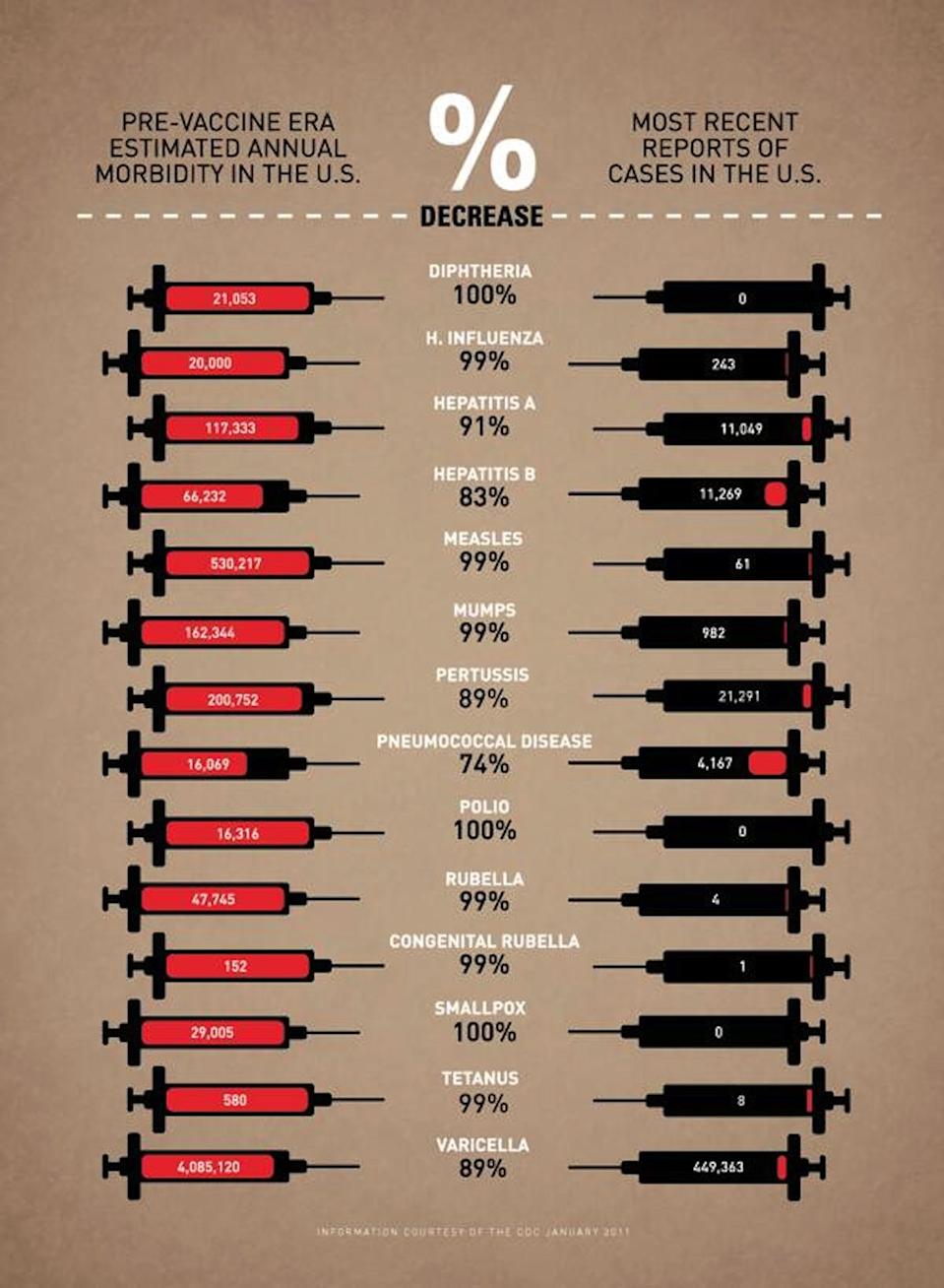
Facts About Hepatitis B
- Two billion people, or one in three, have been infected with hepatitis B worldwide. Of these, about 260 million live with chronic hepatitis B.
- Each year about 900,000 people die from hepatitis B worldwide, and about 2,000 of these deaths occur in the United States.
- Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood and is 100 times more infectious than HIV. An estimated one billion infectious viruses are in one-fifth of a teaspoon of blood of an infected person, so exposure to even a minute amount, such as on a shared toothbrush can cause infection.
- Hepatitis B is sometimes referred to as the silent epidemic because most people who are infected do not experience any symptoms.
- Liver cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer deaths throughout the world, behind lung, colorectal and stomach cancers.
- Almost half of liver cancers are caused by chronic infection with hepatitis B.
- The World Health Organization recommends the inclusion of hepatitis B vaccine in immunization programs of all countries in 2017, about 8 of 10 infants born throughout the world received three doses of hepatitis B vaccine.
Hepatitis B Vaccine On The Nhs
A hepatitis B-containing vaccine is provided for all babies born in the UK on or after 1 August 2017. This is given as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine.
Hospitals, GP surgeries and sexual health or GUM clinics usually provide the hepatitis B vaccination free of charge for anyone at risk of infection.
GPs are not obliged to provide the hepatitis B vaccine on the NHS if you’re not thought to be at risk.
GPs may charge for the hepatitis B vaccine if you want it as a travel vaccine, or they may refer you to a travel clinic for a private vaccination. The current cost of the vaccine is around £50 a dose.
How Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Series Work
The vaccine protects you from the hepatitis B virus by getting your body’s immune system to make antibodies. Those antibodies protect you by fighting off the virus if it ever gets into your body.
Usually, the vaccine is spaced out into three different shots called a hepatitis B vaccine schedule. One month after your first shot, you get the second shot. Six months after your first shot, you get the third shot. If you miss your second or third dose, get it as soon as you remember.
The hepatitis vaccine is super effective. Its worked really well to lower the number of people who get hepatitis B every year.
You May Like: Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Vaccination In The Travel & Immunization Clinic For High Risk Populations
There are many ways that people can get hepatitis B. It is possible for people to have hepatitis B and not know it because they do not feel sick. That is why some people need to be tested for hepatitis B before they get the vaccine.
If you would like to get the hepatitis B vaccine , please complete the health risk assessment first and ask yourself the following questions:
If you answered yes to any of the questions, you should be testedfor hepatitis B beforegetting the vaccine.
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
Read Also: Where To Get Tested For Hepatitis B
Health Effects Of Aluminum
The health effects of aluminum have been studied however, few have been shown to result from aluminum exposure. Kidney dialysis patients have developed disorders of the brain and bones due to the aluminum content in intravenous fluids and antacids following years of dialysis. Both disorders have decreased in occurrence due to improvements to dialysis systems. The bone disease was due to poor absorption of phosphate in the presence of high quantities of aluminum. Children taking large amounts of aluminum-based medications have also been found to suffer from this bone disorder.
It has been suggested that some diseases involving the brain, such as Alzheimer’s disease, are caused by aluminum accumulation in brain tissues. However, studies have not consistently found increased levels of aluminum leading some to hypothesize that the aluminum accumulation may be the result of tissue damage rather than the cause of disease.
Do I Need To Pay For Hepatitis B Immunisation
Vaccines covered by the NIP are free for people who are eligible. See the NIP Schedule to find out which vaccines you or your family are eligible to receive.
Eligible people get the vaccine for free, but your health care provider may charge a consultation fee for the visit. You can check this when you make your appointment.
If you are not eligible for free vaccine, you may need to pay for it. The cost depends on the type of vaccine, the formula and where you buy it from. Your immunisation provider can give you more information.
Recommended Reading: How Can I Tell If I Have Hepatitis
How To Get Vaccinated Against Hepatitis B
All babies in the UK born on or after 1 August 2017 are given 3 doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine as part of the NHS routine vaccination schedule.
These doses are given at 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age.
Babies at high risk of developing hepatitis B infection from infected mothers are given extra doses of the hepatitis B vaccine at birth, 4 weeks and 1 year of age.
If you think you’re at risk and need the hepatitis B vaccine, ask your GP to vaccinate you, or visit any sexual health or genitourinary medicine clinic.
If your job places you at risk of hepatitis B infection, it’s your employer’s responsibility to arrange vaccination for you, rather than your GP. Contact your occupational health department.
Emergency Hepatitis B Vaccination
If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and have not been vaccinated before, you should get immediate medical advice, as you may benefit from having the hepatitis B vaccine.
In some situations, you may also need to have an injection of antibodies, called specific hepatitis B immunoglobulin , along with the hepatitis B vaccine.
HBIG should ideally be given within 48 hours, but you can still have it up to a week after exposure.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis A Be Cured
How To Get The Most For Your Money
Here are some best practices to make sure youre getting the most care for your money:
-
Ask your insurance company about your costs, like co-insurance, copays, and deductibles.
-
Utilize your Health Savings Account , Flexible Spending Account , and Health Reimbursement Account to cover out-of-pocket expenses, if you have any.
-
Use Amino to compare prices for different doctors.
-
If you dont have insurance, look into local health or travel centersthey sometimes have more affordable vaccine options.
Which Adults Should Be Vaccinated Against Hepatitis B
According to CDC recommendations, adults in the following groups are recommended to receive hepatitis B vaccine:
General
- All people age 18 years and younger.
- Anyone 19 years and older who wants to be protected from hepatitis B.
People at risk for infection by sexual exposure
- Sex partners of people who are hepatitis B surface antigen -positive.
- Sexually active people who are not in long-term, mutually monogamous relationships.
- People seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease.
- Men who have sex with men.
People at risk for infection by percutaneous or permucosal exposure to blood or body fluids
- Current or recent illegal injection drug users.
- Household contacts of people who are HBsAg-positive.
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally challenged people.
- Healthcare and public safety workers with reasonably anticipated risk for exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids.
- People with end-stage renal disease, including predialysis, hemo-, peritoneal- and home-dialysis patients.
Others
- International travelers to regions with intermediate or high levels of endemic HBV infection.
- People with chronic liver disease.
- People with HIV infection.
- People with diabetes who are age 19 through 59 years. For those age 60 and older, clinicians should make a determination of need for
- vaccination based on their patients’ situation.
In a future issue, we will review the various hepatitis B serologic tests, who needs testing, and when they need it .
Also Check: How Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted
Sbp Adjuvant For Hepatitis B Vaccine
Wang and colleagues stated that although adjuvants are a common component of many vaccines, there are few adjuvants licensed for use in humans due to concerns about their toxic effects. There is a need to develop new and safe adjuvants, because some existing vaccines have low immunogenicity among certain patient groups. In this study, SBP, a hepatitis B surface antigen binding protein that was discovered through screening a human liver cDNA expression library, was introduced into hepatitis B vaccine. A good laboratory practice, non-clinical safety evaluation was performed to identify the side effects of both SBP and SBP-adjuvanted hepatitis B vaccine. The results indicated that SBP could enhance the HBsAg-specific immune response, thus increasing the protection provided by the hepatitis B vaccine. The authors concluded that given the encouraging safety data obtained in this study, further evaluation of SBP as a vaccine adjuvant for human use is warranted. They stated that this research has the potential to accelerate adjuvant development for HBV vaccine and for other vaccine types in the future.
Babies And Hepatitis B Vaccination
Pregnant women have a routine blood test for hepatitis B as part of their antenatal care.
Babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B need to be given a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of their birth, followed by further doses at 4, 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age, plus a final dose when they’re 1 year old.
Babies of mothers identified by the blood test as particularly infectious might also be given an injection of HBIG at birth on top of the hepatitis B vaccination to give them rapid protection against infection.
All babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B should be tested at 1 year of age to check if they have become infected with the virus.
Also Check: How Do You Cure Hepatitis C
What Are The Side Effects
Vaccines are very safe. It is much safer to get the vaccine than to get hepatitis A.
Many people have no side effects from the vaccine. However, for those that do, common side effects may include soreness, redness and swelling where the vaccine was given. Headache, fatigue, fever, and stomach upset may also occur after getting the vaccine. These reactions are mild and generally last 1 to 2 days.
It is important to stay in the clinic for 15 minutes after getting any vaccine because there is a very rare possibility, between one in 100,000 and one in a million, of a life-threatening allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. This may include hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the throat, tongue or lips. Should this reaction occur, your health care provider is prepared to treat it. Emergency treatment includes administration of epinephrine and transfer by ambulance to the nearest emergency department. If symptoms develop after you leave the clinic, call 9-1-1 or the local emergency number.
It is important to always report serious or unexpected reactions to your health care provider.
Guidance On Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization
Vaccine providers are asked to report, through local public health officials, any serious or unexpected adverse event temporally related to vaccination. An unexpected AEFI is an event that is not listed in available product information but may be due to the immunization, or a change in the frequency of a known AEFI.
Refer to Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization in Canada and Adverse events following immunization in Part 2 for additional information about AEFI reporting.
Recommended Reading: How To Manage Hepatitis C
Are Hepatitis B Virus Infections Easily Avoided
Large quantities of hepatitis B virus are present in the blood of people with hepatitis B in fact, as many as one billion infectious viruses can be found in a milliliter of blood from an infected individual. Therefore, hepatitis B virus is transmitted in the blood of infected individuals during activities that could result in exposure to blood, such as intravenous drug use, tattooing, or sex with people who are infected. However, it is also possible to catch hepatitis B virus through more casual contact, such as sharing washcloths, toothbrushes or razors. In each of these cases, unseen amounts of blood can contain enough viral particles to cause infection. In addition, because many people who are infected don’t know that they are infected, it is very hard to avoid the chance of getting infected with hepatitis B virus.
A Look At Each Vaccine: Hepatitis B Vaccine
The hepatitis B vaccine is given to prevent the severe liver disease that can develop when children or adults are infected with hepatitis B virus. The hepatitis B vaccine is given as a series of three shots. The first dose is given within 24 hours of birth. The second dose is given one to two months after the first dose, and the third dose is given between 6 months and 18 months of age.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Can You Get It From Intercourse
Is It Okay To Get An Extra Dose Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Yes. Although extra doses of vaccine are not recommended, you can think of the extra dose as another chance for the immune system to see the hepatitis B virus. A vaccine is not the only time the immune system will see the virus or bacteria contained in it. People may be exposed to the virus or bacteria at school or the store or when visiting family or friends. An extra dose of vaccine is like one more exposure, except the difference is that the virus or bacteria in any vaccine has been made safe, so it wont make you ill.
How And When Do Doctors Give Vaccines
For the hepatitis A vaccine:
You should get two doses, given as shots, 6 months apart for complete protection. The virus in the vaccine is killed .
Children should get the first dose between 12 and 23 months of age. Children older than age 2 can get the first dose at their next doctorâs visit.
If you need the vaccine because of upcoming travel, get it at least 1 month before you go.
For the hepatitis B vaccine:
For long-lasting immunity, you need three to four doses, depending on which type of vaccine is used. You get them as shots.
Children should get their first dose at birth and complete the series by age 6 months. Usually, the baby would get a second dose at 1 month old and the third dose at 6 months.
Babies born to women who have hepatitis B need a shot of hep B antibodies, as well as their first hep B vaccine shot, when theyâre born. They will also need follow-up blood tests to make sure theyâre OK.
Catch-up vaccinations are recommended for children and teens who were never vaccinated or who did not get all three shots.
If you’re an adult who wants to be vaccinated, you should talk about it with your doctor or pharmacist. If you are considering both vaccines, ask your doctor about vaccines that combine hep A and B.
Show Sources
Don’t Miss: Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Who Should Receive Hepatitis B Vaccination
- All newborns before hospital discharge. Infants born to hepatitis B-positive women need hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG within 12 hours of birth.
- All children and adolescents not previously vaccinated.
- Children born in the U.S. to individuals born in a country with high hepatitis B endemicity.
- All individuals at risk of hepatitis B infection:
- Sex partners of hepatitis B-positive persons
- Sexually active persons who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship
- Persons seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually-transmitted disease
- Men who have sex with men
- Persons who inject drugs
- Household contacts of hepatitis B-positive persons
- Persons born in countries where hepatitis B infection is endemic should be tested and vaccinated if susceptible
- International travelers to regions with high or intermediate rates of endemic hepatitis B infection
- Health care and public safety workers that may be exposed to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally disabled persons, corrections facilities, and other facilities that serve adults at risk for hepatitis B infection
- Persons with end-stage renal disease, including pre-dialysis, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and home dialysis patients
- Persons with chronic liver disease
- Persons to age 60 years with diabetes
- Persons with HIV infection
- All other persons seeking protection from hepatitis B infection.
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records

Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Read Also: Can You Get Hepatitis C Through Saliva
What Hepatitis B Immunisation Involves
Full protection involves having 3 injections of the hepatitis B vaccine at the recommended intervals.
Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B infection will be given 6 doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine to ensure long-lasting protection.
If you’re a healthcare worker or you have kidney failure, you’ll have a follow-up appointment to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
If you have been vaccinated by your employer’s occupational health service, you can request a blood test to see if you have responded to the vaccine.