What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. It spreads through contact with infected blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not spread through sharing utensils or kissing. It also doesnt spread through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding. Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure and can last for 212 weeks. However, you are still contagious, even
To screen for hepatitis B, your doctor will perform a series of blood tests.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Symptoms In Females
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Non Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Also Check: Ok Google How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days . Common symptoms include malaise, fever, gastroenteritis, and jaundice . After acute infection, HBV infection becomes chronic in 30% to 90% of infected children younger than 5 years of age and in 5% to 10% of infected individuals age 5 or older. Some of these chronic carriers are asymptomatic, while others progress to chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first serologic marker, appearing in the serum 6 to 16 weeks following HBV infection. In acute cases, HBsAg usually disappears 1 to 2 months after the onset of symptoms with the appearance of hepatitis B surface antibody . Anti-HBs also appears as the immune response following hepatitis B vaccination.
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After three intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Go Away On Its Own
Question 3 How Is The Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test Performed
An immunometric technique is used. The anti-HBs binds to HBsAg ad and ay subtypes, which are coated on the test wells. Binding of a horseradish peroxidase-labeled HBsAg conjugate to the anti-HBs completes the sandwich formation. Unbound materials are then washed away. In the next step, the horseradish peroxidase catalyzes oxidation of a luminogenic substrate, producing light. Light signals are detected and quantified. Intensity of the light is proportional to the amount of anti-HBs present in the patient sample. The result is standardized to an international unit system and reported as milliinternational units per milliliter .
Reactivation Risk In Anti
Table 1 American Gastroenterological Association classification of reactivation risk in HBsAg/anti-HBc patients Full size table
The risk of HBV reactivation can be assessed based on positivity for HBV serum biomarkers and the type, duration, combination of agents, and dosing of immunosuppressive or chemotherapeutic agents . HBV reactivation risk can be as high as 4070% in anti-HBc-only, patients who are undergoing chemotherapy with B cell depleting antibodies like rituximab .
Noting that reactivation after immunosuppressive therapy is associated with significant morbidity and mortality, the AGA recommends antiviral prophylaxis for patients classified as at either moderate or high risk for reactivation for low-risk patients, there is no prophylaxis recommendation monitoring is per provider preference but seemingly sufficient . Entecavir and tenofovir prodrugs should be used as first-line prophylaxis or therapy due to their stronger antiviral potency and high threshold for resistance.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
Addressing Hepatitis For The First Time
It is crucial that a treatment counselor or health professional use a nonjudgmental and compassionate tone. Clients need to feel comfortable disclosing information about their health and risky behaviors. The following strategies can help initiate the conversation:
- Display posters, literature, or other -related items that could help prompt the client to ask questions about hepatitis. .
- Assess clients ability to discuss , based on their degree of openness in the counseling session, the amount of detail they provide in their responses, and the length of the therapeutic relationship.
- Raise the subject in a way that avoids making clients feel defensive or afraid. Consider introducing the subject by making parallels with other conditions that have been discussed. Say, for example, You said you were tested for HIV several times. Were you ever tested for viral ? or You mentioned that your friend is sick with HIV. Have you been tested for HCV or HIV? Tell me about those tests.
- Be patient and allow time for multiple, short conversations about the subject. This might ease feelings of fear, anxiety, or shame.
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood and sexual fluids. This can most commonly occur in the following ways:
Direct contact with infected blood
Unprotected sex
Use of illegal or street drugs
Needles and other medical/dental equipments or procedures that are contaminated or not sterile
From an infected woman to her newborn during pregnancy and childbirth
Body piercing, tattooing, acupuncture and even nail salons are other potential routes of infection unless sterile needles and equipment are used. In addition, sharing sharp instruments such as razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, earrings and body jewelry can be a source of infection.
Hepatitis B is NOT transmitted casually. It cannot be spread through toilet seats, doorknobs, sneezing, coughing, hugging or eating meals with someone who is infected with hepatitis B.
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis B Do
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to hepatitis B, your body mounts an immune reaction against it as an invader. This happens whether you are exposed due to blood or sexual contact or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The hepatitis B virus has proteins on its surface that cause your immune system to produce antibodies. With the vaccine, the sample contains the protein only and not the virus itself.
The first response your body will make when exposed to hepatitis B is to manufacture hepatitis B IgM antibodies. These early antibodies are produced to fight against several parts of the virus including its core. These antibodies are seen in the initial response, but they eventually fade away.
Your immune system then begins to produce IgG antibodies. It continues to produce these antibodies for the rest of your life. In this way, your immune system is always ready to attack hepatitis B virus when it is exposed to it.
Preparing Clients For Screening

Once clients are comfortable talking about viral , they might be more willing to undergo screening. However, clients might be anxious about the test itself a reassurance that testing is a simple procedure can help allay these concerns. Many substance use treatment facilities do not offer screening, and clients might need to be referred elsewhere. The following strategies can enhance the discussion of the hepatitis screening process and hepatitis prevention:
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva
About The Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. Related viruses in this family are also found in woodchucks, ground squirrels, tree squirrels, Peking ducks, and herons.
Structure of the Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus contains an outer envelope and an inner core.
- The outer envelope of the virus is composed of a surface protein called the hepatitis B surface antigen or “HBsAg”. The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or “HBcAg,” which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus has a complex life cycle. The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a template for viral replication . New HBV virus is packaged and leaves the liver cell, with the stable viral cccDNA remaining in the nucleus where it can integrate into the DNA of the host liver cell, as well as continue to create new hepatitis B virus. Although the life cycle is not completely understood, parts of this replicative process are error prone, which accounts for different genotypes or genetic codes of the hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B Surface Ab Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Read Also: What Is Hepatic Function Panel
We Implement Proven Measures To Keep Your Data Safe
At HealthMatters, we’re committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We’ve put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
Popular search
Identifying Patterns Of Risky Behavior
Screening is an opportunity to draw attention to the clients behaviors that put him or her at risk for contracting :
- Ask for the clients perception of his or her risk for having contracted : How likely do you think it is that the test will be positive?
- Listen for and identify behaviors that put the client at risk for contracting , B, and C and HIV, especially unprotected sex and sharing injection drug paraphernalia.
- Assess the clients alcohol consumption.
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Liver Cirrhosis Hepatitis B
Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
Question 5 What Is The Natural History Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibody During Acute Hepatitis B Infection And Convalescence
HBsAg can be detected in the blood 4 to 10 weeks after exposure. This corresponds to onset of symptoms and viremia detectable by nucleic acid amplification methods. Most hepatitis B infections are self-limited and are associated with disappearance of HBsAg within 4 weeks of onset of symptoms. The anti-HBs then appears and increases to a plateau level that persists indefinitely.2
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis C From
Understanding Your Test Results
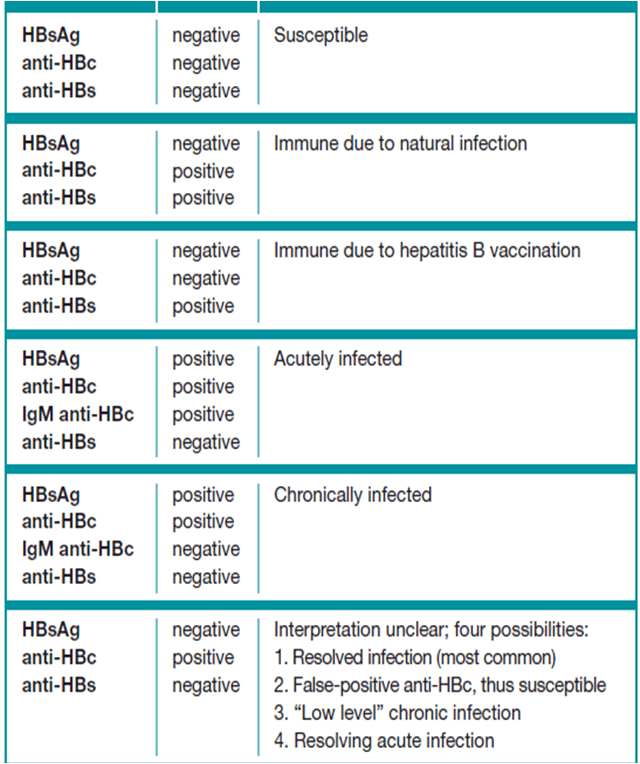
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
What Does A Reactive Result To A Hepatitis B Test Mean

The meaning of a reactive result for a hepatitis B test depends on the type of test performed, according to the Hepatitis B Foundation. The three most common blood tests detect the presence of hepatitis B surface antigens, hepatitis B surface antibodies or hepatitis B core antibodies.
In the hepatitis B surface antigen test, a reactive or positive result means that a person is currently infected with the hepatitis B virus, explains the Hepatitis B Foundation. Reactive results from the hepatitis B surface antibody test means that people are now immune to the virus because they have been infected in the past and their immune systems produced antibodies to fight the infection. For the hepatitis B core antibody test, a reactive or positive result can mean either that a person is currently infected with hepatitis B virus or have been some time in the test. A reactive result for this test can also be a false positive, meaning that the person has never been infected with the virus.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Mayo Clinic
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Ql Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Can Hcv Cause Psychosis
At least 50% of patients infected with HCV suffer from a psychiatric illness, and the lifetime prevalences of psychotic, anxiety, affective, personality, and substance use disorders are all higher among patients with HCV,10,47 as compared to the general US population studied in the Epidemiologic Catchment Area study.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis A And B And C