What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
Each type of hepatitis is treated differently.
Hepatitis A often goes away on its own and home treatment is all that is needed to help the liver recover, such as:
- Rest
- Avoiding alcohol
- Avoiding certain medicines that can be harmful to the liver
Hepatitis B often goes away on its own in about 6 months, and can also be treated at home with the above remedies. Other treatments for hepatitis B include:
- Antiviral medications
- Liver transplant in severe cases
Treatment for hepatitis C is effective on certain forms of the hepatitis C virus. The choice of medications depends on the type of hepatitis C you have, whether you have been treated for the illness before, how much liver damage has occurred, any other underlying medical issues, and other medicines you take. Treatment for hepatitis C usually involves 8 to 12 weeks of oral antiviral medications, such as:
- Elbasvir-grazoprevir
How Does Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C is a blood-borne virus, meaning that a person must come into contact with blood that contains the virus to contract it.
Most new cases of hepatitis C in the U.S. are due to injecting recreational drugs. Transmission can happen when a person with the virus shares needles or contaminated drugs with others.
The hepatitis C virus is very difficult to kill, and even tiny spots of blood that are invisible to the human eye can contain the virus.
People can also contract the virus in healthcare settings through exposure to blood that contains the virus, such as through accidental needlesticks.
According to the , the most common ways for hepatitis C to spread include:
- using injectable drugs
- receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992, which is before regular blood screens took place
- being accidentally poked with a used syringe, which can occur in healthcare settings
- being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can also spread through the following actions, though these are less common:
- engaging in sexual contact without using barrier protection, especially contact that may involve blood, such as rough or anal sex
- sharing personal items that may contain blood, such as toothbrushes or razors
- getting a tattoo or piercing from an unregulated provider
Hepatitis C often has no symptoms. This means that a person can contract hepatitis C without knowing it. This makes it easier for them to transmit it to others.
Contact With Blood Or Body Fluids: Protecting Against Infection
Blood and body fluids, such as saliva, semen and vaginal fluid, can contain viruses that can be passed on to other people. If you have contact with a persons blood or body fluids you could be at risk of HIV, hepatitis B or hepatitis C, or other blood borne illnesses. Body fluids, such as sweat, tears, vomit or urine may contain and pass on these viruses when blood is present in the fluid, but the risk is low.
Recommended Reading: How Can Someone Contract Hepatitis C
Can Cats Transmit Disease To Humans
Cats can transmit Toxoplasma to people through their feces, but humans most commonly become infected by eating undercooked or raw meat, or by inadvertently consuming contaminated soil on unwashed or undercooked vegetables. The symptoms of toxoplasmosis include flu-like muscle aches and fever, and headache.
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Contact Hepatitis C
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is really contagious. Its transmitted through contact with semen , vaginal fluids, and blood. You can get it from:
-
having vaginal, anal, or oral sex
-
sharing toothbrushes and razors
-
sharing needles for shooting drugs, piercings, tattoos, etc.
-
getting stuck with a needle that has the Hep B virus on it.
Hepatitis B can also be passed to babies during birth if their mother has it.
Hepatitis B isnt spread through saliva , so you CANT get hepatitis B from sharing food or drinks or using the same fork or spoon. Hepatitis B is also not spread through kissing, hugging, holding hands, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding.
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious liver disease. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus . Infections of hepatitis B occur only if the virus is able to enter the blood stream and reach the liver. Once in the liver, the virus reproduces and releases large numbers of new viruses into the bloodstream.
To combat the disease, the body has several defenses. White blood cells, which protect the body from infections, attack and destroy the infected liver cells. The body also produces antibodies which circulate in the blood to destroy the virus and protect against future infections of hepatitis B. During the infection and recovery process, the liver may not function normally causing illness that affects the entire body.
For reasons that are not completely understood, 10 percent of people who develop hepatitis B become carriers of the disease. Their blood remains infected for months, years, sometimes for life. Seventy percent of carriers develop chronic persistent hepatitis B. Most do not appear to be ill. The remaining 30 percent of carriers experience continuous liver disease. This condition often progresses to cirrhosis and then, after 30 to 40 years, possibly to liver cancer. At present, there is no way of curing carriers. The risk of becoming a chronic carrier is related inversely with a person’s age when infected. For example, the risk of an infant becoming a carrier is 90-95% whereas the risk of an adult becoming a carrier is 3-10%.
Also Check: How Much Does Hepatitis C Medicine Cost
What Causes Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18
What Drugs Treat And Cure Hepatitis C
The treatment of chronic hepatitis C has gone through several generations of medications. Not long ago, treatment was limited to interferon alpha-2b or pegylated interferon alpha-2b , and ribavirin . Interferon and pegylated interferon need to be injected under the skin , while ribavirin is taken by mouth. This combination therapy is infrequently used today, being recommended for only the least common genotypes of hepatitis C virus .
Since 2010, direct-acting antiviral drugs have been in use. The second generation of antivirals for HCV was the protease inhibitors telaprevir and boceprevir , both taken by mouth. These were used in combination with the earlier drugs to increase effectiveness . These drugs are also no longer in common use, and have been replaced by better options.
As more has been learned about how hepatitis C virus multiplies within the liver cells, new drugs continue to be developed to interfere with this multiplication at different stages. As such, we no longer think in terms of generations of drugs, but rather categories of action. Research and development of these direct-acting antivirals continue, with new agents coming to market every few months. Each category is improved and expanded by the addition of new drugs, which are safer and more effective.
Currently available and commonly used direct-acting antiviral drugs include:
- simeprevir
- Muscle aches
You May Like: Where Can I Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine For Free
Can You Prevent Hepatitis C Infection
Thereâs no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To avoid getting the virus:
- Use a latex condom every time you have sex.
- Don’t share personal items like razors.
- Don’t share needles, syringes, or other equipment when injecting drugs.
- Be careful if you get a tattoo, body piercing, or manicure. The equipment may have someone else’s blood on it.
Hcv Transmission During Sex: Is It Possible
Some research suggests that a small percentage of people do contract hep C through blood-to-blood contact that may occur during sexual contact. Thus, transmission of hep C during sex is seen as possible but is believed to be rare.
If hep C is transmitted during sex, it is likely to be through blood-to-blood contact. This emphasises the need for safe sex practices where there is a risk of blood-to-blood contact, e.g. sex when you have cuts or lesions on or close to the genitals, during anal sex , during menstruation, and during sexual practices that may involve bleeding or broken skin.
Some studies suggest a slightly increased rate of hep C transmission in people with multiple sexual partners and high levels of sexual activity. These studies, though, have usually found it difficult to exclude other possible routes of transmission, e.g. injecting drug use.
Research increasingly suggests the risk of transmission of hep C through sexual contact among heterosexual people is minimal.
Don’t Miss: Is There Immunization For Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis C
To efficiently reduce the risks of acquiring the disease by accident or any other possible chances, we must have a full understanding of what it is. In this way, we will have an idea about the things to avoid and help the community to suppress the actual spread of the disease. Hepatitis c by definition is an infection of the liver that is caused by the hepatitis c virus. The severity of the illness can range from mild that typically lasts for a few weeks, or severe that may last for years. The two most common types of hepatitis c are:
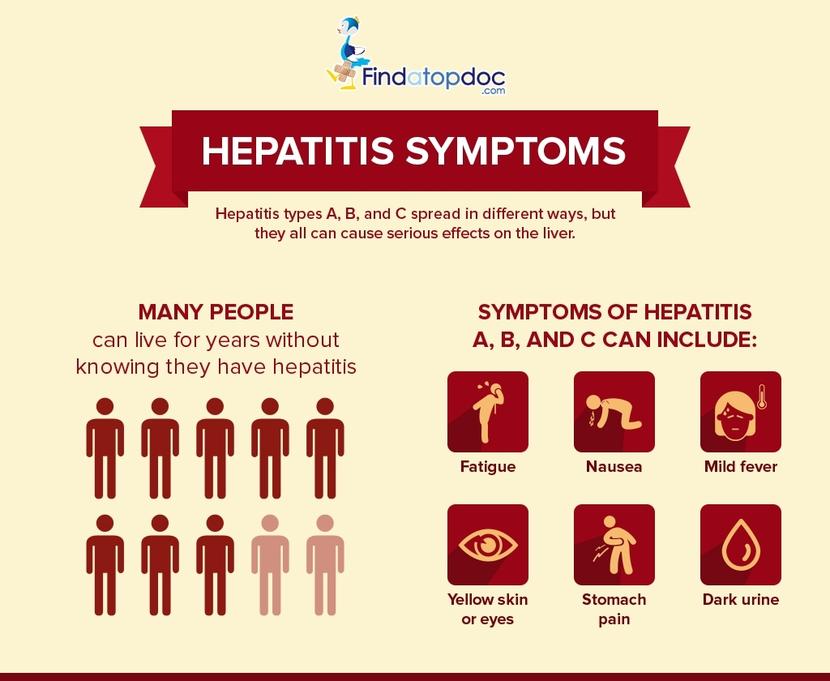
- Acute Hepatitis C: The symptoms of this type of hepatitis c usually appears within the first six months after the persons initial exposure to the virus. It may last for a few weeks, and it may go away on its own. However, some cases may lead to chronic infection. The common symptoms are yellow eyes or skin, upset stomach, nausea, fever, fatigue, light stool colour, loss of appetite, joint pain, or dark urine.
- Chronic Hepatitis C: This type of hepatitis c is more severe and may last a lifetime if left unchecked. The adverse health effects of this type may damage your liver permanently. You may be at risk of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer. The worst-case scenario can lead to death. There are no standard or apparent symptoms for this type of hepatitis. You will only know if youre infected through blood examination.
What Is The Connection Between Hiv And Hcv
Because both HIV and HCV can spread in blood, a major risk factor for both HIV and HCV infection is injection drug use. Sharing needles or other drug injection equipment increases the risk of contact with HIV- or HCV-infected blood.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , approximately 21% of people with HIV in the United States also have HCV. Infection with both HIV and HCV is called HIV/HCV coinfection.
In people with HIV/HCV coinfection, HIV may cause chronic HCV to advance faster. Whether HCV causes HIV to advance faster is unclear.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Symptoms In Females
What Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Look Like
Hepatitis C infection can go through two stages: acute and chronic. In the early, or acute stage, most people don’t have symptoms. If they do develop symptoms, these can include:
- flu-like symptoms, tiredness, high temperature and aches and pains
- loss of appetite
- tummy pain
- jaundice, meaning your skin and the whites of your eyes turn yellow
While for some people, the infection will clear without treatment, in most cases, acute infection will develop into long-term chronic infection. Chronic infection may not become apparent for a number of years until the liver displays signs of damage. These symptoms can include:
- mental confusion and depression these are specific to hepatitis C
- constantly feeling tired
- nausea, vomiting or tummy pain
- dark urine
- feeling bloated
- joint and muscle pain
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can cause scarring of the liver , which can cause the liver to stop working properly. A small number of people with cirrhosis develop liver cancer and these complications can lead to death. Other than a liver transplant, theres no cure for cirrhosis. However, treatments can help relieve some of the symptoms.
Contaminated Needles And Infected Blood
You can get hepatitis C from sharing contaminated needles, syringes and other injecting equipment during recreational drug use. Banknotes and straws used for snorting may also pass the virus on.
Being exposed to unsterilised tattoo and body piercing equipment can also pass hepatitis C on. Occasionally, you can get it from sharing a towel, razor blades or a toothbrush if there is infected blood on them.
Hepatitis C infection is also passed on in healthcare settings, from needle stick injuries or from medical and dental equipment that has not been properly sterilised. In countries where blood products are not routinely screened, you can also get hepatitis C by receiving a transfusion of unscreened blood and blood products.
You can prevent hepatitis C by:
- never sharing needles and syringes or other items that may be contaminated with infected blood
- only having tattoos, body piercings or acupuncture in a professional setting, where new, sterile needles are used
- following the standard infection control precautions, if youre working in a healthcare setting.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
Who Gets Hepatitis C
Persons at highest risk for HCV infection include:
- persons who ever injected illegal drugs, including those who injected once or a few times many years ago,
- people who had blood transfusions, blood products or organ donations before June 1992, when sensitive tests for HCV were introduced for blood screening, and
- persons who received clotting factors made before 1987.
Other persons at risk for hepatitis C include:
- long-term kidney dialysis patients,
- health care workers after exposures to the blood of an infected person while on the job,
- infants born to HCV-infected mothers,
- people with high-risk sexual behavior, multiple partners and sexually transmitted diseases,
- people who snort cocaine using shared equipment, and
- people who have shared toothbrushes, razors and other personal items with a family member who is HCV-infected.
How Common Is It
In 2006, the Public Health Agency of Canada reported the incidence of HBV as 2.0 cases for every 100,000 or about 650 cases reported annually in Canada. In the year 2013, the incident rate was 0.5 per 100,000 . Incidence of the disease varies from region to region but has been declining due to increasing use of the vaccine and universal immunization programs.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Shot Side Effects
How Hepatitis C Can Spread
Hepatitis C spreads through contact with blood from a person with an HCV infection. The most common cause of hepatitis C is from sharing needles with an infected person. The infection also can be passed through unsterilized tattoo needles. Mothers can transmit the virus to their babies at birth, but not through breastfeeding.
Although chances are low, the infection can be spread through contact with fresh or dried blood. When cleaning stray blood, wear rubber gloves and use a of 1 part household bleach to 10 parts water.
More Ways To Reduce The Risk Of Infection
If you arent sure whether you have hepatitis C, get tested. Testing is especially important if you have sex with more than one person or if you have other risk factors for hepatitis C, including being born being 1945 and 1965, having had a blood transfusion prior to 1992, and injecting drugs .
Talk to your partner about getting tested as well, for hepatitis C and other STDs, so you know the risks before having sex. People who are at risk for hepatitis C are also at risk for HIV and other STDs, emphasizes Talal.
Also Check: Is Viral Hepatitis C Contagious
What Are The Symptoms And Consequences Of Infection
Approximately 20 percent of persons exposed to the virus develop symptoms which may include jaundice , fatigue, dark-colored urine, stomach pain, loss of appetite and nausea. After the initial infection, 15-25 percent will recover and 75-85 percent will become chronically infected . Approximately 70 percent of persons chronically infected may develop liver disease, sometimes decades after initial infection.