What Does A Positive Hepatitis B Core Antibody Mean
anti-HBc or HBcAb A positive or reactive anti-HBc test result indicates a past or current hepatitis B infection. The core antibody does not provide any protection against the hepatitis B virus .
Is hepatitis B core antibody curable?
Hepatitis B cant be cured, but it almost always goes away on its own. There are medications that can help treat long-lasting hepatitis B infections.
What does hep B core reactive mean? 3. Hepatitis B Core Antibody This antibody does not provide any protection or immunity against the hepatitis B virus. A positive or reactive test indicates that a person may have been infected with the hepatitis B virus at some point in time.
Is hepatitis B core antibody contagious?
If this test is positive or reactive, then your immune system has successfully developed a protective antibody against the hepatitis B virus. This will provide long-term protection against future hepatitis B infection. Someone who is HBsAb+ is not infected and cannot pass the virus to others.
Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
Blood Transfusion Issues And Donor Counseling
Guidelines for donor notification for donors positive for transfusion transmissible infections are outlined in An Action Plan for Blood Safety by National AIDS Control Organization 2004. A blood donor is offered an option to know his TTI status at the time of registration for blood donation after due counseling and give consent for the same.
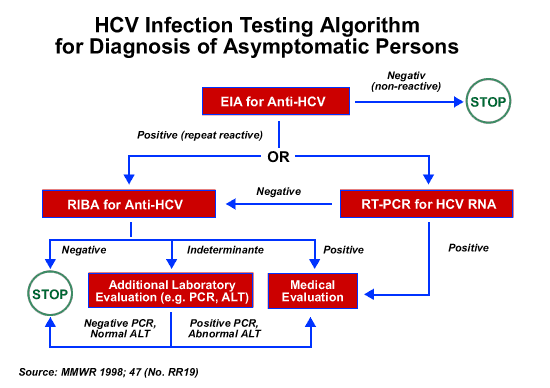
Notifying donors regarding a single positive screening test is fraught with the risk of causing undue anxiety and stress to a donor. If a screening test is positive, the blood unit should be immediately discarded. Presently there are no guidelines regarding confirming the test results before informing the donor. In case of samples with low S/CO and grey zone samples, a retesting of the donor samples using a different assay would be imperative before notifying the donor. There are clear cut guidelines regarding donor notification and referral for HIV positive blood donors with integrated counseling and testing centers available for the same. Donors who are positive for viral hepatitis markers have to be counseled by blood bank staff. An algorithm for donor counseling for HCV positive donors is outlined in .
Algorithm for donor counseling for HCV positive donors
Also Check: Can A Hepatitis B Carrier Get Vaccinated
Patient Discussion About Hepatitis A
Q. Is there a vaccination against hepatitis? I want to volunteer in a charity organization abroad soon, and I heard that currently theres and outbreak of hepatitis in the town I intend to go to. Is there anything I can do to prevent me from getting hepatitis? Is there a way to get a vaccination against it?
A.
Q. Is hepatitis a sexually transmitted disease? I mean hepatitis B and C mainly
A.
Q. can hepatitis be transferred from fathers sperm when concieving a child? My partner has hepatitis C and he has gotten me pregnant will our baby have it too?
A.
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis C testing is performed by a doctor. Testing requires a blood sample, which can be collected in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Blood is often drawn from a vein in the arm or, in children, taken by pricking the skin. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Don’t Miss: Is There Now A Cure For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Virus Antibody Confirmation Serum
Confirming the presence of hepatitis C virus -specific IgG antibodies in serum specimens that are reactive by HCV antibody screening tests
Distinguishing between true- and false-reactive HCV antibody screening test results
This test is not intended for use as an HCV antibody screening test for blood or human cells/tissue donors
This assay is not usefulfor detection of early or acute hepatitis C as immunocompromised patients may not develop detectable HCV antibodies in blood until 6 months after infection
This assay is not useful for differentiating between past and chronic hepatitis C
What Does A Hepatitis Panel Involve
Hepatitis panels are simple blood tests. They do not involve any preparation and have a very low risk of side effects.
To perform the test, a healthcare professional will insert a needle into a vein in the arm. They will collect a small blood sample in a test tube and seal it. The needle may sting a little, but the process takes only a few minutes. A person may feel a small amount of pain or bruising around the vein, but this should subside quickly.
People can also get at-home testing kits for hepatitis. These come with a sterile lancet that a person uses to prick their finger to collect the blood sample.
When using at-home kits, be sure to take safety precautions to prevent others from coming into contact with blood. Even dry blood or tiny amounts of blood can potentially transmit HBV or HCV to others.
Dispose of items that come into contact with blood in a sealed bag and wash the blood from the skin using soap. Completely cover the finger prick wound with a sterile dressing until it heals.
- of the population have hepatitis B and have not had a vaccination
- spent time in a facility that had a hepatitis outbreak, such as a hospital or prison
- received a blood transfusion that did not undergo hepatitis screening
In the United States, screening eliminated HCV from donated blood in 1992. People who received blood transfusions before 1992 should ask their doctor for a hepatitis C test.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B How Long Does It Last
Clinical Information Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B e antigen is a small polypeptide that exists in a free form in the serum of individuals during the early phase of hepatitis B infection, soon after hepatitis B surface antigen becomes detectable. Serum levels of both HBeAg and HBsAg rise rapidly during the period of viral replication. The presence of HBeAg in serum correlates with hepatitis B virus infectivity, the number of infectious virions, and the presence of HBV core antigen in the infected hepatocytes.
During recovery from acute hepatitis B, HBeAg level declines and becomes undetectable in the serum, while hepatitis B e antibody appears and becomes detectable in the serum. Anti-HBe usually remains detectable for many years after recovery from acute HBV infection.
In HBV carriers and patients with chronic hepatitis B, positive HBeAg results usually indicate presence of active HBV replication and high infectivity. A negative HBeAg result indicates very minimal or no HBV replication. Positive anti-HBe results usually indicate inactivity of the virus and low infectivity. Positive anti-HBe results in the presence of detectable HBV DNA in serum also indicate active viral replication in these patients.
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a liver infection that can lead to serious liver damage. Itâs caused by the hepatitis C virus. About 2.4 million people in the U.S. have the disease. But it causes few symptoms, so most of them don’t know. The virus spreads through an infected personâs blood or body fluids.
There are many forms of the hepatitis C virus, or HCV. The most common in the U.S. is type 1. None is more serious than any other, but they respond differently to treatment.
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis B Do
How Is Liver Damage Assessed
If you have hepatitis C, doctors can gauge the level of liver damage you’ve experienced. One useful diagnostic tool is called a hepatic function panel, a group of blood tests performed together that examine the levels of certain liver enzymes, bilirubin , and proteins circulating in the blood.
Higher-than-normal levels of the liver enzymes, indicate that your liver is damaged, possibly from cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Albumin may be low, and your total bilirubin levels may also be elevated.
Along with the hepatic function panel, your doctor may also order two other tests: one test to determine the levels of the liver enzyme gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in your blood, and a prothrombin time test that measures how well your blood clots.
A liver biopsy, in which a liver tissue sample is removed with a thin needle inserted through your skin and into your liver, can provide more details about the amount of scarring and damage HCV has caused.
Your doctor may also order an imaging test, such as a computerized tomography scan, magnetic resonance imaging , or ultrasound, to see if your hepatitis C has caused liver cancer, a possible complication of hepatitis C.
Additional reporting by Deborah Shapiro.
Who Should Get Tested
You should consider getting tested for hepatitis C if you’re worried you could have been infected or you fall into one of the groups at an increased risk of being infected.
Hepatitis C often has no symptoms, so you may still be infected if you feel healthy.
The following groups of people are at an increased risk of hepatitis C:
- ex-drug users and current drug users, particularly users of injected drugs
- people in the UK who received blood transfusions before September 1991
- UK recipients of organ or tissue transplants before 1992
- people who have lived or had medical treatment in an area where hepatitis C is common high-risk areas include north Africa, the Middle East and central and east Asia
- babies and children whose mothers have hepatitis C
- anyone accidentally exposed to the virus, such as health workers
- people who have received a tattoo or piercing where equipment may not have been properly sterilised
- sexual partners of people with hepatitis C
If you continue to engage in high-risk activities, such as injecting drugs frequently, regular testing may be recommended. Your doctor will be able to advise you about this.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
Testing Procedures And Costs
The test for HCV antibodies, as well as follow-up blood tests, can be done in most labs that perform routine blood work.
A regular blood sample will be taken and analyzed. No special steps, such as fasting, are needed on your part.
Many insurance companies cover hepatitis C testing, but check with your insurer first to be sure.
Many communities offer free or low-cost testing, too. Check with your doctors office or local hospital to find out whats available near you.
Testing for hepatitis C is simple and no more painful than any other blood test.
But if youre at risk for the disease or think you may have been exposed to the virus, getting tested and starting treatment if necessary can help prevent serious health problems for years to come.
CDC recommends that all adults ages 18 years and older should be screened for hepatitis C except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%.
Also, all pregnant women should be screened during each pregnancy, except in setting where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%.
Hepatitis C is often associated with sharing needles . But there are other methods of transmission.
For example, healthcare workers who are regularly exposed to other peoples blood are at higher risk for contracting the virus.
Getting a tattoo from an unlicensed tattoo artist or facility where needles may not be properly sterilized also increases the risk of transmission.
Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
A positive result indicates the presence of hepatitis C virus -specific IgG antibodies due to past or chronic hepatitis C. Past HCV infection can be distinguished from chronic HCV infection only by direct detection of HCV RNA using molecular test methods eg, HCVQN / Hepatitis C Virus RNA Detection and Quantification by Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR , Serum. HCV RNA is present in acute or chronic hepatitis C but not in past HCV infection.
A negative result indicates the absence of HCV-specific IgG antibodies. A reactive HCV antibody screening test result with a negative HCV antibody confirmatory result indicates a probable false-reactive screening test result.
An indeterminate result indicates that HCV-specific IgG antibodies may or may not be present. Indeterminate results should be interpreted along with patient’s risk factors for HCV infection and clinical findings. Individuals at risk for HCV infection with indeterminate results should be retested with an HCV antibody confirmatory test in 1 to 2 months to determine the definitive HCV antibody status. Molecular tests to detect HCV RNA may be necessary to determine HCV infection status in those at-risk immunocompromised patients with indeterminate HCV antibody confirmatory test results due to delayed appearance of fully complement of HCV-specific antibodies.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Besides Hcv Testing What Other Tests Might Be Done
Healthcare practitioners may also order a liver panel, which is a group of tests that help assess the health of your liver. Liver tests such as ALT and AST may be used to detect ongoing liver injury. You will likely be checked to see if you are immune to hepatitis A and hepatitis B, and if not, you will be offered vaccination, since infection with these other viruses can further damage your liver. Other tests such as albumin, prothrombin time, and bilirubin can also be used. They are typically normal unless you have developed cirrhosis. Sometimes a liver biopsy may be performed to determine the severity of liver damage. If you are going to be treated, you will be checked for exposure or infection with hepatitis B virus, as HCV treatment can cause a flare-up of hepatitis B.
Hcv Core Antigen Testing
The hepatitis C core antigen is a viral protein. Since the core antigen is part of hepatitis C virus, it can usually be found in the bloodstream two weeks after infection.
Since HCV core antigen testing is simpler and less expensive than viral-load testing, some experts suggest using it in resource-limited settings. Core antigen testing can be usedoften with HCV antibody testingto detect acute HCV or to confirm chronic HCV infection. HCV core antigen testing can also be used to measure treatment outcome. Although it does not detect low levels of HCV , usually the hepatitis C viral load is much higher in people who relapse after HCV treatment.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Go Away On Its Own
How Can I Tell If I Am Contagious And Can Spread The Infection To Others
If you have detectable HCV RNA in your blood, you have the potential to spread the disease to other people. Hepatitis C is spread by exposure to contaminated blood. The most common mechanism of exposure is the sharing of needles or other ‘works’ used in consuming drugs such as cocaine or heroin. Other routes of transmission include use of contaminated equipment for body piercing and tattooing, occupational exposure of healthcare workers to used needles or other sharp objects, and, less commonly, through sexual activity that results in tissue tears or from mother to baby during childbirth.
What Does A Reactive Hcv Antibody Test Result Mean
A reactive or positive antibody test means you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time.
Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true if they have cleared the virus, have been cured, or still have the virus in their blood.
A reactive antibody test does not necessarily mean that you currently have hepatitis C and a follow-up test is needed.
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis B Come From
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
A blood test, called an HCV antibody test, is used to find out if someone has ever been infected with the hepatitis C virus. The HCV antibody test, sometimes called the anti-HCV test, looks for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus in blood. Antibodies are chemicals released into the bloodstream when someone gets infected.
Test results can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks to come back. Rapid anti-HCV tests are available in some health clinics and the results of these tests are available in 20 to 30 minutes.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C spreads when blood or body fluids contaminated with the hepatitis C virus get into your bloodstream through contact with an infected person.
You can be exposed to the virus from:
- Sharing injection drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV, another STD, several partners, or have rough sex
- Being stuck by infected needles
- Birth — a mother can pass it to a child
- Sharing personal care items like toothbrushes, razor blades, and nail clippers
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unclean equipment
You canât catch hepatitis C through:
- Breastfeeding
- Casual contact
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Have HIV
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Since July 1992, all blood and organ donations in the U.S. are tested for the hepatitis C virus. The CDC says it is now rare that someone getting blood products or an organ would get hepatitis C. That said, The CDC recommends that anyone over the age of 18 get tested for Hepatitis C. If you haven’t been screened, you should consider having it done.
Learn more about the risk factors for hepatitis C.
Also Check: What Does It Mean If You Have Hepatitis C Antibodies