Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
Hcv Infection And Cerebrovascular Events
In chronic HCV infection, cerebrovascular acute and chronic events have been reported with a higher prevalence than that observed in the general population in many cases, such neurologic conditions were associated with the presence of mixed cryoglobulinemia. Enger et al, in the largest retrospective study to date, including 21919 HCV-positive subjects and 67109 HCV-negative control subjects, reported a strict association between HCV and stroke, with a higher adjusted estimated risk of stroke for anti-HCV positive subjects . Gutierrez et al showed a close association between HCV infection and stroke in a retrospective study of subjects from the NHANES cohort during the period 2005-2010. However, it should be underscored that the two above studies have thus far been published only in an abstract form. Nonetheless, in a prospective study, involving a large population cohort from Taiwan, Liao et al established an association between HCV infection and stroke . Recently, in a large retrospective cohort from Taiwan, Hsu et al also found a higher risk of stroke in HCV infected subjects. Likewise, we recorded a higher prevalence of HCV infection in patients with stroke when compared with a large age- and gender-matched control group . In addition, HCV infection turned out to be an independent risk factor for stroke .
Estimated Chc Prevalence And Number Of Infected Cases In 31 Eu/eea Countries
The anti-HCV prevalence in the general population in the EU/EEA is estimated at 1.4% . However, prevalence estimates range from 0.2% in the Netherlands to 4.4% in Italy and 14 EU/EEA countries are considered endemic by the definition adopted in our study . Table lists the estimated number and range of CHC cases among adults in EU/EEA countries. An estimated 4.2 million adults in the EU/EEA have CHC infection. Italy has the highest absolute number, with an estimated 1.6 million CHC cases. Other EU/EEA countries with a high absolute number of CHC cases among adults are Romania, with 380,000, and Spain, with 470,000.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Elevated Liver Enzymes
What Causes Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18
Clinical Course And Disease Progression
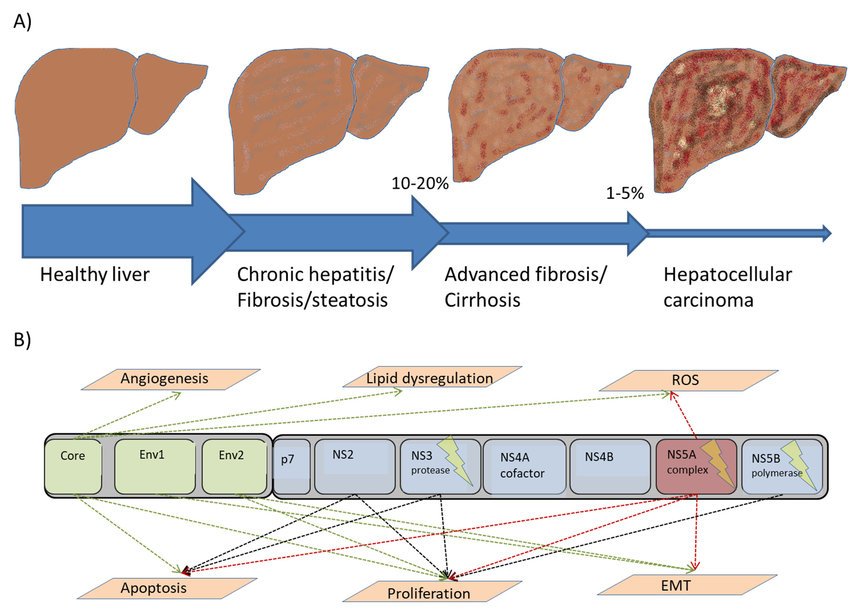
Acute hepatitis C virus infection is usually subclinical, and there are no reliable predictive factors for chronic infection. The relatively small size of the virus’s RNA polyprotein, rapid viral replication, and high mutation rates all contribute to the virus’s genetic heterogeneity and allow it to escape the host’s immune response, resulting in chronic infection for most patients . Progression of the disease is variable, and despite inherent limitations, histological evaluation of serial liver biopsy specimens remains the only reliable method to determine changes in severity of disease over time. On the basis of various study designs and models that predict rates of fibrosis progression, 20% to 30% of patients may be expected to develop cirrhosis over 20-30 years. This is reflected in the steady rise in the incidence of complications related to chronic liver disease, such as hepatocellular carcinoma, in many countries that are beginning to reach peak hepatitis C virus seroprevalence, such as Japan. Several host and viral factors affect disease progression, although determinants of individual risk and precise mechanisms of liver injury have yet to be determined . Better understanding of host-viral interactions may allow for targeted antiviral or other therapy aimed primarily at those at greatest risk of disease progression.
Box 2 Screening recommendations for hepatitis C virus infection
History of injecting drug use
HIV infection
Haemophilia
Also Check: How Do You Get Viral Hepatitis
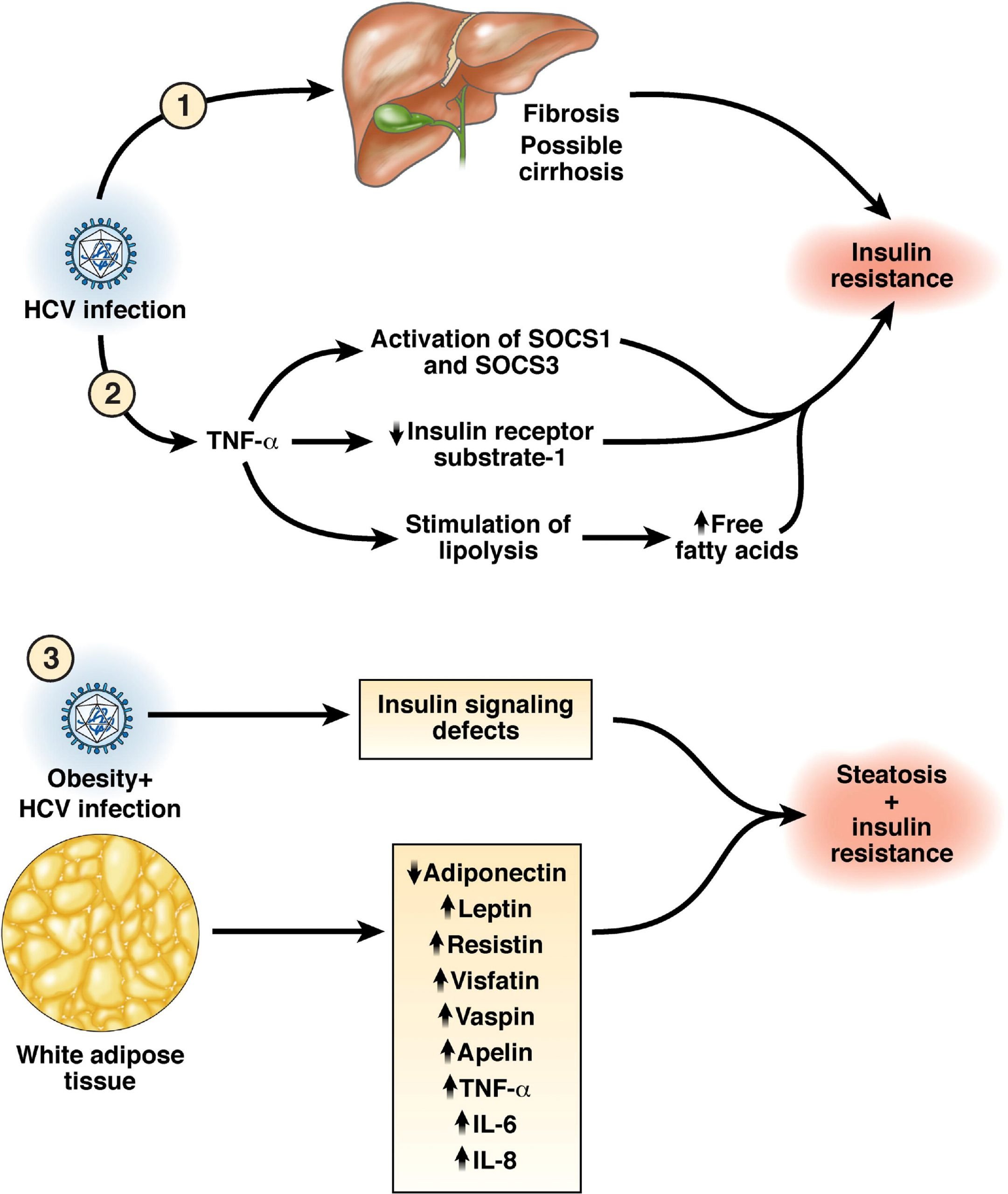
Insulin Resistance And Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin resistance is a frequent condition, coexisting with obesity and metabolic syndrome, possibly evolving to type 2 diabetes. In a small cohort of patients treated with anti-HCV therapy, Taskoparan and colleagues failed to establish a correlation between IR and chronic HCV infection . The presence of IR was evaluated in patients with HCV achieving a SVR after pegIFN plus ribavirin. On the one hand, the treatment response was not impaired by IR. On the other hand, treatment failure and high body mass index were independent risk factors for de novo appearance of IR after treatment. No new IR cases were registered in patients with SVR, suggesting that HCV eradication could prevent IR onset and its evolution to diabetes . Insulin resistance has been shown to impair SVR rate to pegIFN plus ribavirin in patients coinfected with HIV and HCV .
HCV-related type 2 diabetes mellitus may arise from a complex interaction between IR, steatosis and inflammatory processes . Epidemiologic studies supporting the association between type 2 diabetes and HCV infection have been published in the early 1990s. In larger epidemiologic studies , the prevalence of diabetes was higher in HCV- than in HBV-related cirrhosis . Diabetes was associated with the presence of cirrhosis and male sex. An epidemiologic study conducted in Egypt in a pediatric population of 150 patients with type I diabetes revealed a prevalence of HCV infection higher than in controls .
Progression Of Liver Fibrosis
In the setting of persistent hepatitis C viremia, the rate of progression of liver fibrosis varies widely. There have been extensive studies focusing on the natural course of disease progression from chronic hepatitis C to cirrhosis, HCC, and death. The liver biopsy is the gold standard for the grading and staging of chronic hepatitis C. The activity of liver disease or grade, is gauged by the number of mononuclear inflammatory cells present in and around the portal areas, and by the number of dead or dying hepatocytes. The structural liver damage, also known as fibrosis or stage, is variable in chronic HCV infection. Fibrosis implies possible progression to cirrhosis. In mild cases, fibrosis is limited to the portal and periportal areas. More advanced changes are defined by fibrosis that extends from one portal area to another, also known as “bridging fibrosis.â
Table 2
| Coinfection with HIV or HBV |
| Comorbid disease |
Recommended Reading: Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis B And C
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
The Natural History Of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Stephen L. Chen12, Timothy R. Morgan12
1. Gastroenterology Section, VA Medical Center, Long Beach, California2. Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of California-Irvine, Irvine, California
Citation:Int J Med Sci
Don’t Miss: How Much Does Hepatitis C Treatment Cost
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Analysis Of The Inflammatory Infiltrate
Immunolabeling of B lymphocytes , CTL , NK cells , Th lymphocytes , and Th1 , Treg and Th17 at PP areas was observed with scattered lymphocytes in the lobular region . Concerning PP cell frequency, Th lymphocytes were predominant followed by CTL, B lymphocytes, and NK cells. When analyzing Th subset frequency, Th17 showed the lowest counts . On the other hand, there was predominance of CTL and Th1 at the lobular area, together with absence of B lymphocytes and NK cells .
Table 2 Quantification of liver cell populations.
CTL and Th1 cells are well known components of the antiviral immune response. In this cohort despite their lobular predominance, they did not correlate with the number of infected hepatocytes, but they disclosed a negative correlation with viral load . Since viral load mirrored HCV liver replication, this could indirectly suggest CTL and Th1 immune control of the liver process.
Figure 2 Relationship between viral load and frequency of both lobular CTL and Th1. Correlation between viral load and the frequency of lobular CTL and Th1 . Relationship between Treg lymphocytes with both CTL and Th1. Correlation between the frequency of Treg with CTL and Th1 at portal-periportal area. Correlation between the frequency of Treg with CTL and Th1 at lobular area. Spearmans nonparametric correlation was used to compare these data sets.
Don’t Miss: Medicine To Cure Hepatitis C
What Are The Manifestations Of Chronic Hcv
Chronic HCV is in most instances a subclinical disease, and the only evidence of infection are the positive serologic tests. In some patients, LFTs are elevated, but even these people have no clinical signs of infection. Histologic signs of chronic hepatitis may be found by liver biopsy, but the inflammatory infiltrates are usually limited to portal areas, and such hepatitis is classified as mild. Severe chronic hepatitis is found in a minority of cases. Cirrhosis develops in some of these patients, and a small number of patients with cirrhosis will develop hepatocellular carcinoma.
Laura H. Mariani, Jeffrey S. Berns, in, 2014
Chronic Phase Of Hepatitis C
After six months 70% to 85% of those infected will have failed to clear the virus spontaneously. After this period the hepatitis C virus enters what is known as the chronic phase. This is when hepatitis C becomes a chronic or long-term infection. The diagnosis is confirmed when over a six month period hepatitis C RNA viral presence is detectable on at least two occasions.
A diagnosis of chronic hepatitis C means the battle between the virus and the immune system that occurs during the acute stage has finally been won by the virus. It is now highly unlikely that the virus can be cleared without treatment.
How the disease then progresses varies significantly from person to person. After many years some people will have minimal liver damage with no scarring while others can progress to cirrhosis within less than ten years. On average it takes about twenty years for significant liver scarring to develop. It is still not known whether chronic hepatitis C infection inevitably leads to cirrhosis. At present it is thought that this is a very likely outcome, although for some people it may take at least 50 years or more. They may well die of other unrelated diseases or conditions before cirrhosis develops. The rate of progression of liver damage cannot be accurately determined by liver enzyme levels, viral load or by genotype.
Liver damage and fibrosis during the chronic stage
Free Radicals and Fibrosis
Don’t Miss: How Is Hepatitis C Transferred From Person To Person
Impact Of Hcv Treatment On Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Present And Perspectives
Standard of care for HCV treatment is based on a regimen including pegylated interferon plus ribavirin. An improvement in response rates has been obtained with addition of viral protease inhibitors, namely, boceprevir and telaprevir, to standard of care recently, new oral drugs, sofosbuvir and simeprevir, have been approved for use. These drugs warrant even higher response rates and can also be used without interferon. Obviously, data are lacking on the impact of these new drugs on neuropsychiatric disorders in chronic hepatitis C patients, whereas evidence is available with regard to the effects of interferon-based therapy.
Importantly, obtaining a SVR following interferon treatment has been reported to even reduce the risk of stroke in chronic HCV infected patients. Specifically, Hsu et al calculated a 61% reduction in the long-term stroke risk after adjusting for known prognostic factors.
Overall, the studies performed thus far, albeit with limitations due to the small number of patients, seem to indicate a beneficial effect of interferon-induced SVR on both neurological and psychiatric disorders however, further ad hoc trials are needed to confirm these results.
Questionnaire Interview And Blood Collection
All participants were personally interviewed by public health nurses with structured questionnaires. The collected information included demographic characteristics, habits of cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption, and personal history of major diseases. Each participant provided a 10 mL blood sample with a standard sterile syringe for various serological and biochemical tests. Blood samples were separated on the day of collection and kept at 70°C until assay.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Cure Clinical Trials
Jaundice And Immune Response
The rate of chronic HCV infection is lower in patients who develop jaundice or symptoms during the acute onset of HCV infection as compared to those who are anicteric. In a prospective study of 142 HCV-infected subjects with a history of illicit drug use, subjects with viral clearance were more likely to have symptoms of jaundice . Furthermore, the long-term follow-up study of women infected with contaminated Rh immune globulin in Germany exhibited a rate of chronicity in 43% of those with history of jaundice, as compared to 60% among those who remained anicteric . Many have speculated that the jaundice may be associated with a more robust immune Th1 lymphocyte and cytokine response to the HCV. The competency of the immune response plays a significant role in the development of chronic hepatitis C, as well as the progression of liver fibrosis. The rates of chronic HCV infection developing in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection and CD4 < 200, have been higher than in patients without HIV infection.
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
Should pregnant women be tested for HCV antibodies?
Yes. All pregnant women should be screened for anti-HCV during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is < 0.1% . Pregnant women with known risk factors should be tested during each pregnancy, regardless of setting prevalence. Any pregnant women testing positive for anti-HCV should receive a PCR test for HCV RNA to determine current infection status.
Can a mother with hepatitis C infect her infant during birth?
The overall risk of an infected mother transmitting HCV to her infant is approximately 4%8% per pregnancy . Transmission occurs during pregnancy or childbirth, and no prophylaxis is available to protect the newborn from infection. The risk is significantly higher if the mother has a high HCV viral load, or is coinfected with HIV with which the rate of transmission ranges from 8%15% . Most infants infected with HCV at birth have no symptoms.
Should a woman with hepatitis C be advised against breastfeeding?
When should children born to HCV-infected mothers be tested to see if they were infected at birth?
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis C Do To Your Body
The Distribution Of Migrants In The Eu/eea Based On Hcv Endemicity In Country Of Birth
The top 50 migrant populations in each EU/EEA country included in the analysis make up at least 95% of the total migrant population in 19 countries and at least 90% in all but three EU/EEA countries . These migrant populations account for approximately 10.7% of the total adult population in the EU/EEA although the proportion in each country varies, ranging from 0.7% in Romania, 1.1% in Bulgaria and 1.7% in Poland to 42.0% in Luxembourg and 65.2% in Liechtenstein .
Fig. 2
Availability Of Data And Materials
An extensive supplementary annex of data and materials including the two detailed search strategies, inclusion and exclusion criteria, PRISMA flowcharts, selected country level estimates used in the calculations and an epidemiological profile of the contribution of migrants to the burden of CHB and CHC for each EU/EEA member state is available online. Other datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Also Check: Can You Live With Hepatitis C