What Is A Hepatitis B Vaccine
A hepatitis B vaccine prevents hepatitis B virus infection . Engerix-B, Heplisav-B, and Recombivax HB are examples of hepatitis B vaccines approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration . Engerix-B and Recombivax HB are both approved for use in people of all ages. Heplisav-B is approved for use in adults 18 years of age and older.HBV can be an opportunistic infection of HIV. An OI is an infection that occurs more frequently or is more severe in people with weakened immune systemssuch as people with HIVthan in people with healthy immune systems. To learn more about OIs, read the HIVinfo What is an Opportunistic Infection? fact sheet. To learn how HIV and HBV infection are connected, read the HIVinfo HIV and Hepatitis B fact sheet.
Babies And Hepatitis B Vaccination
Pregnant women have a routine blood test for hepatitis B as part of their antenatal care.
Babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B need to be given a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of their birth, followed by further doses at 4, 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age, plus a final dose when theyre 1 year old.
Babies of mothers identified by the blood test as particularly infectious might also be given an injection of HBIG at birth on top of the hepatitis B vaccination to give them rapid protection against infection.
All babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B should be tested at 1 year of age to check if they have become infected with the virus.
Should Pregnant Or Breast
The safety of hepatitis A vaccination during pregnancy has not been determined however, because hepatitis A vaccine is produced from inactivated virus, the risk to the developing fetus is probably low. The risk associated with hepatitis A vaccine should be discussed with your health care provider to determine if vaccination is right for you.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Ab With Reflex To Hcv Pcr
Is Hepatitis B Vaccine Required For Anyone
In Massachusetts, three doses of hepatitis B vaccine are required for all children attending licensed childcare or preschool, and kindergarten through grade 12. Three doses of hepatitis B vaccine are also required for full-time college and graduate students, as well as health science students attending college. Private employers must offer the vaccine to employees who might come in contact with blood and body fluids on the job.
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis C Virus
How You Can Get Hepatitis B
You can get hepatitis B from:
- injecting drugs using shared needles
- being injured by a used needle
- having a tattoo or piercing with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country that does not check blood for hepatitis B. Blood transfusions in the UK are checked for hepatitis B.
If you’re pregnant and have hepatitis B, you can also pass it onto your baby during pregnancy or birth.
Vaccines For Hepatitis A & B
You may have a family member who has viral hepatitis. Or perhaps you recently saw a news brief about a celebrity who contracted hepatitis A or B. Whatever the reason, you want information about a viral illness that you may not have thought much about. What is viral hepatitis? Are you at risk for it? Do you need viral hepatitis vaccines?
Also Check: Symptoms Of Hepatitis B In Males
Hepatitis A And B: Diseases Of The Liver
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, most often caused by a viral infection. There are three common types of hepatitis caused by viruses: hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. Vaccines have been developed that protect people from contracting hepatitis A and B. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
Hepatitis A and hepatitis B can be spread from person to person, although in different ways. They have similar symptoms, which include abdominal pain, fever, fatigue, joint pain, and jaundice .
Over the last 20 years, there has been a 90% decrease in cases of hepatitis A and an 80% decrease in hepatitis B cases in the U.S. Health experts believe that immunization efforts have led to this drop in rates of infection.
Facts About Hepatitis B
- Two billion people, or one in three, have been infected with hepatitis B worldwide. Of these, almost 300 million live with chronic hepatitis B. This means about 1 of every 26 people throughout the world are living with a chronic hepatitis B infection.
- Each year about 900,000 people die from hepatitis B worldwide, and about 2,000 of these deaths occur in the United States.
- Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood and is 100 times more infectious than HIV. An estimated one billion infectious viruses are in one-fifth of a teaspoon of blood of an infected person, so exposure to even a very small amount, such as on a shared toothbrush, can cause infection.
- Hepatitis B is sometimes referred to as the silent epidemic because most people who are infected do not experience any symptoms.
- Liver cancer accounted for about 5% of cancer deaths in the U.S. during 2020.
- Almost half of liver cancers are caused by chronic infection with hepatitis B.
- The World Health Organization recommends the inclusion of hepatitis B vaccine in immunization programs of all countries in 2019, more than 8 of 10 infants born throughout the world received three doses of hepatitis B vaccine.
Recommended Reading: Chronic Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
Adjuvants In Recombinant Hbv Vaccines
Modern recombinant vaccines are very refined and contain less antigenic components . As a result, adding adjuvants is essential to induce a better immune response. Among the adjuvants, aluminum salts are widely used. These salts can form insoluble particles, cause retention and release of vaccine antigens gradually like a depot, and thereby induce innate immunity.14 The various adjuvant systems used with recombinant HBV vaccines are AS01B , AS01E , AS02A , AS02B , AS02V , AS03 , AS04 , etc.14
Dont Miss: How To Reduce Hepatitis B Viral Load Naturally
Hav Hazards In The Workplace
Pupils with mental or physical disabilities are diapered, washed, fed, probed and catheterized by the staff. The regular performance of these activities entails a risk of infection for pathogens that are excreted via the stool. Possible contact can occur here, for example, during assisted toilet use, incontinence care or intimate hygiene. Nevertheless, contact can also occur with nasal secretions, saliva or infected blood during wound care. Claus et al. showed that many pupils at special schools with focus on mental or physical disabilities could not follow elementary hygiene rules, so that body excretions remain on hands, body and objects. There would therefore be an uncontrollable, increased risk of both contact and smear infections and those transmitted via droplet infection.
In the context of the present survey, about 10% of the employees at special schools with a focus on mental or physical disabilities perform catheterization, predominantly by educational specialists. In contrast, 26% of the respondents in the study of Claus et al. stated that they catheterized pupils. This difference could be caused by the fact that the study by Claus et al. was based on a self-selective sample of special schools, resulting in the participation of schools mainly for pupils with severe disabilities.
You May Like: Does Hepatitis A Go Away
Also Check: Is Milk Thistle Good For Hepatitis C
Where Can You Get More Information
- Your doctor, nurse or health care clinic
- Your local board of health
- The Massachusetts Department of Public Health , Division of Epidemiology and Immunization at 983-6800
Chinese, Haitian Creole, Portuguese, Russian, Spanish, and Vietnamese translations of this fact sheet are available under additional resources.
Breakthrough Clinical Or Chronic Hbv Infection
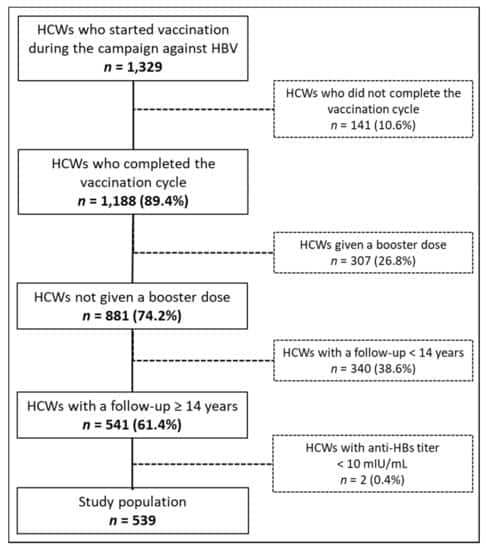
Undoubtedly, breakthrough infection with severe consequences, including acute hepatitis B or chronic infection, in vaccine recipients who had produced protective levels of anti-HBs is the indication for booster vaccination.24,25 Then the question is who may develop severe breakthrough infection following to HBV exposure after a successful primary vaccination. Individuals with protective anti-HBs levels are almost impossible to be infected with wild-type HBV with severe outcomes, whereas vaccinees with undetectable level of anti-HBs or < 10 mIU/ml are assumed to have relatively higher chance of being infected. Thus, the vaccine recipients with anti-HBs < 10 mIU/ml appear to be the candidates for booster vaccination. Here comes a paradoxical situation. Aforementioned decline or loss of anti-HBs is not an indication for booster because loss of anti-HBs does not indicate loss of immunity to HBV. The key point to solve this paradox is to clarify whether and how frequency the severe breakthrough infection of wild type HBV may occur in successfully vaccinated individuals.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis B Be Transmitted Through Saliva
Recommended Doses Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Recommended doses of hepatitis B by vaccine type, age, formulation, dosage and schedule.
Download PDF version formatted for print: Recommended Doses of Hepatitis B Vaccine
|
Vaccine |
|
|
Infants: birth, 1-4, 6-18 monthsOROlder children: 0, 1-2, 4-6 months |
|
|
20 years & older |
|
|
Infants: birth, 1-4, 6-18 monthsOROlder children: 0, 1-2, 4-6 months |
|
|
11-15 years |
|
|
3 doses |
0, 1, 4-6 months |
* The schedule for hepatitis B is flexible, but minimal intervals and minimum ages need to be observed:
- There should be at least 4 weeks between doses 1 and 2, and at least 8 weeks between doses 2 and 3.
- The minimum interval for the overall series from dose 1 to final dose is 4 months .
- Infants, should receive the final dose of hepatitis B vaccine on or after 6 months of age, otherwise long term immunity may be impacted.
Note:
- Adults who are immunocompromised or on dialysis require a larger dose of hepatitis B vaccine.
- The Engerix-B dose required is 40mcg/2.0mL on a scheduled of 0, 1, 2, and 6 months.
- For Recombivax HB, a special formulation is available. The dose is 40mcg/1.0mL given on a schedule of 0, 1, and 6 months
Combination Vaccines:
|
6 weeks thru 6 years |
Hep B as Engerix-B 10 mcg, DTaP as Infanrix, Polio |
0.5 mL |
3 doses |
Give single antigen hep B dose at birth followed by Pediarix at: 2, 4, 6 months |
|
Twinrix |
Hep A as Havrix 720 El.U, Hep B as Engerix-B 20 mcg |
1.0 mL |
0, day 7, day 21-30, 12 months |
I Have Liver Disease Or Cirrhosis Of The Liver Will This Make Me More At Risk With Covid
If you have cirrhosis of the liver there is no evidence that you have a higher chance of catching COVID.
Having cirrhosis of the liver can increase the risk of severe illness if you have COVID.
If you have elevated liver enzymes or abnormal liver function test as a result of liver disease, you may also be at risk of severe illness if you have COVID.
For these reasons, its best to take all necessary precautions to keep yourself safe from COVID by following government and medical recommendations.
Everyone with cirrhosis should see their liver specialist regularly. Call and speak to your specialist about what is best for your health.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C A Disease
What Do I Do If I Am Exposed To Hepatitis B
Contact your healthcare provider as soon as possible after the exposure. If you have not been vaccinated or are incompletely vaccinated, it may make sense for you to get a shot of hepatitis B immune globulin as soon as possible . HBIG provides short-term protection against the hepatitis B virus. When given shortly after an exposure , HBIG is 70-75% effective in preventing hepatitis B infection. Hepatitis B vaccination can be given at the same time, for long-term protection.
Is It Okay To Get An Extra Dose Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Yes. Although extra doses of vaccine are not recommended, you can think of the extra dose as another chance for the immune system to see the hepatitis B virus. A vaccine is not the only time the immune system will see the virus or bacteria contained in it. People may be exposed to the virus or bacteria at school or the store or when visiting family or friends. An extra dose of vaccine is like one more exposure, except the difference is that the virus or bacteria in any vaccine has been made safe, so it wont make you ill.
Read Also: What Is The Worst Hepatitis
You May Like: How Contagious Is Hepatitis B
Vaccination Is The Best Way To Prevent Hepatitis A And B Infection
Narrator: ÂYou are a traveller…Â .
Narrator: …and you are already dreaming of your next getaway. .
Disclaimer on-screen reads: TWINRIX is a combined hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine used in adults, adolescents, children, and infants over the age of 1 year to prevent hepatitis A and hepatitis B diseases
Narrator: ÂWhile your travel plans probably donÂt include hepatitis A or hepatitis B…Â .
Disclaimer reads: 100% protection cannot be guaranteed and booster doses may be required.
Narrator: Â…you know that many common travel activities can put you at risk of acquiring these two serious liver diseases…Â .
Disclaimer reads: TWINRIX does not protect against hepatitis C or E, and is not indicated to treat or reduce the severity of hepatitis A or B infections. .
Narrator: Â…which is why you plan on talking to your doctor about TWINRIX, right? … Of course, right…Â Â…because you are a traveller.Â
Video concludes with TWINRIX logo, GSK logo, You are a traveller slogan, and safety information: Very commonly reported adverse events in adults were pain or discomfort, redness at the infection site, headache, and tiredness. Common adverse events were swelling at the injection site, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, and generally feeling unwell. Allergic reactions may also occur. Full product information can be found on Twinrix.ca. If you need to report an adverse event, please call 1-800-387-7374.
Twinrix.ca
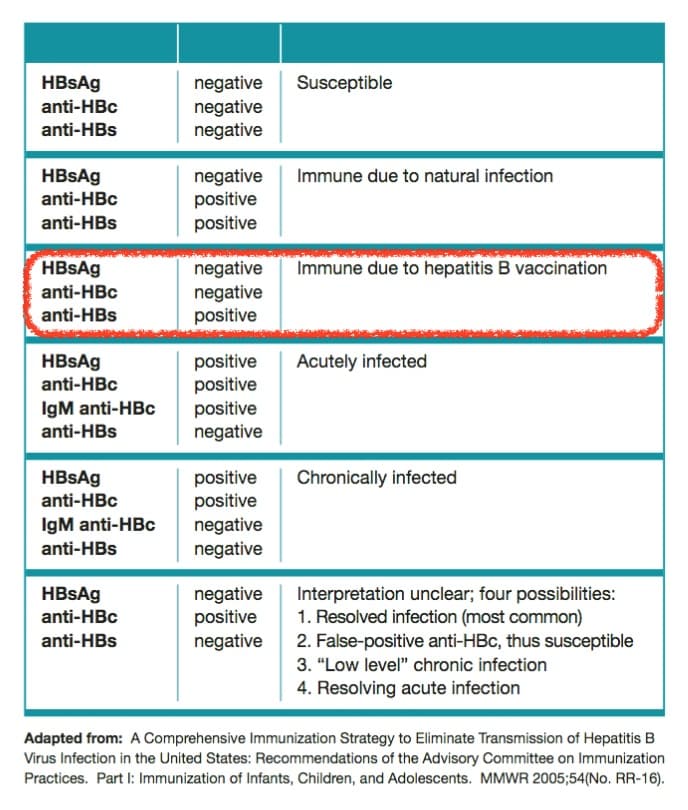
I Am A Healthcare Worker Who Did Not Develop Hepatitis B Antibodies After Immunization What Should I Do
Two versions of hepatitis B vaccine are available. One, called Heplisav-B, contains a novel adjuvant that was not present in previous versions used by adults . Some people did not respond to the older version hepatitis B vaccine. In fact, in a group of adults younger than 40 years of age who received two doses of the older version vaccine 75 of 100 were protected. Following the third dose, this number increased to 90 of 100. However, people older than 40 years of age were less likely to respond to the vaccine with increasing age. On the other hand, 90 to 100 of 100 adults 18 years of age and older respond to Heplisav-B, which was approved for use in 2018.
About 5-10 of every 100 children and adults younger than 40 years of age do not respond to the third dose of the hepatitis B vaccine. Some of these people will be recommended to get vaccinated again. About 5 of 100 people will still not respond after getting all recommended doses of both series. Note that children younger than 18 years of age cannot get Heplisav-B.
If the people who do not respond to vaccination are determined not to have chronic hepatitis B, they will be reliant on taking precautions to reduce the chance of exposure and relying on those around them for protection. In other words, these people will be reliant on herd immunity.
Read Also: What Can Cause Hepatitis C
Are Hepatitis B Virus Infections Easily Avoided
Large quantities of hepatitis B virus are present in the blood of people with hepatitis B in fact, as many as one billion infectious viruses can be found in a milliliter of blood from an infected individual. Therefore, hepatitis B virus is transmitted in the blood of infected individuals during activities that could result in exposure to blood, such as intravenous drug use, tattooing, or sex with people who are infected. However, it is also possible to catch hepatitis B virus through more casual contact, such as sharing washcloths, toothbrushes or razors. In each of these cases, unseen amounts of blood can contain enough viral particles to cause infection. In addition, because many people who are infected dont know that they are infected, it is very hard to avoid the chance of getting infected with hepatitis B virus.
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with a partner who has HBV infection
- injection drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to a person who has HBV infection
- contact with blood from or open sores on a person who has HBV infection
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with a person who has HBV infection that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 9 parts water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to people with HBV infection
- Sex partners of people with HBV infection
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Patients on hemodialysis
Who should be screened for HBV?
Read Also: Hepatitis A Vaccine At Cvs