinic listed in the telephone directory can provide you with more information.
Persons who inject drugs can substantially reduce their risk of getting and transmitting HIV, viral hepatitis and other blood borne infections by using a sterile needle and syringe for every injection. The Massachusetts Department of Public Health supports programs where persons who inject drugs can access sterile needles and syringes through syringe services programs . Through these programs you can get sterile needles and syringes free of cost, dispose of used needles and syringes, and get connected to other services such as testing for hepatitis C, HIV and other sexually transmitted infections, overdose education, and narcan . To find an MDPH-supported SSP program near you, please click here.
Hepatitis C and Related Resources in Massachusetts This provides information about MDPH-supported programs including testing for hepatitis C, linkage to treatment for individuals with hepatitis C infection, and other resources such as overdose prevention programs.
Additional information about substance use disorder treatment programs may be obtained from the MDPH.
Viral Hepatitis Information from the CDC. The CDC provides resources on a variety of topics, including general information regarding transmission and prevention, statistics about HCV, diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C.
How Can I Prevent Hepatitis C
Since there is no vaccine for hepatitis C, the best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to avoid contact with the blood of infected people. This includes:
- If you shoot drugs, never share works with anyone. This includes all drug injection equipment that can get blood on or in it . Sterile syringes can be purchased over the counter in most pharmacies in Massachusetts by anyone 18 years of age or older. Find out about drug treatment programs that can help you stop using drugs.
- Only get tattoos or body piercings at places using sterile equipment and supplies.
- Never share razors, toothbrushes, or nail clippers
- The risk of sexual transmission is low, but use of latex condoms during vaginal or anal sex will reduce the risk even more
You May Like: Treatment To Cure Hepatitis C
How Soon Do Symptoms Appear
When first infected with hepatitis C virus, most people have no symptoms at all, or may have only mild symptoms. For those who do develop symptoms, the symptoms usually appear between six weeks to six months after infection. Many people with chronic hepatitis C infection do not develop symptoms until years, sometimes even decades, later. The longer people live with hepatitis C infection, the more likely they are to develop serious, life-threatening liver disease.
How Does The Program Work
Participation on the part of inmates is voluntary and there is no cost to the inmate while incarcerated or after release. DOCS Health Services staff and facility Parole Officers work with inmates prior to initiation of treatment to:
- Arrange participation
- Select a health care provider for referral for treatment completion in the community.
Read Also: Does Hepatitis C Weaken Your Immune System
Can Hepatitis C Infection Be Spread By Sexual Contact
Yes, but the risk of getting HCV from sexual contact is believed to be low. The risk increases for those who have multiple sex partners, have a sexually transmitted infection, engage in “rough sex” or other activities that might cause bleeding, or are infected with HIV. More research is needed to understand how and when HCV can be spread by sexual contact.
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented

There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another person’s blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Read Also: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis
Hepatitis is any kind of inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis has many causes, including viruses , drugs, chemicals and alcohol, and even ones own immune system attacking the liver. At this time, there are five viruses known to affect the liver in particular. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B and hepatitis C. These viruses are very different from one another, but all are infectious and may cause similar symptoms. They differ in how they are spread, how long the infection lasts, and how they are treated. A healthcare provider can test a persons blood for infection with hepatitis A, B and C virus.
Who Is At Risk
Anyone who has not been vaccinated or previously infected can get infected with the hepatitis A virus. In areas where the virus is widespread , most hepatitis A infections occur during early childhood. Risk factors include:
- poor sanitation
- living in a household with an infected person
- being a sexual partner of someone with acute hepatitis A infection
- use of recreational drugs
- travelling to areas of high endemicity without being immunized.
You May Like: How Dangerous Is Hepatitis C
How Does Drug Use Affect Symptoms And Outcomes Of A Viral Infection
Drug use can worsen the progression of HIV and its symptoms, especially in the brain. Studies show that drugs can make it easier for HIV to enter the brain and cause greater nerve cell injury and problems with thinking, learning, and memory. Drug and alcohol use can also directly damage the liver, increasing risk for chronic liver disease and cancer among those infected with HBV or HCV.
Cases And Clusters Of Potential Public Health Importance
Jurisdictions should review and analyze hepatitis C data regularly to identify cases and clusters of hepatitis C that merit further investigation. When resources are limited, these should be prioritized for investigation according to degree of public health importance. The following are examples of high priority cases and clusters:
- People of childbearing age who are or have the potential to become pregnant, indicating the potential risk for perinatal transmission.
- Children 36 months of age, indicating possible perinatal transmission.
- People in age and demographic groups among whom infection might be acute due to recent transmission. This includes people
- < 40 years of age and
- > 70 years of age .
Read Also: Treatment For Liver Cirrhosis Hepatitis B