How Is Acute Hepatitis B Treated
Acute hepatitis B doesnt always require treatment. Most of the time, a doctor or healthcare professional will recommend monitoring your symptoms and getting regular blood tests to determine whether the virus is still in your body.
While you recover, allow your body to rest and drink plenty of fluids to help your body fight off the infection. You can also take an over-the-counter pain reliever to help with any abdominal pain you have. Speak with a doctor about which medications can help your symptoms.
See a doctor if your symptoms are severe or seem to be getting worse. You may need to take a prescription antiviral medication to avoid potential liver damage.
Like acute hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis B may not require medical treatment to avoid permanent liver damage. For some people, monitoring their symptoms and getting regular liver tests is an appropriate care regimen.
Treatment generally involves antiviral medications, such as:
- peginterferon alfa-2a injections
- antiviral tablets, such as tenofovir or entecavir
Antiviral medications can help to reduce your symptoms and prevent liver damage, but they rarely completely get rid of the hepatitis B virus. Instead, the goal of treatment is for you to have the lowest viral load possible. Viral load refers to the amount of a virus in a blood sample.
You can lower your risk of developing hepatitis B or spreading the virus to others by:
Can I Get The Hep B Vaccinations And Covid Vaccinations Around The Same Time
Speak to your vaccinating nurse or doctor. There isnt much evidence yet about getting vaccinated for hep B and COVID around the same time. Both hep B and COVID vaccines are equally important. If you would like to get both vaccines around the same time, its best that you speak to your vaccinating nurse or doctor.NOTE: This rule has recently changed. In the past, people were told to wait 14 days between vaccinations.
Who Should Not Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B is a safe vaccine that does not contain a live virus.
However, there are some circumstances in which doctors advise against getting the HBV vaccine.
You should not receive the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- youve had a serious allergic reaction to a previous dose of the hepatitis B vaccine
- you have a history of hypersensitivity to yeast or any other HBV vaccine components
You May Like: How Can You Get Hepatitis C From Someone
What Is Hepatitis A And B Vaccine
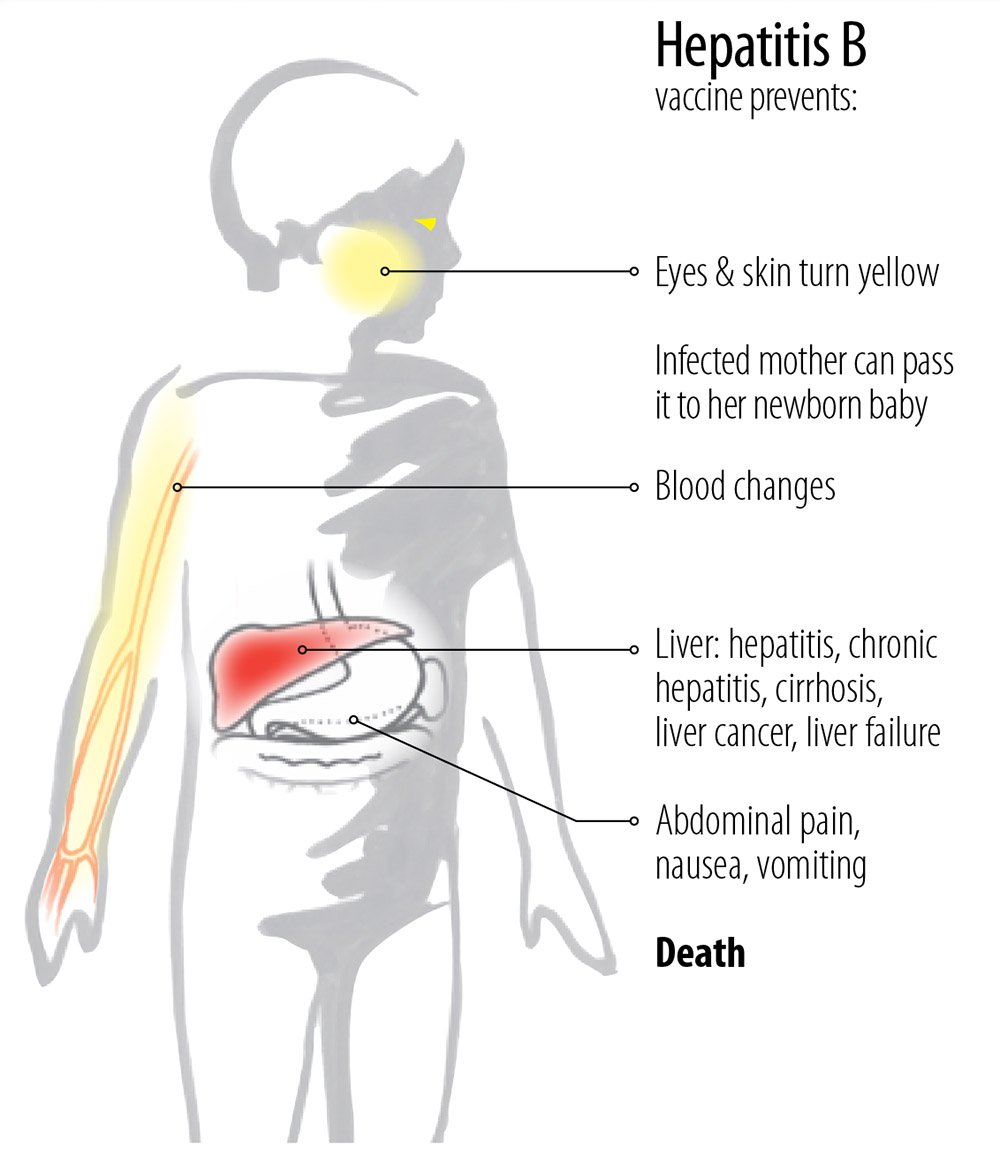
Hepatitis A and B are serious diseases caused by virus. Hepatitis causes inflammation of the liver, vomiting, and jaundice . Hepatitis can lead to liver cancer, cirrhosis, or death.
The hepatitis A and B vaccine is used to help prevent these diseases in adults. The vaccine works by exposing you to a small dose of the virus, which causes the body to develop immunity to the disease. This vaccine will not treat an active infection that has already developed in the body.
This vaccine is recommended for adults with risk factors for getting hepatitis A or B, including:
-
having chronic liver problems, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis C, or needing a liver transplant
-
using intravenous drugs
-
living with a person who has either hepatitis A or B infection
-
having sexual contact with an infected person
-
having a blood clotting disorder such as hemophilia
-
being on dialysis or receiving blood transfusions
-
living in a correctional institution
-
being in the military or traveling to high-risk areas and
-
working in healthcare or public safety and being exposed to infected blood or body fluids.
Like any vaccine, the hepatitis A and B vaccine may not provide protection from disease in every person.
What Causes Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus. It can happen through exposure to infected blood and other bodily fluids in the following situations:
- sharing needles and other injecting drug equipment
- sharing razors, toothbrushes or nail clippers
- tattooing with unsterilised needles and equipment
- close family contact with someone who has hepatitis B
- being born to a mother with hepatitis B
- accidental exposure such as a needle stick injury or being splashed with infected blood or body fluid
- blood transfusion this is now very rare as blood in Australia is screened for hepatitis B
You cannot catch hepatitis B through being coughed or sneezed on by infected people or by consuming contaminated food and drink. You cannot catch the virus from saliva, breast milk or tears.
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Hepatitis Is Contagious
Unlikely Sources Of Infection
Trace levels of HBV can also be found in saliva, tears, urine, and feces but in amounts that are highly unlikely to cause infection.
While vaccination remains the cornerstone of HBV prevention, there are ways to further reduce the risk of transmission, especially if you or someone in your household has hepatitis B:
- Wash your hands with soap and water if exposed to blood.
- Avoid sharing razors or toothbrushes.
- Use condoms during sex.
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
Also Check: How You Get Hepatitis B And C
Whats The Difference Between Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B can be either acute or chronic:
- Acute hepatitis B lasts for a short period of time. If you have acute hepatitis B, you may be asymptomatic or have symptoms and develop icteric hepatitis. It can transition into chronic hepatitis B if the virus doesnt naturally go away after 6 months.
- Chronic hepatitis B lasts for at least 6 months. If you have this type of hepatitis, you may carry the hepatitis B virus for the rest of your life. Its possible to have chronic hepatitis B that started as acute, but many people dont have acute hepatitis B first.
Most people with acute hepatitis B make a full recovery. Some may never even show any symptoms. But those with chronic hepatitis B often need treatment to help manage the infection. Chronic hepatitis B also increases your risk of developing cirrhosis and certain types of liver cancer.
Your risk of developing chronic hepatitis B depends on when you first received your diagnosis of the virus. Children who receive a diagnosis of hepatitis B, especially those under the age of 5 years old, have a higher risk of the infection becoming chronic. Adults are less likely to develop chronic hepatitis B. Around 90 percent of adults who develop it will fully recover.
Keep in mind that hepatitis B can be present for years before you start to show any symptoms.
Should I Test For Antibodies
There is no need for a routine check of vaccination protection with every client. In vaccine studies, hepatitis B vaccines have afforded a protective level of antibodies to over 95% of vaccination recipients.
Checking the protection achieved by the vaccination series is particularly important in cases of continuous significant exposure. These cases include the child of a mother who is a hepatitis B carrier, or the partner of a hepatitis B carrier.
A physician makes the decision on testing for antibodies in situations where it is suspected that protection is insufficiently established and the persons exposure risk is significant and continuous.
Protection may not be established if the vaccine recipient
- is aged over 50
- is severely overweight, or
- has a chronic illness that reduces their resistance.
If a person has a repeated exposure risk at work, the occupational healthcare services will assess if their protection should be checked.
This is done by testing for antibodies 6 to 8 weeks after the last dose. Protection is sufficient if S-HBsAb is 10 IU/l or higher after a series of three or four doses.
If a person has not developed sufficient protection following the primary vaccination series and repeated exposure is obvious, additional vaccinations should be administered in months 0, 2 and 4. Test for antibodies again 6 to 8 weeks after the final dose. If sufficient protection has still not been established, the infection risk must be reduced by other means.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Test Results 0.1
I Have Hep B Do I Need Extra Protection Against Covid
No. You can protect yourself against COVIDin the same ways as everyone else. We all need be careful to stop the spread of COVID, for our own health and for the health of our communities.
You should take extra care to protect yourself from COVID if you: have an additional health condition are over 70 are over 50 and Aboriginal have a weakened immune system.
Follow Government advice on keeping safe and stopping the spread of COVID E> > >
How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
The number of infections had been falling in the U.S., but fewer vaccinations among adults combined with the onset of the opioid crisis and injected drug usage has resulted in the numbers rising again. Infected women can pass the infection on to their babies. Children who are infected before age 5 are more likely to have chronic infection than those infected later in life.
Don’t Miss: Hiv And Hepatitis Are Transmitted Through What Modes
How It’s Passed On
- sharing injecting drug equipment, such as needles and syringes, which can carry infected blood
- childbirth, from a mother to her baby.
It can be found in saliva but there are no proven cases of it being passed on through kissing. Infections from bites are rare.
Avoid sharing razors, toothbrushes, nail scissors, hair clippers and tweezers because traces of blood on them can pass on hepatitis B. This includes dried blood as the virus can survive for at least a week outside of the body.
Im On Treatment For Hep B Can I Still Get The Covid Vaccines

Yes. There is no evidence to suggest that the COVID vaccines have any impact on your hep B treatment. Just like with all other vaccines, the COVID vaccines are safe for people on hep B treatment.
Its really important to always take hep B medication. You should only stop taking it if told to by your specialist.
Read Also: Does Hepatitis B Have A Vaccine
Risk Areas For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B occurs worldwide. In Sweden, Western Europe and the USA, the risk of contracting Hepatitis B is relatively small, but globally it is a common disease. In some parts of the world, as many as 15-20% are chronic carriers and a majority of the rest of the population has at some point been exposed to infection. The highest incidence of hepatitis B virus carriers is seen in sub-Saharan Africa and in Southeast Asia.
How You Can Get Hepatitis B
You can get hepatitis B from:
- injecting drugs using shared needles
- being injured by a used needle
- having a tattoo or piercing with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country that does not check blood for hepatitis B. Blood transfusions in the UK are checked for hepatitis B.
If you’re pregnant and have hepatitis B, you can also pass it onto your baby during pregnancy or birth.
Don’t Miss: Common Signs Of Hepatitis C
What Treatments Are Available For Chronic Hepatitis B If Medications Dont Work
If you have advanced hepatitis B, you might also become a candidate for a liver transplant. This path does not always result in a cure because the virus continues in your bloodstream after a transplant. To prevent being infected again after your transplant, you may be prescribed hepatitis B immunoglobulin with an antiviral agent.
To Whom Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine Administered
A free vaccine is offered as part of the national programme to
- haemophiliacs receiving regular treatment
- persons close to intravenous drug users, including family members, housemates and sexual partners
- men who have sex with men
In case of persons belonging to one of these groups, also check their protection against hepatitis A. If the person has not received either vaccine previously, you can administer a free hepatitis A and B combination vaccine.
Due to increased infection risk, a free hepatitis B vaccine is also offered to
- newborn children and sexual partners of, and those living in the same household with, persons with a hepatitis B infection and asymptomatic HBsAg positive persons
- students exposed to infection risk during internships
- persons at risk of hepatitis B infection resulting from a needlestick injury or other blood exposure and who have been exposed in environments other than the workplace
- children aged under 5 years at a day care centre when a child in the group is known to be HBsAg positive
- newborn infants when at least one of the parents comes from a country where hepatitis B is common
- newborn infants of mothers with a hepatitis C infection.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis B Virus A Std
Hepatitis A And Hepatitis B Vaccine Dosing Information
Usual Adult Dose for Hepatitis B Prophylaxis:
Primary immunization: 1 mL IM in the deltoid area at 0, 1 and 6 months.Alternatively, a 4 dose schedule given on days 0, 7, and 21 to 30 followed by a booster at month 12 may be used.
Usual Adult Dose for Hepatitis A Prophylaxis:
Primary immunization: 1 mL IM in the deltoid area at 0, 1 and 6 months.Alternatively, a 4 dose schedule given on days 0, 7, and 21 to 30 followed by a booster at month 12 may be used.
Hepatitis A And B Vaccine Side Effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives difficult breathing swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Keep track of any and all side effects you have after receiving this vaccine. When you receive a booster dose, you will need to tell the doctor if the previous shot caused any side effects.
You should not receive a booster vaccine if you had a life-threatening allergic reaction after the first shot.
You may feel faint after receiving this vaccine. Some people have had seizure like reactions after receiving this vaccine. Your doctor may want you to remain under observation during the first 15 minutes after the injection.
Hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine may cause serious side effects. Call your doctor at once if you have:
-
numbness, pain, tingling, weakness, burning or prickly feeling, vision or hearing problems, trouble breathing
-
red or blistering skin rash or
-
easy bruising or bleeding .
Common side effects of hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine may include:
-
redness or tenderness where the shot was given
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report vaccine side effects to the US Department of Health and Human Services at 1-800-822-7967.
You May Like: How Do Most People Get Hepatitis C
Should I Keep Taking My Hep B Medication During This Time
Yes. Definitely keep taking your hep B treatment. Only stop taking your treatment if told to by your doctor or specialist.
It is important to take your hep B medication as prescribed otherwise the virus could become resistant and might be harder to keep under control.
REMINDER: not everyone who has hep B needs to be on medication. It is only for those whose specialist has prescribed it to protect their liver.
Administration Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
The hepatitis B vaccine is typically given in a series of two or three injections into a muscle. However, if people who have been vaccinated are exposed to the virus, a doctor measures their antibody levels against hepatitis B. If the antibody levels are low, they may need another injection of hepatitis B vaccine.
-
People who are under age 60 and have diabetes Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes mellitus is a disorder in which the body does not produce enough or respond normally to insulin, causing blood sugar levels to be abnormally high. Urination and thirst are… read more and sometimes people who are age 60 and older who have diabetes
-
People who are employed by or are given care in places where there are people at high risk of hepatitis B
-
Pregnant women if they are at risk of getting the infection or of getting very sick or dying of infection during pregnancy
If people have a temporary illness, doctors usually wait to give the vaccine until the illness resolves .
Also Check: How Long Can Hepatitis B Virus Live Outside The Body
My Partner Has Been Diagnosed With Hepatitis B Can Transmission Be Prevented By Vaccination
A hepatitis B diagnosis can be scary and confusing for both you and your loved ones, especially if you are unfamiliar with the virus. Hepatitis B is known to be sexually transmitted, and you may wonder how you can continue your relationship with someone who has been infected. The good news is that hepatitis B is vaccine preventable. This means that after you complete the vaccine series, you cannot contract hepatitis B through any modes of transmission you are protected for life!
However, it is important to remember that the vaccine willonly work if a person has not been previously infected. Therefore, it is necessary to take certain steps after your partners diagnosis to protect yourself from becoming infected.
The first step is to visit the doctor and get tested, even if you think that you do not have it. Since hepatitis B often has no symptoms for decades, testing is the only way to know your status. The doctor should perform the Hepatitis B Panel test a simple blood draw that shows hepatitis B surface antigen , hepatitis B surface antibody , and hepatitis B core antibody total . Looking at these three blood test results together will show if you have a current infection, have recovered from a past infection, or if you need to be protected through vaccination. Once you receive your results, this chart can help you understand what they mean.
Preventing Transmission through Vaccines: