How Is Hiv Transmitted Or Spread
The following are the means by which the HIV virus is spread:
-
Vertical transmission. HIV can be spread to babies born to, or breastfed by, mothers infected with the virus.
-
Sexual contact. In adults and adolescents, HIV is spread most commonly by sexual contact with an infected partner. The virus enters the body through the lining of the vagina, vulva, penis, rectum, or abraded or irritated tissues in the lining of the mouth through sexual activity.
-
Blood contamination. HIV may also be spread through contact with infected blood. However, due to the screening of donated blood for evidence of HIV infection, the risk of acquiring HIV from blood transfusions is extremely low.
-
Needles. HIV is frequently spread by sharing needles, syringes, or drug use equipment with someone who is infected with the virus. Transmission from patient to health care worker, or vice-versa, through accidental sticks with contaminated needles or other medical instruments, is rare.
No known cases of HIV/AIDS have been spread by the following:
-
Saliva
-
Malaise
-
Enlarged lymph nodes
An HIV-infected child is usually diagnosed with AIDS when the immune system becomes severely damaged or other types of infections occur. As the immune system deteriorates, complications begin to develop. The following are some common complications, or symptoms, of the onset of AIDS. However, each child may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
How Could You Get Hiv From Contact With Blood
The risk of HIV transmission through blood comes when the person has a detectable viral load and their blood enters another persons body or comes into contact with a mucous membrane. These are parts of the body with wet, absorbent skin such as the:
- eyes
- inside of the anus
- mouth.
Theres also a risk if blood from a person who has a detectable viral load comes into contact with a cut or broken skin, giving HIV a way through the skin and into someones bloodstream. If blood gets onto skin that isnt broken, there is no risk.
In a medical setting, its possible for HIV to be transmitted by someone accidentally cutting themselves with a blade or needle they have used to treat a person living with HIV.
This is called a needlestick injury. The risk of being infected in this way is very low. However, if someone thinks they have been exposed to HIV through a needlestick injury, post-exposure prophylaxis may be an option.
Modes Of Transmission Of Diseases
Transmission is the process by which a pathogen spreads from one host to another. Diseases or infections are transmitted in many ways. It may be directly transmitted from one person to another, or by certain bacteria, viruses, protozoa, or fungi. There are two different modes of transmission of diseases:
-
Direct Transmission This occurs when the pathogen is transmitted directly from an infected person. For eg., if an open wound comes in contact with the blood of a Hepatitis B infected patient, the wounded person might contract the disease.
-
Indirect Transmission- When the pathogens are not transmitted directly from the infected person but through vectors such as flies, mosquitoes, ticks, dogs, etc., it is known as indirect transmission.
Read Also: How Us Hepatitis C Transmitted
How Common Is It
In 2006, the Public Health Agency of Canada reported the incidence of HBV as 2.0 cases for every 100,000 or about 650 cases reported annually in Canada. In the year 2013, the incident rate was 0.5 per 100,000 . Incidence of the disease varies from region to region but has been declining due to increasing use of the vaccine and universal immunization programs.
How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
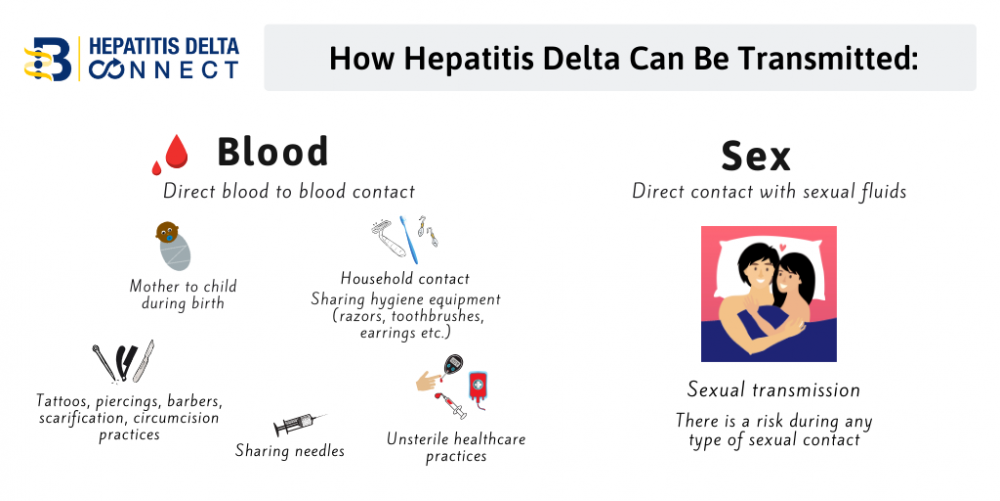
Hepatitis B is spread in several distinct ways: sexual contact sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment or from mother-to-child at birth.
In the United States, in 2018, injection drug use was the most common risk factor reported among people with an acute HBV infection, followed by having multiple sex partners. Less commonly reported risk factors included accidental needle sticks, surgery, transfusions, and household contact with a person with HBV infection. In the United States, healthcare-related transmission of HBV is rare.
Mother-to-child transmission of HBV is especially concerning, because it is preventable. An estimated 25,000 infants are born to mothers diagnosed with HBV each year in the United States, and approximately 1,000 mothers transmit HBV to their infants. Without appropriate medical care and vaccinations, 90% of HBV-infected newborns will develop chronic infection, remaining infected throughout their lives. Up to 25% of people infected at birth will die prematurely of HBV-related causes. For this reason, the standard of care for pregnant women includes an HBV test during each pregnancy so that the appropriate steps can be taken to prevent HBV-positive mothers from transmitting the disease to her infant.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis C Related To Aids
How To Be Safe When Coming Into Contact With Infected Blood
A condom will act as a barrier against any contact with blood during sex.
As well as sex, sharing equipment for injecting drugs is a way blood can get into someones body. This can be avoided by using fresh needles and not sharing needles, syringes and other equipment.
If a woman has HIV, her menstrual blood also carries a risk of transmission if she has a detectable viral load.
If youre HIV negative and taking pre-exposure prophylaxis youll be protected against getting HIV if you come into contact with infectious blood.
The Chain Of Infection
For any disease to spread, several conditions must be present. This is known as the chain of infection. And if you recall from the last lesson, those conditions are as follows:
Pro Tip #1: Infection control strategies help prevent disease transmission by interrupting one or more links in the chain of infection.
You May Like: How Would You Know If You Had Hepatitis C
What Is The Risk Of Coinfection
A coinfection is when someone has two or more infections at the same time. People living with HIV are at risk of developing coinfections such as hepatitis C because HIV weakens the immune system, which leaves the body more vulnerable to other infections and illnesses.
HIV and HCV are also transmitted in similar ways, which means that people who have HIV may be at higher risk of exposure to HCV. In the United States, over a third of people living with HIV also have hepatitis C.
Coinfection of HCV and HIV is higher among those who use injected drugs. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , HCV coinfection occurs in between 62 and 80 percent of people with HIV who use injected drugs.
A systematic review of 783 studies concluded that people living with HIV were six times more likely to have hepatitis C than people without HIV.
Hepatitis C infections are more serious in people with HIV and can lead to more severe damage of the liver. HIV and HCV coinfections can increase the risk of:
- liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, which is a buildup of scar tissue in the liver
- end-stage liver disease
A person can contract HCV through direct contact with blood or other body fluids that contain the virus. Possible modes of transmission include:
Ways to prevent hepatitis C include:
- not sharing needles
Blood Transfusions And Organ Donation
The risk of contracting HIV from a blood transfusion, other blood products, or organ donation is now extremely rare in the United States. All donated blood or blood products in the United States are for several types of bloodborne pathogens, including HIV.
Organ donations are also screened for HIV. Although very rare, its possible for HIV transmission to occur following an organ transplant.
However, testing of organ recipients after surgery can quickly detect transmission so that antiretroviral medications can be started promptly.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis C
What To Do If You Are Exposed
If you are stuck with a needle, get blood in your eye, or are exposed to any bloodborne pathogen:
- Wash the area. Use soap and water on your skin. If your eye is exposed, irrigate with clean water, saline, or a sterile irrigant.
- Tell your supervisor right away that you were exposed.
- Get medical help right away.
You may or may not need lab tests, a vaccine, or medicines.
What Are Bloodborne Pathogens
In this lesson, we’ll take a look at how one gets ill from a bloodborne pathogen or infectious disease. But first, how about a couple of definitions?
Bloodborne Pathogen A bloodborne pathogen is a microorganism that’s present in human blood and can cause disease in humans.
Infectious Disease An infectious disease is a disease that enters the body through various biological routes.
It’s important to note that not all bloodborne pathogens and infectious diseases are created equally, as some can produce mild symptoms, while others can be life-threatening.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Treatment Antiviral Drugs
Occupational Exposure To Bloodborne Pathogens
Occupational exposure means reasonably anticipated skin, eye, mucous membrane, or parenteral contact with blood or other potentially infected materials that may result from the performance of an employees duties.
Exposure incident means a specific eye, mouth, other mucous membrane, non-intact skin, or parenteral contact with blood or OPIM that results from the performance of an employees duties. Examples of non-intact skin at risk include skin with dermatitis, hangnails, cuts, abrasions, chafing, or acne.
Occupational groups that have been widely recognized as having potential exposure to HBV/HCV/HIV include, but are not limited to, healthcare employees, law enforcement, fire, ambulance, and other emergency response, and public service employees.
The compliance directive of the federal Occupational Safety and Health Administration on occupational exposure to bloodborne pathogens, CPL 2-2.69, may be consulted for guidance. For more information or assistance, contact a Department of Labor and Industries consultant in your area. Check the blue government section of the phone book for the office nearest you.
Test Your Learning
Answer: d
Bloodborne Pathogens
Blood and OPIM
Bodily fluids that have been recognized and linked to the transmission of HIV, HBV, and HCV, and to which Standard Precautions apply, are:
- Blood
- Amniotic fluid
- Saliva in dental procedures
- Specimens with concentrated HIV, HBV and HCV viruses
Exposure Control Plan
Bloodborne Pathogens Training
Online Resource
What Is The Treatment For Hiv
Individuals who are HIV positive will likely need to see a specialist. As with many other conditions, early detection offers more options for treatment. Today, there are medical treatments that can slow down the rate at which HIV weakens the immune system. However, there are other treatments that can prevent or cure the conditions associated with HIV. Anti-retroviral drug therapy may be given to a pregnant woman, which has proven to greatly reduce the chance of an infant developing HIV. A cesarean section may be recommended to reduce infant transmission from the birth canal. In the U.S., where other feeding options are available, an infected mother should be discouraged from breastfeeding her infant. Consult your child’s doctor for more information regarding various drug therapies.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Can You Catch It From Saliva
Stage : Acute Hiv Infection
Soon after a person contracts HIV, they may develop flu-like symptoms. These symptoms typically appear within and may last for several days or weeks.
The symptoms of an acute HIV infection can include:
- a skin rash that usually does not itch
- muscle aches
- swollen glands in the throat, groin, or armpits
- sores or ulcers in the mouth or genitals
- nausea, vomiting, or both
This is known as a seroconversion illness. Seroconversion is when the body begins to produce antibodies against the virus. This is the bodys natural response to detecting an infection.
At this stage, the virus replicates rapidly. The person has a large amount of HIV in their blood, and the risk of transmitting the virus to others is high.
Not everyone develops symptoms at this stage. Others experience mild flu-like symptoms that go largely unnoticed. This means that people may contract HIV without knowing it, which makes testing very important.
If a person thinks they may have been exposed to HIV, it is important to talk to a healthcare provider for advice, and to ask them about preventative medication called post-exposure prophylaxis .
Healthcare providers can order tests to check for HIV. can detect the virus after 10 days, while others may not detect the infection until 90 days after exposure. People often need to take more than one test for accurate results.
Parenteral Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis B Hepatitis D And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B, C, and D viruses are all transmitted by what is known as the parenteral route. Parenteral simply means that these viruses can be introduced by all routes except through the intestinal tract, which leaves the door wide open in terms of possible exposure. Let’s look at the possible transmission routes for each of these types of hepatitis virus more closely.
Recommended Reading: How Much Is A Hepatitis A Shot
How Does Hbv Spread From Person To Person
HBV is spread through contact with the blood, semen, or other body fluid of a person who has HBV. Among adults in the United States, HBV is spread mainly through sexual contact.
HBV can also spread from person to person in the following ways:
- From contact with the blood or open sores of a person who has HBV
- From an accidental prick or cut from an HBV-contaminated needle or other sharp object
- From a mother who has HBV to her child during childbirth
Safe And Legal Disposal Of Sharps
Disposal of sharps, which includes syringes, needles, and lancets is regulated. They can carry hepatitis, HIV, and other germs that cause disease. Throwing them in the trash or flushing them down the toilet can pose health risks for others. Regulations governing disposal of sharps protect garbage and other utility workers and the general public from needlesticks and illness. There are different rules and disposal options for different circumstances. Contact your local health department to determine which option applies to your situation.
Found Syringes in Public Locations
Syringes that are found in parks, along roadsides, in laundromats, or in other public locations present potential risk for accidental needlesticks. Risks for infection from a found syringe depends on a variety of factors, including the amount of time the syringe was left out, the presence of blood, and the type of injury . The risk of HIV infection to a healthcare worker from a needlestick containing HIV-positive blood is about 1 in 300, according to CDC data.
Anyone with an accidental needlestick requires an assessment by a medical professional. Clinicians should make certain that the injured person had been vaccinated against hepatitis B and tetanus and may also recommend testing for HIV, HCV, and HBV. If a found syringe is handled, but no needlestick occurred, testing for HIV is not necessary.
Safe Disposal of Found Syringes
For safe disposal of found syringes:
Don’t Miss: What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
Other Body Fluids And Tissues
Hepatitis B is found in semen and vaginal secretions. The virus can be transmitted during unprotected sexual intercourse, and from mother to infant during birth.
Synovial fluid , amniotic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, and peritoneal fluid can contain the hepatitis B virus, but the risk of transmission to workers is not known.
Feces, nasal secretions, sputum, sweat, tears, urine, and vomit have not been implicated in the spread of hepatitis B. Unless they are visibly contaminated with blood, the risk of contracting hepatitis B from these fluids in the workplace is very low.
Hepatitis B is not transmitted by casual contact. For example, hospital employees who have no contact with blood, blood products, or blood-contaminated fluids are at no greater risk than the general public. However, the virus can spread through intimate contact with carriers in a household setting, possibly because of frequent physical contact with small cuts or skin rashes. The virus can also spread through biting and possibly by the sharing of toothbrushes or razors. It is not spread through sneezing, coughing, hand holding, hugging, kissing, breastfeeding, sharing eating utensils, water or food.
How Do You Get Hiv From Semen Or Vaginal Fluid
Body fluids including semen and vaginal secretions can contain HIV. If a person has HIV and a detectable viral load, HIV can passed on to someone if their semen or vaginal secretions get into the body of a sexual partner during vaginal or anal sex.
If a man has HIV and a detectable viral load, one of his body fluids where the virus is found is his semen.
If he has a detectable viral load and his semen gets into the body of his sexual partner during sex, then HIV can get into the other persons bloodstream.
Pre-cum also contains HIV this is why there is a risk of infection even if a man pulls out of his partner before he ejaculates.
If a woman has HIV and she has a detectable viral load, one of her body fluids where the virus is found is in her vaginal secretions.
If these come into contact with a penis during sex, then HIV could be transmitted. The virus in her secretions can enter through the delicate skin of the penis or foreskin.
Don’t Miss: Daa Drugs For Hepatitis C
How Long Can Hiv Survive Outside The Body
Once outside the body, HIV usually cant survive for very long. Coming into contact with blood or semen that has been outside the body doesnt generally pose a risk for HIV transmission.
Similarly, the risk of passing on HIV to someone else if you have a detectable viral load and cut yourself is also very low. Wash away any blood with soap and hot water and cover the wound with a sticking plaster or dressing.