The Need For Vaccination
To prevent the contraction or development of hepatitis A, the following individuals should be sure to get vaccinated:
- 1 to 2-year-old children
- Men who have sexual contact with other men
- People who use drugs on the streets
- Employees working in various parts of the world, except countries such as Canada, the U.S., and Japan
- People who have personal or close contact with persons who come from HAV-infected countries
- People with chronic liver disease
- People experiencing homelessness
- Fatigue
How Do You Get It
HAV can be present in the stool and blood of someone with the virus. Its mainly transmitted through the fecal-oral route, which involves ingesting virus thats present in the stool of someone with hepatitis A.
There are several ways you can get hepatitis A:
- having close person-to-person contact with someone who has hepatitis A, such as:
- taking care of someone whos currently sick
- having sex with someone who has the virus
Diagnosis And Treatment For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will take a complete history about the signs and symptoms of the condition along with time durations, which will be followed by an abdominal examination to elicit signs like hepatomegaly and tenderness of the liver.
Acute HBV infection is diagnosed by the presence of HBsAg and immunoglobulin M antibody to the core antigen, HBcAg whereas the chronic type can be diagnosed with a persistent HBsAg level for at least 6 months duration.
There is no exact treatment for acute hepatitis B symptomatic management plays the hallmark of therapy. In fact, adequate nutritional levels and hydration are mandatory for a quick recovery. Oral antiviral drugs are also helpful for patients with chronic hepatitis B infection since they are proven to be beneficial in reducing the progression of the disease to liver cirrhosis and carcinoma, thus paving the way to improve the quality of life.
At present, there are few vaccines, developed against Hepatitis B virus but they are not used on a universal basis due to high expenditure and inadequate awareness.
Hepatitis B
Also Check: Hepatitis C And Kidney Failure
Hiv Treatment And Prevention
Simple, effective treatments for HIV are widely available in Australia. In addition to protecting the health and wellbeing of people living with HIV, these treatments significantly reduce the risk of HIV transmission. Almost all people on HIV treatments have very low levels of virus in their body. This is called having an undetectable viral load. There is no risk of HIV transmission from a person with an undetectable viral load. This is sometimes referred to as undetectable equals untransmissible, or U=U.
For people who do not have HIV, but may be at higher risk of it, affordable medication is available that is more than 99 per cent effective at preventing HIV. Known as PrEP , this medication is available through the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme from your regular GP.
Hbv Infection: Chronic But Preventable Disease
Current treatment strategies do not allow complete viral eradication in HBV infection. Peg-IFN has significant side effects, but it is able to achieve a functional cure in a number of patients and remains a possible therapeutic option . Lifelong nucleoside analog therapy, on the other hand, has few side effects but achieves functional cure only in a small minority of patients .
What makes hepatitis B infection really different from HIV and HCV is the availability of an effective vaccination since the early 1980s. A long-term study of 14 years conducted in The Gambia showed a high effectiveness of vaccination against chronic carriage and new infection among children and young people at different ages . To date, 183 of the 193 WHO member states have initiated an hepatitis B vaccination program . Approximately 84% of children worldwide received three doses of hepatitis B vaccine and are thus probably protected from HBV infection for life. The additional administration of hepatitis B immune globulin at birth can further reduce the risk of MTCT in high-risk deliveries .
Read Also: How Much Is A Hepatitis A Shot
General Information On Hiv
The human immunodeficiency virus is an enveloped RNA virus belonging to the family of Retroviridae, genus Lentivirus. HIV infection and its natural evolution lead to a set of opportunistic, infectious, or tumoral manifestations, consequences of an immunodepression qualified as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome . To date, there are two types of HIV: the first, called HIV-1, is responsible for the pandemic and HIV-2 is more common in West Africa .
What Are The Risk Factors
Some people are at an increased risk for contracting HAV, including:
- people traveling to areas of the world where hepatitis A is common
- men who have sex with men
- people who use injectable or noninjectable drugs
- caregivers for those who have hepatitis A
- people who are experiencing homelessness
- people living with a child whos been adopted from an area where hepatitis A is common
Recommended Reading: Icd 10 For Hepatic Steatosis
How Should The Liver Be Monitored
Everyone with HIV should have regular tests to monitor the health of their liver. These tests are especially important in cases of coinfection with hepatitis B. In those cases, doctors should closely monitor liver function using blood tests.
Ultrasound examinations may also be performed, particularly if the liver shows signs of damage. Another test, called a FibroScan, can also test the liver for cirrhosis or fibrosis.
Sometimes, people also need a liver biopsy, where a tiny piece of tissue from the liver is removed for investigation.
Whats The Deal With Viral Hepatitis And Hiv
HIV.gov| May 06, 2019
Topics
Since May is Hepatitis Awareness Month, were taking a look at hepatitis B and hepatitis C. Both are common coinfections among people living with HIV in the United States. In fact, about one-third of people with HIV also have one of these forms of viral hepatitis. That is largely because the hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus is spread between people in the same ways that HIV is spread through sexual contact or injection drug use.
These viruses infect the liver and cause it to become inflamed. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Viral hepatitis progresses faster and causes more liver-related health problems among people with HIV than among those who do not have HIV. Liver disease, much of which is related to hepatitis B or C, is a major cause of non-AIDS-related deaths among people living with HIV.
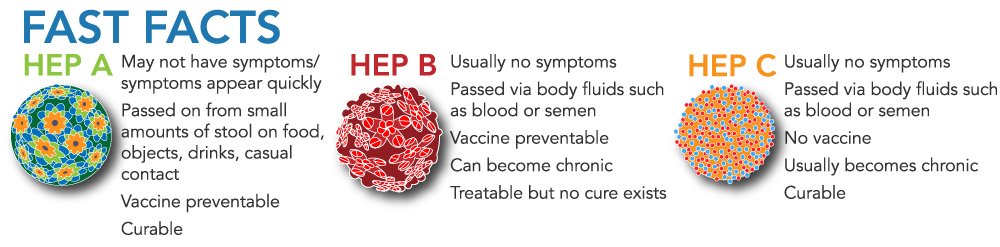
Here are some quick facts on each of these serious infections:
Don’t Miss: How Do You Catch Hepatitis A
Blood Collection And Serological Testing
About 10 ml of venous blood was collected. The sera were screened for HBsAg using commercially available HBsAg rapid test kits according to manufacturers instruction. From those HBsAg positive sera, the HBV e antigen test was done using commercially available enzyme immunoassay kits .
For occult HBV analysis, anti-HBc antibody test was done using Enzygnost®Anti-HBc monoclonal ELISA among 476 HBsAg negative cases. And then, the anti-HBc antibody positive sera were further tested for anti-HBs antibody using the ARCHITECT system . Then, the anti-HBs antibody positive and negative sera were used for HBV DNA detection test and viral load determination.
The HIV-1/2 screening was done using the HIV-1/2 rapid test kits according to the Ethiopian national test algorithm adopted from WHO designed for developing countries . The test algorithm used three rapid diagnostic test kits in series HIV- Antibody Colloidal Gold as a screening test, followed by HIV-1/2 STAT-PAK® in case of a positive screening result. In case of discordant test results with the above two kits, Unigold HIV was used as a tiebreaker to decide the final result.
Causes Of Hepatitis B
As far as the etiology of Hepatitis B is concerned, this is caused by a virus which is mainly transmitted through infected blood, blood products, semen, body fluids, etc. It can spread from infected mothers to infants at the time of birth or from an infected family member to an infant during the early childhood. Furthermore, various invasive medical procedures and blood transfusions can also act as the main routes for introducing infected blood and body fluids to affected individuals.
Therefore, it is highly important that health care workers are appropriately aware and cautious about how to manage these invasive procedures with care, without getting the responsible virus inside their body which usually takes place following needle stick injuries during professional health care.
You May Like: Hepatitis B And C Can Be Spread By
Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hiv
Hepatitis is a disease, affecting the liver which can be caused by several viral entities such as A, B, C, D and E. This condition, in general, is defined as an inflammation of the liver which can either be self-limiting in nature or complicates to fibrosis, scarring, liver cirrhosis or malignancy.
On the other hand, HIV is a virus which invades the human immune system and weakens the immunity of the individual, thus increasing the susceptibility to infections, inflammatory conditions and various other illnesses in the body.
Both Hepatitis and HIV can cause similar signs and symptoms, yet HIV tends to affect the overall body rather than being limited just to the liver.
Hepatitis B, if properly managed can be cured completely.
HIV doesnt have any permanent cure at all except for the treatment with Antiretroviral drugs which is known to control the spread and reduce the incidence of transmitting the disease from infected person to another.
Image Courtesy:
Hepatitis B virus v2 By Original uploader was TimVickers at en.wikipedia via Commons Wikimedia
Symptoms of AIDS By Medical gallery of Mikael Häggström 2014. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 . DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.008. ISSN 20018762. via Commons Wikimedia
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted
Future Prospects For Hbv
Are we progressing to a similar situation for HBV where categorization and treatment decisions are more simple, rapid and clear cut? Or to a situation where treatment is advocated for all?
Assessments of immune responsiveness and exhaustion have allowed classification and monitoring to be revisited, and data on outcomes in those previously defined as immune tolerant have directed a re-appraisal of patient categorization. For example, studies have demonstrated that the previously labeled immune-tolerant phenotype is actually associated with immune activation and increased expression of immune check point inhibitors such as PD-1 . These factors, and a general better understanding of outcomes, have allowed a reassessment of classification of patients with HBV infection.
Table 2 Current EASL Guidelines
This delay in progression of promising agents to general use also means that we remain in a situation where not all patients meet criteria for treatment. If we develop an agent, or combination, that has a significant impact on ccc-DNA, then it is possible that we move to a situation in HBV analogous to that currently in HIV and HCVtreatment for all and not dependent on sub-classification.
How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
Hepatitis B is passed on by contact with:
- blood
- vaginal fluids of a person with hepatitis B.
It’s easily passed on:
- during unprotected sex
- from mother to baby during delivery.
It can also be passed on through:
- infected blood getting into an open wound
- tattooing or body piercing done with contaminated equipment
- using items such as toothbrushes or razors contaminated with infected blood.
Hepatitis B is many times more infectious than HIV and it can survive outside the body in dried blood for at least a week.
Don’t Miss: What Happens When You Get Hepatitis C
Detection Of Hiv1/2 Antibody
Plasma samples were screened for antibodies against HIV1/2 following the national serial rapid HIV testing algorithm and the WHOs guidelines on HIV testing and counseling strategy.20,21 Accordingly, three commercially available rapid tests were used in the following order: Wantai , Uni-GoldTM , and Vikia . According to the HIV testing algorithm, to declare a person HIV positive, he/she should be positive with at least two tests. The sensitivity and specificity of each rapid test are summarized in the Supplementary Table 1.
Briefly, plasma samples that tested positive with the first test were subjected to the second test , and those found positive with the second test too considered positive for HIV1/2 antibodies. Likewise, those samples positive with the first test and negative with the second test were tested with the third test , and samples that turned positive were considered positive for HIV1/2 antibodies. Results from each test were interpreted as per the manufacturers instruction.
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus . The abbreviation HBV can stand for either the virus or the infection it causes.
HBV can be a short-term or a long-term illness:
- Acute HBV occurs within 6 months after a person is exposed to HBV. In some people, acute HBV can lead to chronic HBV.
- Chronic HBV is a lifelong disease. Without treatment, chronic HBV can cause liver cancer or liver damage that leads to liver failure.
HBV is a contagious infection that can spread from person to person.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis Be Sexually Transmitted
Can Hbv Infection Be Prevented
Yes. The best way to prevent HBV is to get the hepatitis B vaccine.
CDC recommends that people with HIV and people who are at risk for HIV get the HBV vaccine . The housemates and sexual partners of people with HBV should get the HBV vaccine, too.
People, including people with HIV, can also take the following steps to reduce their risk of HBV infection:
- Use condoms during sex to reduce the risk of HBV infection and infection with other sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea and syphilis.
- Do not inject drugs. But if you do, do not share needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment.
- Do not share toothbrushes, razors, or other personal items that may come in contact with another person’s blood.
- If you get a tattoo or body piercing, make sure the instruments used are sterile.
Hiv And Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Coinfection
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are liver infections caused by a virus. Because these infections can be spread in the same ways as HIV, people with HIV in the United States are often also affected by chronic viral hepatitis.
Viral hepatitis progresses faster and causes more liver-related health problems among people with HIV than among those who do not have HIV. Liver disease, much of which is related to HBV or HCV, is a major cause of non-AIDS-related deaths among people with HIV.
Given the risks of hepatitis B or hepatitis C coinfection to the health of people living with HIV, it is important to understand these risks, take steps to prevent infection, know your status, and, if necessary, get medical care from someone who is experienced in treating people who are coinfected with HIV and HBV, or HIV and HCV.
You May Like: Hepatitis C At Home Test
Is Hbv The Same As Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is caused by HBV, or the hepatitis B virus. Most HBV infections resolve within 1-2 months even without active treatment. If the infection lasts longer than 6 months, it can progress to chronic HBV, which can lead to serious complications including livercirrhosis, liver failure, liver cancer and even death.
Although there is no cure for hepatitis B, most people recover fully with treatment. Getting the hepatitis B vaccine is the only way to prevent the disease.
Specimen Collection And Processing
Ten milliliters of venous blood were taken from each study participant at each site and was dispensed into an ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid tube and transported on dry ice to Armauer Hansen research institute , where the plasma was separated via centrifugation at 3500 rpm/ 5min, transferred into cryotubes, and stored at – 20 °C until used for HIV, HBV, and HCV serology.
You May Like: What Is Acute Hepatic Porphyria
Hiv And Hepatitis And Participation In Sport
The Equal Opportunity Act 2010 makes it unlawful in Victoria to fail or refuse to select a person with HIV or hepatitis B or C for a sporting team, or to exclude them from participating in a sporting activity, because they have HIV or hepatitis B or C. People with these viruses are not required to disclose their health status to coaches, sporting teams or sporting organisations. They are entitled to keep the fact that they have HIV, hepatitis B or C confidential.