Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
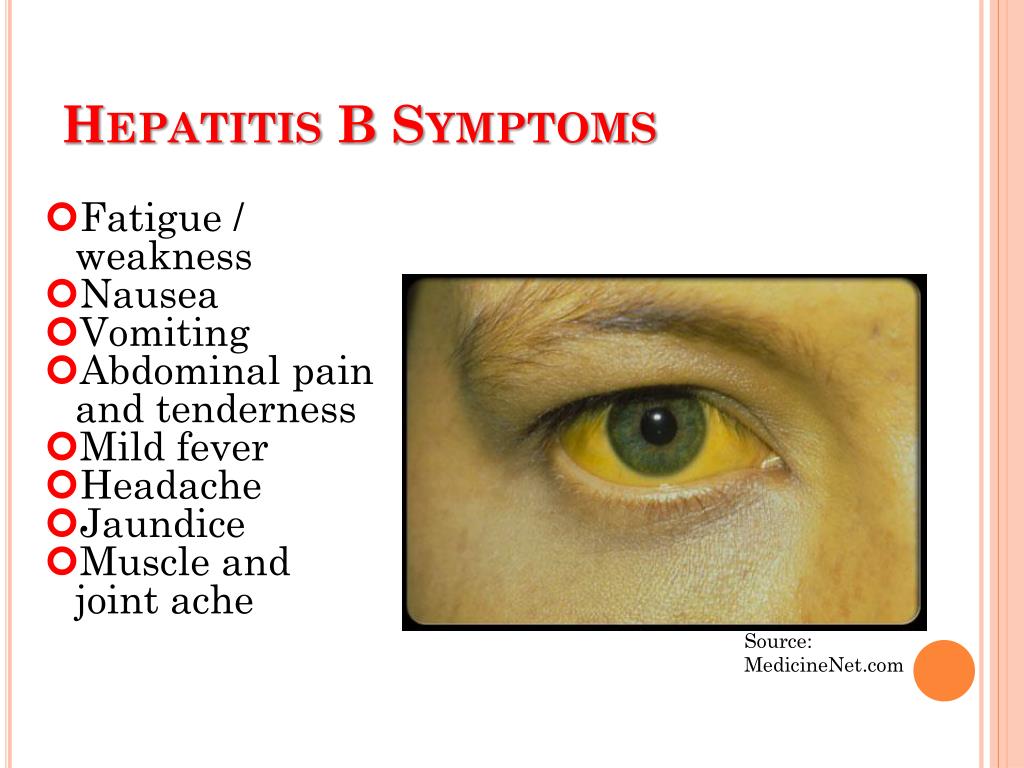
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B Early Symptoms And Signs Of Hepatitis B
- 2021-09-29 20:19:29
Hepatitis B symptom
Early symptoms: fatigue, anorexia, nausea, vomiting and yellow skin
Late symptom: Liver function impairment worsens sharply until exhaustion, continuous aggravation of aundice, oliguria, anuria, ascites, confusion, delirium, coma
Related symptoms: increased transaminase, hepatomegaly, positive hepatitis B surface antigen , positive hepatitis B e antigen , abnormal liver function and loss of appetite
I. Symptoms
Weak limbs, lack of concentration, drowsiness, fatigue, listlessness, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, and symptoms of fever, listlessness, abdominal pain and indigestion. In addition, when bilirubin in hepatitis B patients rises, jaundice symptoms, yellow skin, yellow eyes and yellow urine will appear. Often there are no symptoms, so the disease is not detected.
Second, the signs
1. Acute hepatitis B
2. Chronic hepatitis B
According to the condition, it can be divided into three types: mild, moderate and severe.
Mild: The condition is mild, with repeated fatigue, dizziness, loss of appetite, oil aversion, yellow urine, discomfort in liver area, poor sleep, slightly larger liver with mild tenderness and mild splenomegaly. Symptoms and signs were absent in some cases. There were only 1 or 2 mild abnormalities in liver function indexes.
Moderate: Symptoms, signs and laboratory examinations are between mild and severe.
3. Severe hepatitis
Extreme fatigue, severe digestive tract symptoms, neurological and mental symptoms
Hepatitis C: Who Is At Risk
People who have injected illegal drugs at any time, even one time, many years ago, could be walking around with chronic hepatitis C. Because there are often no symptoms, many former drug users may not realize they have the infection. People who received a blood transfusion before 1992 also have a higher risk. Before that year, donated blood was not screened for the hepatitis C virus.
You May Like: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B
Blood Tests For Hepatitis B
If you test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen , you have HBV in your blood. You have a chronic infection if you test positive for HBsAg consistently for at least 6 months.
If you test negative for HBsAg but positive for the hepatitis B surface antibody , you are protected from HBV because you’ve received the vaccine or recovered from an acute infection.
Another test to detect acute hepatitis B looks for the IgG antibody to hepatitis B core antigen .
Testing positive for the antibody to this antigen the hepatitis B core antibody means either that you’re currently infected with HBV, or that you were in the past, depending on the results of the HBsAg and anti-HBs tests.
The hepatitis B “e” antigen can only be found in the blood during an active infection and signifies high levels of the virus .
On the other hand, having the hepatitis B “e” antibody means that you have chronic hepatitis B but low levels of the virus, and thus a lower risk of complications.
Unlike these antigen and antibody tests, the hepatitis B viral DNA test can directly detect the presence of the virus’s DNA in your blood.
Remember that only your doctor can interpret the results of your tests.
Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B

No, there isnt a cure for Hepatitis B, but most people recover and have no symptoms after 6 months. Treatment involves getting enough rest, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding alcohol. Your health care provider will check to make sure your liver is working normally by doing a liver function test on a blood sample.
Some people carry the virus without symptoms and can pass it on to others. Hepatitis B can also cause long-term symptoms, permanent liver disease, and in some cases cancer of the liver. There are some prescription medications available to people who have the long-term infection.
How can I prevent spreading the Hepatitis B virus?
If youre infected, dont have sex or share personal items with anyone until your health care provider says its okay. You can have Hepatitis B and not even know it and be able to pass it on to others. Make sure you tell all current and past sexual partners that you have Hepatitis B, since you could have passed the infection to them before you knew you had it. Encourage them to see their health care provider as soon as possible to get tested and check if theyve already been vaccinated. They will likely need a booster dose of the HBV vaccine and they could need a dose of medication if they havent been fully vaccinated against HBV. Once your health care provider says its okay to have sex, be sure to use latex condoms during oral, anal, or vaginal sex.
How can I avoid getting the Hepatitis B virus?
Don’t Miss: Interpretation Of Hepatitis A Serologic Test Results
How Is Hepatitis B Prevented
Testing & Vaccination
- The hepatitis B vaccine offers excellent protection against HBV. The vaccine is safe and highly effective. Vaccination consists of 3 doses of vaccine over the course of 6 months. Protection lasts for 20 years to life.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children should receive hepatitis B vaccine starting at birth. .
- The CDC recommends hepatitis B vaccine for persons traveling to countries where HBV is common .
- If you have one or more risk factors for hepatitis B infection, you should get a simple HBV blood test. The blood test will determine whether you are:
- immune to hepatitis B or
- susceptible to hepatitis B and need vaccination or
- infected with hepatitis B and need further evaluation by a physician
Perinatal Hepatitis
- California law requires testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B infection
- If the mother is HBV-infected, she will pass the infection to the baby during the birth process, unless the baby gets immunized within hours of birth
- Giving the infant HBIG and HBV vaccine right away will reliably prevent infection of the infant
- Other family members should best tested for hepatitis B too, and given vaccine if they are not already infected or immune
Healthy Habits
After Exposure to Hepatitis B
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with a partner who has HBV infection
- injection drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to a person who has HBV infection
- contact with blood from or open sores on a person who has HBV infection
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with a person who has HBV infection that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 9 parts water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to people with HBV infection
- Sex partners of people with HBV infection
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Patients on hemodialysis
Who should be screened for HBV?
Don’t Miss: How To Test For Hepatitis C Virus
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
Learn About The Different Types Of Sexually Transmitted Infections Their Symptoms And Other Sti Information
It is important to be aware of the different types of sexually transmitted infections . Some STIs have symptoms and some dont, and some are more common in B.C. than others. Remember, many STIs are curable and all are treatable. If you think you have one, consider getting tested as soon as possible.
You May Like: Can Drinking Cause Hepatitis C
Read Also: What Is Hepatic Metastatic Disease
Immunisation For Hepatitis B
Immunisation is the best protection against hepatitis B infection. A course of vaccination is recommended for all babies and people in high-risk groups.
Immunisation can be with a vaccine against hepatitis B alone or with a combination vaccine. To be immunised, contact your doctor or local council.
Protection against hepatitis B is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule. In Victoria, immunisation against hepatitis B is free for:
- Babies at birth immunisation against hepatitis B alone as soon as possible after birth.
- Babies at 2, 4 and 6 months combination immunisation in the form of a diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hepatitis B, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine .
- Premature babies at 12 months premature babies born under 32 weeks gestation or under 2,000g birth weight receive a single booster dose.
- Children up to and including 9 years of age.
- People aged less than 20 years having a catch-up immunisation.
- Refugees and humanitarian entrants aged 20 years and above.
In Victoria, free hepatitis B vaccine is provided for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
Immunisation is also recommended, but not necessarily free, for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Read Also: How To Reverse Hepatic Steatosis
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Some people who are infected with the hepatitis B virus have mild, flu-like symptoms and some do not become sick at all. Children who are infected are less likely to have an illness or get sick after getting hepatitis B than adults.
In more severe cases, hepatitis B can cause:
- Loss of appetite.
- Pain in the joints.
- Jaundice .
Normally, these health problems disappear in a few weeks, but even when the person feels much better, they may still be infectious.
Most adults who become infected with the hepatitis B virus recover completely and do not become infected again. A few people become very ill in the time just after infection and need to go to hospital some may even die.
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis C
The latest drug to be approved by the FDA is glecaprevir and pibrentasvir . This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with all types of HCV who donât have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated. The length of treatment is longer for those who are in a different disease stage. The prescribed dosage for this medicine is 3 tablets daily.
There are several other combination drugs available, as well as some single drugs that may be used in combination. Your doctor will choose the right one for you depending on the type of hepatitis C you have, how well your liver is functioning and any other medical problems you may have. Also be sure to discuss your insurance coverage since these medications are expensive.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Hepatitis Panel
Hepatitis A: Who Is At Risk
A prime risk factor for hepatitis A is traveling to or living in a country with high infection rates. You can check the CDC’s travel advisories to learn about recent outbreaks. Eating raw foods or drinking tap water can raise your risk while traveling. Children who attend daycare centers also have a higher risk of getting hepatitis A.
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis B
People are more likely to get hepatitis B if they are born to a mother who has hepatitis B. The virus can spread from mother to child during birth. For this reason, people are more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- were born in a part of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection
- were born in the United States, didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant, and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection
People are also more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- are infected with HIV, because hepatitis B and HIV spread in similar ways
- have lived with or had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have sex with men
- are injection drug users
- work in a profession, such as health care, in which they have contact with blood, needles, or body fluids at work
- live or work in a care facility for people with developmental disabilities
- have been on kidney dialysis
- live or work in a prison
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before the mid-1980s
In the United States, hepatitis B spreads among adults mainly through contact with infected blood through the skin, such as during injection drug use, and through sexual contact.12
Recommended Reading: Medications To Treat Hepatitis C
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
Hepatitis C: What Happens
About 25% of people who get hepatitis C defeat the virus after a short-term infection. The rest will carry the virus in their body for the long term. Chronic hepatitis C can cause very serious complications, including liver failure and liver cancer. There are effective treatments for the virus, though.
Don’t Miss: What Happens When You Have Hepatitis B
How You Can Get Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is caused by a virus that is spread through blood, semen and vaginal fluids.
You can get hepatitis B from:
- having vaginal, anal or oral sex without using a condom or dam
- injecting drugs using shared needles
- being injured by a used needle
- having a tattoo or piercing with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country that does not check blood for hepatitis B. Blood transfusions in the UK are checked for hepatitis B.
If you’re pregnant and have hepatitis B, you can also pass it onto your baby during pregnancy or birth.
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
You May Like: What Is Hepatic Luciferase Expression
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis B
There are two types of hepatitis B infection: acute and chronic.
Acute
An acute infection happens at the beginning, when you first get infected with hepatitis B. Many people are able to clear it from their bodies and recover. In fact, this is true of about 4 in 5 adults who are infected.
Chronic
If you are not able to clear the infection within six months or longer, you have chronic hepatitis B. It is chronic hepatitis B that leads to inflammation and the serious, and possibly fatal, illnesses of cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer. Treatment can slow disease progress, reduce the chance of liver cancer and increase your chances of surviving.