Transmission Of Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood and sexual fluids. This can most commonly occur in the following ways:
Direct contact with infected blood
From an infected pregnant person to their newborn during pregnancy and childbirth
Needles and other medical/dental equipments or procedures that are contaminated or not sterile
Unprotected sex
Use of illegal or street drugs
Body piercing, tattooing, acupuncture and even nail salons are other potential routes of infection unless sterile needles and equipment are used. In addition, sharing sharp instruments such as razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, earrings and body jewelry can be a source of infection.
Hepatitis B is NOT transmitted casually. It cannot be spread through toilet seats, doorknobs, sneezing, coughing, hugging or eating meals with someone who is infected with hepatitis B.
How Do Doctors Test For Hepatitis B Immunity
Doctors may order a panel of blood tests to check if someone has HBV:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen : This test looks for the presence of HBV in the blood by looking for antigens found on the virus. A positive result means that a person has HBV.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody : This test can show if a person is immune and protected against HBV. A positive result indicates that the person has overcome a past HBV infection or it is the result of receiving the hepatitis B vaccine.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : This test looks for another antibody in the HBV, but this one does not provide protection. A positive result indicates that a person had a past infection or currently has HBV.
Some people with certain risk factors for hepatitis B infection, such as those who inject drugs, pregnant people, and other populations, may require testing postvaccination to check their immunity.
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Symptoms In Females
How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
The number of infections had been falling in the U.S., but fewer vaccinations among adults combined with the onset of the opioid crisis and injected drug usage has resulted in the numbers rising again. Infected women can pass the infection on to their babies. Children who are infected before age 5 are more likely to have chronic infection than those infected later in life.
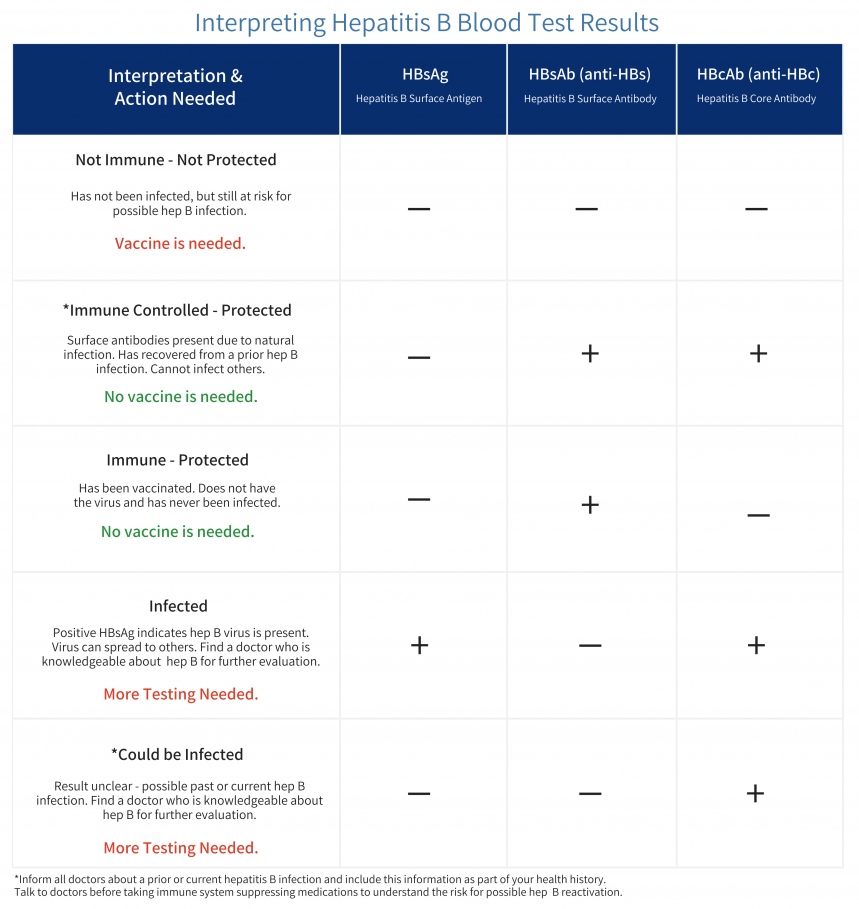
Understanding Your Test Results
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Flare Up Symptoms
Can Hepatitis B Positive Become Negative
It can happen, especially in older adults after a long period of inactive hepatitis B infection. About 1 to 3 percent of people with chronic hepatitis B lose HBsAg each year, and about half of all people with chronic infections who live up to age 75 will lose HBsAg, depending on the amount of HBV DNA in their blood.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis C Virus Transmitted
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Qualitative
Presence of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen is used to determine immune status to HBV or disease progression in individuals infected with HBV. Anti-HBs levels can be measured to determine if vaccination is needed, or following a vaccination regimen, to determine if protective immunity has been achieved.
â Anti-HBs usually can be detected several weeks to several months after HBsAg is no longer found, and it may persist for many years or for life after acute infection has been resolved.
â It may disappear in some patients, with only antibody to core remaining.
â People with this antibody are not overtly infectious.
â Presence of the antibody without the presence of the antigen is evidence for immunity from reinfection, with virus of the same subtype.
What is the Hepatitis B virus?
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days .
What are common symptoms?
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis D Coinfection Vs Superinfection
Why It Is Done
You may need testing if:
- You have symptoms of hepatitis.
- You may have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus. You are more likely to have been exposed to the virus if you inject drugs, have many sex partners, or are likely to be exposed to body fluids .
- You’ve had other tests that show you have liver problems.
- You are pregnant.
- You or your doctor wants to know if you are protected from getting the disease.
The tests also are done to help your doctor decide about your treatment and see how well it’s working.
Educating Clients About Viral Hepatitis
Clients may believe they know about viral , but their understanding of the disease may not be accurate. It is easy to confuse the three main types of viral , B, and C. Clients may have formed impressions based on limited or incorrect information. Counselors should briefly describe hepatitis A, B, and C, including their prevalence, , and relationship to drug use, as well as to other infections, such as HIV and sexually transmitted diseases. Specific strategies for speaking with clients include:
- Speak clearly and keep the message simple, focused, and brief.
- Use language, examples, and concepts that the client understands.
- Use appropriate visual aids.
- Frame numerical statements in terms that are easy to visualize. Say 5 out of 100 people rather than 5 percent of the population say more than half instead of the majority.
- Repeat the information at different times in different ways. The average client retains only approximately one-third of what he or she is told. Summarize essential points.
- Pay attention to a clients response to the information. For example, if a client stiffens his or her posture, consider saying, I notice that this topic seems to make you uncomfortable. It does for a lot of people. Please tell me what youre feeling right now. Id really like to help you with this.
- Use the opportunity to describe the potential detrimental effects of alcohol and other substance use on the liver of a person who is infected with HCV.
Don’t Miss: Most Common Way To Get Hepatitis C
What Blood Tests Are Important To Diagnose And Evaluate My Hepatitis B Infection
In order to understand your hepatitis B status, it is important that your doctor order the hepatitis B blood panel. This panel includes 3 basic biomarkers, but only one sample of blood is needed. Make sure you request a written copy of your blood test results so that you fully understand what tests were ordered and the actual results of each. Also, be sure to have your doctor clearly explain the results to you so that you fully understand your situation.
It is important to wait 6-8 weeks after a possible exposure before getting tested. If done before this time , the blood tests can have a false negative result. The window period is the time between exposure and the appearance of these markers in blood. The 3-part blood test includes the following:
1) Hepatitis B surface Antigen – This directly tests for the presence of the hepatitis B virus. It should be negative if there is NO virus present. 2) Hepatitis B surface Antibody – This tests for the production of protective antibodies against the hepatitis B virus. This blood test should be positive if the protective antibodies are produced in response to vaccination or recovery from a natural infection. 3) Hepatitis B core Antibody – This antibody does not provide any protection. A positive result may indicate that a person has been exposed to the hepatitis B virus. This test must be interpreted in relation to the above 2 test results.
What Do The Results Mean
A hepatitis B blood panel consists of three tests that can be done with just one blood sample:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen . A positive test indicates that youre infected with hepatitis B and that you can spread it to other people. Further tests are needed to see if you have an acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody . A positive result can indicate a past or current hepatitis B infection, but doesnt mean youre immune. A positive result needs to be interpreted by a doctor by examining the results of the other two tests.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody . A positive test indicates that youre protected from hepatitis B either through previous infection or vaccination .
The combination of these tests can indicate your hepatitis B status and whether you need to be vaccinated. Your test will give a negative or positive result for each category depending on whether your results are above or below the cutoff value.
Most peoples test results fall into the following categories. But its possible to have a result that doesnt fall into one of these groups. If youre reading your results yourself, be careful not to confuse HBsAb with HBcAb.
| HBsAG |
is associated with hepatitis B immunity after vaccination. But research has found that anti-HBs decline over time.
A found that more than 95 percent of people had anti-HBs levels greater than 10IU/L two years after vaccination. But this rate decreased to 70 percent after eight years.
You May Like: Home Remedies For Hepatitis B
What’s The Worst Hepatitis Ab Or C
There are 3 main types of hepatitis: hepatitis A, B, and C. Hepatitis C can be more severe and is the most deadly, but even those with acute illness can recover without lasting liver damage. Up to 70% of those chronically infected with hepatitis C develop chronic liver disease, and up to 20% develop cirrhosis.
Recommended Tests To Investigate Chronic Hbv Infection And The Interpretation Of Results
Chronic HBV infection is defined by the continued presence of HBsAg in the blood for longer than six months. Figure Figure11 and Table Table22 outline the tests used to diagnose most cases of chronic HBV. Test selection should be based on the person’s risk factors, vaccination history and findings from previous tests .
Diagnostic tests for acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection . ALT Alanine aminotransferase Anti-HAV-IgM Immunoglobulin M class antibody to HAV Anti-HCV Antibody to HCV antigens HBsAg Hepatitis B surface antigen
Read Also: What Is The Difference Between Hiv And Hepatitis B
What Is The Outlook For People With Hepatitis B
The outlook for people with HBV is better now than ever before. You are certainly able to live a full life and help yourself stay healthy. You should make sure to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider who is qualified to treat hepatitis B, possibly a liver doctor.
Make sure you are vaccinated against hepatitis A. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking other medications or over-the-counter products, including supplements and natural products. These could interfere with your medication or damage your liver. For instance, taking acetaminophen in large doses may harm your liver.
Follow the usual guidelines for living a healthy life:
- Eat nutritious foods, choosing from a variety of vegetables, fruits and healthy proteins. It is said that cruciferous vegetables are especially good at protecting the liver.
- Exercise regularly.
- Dont smoke and dont drink. Both tobacco and alcohol are bad for your liver.
- Do things that help you cope with stress, like journaling, talking with others, meditating and doing yoga.
- Avoid inhaling toxic fumes.
Hep C Antibodies Do Not Prevent Re
What does it mean, in any real terms? Well, in terms of my status as being cured, it means nothing at all, because we do believe, as a fact, that antibodies for hep C offer no protection and so have no real value. It is interesting to me, and that is only because of my interest in the science of why and how things work, and there is some science that points to diminished antibody presence over time, and is it the same with all treatments? We dont know, and no need to be concerned, unless you too have a mildly science and nerdy side like me.
Also Check: Can You Give Yourself Hepatitis From Your Own Blood
You May Like: How Many Genotypes Of Hepatitis C Are There
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus . HBV is one of five types of viral hepatitis. The others are hepatitis A, C, D, and E. Each is a different type of virus. Types B and C are most likely to become chronic, or long lasting.
According to the , around 296 million people around the world are living with hepatitis B. Around 1.5 million people newly contracted chronic hepatitis B in 2019.
HBV infection can be acute or chronic.
Acute hepatitis B causes symptoms to appear quickly in adults. Infants who contract it at birth rarely develop only acute hepatitis B. Nearly all hepatitis B infections in infants go on to become chronic.
Chronic hepatitis B develops slowly. Symptoms may not be noticeable unless complications develop.
Symptoms of acute hepatitis B may not be apparent for months. But common symptoms include:
- yellowing of the whites of the eyes and skin
Any symptoms of hepatitis B need urgent evaluation. Symptoms of acute hepatitis B are worse in people over age 60.
Let your doctor know immediately if youve been exposed to hepatitis B. You may be able to prevent infection.
Some of the ways hepatitis B can be transmitted include:
Although the virus may be found in the saliva, hepatitis B is not transmitted through:
To screen for hepatitis B, your doctor will perform a series of blood tests.
Read Also: Hiv And Hepatitis B And C Are Incurable