Sof Plus Ledipasvir Rbv
Ledipasvir is a NS5A inhibitor with potent antiviral activity against HCV genotype 1a and 1b. Inhibition of NS5A viral phosphoprotein leads to disruption in viral replication, assembly and secretion. Most drug interactions with ledipasvir involve drugs that are Pgp-inducers such as rifampin or St. Johns wort. The following studies evaluated the use of ledipasvir in combination with SOF.
Disadvantages To Treatment In Hcv Cirrhosis Patients
The treatment of patients with HCV cirrhosis has shown to have lower SVR rates than in patients who are non-cirrhotic. Studies show that treatment with peg IFN plus ribavirin in patients with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis leads to a significantly lower SVR when compared with patients with mild to moderate fibrosis. Additionally, previous studies evaluating the use of triple therapy in patients with cirrhosis showed not only a lower SVR but also a high incidence of significant adverse events including worsening of liver disease, severe infection and difficult to manage anemia. Hence due to the risk of adverse effects, treatment of these patients requires significant oversight and should be considered only at experienced centers with transplantation capabilities leading to increasing cost and accessibility issues. Unfortunately, the treatment in some transplant centers is also controversial. There may be a tendency in some liver transplant centers to wait until transplantation and pursue treatment post-transplant. Additionally, having positive HCV infection in a cirrhotic liver may also provide access to HCV positive liver transplant options in such patients given the paucity of available organs.
How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C spreads through contact with the blood of someone who has HCV. This contact may be through
- Sharing drug needles or other drug materials with someone who has HCV. In the United States, this is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.
- Getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on someone who has HCV. This can happen in health care settings.
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not sterilized after being used on someone who has HCV
- Having contact with the blood or open sores of someone who has HCV
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another person’s blood, such as razors or toothbrushes
- Being born to a mother with HCV
- Having unprotected sex with someone who has HCV
Before 1992, hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Since then, there has been routine testing of the U.S. blood supply for HCV. It is now very rare for someone to get HCV this way.
You May Like: What Are The Signs Of Having Hepatitis C
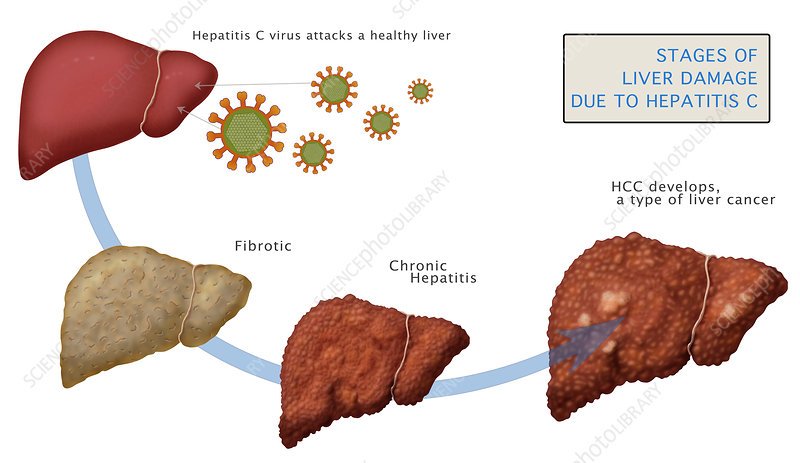
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B: Although most commonly acquired early in life, adults can also contract it. Hepatitis B is largely transmitted through bodily fluids. It can be passed at birth from a hepatitis B-infected mother or through exposure in early childhood to body fluids, blood or contaminated medical instruments. Hepatitis B can also be transmitted through intranasal and injection drug use as well as infected tools used during tattooing and body piercing.
Hepatitis C: The key risk factors are also intranasal and injection drug use, tattoos and body piercings, high-risk sexual contact, blood transfusions before 1992 and organ transplantation.
Another key risk factor for hepatitis C is being born from 1945 to 1965, during the baby-boom years. Eighty percent of all people who currently have hepatitis C in the United States were born in that timeframe.
Although the reasons that baby boomers are more likely to have hepatitis C than others arent entirely understood, its believed that most were infected in the 1970s and 1980s, when rates of hepatitis C were at their peak.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend that all U.S. adults born from 1945 to 1965 undergo a one-time screening test for hepatitis C. Connecticut is one of several states that has written this recommendation into law. In Connecticut ,the law requires that primary care clinicians screen all adults born within those years.
Also Check: How Soon Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Appear
What Are The Complications Of Cirrhosis
There are many complications of cirrhosis of the liver. Because cirrhosis develops over many years, some of these complications may be your first noticeable signs and symptoms of the disease.
Portal hypertension: This is the most common serious complication. Portal hypertension is an increase in the pressure in your portal vein . This increase in pressure is caused by a blockage of blood flow through your liver as a result of cirrhosis. When blood flow through veins is partially blocked, veins in your esophagus, stomach or intestines can become enlarged . As the pressure in these veins builds, the veins can bleed or even burst, causing severe internal bleeding.
Additional complications of portal hypertension include:
- Swelling in your legs, ankles or feet.
- Buildup of fluids in your abdomen .
- Swelling/enlargement of your spleen .
- Formation and dilation of blood vessels in the lungs , leading to low levels of oxygen in the blood and body and shortness of breath.
- Failure of kidney function as a result of having portal hypertension as a complication of cirrhosis . This is a type of kidney failure.
- Confusion, difficulty thinking, changes in your behavior, even coma. This occur when toxins from your intestines arent removed by your damaged liver and circulate in the bloodstream and buildup in your brain .
Hypersplenism: Hypersplenism is an overactive spleen. This condition causes quick and premature destruction of blood cells.
What Are The Risk Factors That Increase The Chance Of Developing Cirrhosis With Hcv
In a person with HCV, several risk factors can increase the chances of developing cirrhosis. These include1,2,6:
- Drinking alcohol. Drinking large amounts of alcohol over a long period of time can increase the chances of developing cirrhosis.
- Increasing age. People over the age of 50 years are at higher risk of developing cirrhosis.
- Fatty liver disease. A disease called steatosis where fat is deposited in the liver cells, increases risk for cirrhosis.
- Gender. Men with HCV appear to progress to cirrhosis more quickly than women.
- Co-infection with HIV. HCV/HIV co-infection is associated with increased risk for developing cirrhosis.
- Immune system dysfunction. A weakened or malfunctioning immune system may increase the risk of cirrhosis.
- Uncontrolled, elevated blood sugar. There is some evidence that people who have insulin resistance or diabetes are at greater risk for developing cirrhosis.
- Presence of another type of liver disease
Recommended Reading: What Is A Hepatitis Panel
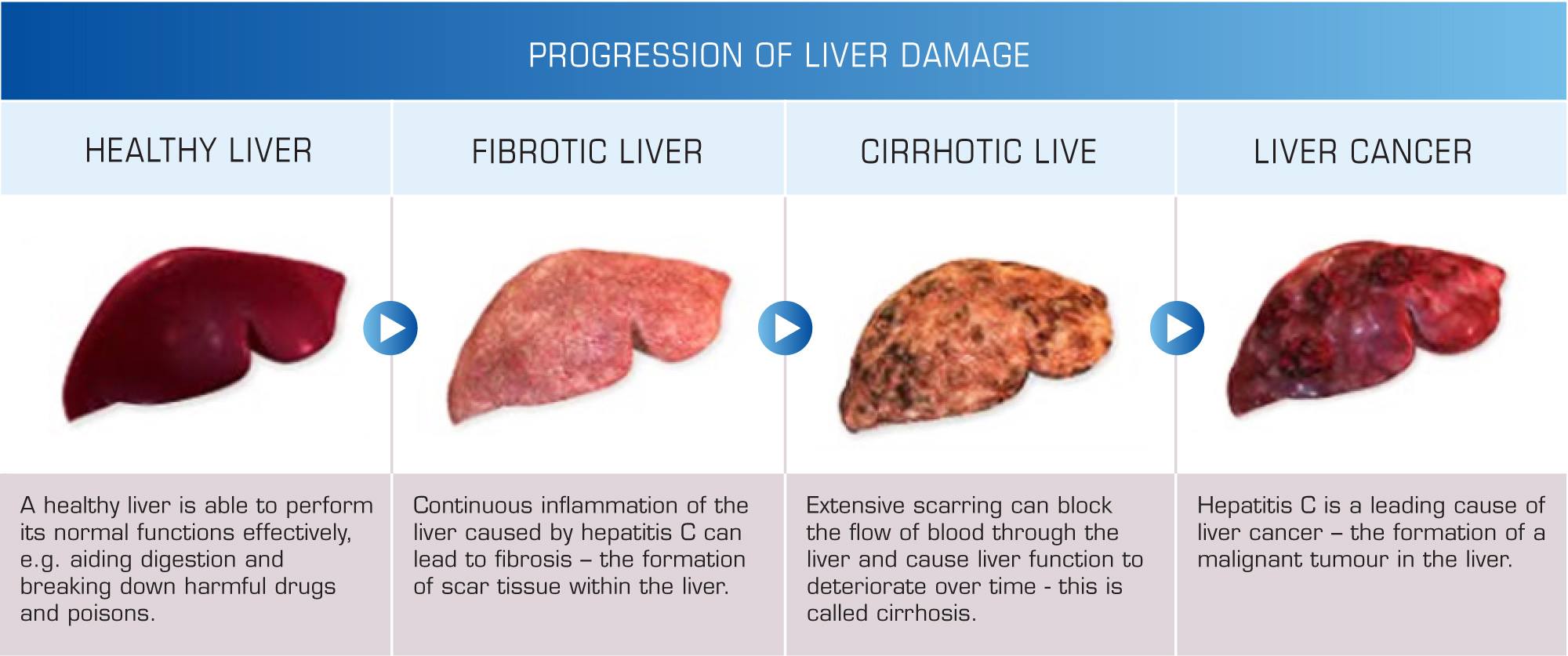
Out Of Date Cirrhosis Information
Many doctors will tell Hepatitis c patients that the liver cannot recover from liver cirrhosis. This is not true. Fibrosis is rated by a score that begins at F0 and rises to F4 . In the past liver Cirrhosis has long been regarded as the end the point of no return. People believed that liver functions were ruined and the chance of developing liver cancer was high.
There is now a huge body of evidence that proves that the liver will heal from cirrhosis once Hepatitis C is removed.So the perception that liver cirrhosis is final and irreversible is changing. The very good news is that once the Hep C virus is removed many people are reporting that the liver is healing better than was expected. People with cirrhosis are finding that their liver fibrosis levels return to F2 or F1. The chance of liver cancer reduces by more than 70% and the liver functions return to normal.
New Treatments For Hcv Infection In Cirrhotic Patients
The treatment of HCV infection has evolved over the past decades and many more changes are anticipated in the treatment of patients in the coming years. The focus of this paper is to discuss treatment regimens based on recent clinical trials that have included patients with cirrhosis and discuss their success rates in achieving SVR. Although many changes are anticipated in the coming months, currently the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease guidelines for the treatment of cirrhotic patients recommend that treatment-naïve patients with compensated cirrhosis, including those with HCC, may be treated with the same regimen as patients without cirrhosis. Tables and provide AASLD recommendations for treatment based on genotype and peg IFN eligibility. For patients who are decompensated who may or may not be candidates for liver transplantation including HCC, AASLD recommends referral to an experienced treatment center ideally with liver transplantation capabilities. In this paper, we present the current treatment regimens and trials which have included patients with compensated cirrhosis and provide information for physicians who may be interested in learning further or pursing treatment for chronic HCV infection in patients with cirrhosis.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Go Away On Its Own
Paritaprevir/ritonavir + Ombitasvir Ribavirin
Dasabuvir has no significant antiviral activity in genotype 4 therefore, treatment with paritaprevir/ritonavir and ombitasvir is sufficient. In a recently published study, paritaprevir/ritonavir + ombitasvir + ribavirin was compared for 12 and 16 weeks in patients with cirrhosis. In both groups high SVR rates were achieved . The combination is approved for a 24-week treatment with ribavirin in patients with cirrhosis.
When Should I Call 911 Or Go To The Emergency Room
If you have cirrhosis and experience the following, call 911:
- Your poop are black and tarry or contain blood .
- You are vomiting blood.
- You have muscle tremors or shakiness.
- You are confused, irritable, disoriented, sleepy, forgetful or foggy.
- You have a change in your level of consciousness or alertness you pass out.
You May Like: Hepatitis B And C Test
Diagnosis And Disease Course For Chronic Hcv Infection
HCV infection is rarely diagnosed during in the acute phase of infection. Although a variety of host-factors play a role in eradication of HCV, only 15%-25% of adults spontaneously clear the infection. The remaining proportion of patients continue to have persistent viremia and retrospective studies on the natural history of HCV infection, have found that about 15%-30% of people with chronic infection would progress to cirrhosis over the duration of two to three decades. Progression to cirrhosis has been shown to occur at an accelerated pace in those with concomitant alcohol use , co-infection with HIV and hepatitis B virus , as well as male sex, and older age at time of infection . In the patients that develop HCV related cirrhosis, the risk of development of HCC has been shown to be 1%-4% per year and warrant surveillance for complications.
Natural progression of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States. HBV: Hepatitis B virus HCV: Hepatitis C virus HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus.
How Common Is Cirrhosis
Scientists estimate that cirrhosis of the liver affects about one in 400 adults in the U.S. It affects about 1 in 200 adults age 45 to 54, the age group most commonly affected by cirrhosis. Cirrhosis causes about 26,000 deaths each year in the U.S. and is the seventh leading cause of death in the U.S. among adults 25 to 64 years of age.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Sexually
What Type Of Healthcare Providers Will Treat My Cirrhosis
Depending on the stage of your cirrhosis, different healthcare providers may be involved in your care. Healthcare professionals likely to be part of your care team include:
- Your primary care provider.
- Gastroenterologist .
- Hepatologist .
- Nephrologist .
- Dietitian.
- Members of a liver transplant team include: hepatologist, transplant surgeon, anesthesiologist, infectious disease specialist, nephrologist, dietitian, transplant pharmacist, physical and occupational therapist, case manager/social worker and nurses.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Cirrhosis of the liver is a late-stage result of liver disease and its complications. Cirrhosis causes your liver to not function properly. Your liver plays a vital role in many of the processes and functions that keep you alive.
Although scarring from liver disease causes permanent damage, its still possible to live a long life. Depending on the underlying cause, its possible to slow or stop cirrhosis from worsening. Many of the causes and complications that lead to cirrhosis are treatable or manageable. If you drink alcohol, stop. If you have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, lose weight and control your metabolic risk factors. If you have diabetes, make sure you are following your healthcare providers management recommendations. Take all medications for all your medical conditions as directed by your healthcare team. Get vaccinated for hepatitis A and B.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/01/2020.
References
Sofosbuvir + Daclatasvir + Ribavirin
The ALLY-1 study evaluated the treatment of sofosbuvir + daclatasvir + ribavirin over 12 weeks in cirrhotic patients as well as after liver transplantation and HCV recurrence. Patients with compensated cirrhosis achieved an SVR in 92% of cases . Before the approval of the two components, a compassionate use program treated mainly cirrhotics with sofosbuvir + daclatasvir with and without ribavirin for 24 weeks. In this difficult-to-treat population high SVR rates were found , but the numbers of patients with only 12 weeks of therapy were low . The EASL guidelines favor a 12-week therapy with ribavirin in cirrhotic patients. When ribavirin is contraindicated, a treatment duration of 24 weeks is recommended.
Don’t Miss: Where To Get A Hepatitis B Shot
What To Do If You Have Both Hepatitis C And Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis that is caused by HCV generally takes decades to develop fully. If somebody already knows that they have hepatitis C, it is essential to seek proper medical care to prevent hepatitis C from causing cirrhosis.
Due to this, doctors typically recommend that a person who has the following risk factors undergo testing for hepatitis C:
- Receiving long-term hemodialysis
- Born to mothers who have hepatitis C
- Are current or former intravenous drug users
- Have a history of exposure to HCV, for example, hospital/healthcare workers
- Have tattoos that have been done by unlicensed artist
- Have had a blood transfusion before July 1992, from which point screening became widespread
- Is or was in prison or jail
- Has HIV infection
- Was born from 1945 to 1965
If you are lucky and your doctor detects hepatitis C before it leads to major liver damage, they will prescribe medications that will help cure a majority of patients. However, if you already have liver cirrhosis, then also treating and curing hepatitis C that will not reverse the liver damage that has already been caused.
When a hepatitis C patient has cirrhosis, the goal of the treatment revolves around minimizing and preventing any further damage to the liver. Let us take a look at the different treatment options for achieving the same.
Therapy Regimens In Patients With Decompensated Cirrhosis
Current guidelines recommend urgent antiviral treatment in HCV-infected patients with significant fibrosis or cirrhosis. However, several DAA treatment regimens ide polymerase inhibitors) should not be used in patients with decompensated cirrhosis due to their pharmacokinetic profiles and impaired drug-metabolizing capacity. Moreover, all these patients should be referred to a hepatologist with experience in this condition, ideally a liver transplant center.,
Historic regimens combining pegylated IFN with ribavirin or PEG IFN with RBV and telaprevir or boceprevir are contraindicated and outdated in this group because severe treatment-related side effects eg bacterial infections, cytopenia and worsened liver disease have been described.-
This paper will discuss possible regimens for HCV therapy in patients with decompensated cirrhosis according to current guidelines with a special focus on major randomized controlled trials. A summary of available treatment options is given in Tables and .
| HCV Genotype |
|---|
| b No data on decompensated cirrhosis exits, based on data from studies with compensated cirrhosis. |
- a Low initial dose of RBV is recommended, increased as tolerated.
- b No data on decompensated cirrhosis exits, based on data from studies with compensated cirrhosis.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quant
Symptoms Of Cirrhosis Caused By Hcv
It is highly likely that you will not experience any symptoms of liver cirrhosis until a considerable amount of damage has already happened to your liver. When you do start experiencing the symptoms, they may include:
- Jaundice or yellow discoloration in eyes and skin
- Fluid present in the abdomen
- Abnormal blood test reports, including albumin, bilirubin, and coagulation factors
- Enlarged veins in the upper stomach and esophagus that may lead to bleeding, a condition known as variceal hemorrhage
- Infection of the abdominal lining and ascites
- Impaired mental functioning due to accumulation of toxins, a condition known as hepatic encephalopathy
- During the diagnosis process, a liver biopsy will show scarring, confirming the presence of cirrhosis in people who have hepatitis C already.
- Laboratory tests, as well as a physical exam, will also help your doctor diagnose advanced liver disease without requiring a biopsy.